implementing macro policy (chap 30-33)
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fiscal policy, monetary policy, supply side policy, ( not done but the Phillips curve and policy conflicts)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
fiscal policy
process of regulating government spending and taxation in order to control the economy
what are the roles of fiscal policy
finance spending, redistributing income, welfare, tackling failure, improving competitiveness
current expenditure
money spent on current goods and services e.g hospital equipment, staff in public sector
capital expenditure
money spent on capital that is used to produce/ support goods and services for current expenditure e.g investments into infrastructure
transfer payments
money that provides the welfare net e.g benefits, nhs
what is government spending generally on
education, welfare, healthcare, infrastructure, services etc, all are merit goods
what are the two types of fiscal policy
expansionary and discretionary
expansionary fiscal policy and examples
policy that increases the money supply and therefore spending, cuts in income tax, cuts in indirect tax, cuts in corporation tax, cut in interest from saving tax
discretionary fiscal policy and examples
policy to control inflation or decrease spending, increasing taxation such as income and vat
automatic stabilisers
automatic policies and government behaviours that aid the economy through the cycle e.g more spending in a recession and increase in benefits when unemployment is rising
what are the two main ways the government funds its spending
taxation and borrowing
direct tax
taxation on income
progressive tax and example
tax rate that rises as income rises such as tax brackets
proportional tax and example
tax that is constant no matter what income is earned e.g flat business tax in Poland that has the same percentage for all businesses
regressive tax and example
tax that is more of a burden on those with lower incomes e.g smoking tax is a larger proportion of a lower income persons’ income
what are some influences on supply/ producers when tax changes *includes citizens
work incentives, inward migration of workers, more investment, more enterprise and entrepreneurship, incentives to study, incentives for research and development, lower business costs when carbon tax reduces
what are some examples of UK fiscal policy
raising vat to 20%, raising national insurance, cuts in local authority spending e.g bins and bus routes, welfare caps and reform
what are some global examples of fiscal policy *don’t have to name country
Poland flat business tax, freezing fuel duties, cutting corporation tax, freezing council tax, cutting NI
government budget
proposal for the years fiscal behaviour including spending, taxation, borrowing etc
what are the three stages a budget can be in
balance, surplus (too much taxation), deficit (too much borrowing)
what is the governments opportunity cost when predicting a budget deficit
subsequent years of interest payments on the borrowing, creates burden on future generations
what is the cyclical budget deficit
deficit is in line with business activity
structural budget deficit
deficit is still there even when employment is full
national debt
money the government owes from borrowing, UK always in debt, currently at around £2.5 trillion
what are the justifications for the UKs national debt
more spending boosts AD, encourages more employment, investment helps fix long run deficit
what did Keynes say about the budget and fiscal behaviour
we must spend our way out of trouble
monetary policy
government policy that can influence the money supply and interest rates
money supply
amount of money in the economy
who are the MPC
monetary policy committee, there to discuss every month if the base interest rate should be changed to make sure the inflation target is met
what is the inflation target and who sets it
UK target for inflation 2%, set by the government
what are the two types of monetary policy
expansionary and deflationary
what is the aim of expansionary monetary policy
increase the money supply, fall in interest rate, growth in spending, depreciating exchange rate to increase exports
what is the aim of deflationary monetary policy
raise the interest rate, make credit/ money supply tighter, appreciate exchange rate
who sets the base interest rate and what is it
basic interest rate that all businesses build off of, bank of England set in in relation to how the inflation target is being met
what is the base interest rate also known as
bank rate as banks are the lenders of credit and loan agreements
what factors do the MPC take into account when deciding on adjusting the interest rate
spare capacity, GDP growth, trends in global markets, unemployment data, commodity prices, demand, credit availability, consumer confidence
liquidity trap
when the interest rate is lowered yet doesn’t stimulate increased consumption
what may the government do to stimulate the economy when a liquidity trap occurs
borrow and spend more to increase the overall GDP and account for any projected consumption that did not take place
what way can the government create more money for the money supply
quantitative easing
quantitative easing
increasing the money supply through the purchase of financial assets, bank of england buys the assets from the government
what is the point of quantitative easing
prevent the liquidity trap and subsequent recession
what are the benefits of low interest rates
more consumer and business confidence therefore more consumption and investment, less export pressure as the pound appreciates, preventative of deflation, encourages the multiplier
what are the drawbacks of low interest rates
consumers less likely to save, high pressure on credit supply, less exports means businesses fail, mortgage debt, bad for savers, doesn’t aid times of low unemployment where higher interest can benefit more
evaluate monetary policy
time lags are long as inflation takes approx 2 years to cycle through economy, assumes consumers and business behaviour which may be wrong, need to acknowledge fiscal too as they work in conjunction, costs can fluctuate and change rate of inflation and behaviours, long run sustainability?!
supply side policy
policies that directly aim to improve productivity and promote an outward shift in the PPF or LRAS
what are some key challenges that SSP focuses on
real gdp growth, productivity gap, emerging nations, youth unemployment, regional economic divides, trade deficit, inequality and relative poverty, capital research and investments
what are the two branches of SSP policies
market led policies and interventionist policies
what are market led policies
policies that allow a more free working market, reducing government intervention
what are some generic examples of market led SSP
privatisation, deregulation, tax and benefit reforms, labour market flexibility through migration trade union power and minimum wage
what are some specific UK examples of market led SSP
privatising Royal Mail, reducing the national insurance payments
what are interventionist policies
policies that surround government intervention in order to stimulate AS
what are some generic examples of interventionist policies
public sector investment, education initiatives, more housing, subsidies, r+d investment, immigration control, competition policies
what are some specific examples of interventionist policies
migrants minimum earning (around £39,000), HS2 investment, CMA forming
trade off
a gain in one item must be accompanied by a loss in another
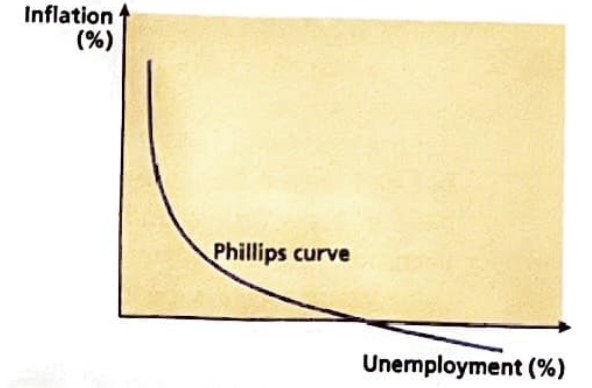
phillips curve
diagram that illustrates the trade off between unemployment and inflation
what does the philips curve look like in the short run and why
downward sloping inverse relationship, as unemployment is high inflation is low as people cannot afford to spend and vice versa, when unemployment is low inflation is high
politically link the phillips curve to economic policy
aspiring political candidates can say they will decrease inflation through increasing unemployment. and vice versa yet this doesn’t always work in the long run, cannot really use the curve for policy due to the long run effects
stagflation
high unemployment and high inflation, the phillips curve has effectively disappeared in this case
what is another theory for the disappearance of the phillips curve in the event of stagflation
an upward shift of the phillips curve whereby wage bargaining takes place on the expectations of inflation as it has become so normalised in society
what is the natural rate of unemployment
rate at which there is only frictional and structural unemployment and real wages are at an equilibrium level
NAIRU (non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment)
rate of unemployment that is consistent with a constant rate of inflation or just the natural rate of unemployment (full employment on LRAS)
what does the long run phillips curve look like and why
a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment as neoclassical assumptions argue that there is no long run trade off between inflation and unemployment as they will both occur due to growth and the natural rate of unemployment
what are the seven key macro policy objectives
economic growth, low inflation, full employment, BOP stability, balanced budget, sustainable growth environmentally, acceptable income distribution
how can economic growth and the balance of payments conflict
more growth means more real income which means more imports of goods and services which results in a disrupted trade balance
how did economic growth and the balance of payments conflict in the 50s and 60s
fixed exchange rate and lost of abroad spending meant that growth was short lived as the deficit on the current account came quickly
how can economic growth and inflation conflict
demand side policies for growth may cause demand pull inflation, governments may want to work on supply side policies to reduce the effect that growth may have on inflation
how can fiscal and monetary policy conflict
an increase in government spending (fiscal) can push up interest rates for banks as the government decides to borrow more (monetary) which results in less spending as a country (economic growth)
how can hot money link to the conflict between fiscal and monetary policy
higher interest rates attract hot money flows which affects the international position of domestic economies
how do growth and inequality link
rapid economic growth can cause more inequality within society as skills are adopted but not by all, certain sectors such as investment may grow more than working class jobs, may be education gaps
why is it important to create a stable macroeconomic environment
promotes effective operation of microeconomic markets whereby supply and demand are boosted, profits are more likely to be domestically reinvested and social welfare will go up