Physiology 1-5
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Describe the concept of emergent properties
An emergent property is a trait that becomes something when you combine things together
What are cells
Cells are made up from atoms and molecules
What is an example of a cell?
neurons are cells that make nerve tissue
red blood cells: carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body
How are cells protected from their external environment?
By a lipid and protein barrier
What is the general name of the fluid inside cells?
Intracellular fluid
What is the general name of the fluid outside cells?
Extracellular fluid
Which of these fluids is the key site of homeostasis as it applies to
physiology?
Extracellular fluid
Describe the relationship between cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems
Cells are in every living thing and they group together to form tissues, tissues combine to create organs that have specific functions and organs work together to create a organ systems and keep the body functioning
What is one key functional feature that is common among the following organ
systems: respiratory system, digestive system, urinary system, and reproductive
system?
They all exchange material between the internal and external environment
What is a structural feature that is common among the following organ systems:
circulatory system, nervous system, endocrine system, and immune system?
Transport material within the body
List the 10 organ systems of the body, their major components, and a
representative function.
integumentary- protective layer
musculoskeletal- supports body movement
respiratory-exchange gasses
digestive- eliminates waste
urinary (renal)- removes excess water and waste
reproductive- produces eggs and sperm
cardiovascular - pumps blood through vessels
nervous- coordinates body function
endocrine- coordinates body function
immune- protects internal environment
Contrast between teleology and mechanism.
Teleology approach explains the “why”
mechanism approach explains the “how”
Why is homeostasis required for the body?
It helps keep the body stable
How is homeostasis achieved in the body
The body monitors its internal stat and takes action to correct disruptions that threaten its normal function
What is the difference between normal physiology and pathology (or
pathophysiology)?
Normal physio is how the body works and the organ system working together to keep the body healthy.
pathology occurs when something goes wrong (when body fails to maintain homeostasis), often leading to a disease or illness
T/F: homeostasis is responsible for correcting external causes of pathology.
False
T/F: homeostasis may correct internal causes of pathology.
true
What is the significance of the body being an open system in terms of
homeostasis? As part of your response, describe, in general, what the body
would need to do when someone drank an excess amount of water. What
happens to this water?
it exchanges mater and energy with its environment so when it takes in things like water, oxygen and food it releases them as carbon dioxide, urine, and heat. This is important in homeostasis because our body has to adjust its internal environment . When someone drinks an excess amount of water the excess water filters through the kidneys and is eliminated by urine.
What is homeostasis?
Keeping the internal environment relativley stable
What is equilibrium?
Equilibrium means that something is in a state of balance
What is disequilibrium?
Something not being balanced (ex: drinking excess water)
An example of disequilibrium in the body
When blood sugars rises the body releases insulin to level it down
What are examples of regulated variables in the body?
Blood pressure
Blood glucose
a diagram with the four major components of a Control Syste
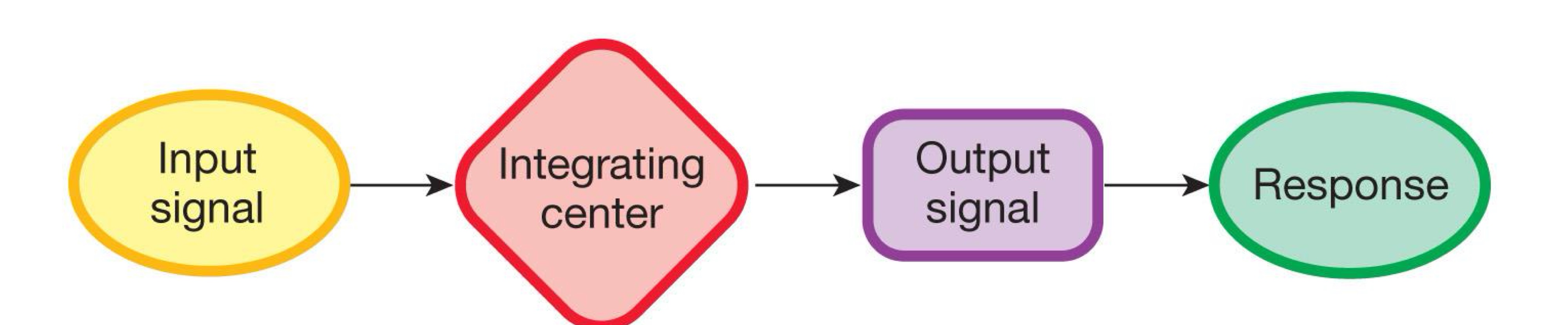
a diagram of a reflex pathway.
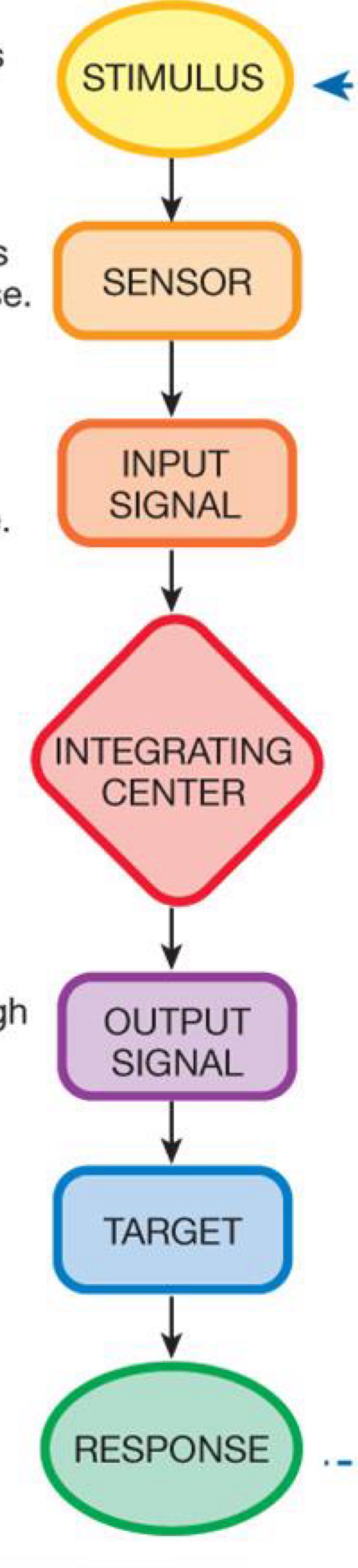
Describe the difference between
negative feedback and positive
feedback.
Negative: the espouse counteracts the stimulus, shutting off the response loops.
Positive: the espouse reinforces the stimulus , sending the variable farther from the set point
Giving birth is an example of (choose):
a. Positive feedback
b. Negative feedback
c. Response loop
d. Homeostasis
a. Positive feedback
What is feedforward control?
Anticipation that a change is about to happen to prepare the body for the change
What is the abbreviation for the following ions?
a. Sodium ion →
b. Potassium ion
c. Calcium ion
d. Hydrogen ion
e. Magnesium ion →
f. Chloride ion
g. Bicarbonate ion
h. Phosphate ion
a. Na+
b. K+
C. Ca2+
D. H+
E. Mg2+
F. Cl-
G. HCO-3
H. HPO4 2-
What are two functions of ions in the body?
Forms the basis for the electrical signaling in the body
Some act as buffers to prevent changes in ph
Why do we need buffers in the body?
To maintain a Stable ph
What are two types of biomolecules where a phosphate group is present?
Nucleotides and nucleic acids
Phospholipids
What type of biomolecule is a triglyceride?
A lipid
Explain in your own words the relevance of cholesterol in physiological function. In other words, what does cholesterol do in the body? And what happens if there is too much of it?
Cholesterol is the primary source in the human body. It balances salt and water, it’s a stress respond and dietary nutrient absorption, if there is too much there could be liver dysfunction, atherosclerotic vascular disease and dermatological abnormalities.
What is the major component of cell membranes?
phospholipid bilayer
What are the differences between sucrose, glucose, and glycogen?
Glucose is our body’s source of energy
Sucrose is sugar we eat that breaks down into glucose + fructose
Glycogen is how the body stores extra glucose for later use
What is the technical term used to describe diabetes
Diabetes mellitus
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
List the 7 major functions of proteins
Enzymes
Membrane transporters
Signal molecules
Receptors
Building proteins
Immunoglobulins
Regulatory proteins
Insulin is a type of which biomolecule? What type of molecular interaction
connects the two chains of insulin together?
A protein. Chain A connects to chain B by covalent bonds
Hemoglobin is which type of biomolecule?
Protein
DNA stands for
Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA stands for
Ribonucleic acid
ATP stands for
Adenosine tri phospate
All dna, rna, atp are types of
Nucleic acids
Water molecules are made up of 1 oxygen and 2 hydrogens. Both hydrogens
interact with the oxygen through covalent bonding. However, the whole water
molecule must interact with other water molecules around it. What is the name
of this type of interaction?
Hydrogen bond
Things that are hydrophilic can easily dissolve in water. Things are hydrophobic
dissolve poorly in water or not at all. Salts, which can break down into their
positively and negatively charged ions such as NaCl → Na+ + Cl- easily dissolve
in water while molecules such as fats do not dissolve in water
Fats (fatty acids) are not charged and not polar. Water is polar, which means it
has a partial positive and a partial negative. As a result, ions that came from salts
can easily dissolve in water because they have a charge.
T/F: a protein that normally functions properly in the saliva (pH ~ 6.5) will be denatured (lose its structure) in the stomach (pH ~ 1) and fail to function.
True
Drug A works by entering cells and binding to Protein X, which can then act as an enzyme to break apart DNA. However, Drug A does not bind to the active site of Protein X.
a. Which of the following would be true of Drug A?
Drug A is an allosteric modulator
Drug A works by entering cells and binding to Protein X, which can then act as an enzyme to break apart DNA. However, Drug A does not bind to the active site of Protein X.
B. Which of the following is true of DNA in this situation
DNA is a ligand (same as substrate)