Chemistry Extended Answer
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bank for all types of questions asked in ER for WACE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the primary structure of a protein
primary structure of a protein is the sequence of α-amino acids.
α-amino acids are joined by peptide or amide bonds
What is the secondary structure of a protein
secondary structures result from hydrogen bonding between amide group hydrogen atoms and carbonyl group oxygen atoms.
secondary structures are either classified as α-helixes and/or β-pleated sheet.
α-helix is a secondary structure that results from hydrogen bonding between amide and carbonyl functional groups within a peptide chain
β-pleated sheet is a secondary structure resulting from hydrogen bonding between amide and carbonyl functional groups along adjacent polypeptide chain
what is the teritary structure of a protein
tertiary structure of a protein is a result of folding of the polypeptide chain/overall shape of the protein.
tertiary structure forms due to interactions between side chains of α-amino acids in the polypeptide
what are the different types of side chain interactions?
disulfide bridges
hydrogen bonding
dipole-dipole interactions
dispersion forces
ionic interactions
Use collision theory to explain how the presence of catalysts in production proccesses are viable.
Catalysts improve the viability of proccess by increasing reaction rates.
The catalyst provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
With a reduced activation energy, there will be a greater proportion of successful collisions occuring with sufficient energy, and thus a higher frequency of successful collisions
Use collision theory to explain how increasing the temperature of a system in production impacts yield
An increase in temperature increases the average kinetic energy of all particles.
There is an increase in the frequency of collisions in both forward and reverse reactions.
There is also an increase in the proportion of collisions that reach the activation energy in both forward and reverse reactions.
But as the proportion increase is greater for the [F/R] endothermic reaction, the equilibrium position shifts [L/R]
use collision theory to describe the effect of raising the total pressure on the yield
When pressure is increased, (the reactant and product) particles are forced closer together increasing rate (frequency) of collision.
therefore increases the rate of reaction of both the forward and reverse reactions. Ratio of gaseous particles of LHS to RHS as written is x:y.
The [r/f] reaction as written has a greater proportion of gas particles hence forward reaction proceeds faster than the reverse reaction until the equilibrium conditions are re-established.
This results in a greater proportion of [p/r] of the [r/f] reaction
use collision theory to describe the following conditions:
high temperature
catalyst
high temperature
high pressure
catalyst:
increases rate of reaction by providing an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy.
There will be an increased proportion of particles colliding with energy greater than activation energy, resulting in increased frequency of successful collisions
Temperature:
increased temperature increases the average kinetic energy of particles and they collide more frequently
increased proportion of collisions will have energy higher than the activation energy
greater proportion of collisions are successful
Pressure:
ncreased pressure reduces the space between reacting particles
particles collide more frequently
higher frequency of successful collisions
what are 3 conditions for a good primary standard?
relatively high molar mass
soluable in water
non-hygroscopic(tendancy to absorb with water)
justifications for choice of an indicator?
That a change in colour of the indicator (end point) indicates that the equivalence point has been reached.
The (appropriate) indicator changes colour in the range of the equivalence point.
____ is the only indicator that changes colour in the range of the equivalence point
Why is compound 1 soluble in water but compound 2 not?
compound ____ is soluble/insoluble
compound 1 is predominantly attracted via _______ forces. compound 2 is predominantly attracted via _______ forces.
For a compound to be soluble, the solute-solvent interactions must be greater than original solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions
compound 1 and water _____ forces are not strong enough to overcome original solute-solute and solvent-solvent forces.
compound 2 and water _____ forces are strong enough to overcome original solute-solute and solvent-solvent forces.
hence, new bonds are formed between between compound 2 and water.
therefore, compound 1 will dissolve, and compound 2 will not.
why is compound 1 soluble in ethanol but not water
compound 1 predominantly has __ forces
water has hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole and dispersion forces
ethanol has hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole and dispersion forces
compound 1 can form dispersion forces with water and ethanol
however, compound 1 forms greater dispersion forces with ethanol rather than water
the energy released in the formation of hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole and dispersion forces between ethanol and compound 1 are sufficient to overcome existing forces of attraction between compound 1 molecules and ethanol molecules
the energy released in the formation of hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole and dispersion forces between water and compound 1 are insufficient to overcome existing forces of attraction between compound 1 molecules and water molecules
what is the production steps for producing biodiesel
filteration
remove water
Remove Free Fatty Acids(FFA) through esterification:
FFA + methanol =(eq, H2SO4)= FAME + H2O
trans-esterification:
TG + methanol =(NaOH)= 3FAME + glycerol
// FAME= Fatty Acid Methyl Ester, AKA biodiesel
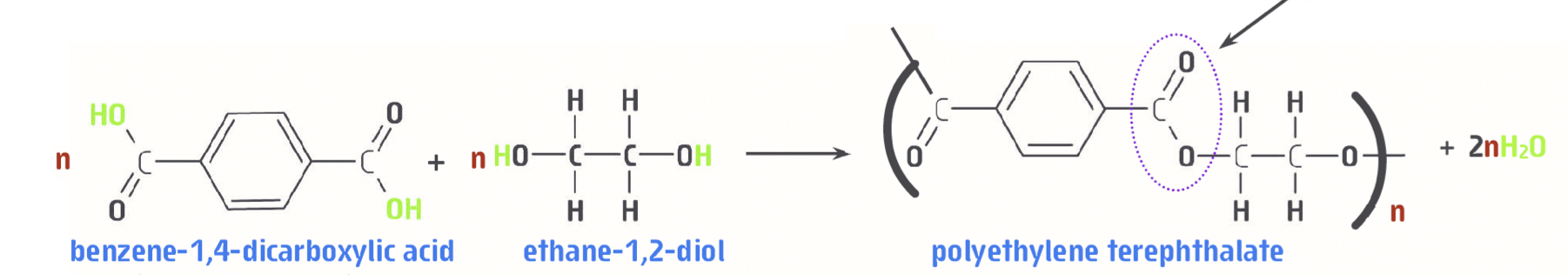
What is PET (the polymer)
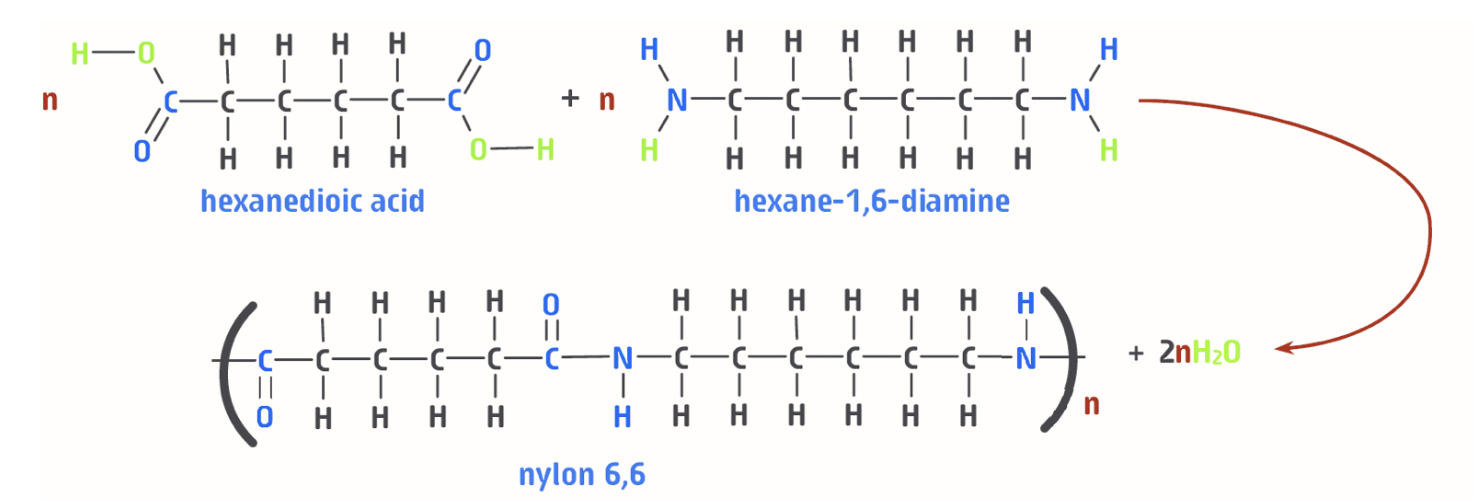
what is nylon 6,6 (the polymer)
what is the purpose of a salt bridge?
what is a type of salt used and which ions flow to which cell
To prevent the build of polarity on either side of the cell
KNO3; anion to anode and cation to cathode
what are the half equations for an ALKALINE cell
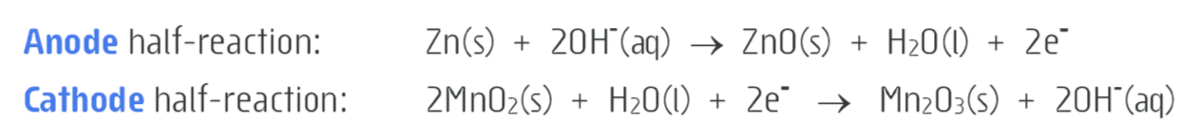
what are the half equations for a LECLANCHE(acidic/dry) cell
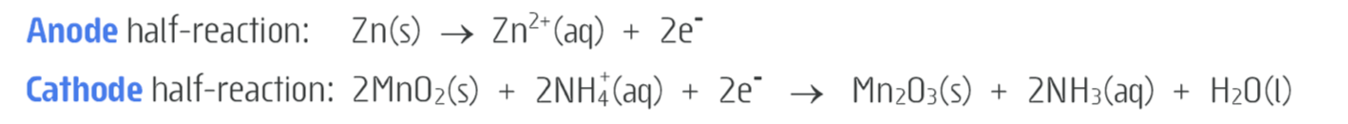
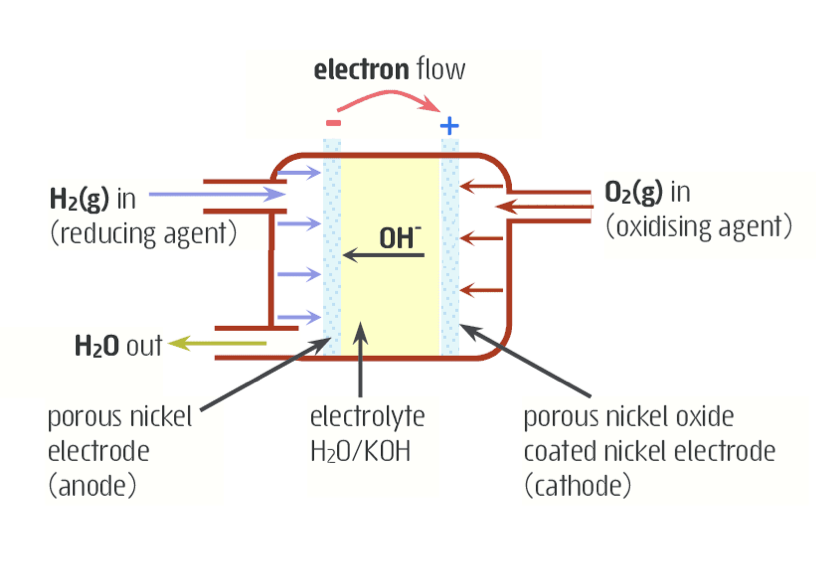
Explain everything about an alkaline fuel cell
anode = nickel, fueled by H2 gas
cathode = nickel oxide, fueled by O2 gas
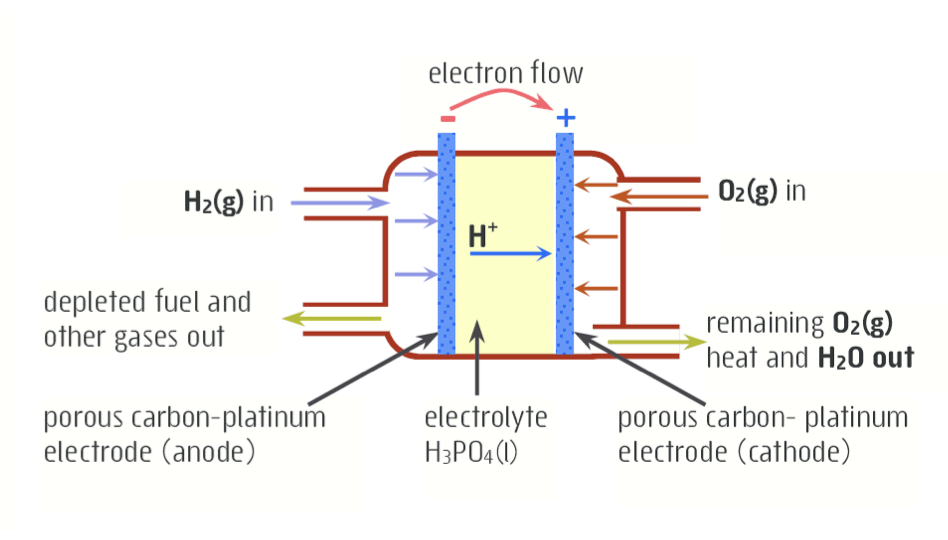
Explain everything about an acidic fuel cell
anode = carbon-platinum, fueled by H2 gas
cathode = carbon-platinum, fueled by O2 gas
explain how in electrorefining, the cathode remains pure
The applied cell voltage is carefully controlled so that only Cu+ (aq) ions are able to be reduced
less reactive metals simply fall to the
bottom of the electolysis cell(anode sludge/slime) [e.g. gold]
Other cations unaffected and remain in
solution. [e.g. nickel]
electrolyte = CuSO4 and H2SO4
rust equations and anode/cathode
anode = iron and water meet
cathode = iron, water and air meet
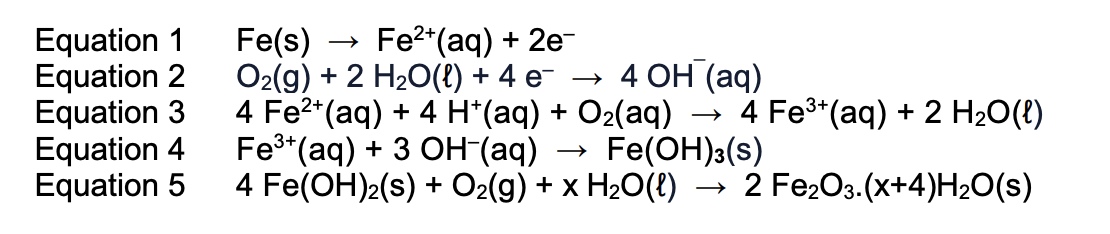
eq1: anode
eq2: cathode
how to prevent rust?
galvanising - covering iron in another metal that is more likely to oxidise(like zinc) so work even if its scratched
DC current - connecting negative terminal to iron supplies it with electrons, meaning it does not have ability to oxidise(due to it being cathode), however another piece of iron or metal is needed to be connected to anode for it to be oxidised.
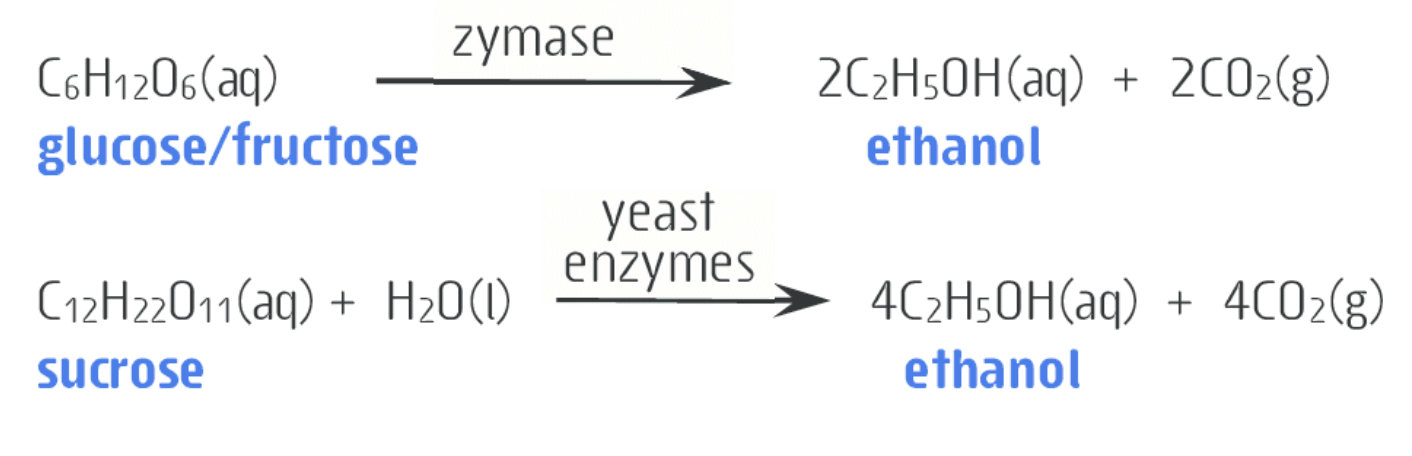
what is the overall equation for the process of fermentation being used to make ethanol
Glucose
sucrose
what are the basic reactions of acids, bases and metals
acid + metal
acid + base
acid + metal carbonate
metal + water
___/____ displacement
acid + metal = salt + h2
acid + base = salt + h2o
acid + metal carbonate = salt + co2 + h2o
metal + water = metal hydroxide + h2
___/____ displacement = halogen, metal