BCS2005 Exam 2 Module 6: Inheritance
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are the products of meiosis? How many cells? How does their DNA compare to the original cell?
meiosis produces four haploid gametes
they contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
· What happens a) to the chromosomes, and b) to the rest of the cell during each of the phases of meiosis 1? Meiosis 2?
Meiosis 1: homologous chromosomes seperate, halving the chromosome number
Meiosis II: sister chromatids seperate
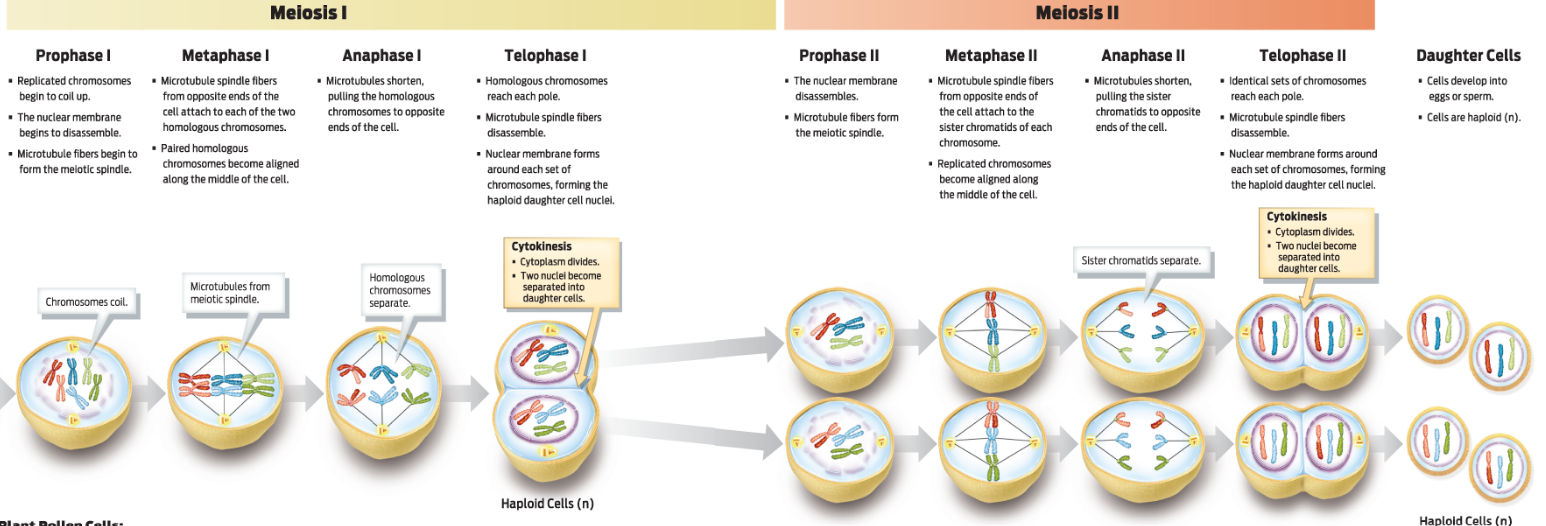
· What are homologous chromosomes? What are chromatids?
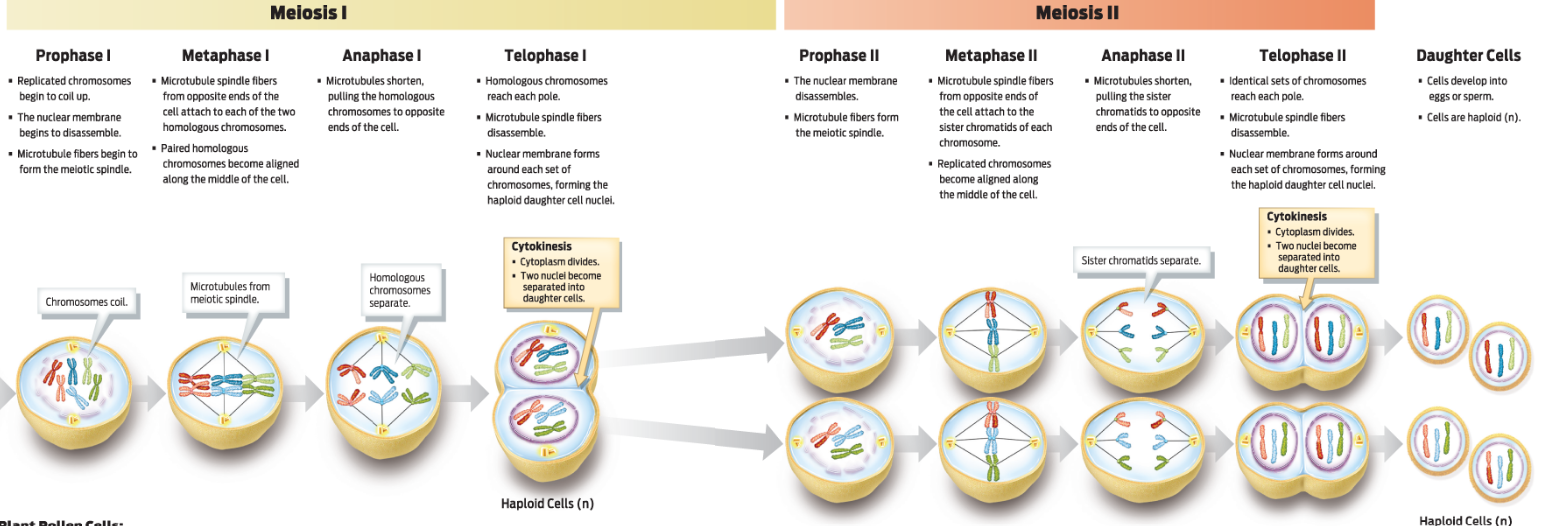
· Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis.
Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. | Production of gametes (sperm and egg) for sexual reproduction. |
Number of Divisions | One division. | Two divisions (Meiosis I and Meiosis II). |
Number of Daughter Cells | Two daughter cells. | Four daughter cells. |
Chromosome Number | Daughter cells are diploid (2n), same as the parent. | Daughter cells are haploid (n), half the number of chromosomes of the parent. |
Genetic Composition | Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent and each other. | Daughter cells are genetically diverse due to crossing over and independent assortment. |
Occurs in | Somatic (body) cells. | Germ cells (to produce gametes). |
Crossing Over | Does not occur. | Occurs during prophase I, exchanging genetic material between homologous chromosomes. |
Homologous Chromosomes | Do not pair or align. | Pair up during prophase I (synapsis) and align during metaphase I. |
Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate. | - Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate. - Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate. |
· What is the principle of independent assortment? When does it happen?
when sex cells undergo meiosis, or division, they do not make exact copies of the parent’s genotype. Instead, they form unique combinations of alleles, or dominant and recessive genes, that may express themselves differently than those of the parent.
divided sex cells undergo recombination to produce unique offspring
occurs during prophase I or meiosis I
What is recombination? When does it happen?
Occurs during meiosis
includes crossing ober
· What is aneuploidy? When does it happen?
aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal numbr of chromosomes in a cell
occurs during meiosis
· What is a gene? What is an allele?
Gene: a unit of hereditary information that occupies a fixed position on a chromosome
allele: a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a locus on a DNA molecule
any one of two or more genes
· What does it mean if an organism is heterozygous? Homozygous?
homozygous: two identical alleles for a specified gene
heterozygous: two different alleles for a specified gene
· What’s the difference between an organism’s genotype and its phenotype?
phenotype is the physical expression of the genotype
genotype is its genetic makeup
· What does it mean for a phenotype to be dominant? Recessive?
recessive alleles can only produce a recessive phenotype if the genotype is homozygous
What is blending inheritance? How did Mendel prove it wrong?
blending inheritance: offspring are just a smooth blend of their parents traits
if this were true, genetic variation would disapear over time
mendel cross bred pure short and tall pea plants
all of the first generation were tall- showed tall was dominant
later generations had a mix of tall and short
· Given an individual’s genotype, be able to list all of the possible types of gametes that individual could make. Be able to do this for one gene at a time, but also be able to list all of the combinations of alleles in the gametes for more a genotype containing more than one gene.
· Be able to use Punnett squares to get from parental genotypes (or phenotypes) to predicted frequencies of offspring genotypes (or phenotypes). Be able to do this for monohybrid AND dihybrid crosses.
· What’s the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes?
autosomes are body chromosomes
humans have 22
diploid
sex chromosomes
haploid
1 pair
· What does it mean to be hemizygous? Which individuals (in humans) are hemizygous? For which genes?
hemizygous: organism only has one copy of a gene instead of the usual two in a diploid organism
males are hemizygous for x-linked genes
· What are sex-linked/X-linked traits? Which sex (in humans) is more likely to express the phenotype of these traits? Which is more likely to be a carrier? Be able to use this to trace the inheritance of these traits through a pedigree.
males are more likley to express the phenotype and females are more likley to be carriers
· How does genotype relate to phenotype in a trait with Mendelian (typical) dominance? Incomplete dominance? Codominance? Be able to use Punnett squares to give offspring genotype & phenotype frequencies for each.
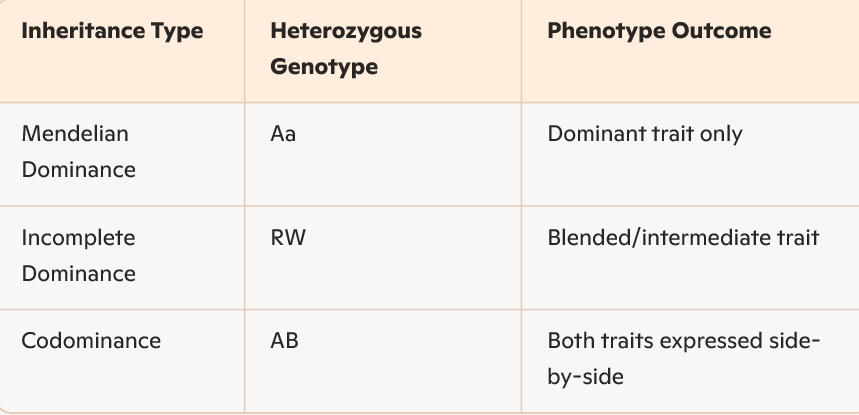
· How does ABO blood typing work? What kind of trait is this? Be able to use Punnett squares… etc. etc.
codominant (both alleles are expressed in the phenotype)
A and B are codominant, O is recessive
· What are polygenic traits? How do they differ from traits with multifactorial inheritance?
polygenic traits: characteristics taht are controlled by multiple genes
multifactorial traits have multiple genes PLUS ENVIORONMENTAL factors
while all multifactorial traits are polygenic, not all polygenic traits are multifactorial