NET4009-Module 8b - IS-IS basics review
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What was the intention of IS-IS?
IS-IS was intended to be used as a dynamic routing protocol for routing Connectionless Network Protocol (CLNP) packets in the ISO CLNS environment
Where does IS-IS operate?
directly on top of an Ethernet header, using its own header format
IS-IS NSAP Addressing consists of what 3 parts?
Area
SYS ID
SEL (Selector)
Network Service Access Point (NSAP) Address format used for IS-IS
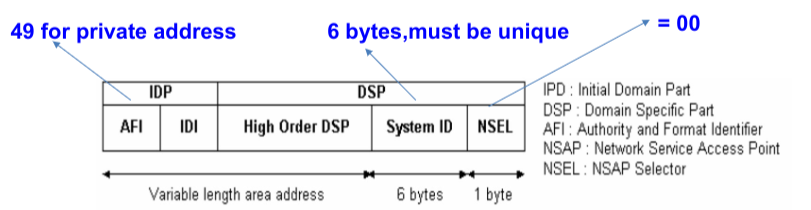
IS-IS NSAP Addressing: Examples
• 49.0001.aaaa.bbbb.cccc.00
• Area = 49.0001, SysID = aaaa.bbbb.cccc, NSel = 00
IS-IS Adjacency States
Down
Initialising
Up
IS-IS Layer Hierarchy
The backbone (Level 2)
The areas (Level 1)
What can the routers be in IS-IS?
Level 1 router (intra-area routing)
Level 2 router (inter-area routing) ~ backbone router
L1/L2 router (inter and intra area routing
IS-IS PDUs
IS-IS Hello Packet: timers do not have to match
Link State Packets (LSPs)
PSNP (Partial Sequence Number PDU)
CSNP (Complete Sequence Number PDU)
How is IS-IS link-state database synchronized?
using special PDUs: PSNPs and CSNPs
All routers in IS-IS establish adjacency with which router?
to the DIS (Designated IS)
What happens if the DIS fails?
If the DIS fails, another router can take over immediately with little or no impact on the topology
On a broadcast network which router will be the DIS?
There will be no DIS
What does the DIS do?
the DIS is responsible for flooding. it creates and floods a new pseudonode LSP for each routing level in which it is participating and for each LAN to which it is connected
How is the DIS elected?
based on interface priority (default = 64)
When does the DIS election happen?
It is preemptive. When a new router boots on the LAN with a higher interface priority then the new router becomes the DIS and purges the old.
When does the DIS flood a new pseudonode LSP?
When a new neighbor comes up or goes away
When refresh interval timer expires
Is the DIS for Layer 1 or Layer 2?
BOTH!
Pseudonode LSP is created by the DIS (DIS election is per level):
• One for each level (Level 1 and/or Level 2)
• One for each LAN
What are the two tasks that a DIS does?
1- Create and update a pseudonode LSP that reports links to all neighbors.
2- Create a CSNP (Complete Sequence Numbers Protocol).
IS-IS TLVs
IS-IS Metrics
Narrow Metric: default, 10 bits wide
Wide Metric: 24 bits
How to allow both IS-IS metrics?
The metric-style transition command can be configured in case of mixed metric environment to advertise both metrics (narrow and wide metrics)
What are the two mandatory requirements for IS-IS IPv6?
Wide Metric
Multi-Topology
Multi-Topology (MT) IPv6 IS-IS configuration
The optional keyword “transition” can be used for transitioning existing IS-IS IPv6 single topology to IS-IS IPv6 Multi-topology