THERAPEUTICS EX3 L(?) (ATRIAL FIBRILLATION) (MIRANDA)
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Describe a supraventricular arrhythmia
Originates from ABOVE the bundle of His
Types of supraventricular arrhythmias? (four)
1. Afib
2. Aflutter
3. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
4. Autonomic atrial tachycardia
Describe a ventricular arrhythmia
Originates from BELOW the bundle of His
Types of ventricular arrhythmias? (three)
1. Premature ventricular complexes
2. Ventricular tachycardia
3. Ventricular fibrillation
Define atrial fibrillation
A supraventricular arrhythmia with uncoordinated atrial activation and consequently ineffective atrial contraction
Afib is defined by what kind of heartrate? Bpm?
Chaotic, rapid (300-500 bpm); irregular atrial rhythm
Conditions which predispose a person to Afib?
Advanced age
Smoking
Physical activity
Alcohol
Obesity
Height
Blood pressure (HTN)
Resting heart rate
Diabetes
Cardiovascular conditions which predispose a person to Afib?
HF
CAD
VHD
Cardiac surgery
Acute cases which can precipitate Afib?
Thyrotoxicosis
Surgery
Alcohol withdrawal
Sepsis
Excessive physical exertion
T/F: Afib is a progressive disease.
True
Describe AF Stage 2
Evidence of structural or electrical findings further predisposing a patient to AF
(atrial enlargement, frequent atrial ectopy)
Describe AF Stage 3
Has diagnosed AF
Paroxysmal, persistent, long-standing persistent, or successful AF ablation
Describe AF Stage 4
Permanent AF
Testing used to diagnose AF?
12-lead ECG (gold standard)
Holter/event monitor (paroxysmal)
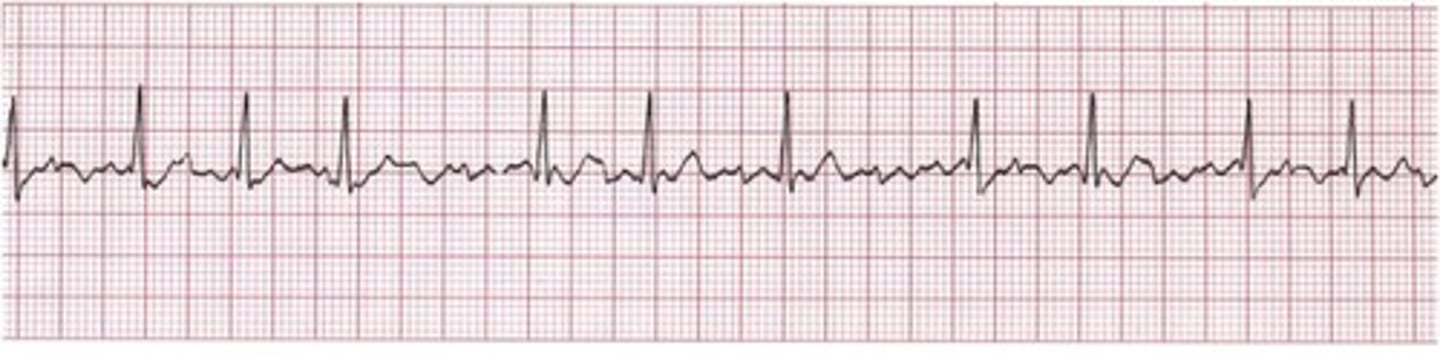
Afib graph looks like what?
Extra spiky
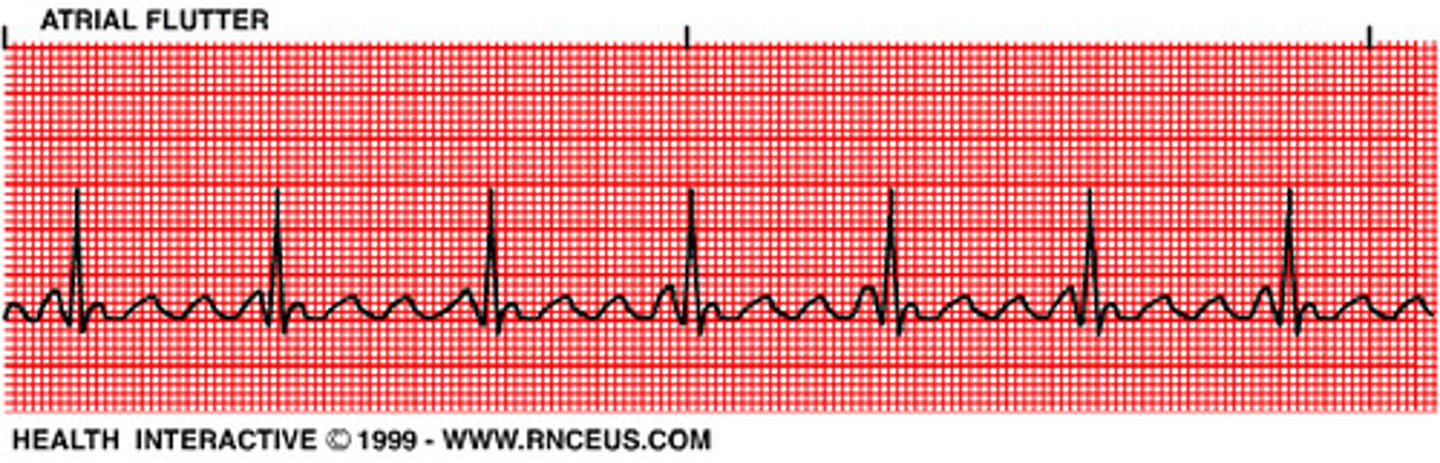
Aflutter graph looks like what?
More squiggly in the middle
What are the FDA-cleared Direct to Consumer monitor types? (four)
Apple Watch
Fitbit sense
Samsung Galaxy Watch 3
Withings ScanWatch
Clinical characteristics of AF?
Palpitations, exertional fatigue, lightheadedness, exercise intolerance, dyspnea
Syncope is possible but uncommon
What are the 4As of AF management?
Access to All Aspects of Care for All
What does SOS stand for in AF management?
Stroke risk
Optimize (modifiable risk factors)
Symptom management
What does HEAD 2 TOES stand for in AF management?
Heart failure, exercise, arterial hypertension, diabetes, tobacco, obesity, ethanol, sleep
These are the most common/pertinent risk factors for AF
Primary prevention recommendations (LRFM) for management of AF?
Patients at increased risk of AF should receive comprehensive guideline-directed LRFM for AF, targeting obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy alcohol consumption, smoking, diabetes, and hypertension.
What is the recommended percentage weight loss for secondary prevention in AF management?
Target of 10%
What is the recommended weekly physical fitness guideline for secondary prevention in AF management?
210 minutes/wk
Which risk score assessment do we prefer for assessing AF risk?
CHADS-VASc
T/F: For stroke management in Afib, we prefer DOACs over warfarin.
True
DOACs include? (four)
Apixaban
Dabigatran
Edoxaban
Rivaroxaban
T/F: ASA alone or with clopidogrel is an acceptable alternative to DOAC or warfarin in stroke management of AF.
False; only in the presence of another indication
Dosing for apixaban in Afib? Include adjusted dosing and why?
5 mg PO BID
2.5 mg PO BID if patient has any 2 of the following:
Age 80+
Body weight < or equal to 60
SCr > or equal to 1.5
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) dosing in Afib?
150 mg PO BID
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) dosing in Afib patients that have a CrCl of 15-30 mL/min?
75 mg PO BID
Contraindications associated with dabigatran?
Hypersensitivity, active pathological bleeding, mechanical heart valves
Edoxaban dosing in Afib?
60 mg PO daily
Edoxaban dosing in Afib for patients with a CrCl of 15-50 mL/min?
30 mg PO daily
Rivaroxaban dosing in Afib?
20 mg PO daily
With biggest meal
Rivaroxaban dosing in Afib for patients who have a CrCl of 15-50 mL/min?
15 mg PO daily
With biggest meal
What drug is responsible for the reversal of dabigatran?
Idarucizumab
What drug is responsible for the reversal of apixaban, rivaroxaban?
Andexanet alfa (Andexxa)
What drug is responsible for the reversal of acute major bleeding in patients receiving VKAs?
4-Factor PCC (Kcentra)
What drug is responsible for control and prevention of bleeding episodes, and is sometimes use off-label to reverse dabigatran-associated life-threatening bleeds?
Activated PCC
T/F: Most patients will need therapies to control HR, revert to SR, or maintain SR to limit symptoms or improve outcomes; most of these patients require a combination approach.
True
T/F: In older patients, we prefer rate control.
True
What are the three criteria we look for to determine that we prefer rate control over rhythm control?
If a patient is:
Older
Has a longer history of AF
Has fewer symptoms
We prefer rate control
What are the three criteria we look for to determine that we prefer rhythm control over rate control?
If a patient is:
Younger
Has a shorter history of AF
Has more symptoms
We prefer rhythm control
What is our goal HR in Afib patients without HF?
Less than 100-110 bpm
T/F: Non-DHP CCBs should be avoided in HFrEF.
True
Antiarrhythmic medications for rhythm control? (five)
Dofetilide
Donedarone
Flecainide
Propafenone
Sotalol
Non-pharm rhythm control options?
Cardioversion
Catheter ablation
Key features of pharmacological cardioversion?
Success rate varies with agent and duration of AF
No need for general anesthesia
Concerns with side effects/toxicity of AAD
Key features of direct current cardioversion (DCC)?
Associated with higher success rates
Treatment of choice for hemodynamic instability
Need for general anesthesia
T/F: Patients that undergo cardioversion need to be anticoagulated with UFH or LMWH.
True
When is pharmacological cardioversion a reasonable alternative?
For those who are hemodynamically stable, pharmacological cardioversion is a reasonable alternative to electrical cardioversion.
Pharmacological agents used for cardioversion? (four)
Ibutilide (if LVEF > or equal to 40%)
Amiodarone IV (longer to convert)
Flecainide, propafenone
Alternative: IV procainamide
When do we consider maintenance of sinus rhythm?
Reasonable for long-term therapy in those who are not candidates or decline catheter ablation, or prefer antiarrhythmics.
Pharmacological agents used for maintenance of sinus rhythm? (four)
Dofetilide, amiodarone (if LVEF < or equal to 40%)
Flecainide, propafenone (no previous MI, structural heart disease, ventricular scar or fibrosis)
Dronedarone
Alternative: Sotalol
Class Ia antiarrhythmics include? (three)
Disopyramine
Procainamide
Quinidine
Class Ib antiarrhythmics include? (two)
Lidocaine
Mexelitine
Class Ic antiarrhythmics include? (two)
Flecainide, propafenone
Class II antiarrhythmics include? (three)
Beta blockers
Metoprolol
Esmolol
Labetalol
Class III antiarrhythmics include? (five)
Amiodarone
Dronedarone
Dofetilide
Sotalol
Labetalol
Class IV antiarrhythmics include? (two)
CCBs
Verapamil
Diltiazem
T/F: Amiodarone has class I, II, III, and IV effects.
True
Side effects associated with amiodarone?
Photosensitivity
Blue-gray skin discoloration
Hypothyroidism
Elevation of 2x or greater in UNL
Tremors, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, insomnia
Corneal micro deposits
Optic neuropathy
Indication of dofetilide?
Maintenance of NSR in patients with highly symptomatic AF
Dosing for dofetilide?
500 mcg po BID
Renally adjusted dosing for dofetilide in patients with CrCl 40-60 mL/min?
250 mcg po BID
Renally adjusted dosing for dofetilide in patients with a CrCl < 40 mL/min?
125 mcg BID
T/F: Dofetilide is contraindicated in patients with a CrCl of less than 20 mL/min.
True
Contraindications associated with dofetilide?
Congenital or acquired long QT syndrome, concurrent use with verapamil, cimetidine, HCTZ, trimethoprim, itraconazole, ketoconazole, prochlorperazine, megestrol
Adverse effects associated with dofetilide?
HA, dizziness, syncope, insomnia, QT prolongation
T/F: Prior to administration of dofetilide, previous AAD should be held for at least 3 half-lives.
True
T/F: During its initiation phase, dofetilide can potentially increase the risk of TdP.
True
Dronedarone (Multaq) dosing?
400 mg PO BID
US boxed warning for Multaq says what?
Increased risk of death, stroke, and HF
T/F: Multaq is used in the treatment of AF in patients with NYHA class III and/or IV, or patients who have had an episode of decompensated HF in the past 4 weeks.
False; explicitly not used for these.
Adverse effects associated with Multaq?
Abdominal pain
Bradycardia
N/V/D
QT prolongation
TdP
T/F: Multaq is hepatotoxic.
True
Dronedarone vs. Amiodarone: Approved Uses
Dronedarone is approved for the treatment of paroxysmal or persistent AFib or AFlu (not permanent)
It is not for ventricular arrhythmias
Amiodarone is approved for the treatment of supraventricular and ventricular tachyarrhythmias (VF, VT, AF, AFlu)
Dronedarone vs. Amiodarone: Half-life
The half-life of dronedarone is 15 hours.
The half-life of amiodarone is 40-100 days.
Ibutilide (Corvert) IV dosing
Cardioversion only
< 60 kg: 0.01 mg/kg over 10 min
> or equal to 60 kg: 1 mg over 10 min
Adverse effects associated with ibutilide (Corvert)
Nonsustained VT, QT prolongation, TdP
For how long after administration of Ibutilide (Corvert) should ECG monitoring be done?
At least 4 hours, or until QTc has returned to baseline
Treatment for Torsades de Pointes includes? (four)
1. Magnesium sulfate 1-2g IV over 1-2 min
2. Beta-blockers (long-term treatment)
3. Permanent pacing
4. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Adverse effects associated with propafenone?
AFlu, bradycardia, dizziness, dyspnea, HF exacerbation, taste disturbances, VT, visual disturbances
Cardioversion dosing for propafenone?
> or equal to 70 kg, 600 mg x 1
< 70 kg, 450 mg x 1
Maintenance dosing for propafenone?
150 - 300 mg PO q8h
ER 225 - 425 mg PO q12h
Adverse effects associated with flecainide?
AFlu, AV block, dizziness, dyspnea, HF exacerbation, HA, QT prolongation, VT, visual disturbances
Antiarrhythmic drugs that prolong QT?
Class I (especially Class Ia and III??)
Antibiotics that prolong QT?
quinolones and macrolides
Azole antifungals that prolong QT?
Fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole
Antidepressants that prolong QT?
TCAs, SSRIs, SNRIs, mirtazapine, trazodone
Antiemetic agents that prolong QT?
5-HT3 receptor antagonists
Droperidol
Phenothiazines
Antipsychotics that prolong QT?
Most of them I think
In hospital initiation of dofetilide requires patients do be in the hospital how long?
At least 3 days; must remain in hospital at least 12 hours after conversion (~5 doses)
What lab values do we monitor for dofetilide?
Mg
K
SCr
Guidelines for who should not receive dronedarone?
NYHA class III or IV, or in patients who have had an episode of decompensated HF in the past 4 wks
Adverse effects associated with dronedarone?
GI upset, bradycardia, inc. SCr, QTc prolongation
T/F: Ibutilide (Corvert) is only administered IV for cardioversion.
True
Adverse effects associated with ibutilide?
Non-sustained VT, QT prolongation, TdP
For how long must patients be in the hospital to be administered sotalol?
At least 3 days