Chapter 52 | Ecology and the Biosphere
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Ecology
The study of the interactions that living organisms have with the living and nonliving components of their environment
Organismal Ecology
Individual organisms and their interactions with the environment and other organisms
Population Ecology
Studies how individuals of the same species interact with each other and their environment, including factors like population size
Community Ecology
Examines all populations of different species in a given area and their interspecies relationships and interactions
Ecosystem Ecology
The interactions between living organisms and nonliving components in an environment, combining community dynamics with physical factors
Landscape Ecology
Mosaic of ecosystems
Global Ecology
The biosphere - sum of all the planet’s ecosystems and landscapes
Terrestrial organisms & their environment
Depend on climate
Climate
Long-term weather conditions in a particular area
Weather
Sunlight & temperature, air circulation, precipitation, ocean currents
Latitudinal variation
At higher latitudes, there’s less sunlight. Most sunlight is at the equator (0°), with a 23.5° tilt. Near the poles, the sun's angle is lower, resulting in less sunlight
Tropic of Cancer
23.5 degrees North
Tropic of Capricorn
23.5 degrees South
Seasonal variation
Caused by the tilt of the Earth
March/September Equinox (spring/autumn)
The sun hits the equator directly
June solstice (summer)
The sun directly hits the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N), bringing increased sunlight and temperature to the Northern Hemisphere
December solstice (winter)
The sun directly hits the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S), bringing increased light and temperature to the Southern Hemisphere
Wind patterns
Trade Winds: E → W
Westerlies: W → E
Precipitation patterns
Most occurs at the equator. At 30°N & 30°S, dry air results in very little rain
Ocean currents
Affect only coasts, moderating temperatures
Near the equator (E → W), east coasts get warmer ocean temperatures
Near poles (W → E), west coasts get cooler ocean temperatures
Regional effects
Mountain ranges disrupt air circulation, creating a rain shadow—precipitation falls on one side, leaving the other dry
Deforestation
Loss of vegetation leading to reduced photosynthesis and higher temperatures
Microclimates
Focused, specific localized climate
Climate change
A long-term change in climate (over 30+ years) that impacts the distribution of organisms
Biomes
Major life zones characterized by vegetation (land biomes) or physical factors like temperature and water (aquatic biomes)
Characteristics of terrestrial biomes
Each biome has a climate range shown by climographs
Ecotones
Many biomes, especially forests, have vertical layers
Organisms share characteristics due to convergent evolution
Disturbances (fires, hurricanes, landslides) are common
Climate range
The temperature and precipitation conditions typical for each biome
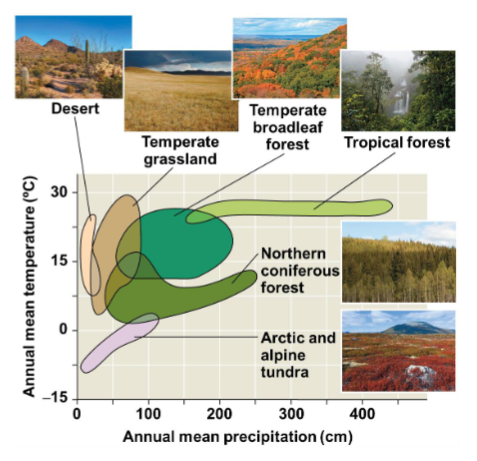
Climograph
Graph showing the average/mean temperature vs precipitation
Ecotones
Gradations that exist between each biome
Vertical layering in forests
Canopy - tree tops
Understory - lower trees & shrubs
Floor
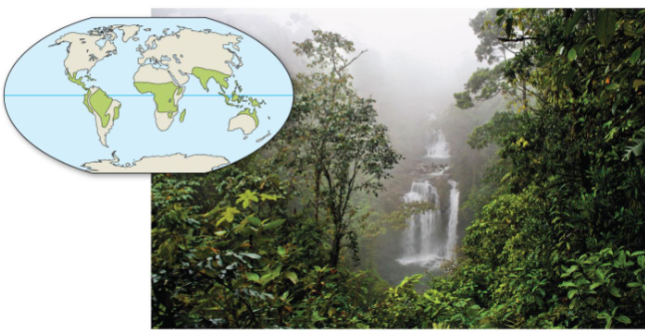
Tropical forest
Located at the equator with consistent warm temperatures (25-29°C)
The wettest biome (200-400cm rain/year)
High biodiversity and competition for resources
Has multiple layers, including emergent and midstory
Most competition occurs on the nutrient-poor forest floor

Desert
Less than 30cm of precipitation per year
Found near 30°N or 30°S
Variable temperatures (-30°C to 50°C) often seasonal or daily
Organisms are adapted to dryness and drought, with many being nocturnal
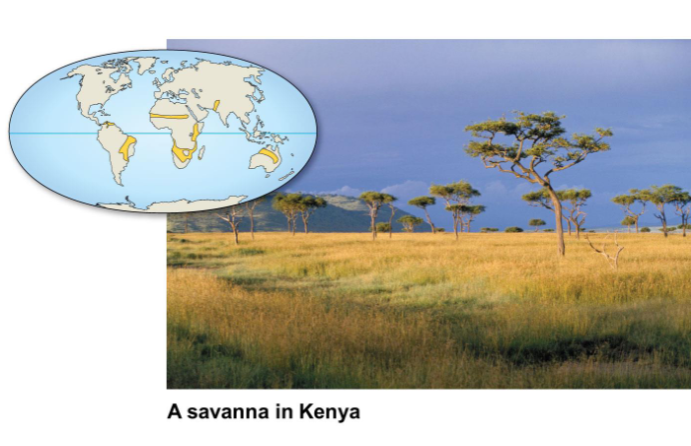
Savanna
Consistently warm (24-30°C)
Dry season (~9 months)
Wet season (30-50cm rain)
Organisms are adapted to drought and fire, with grasses and scattered trees
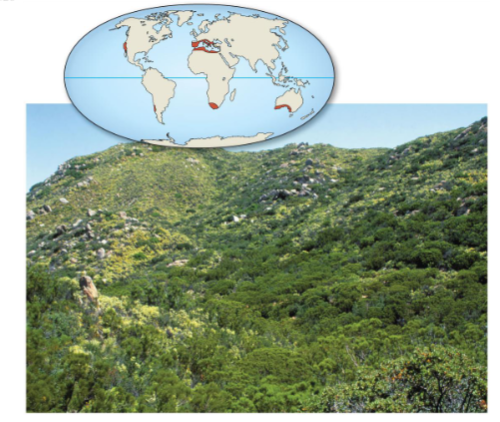
Chaparral
Wet winters (~10°C, 30-50cm rain)
Dry, hot summers (30-40°C)
Organisms are adapted to drought and fire
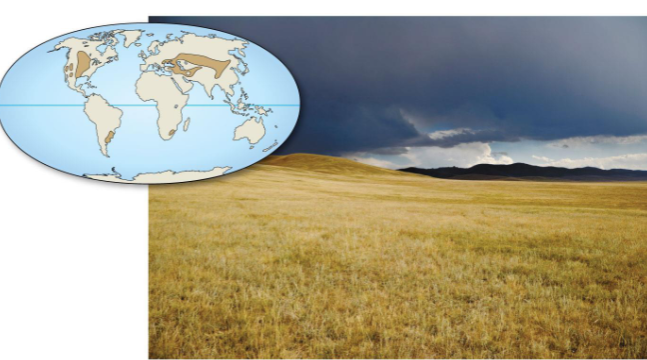
Grassland
Dry, cold winters (-10°C, snow/ice)
Wet, hot summers (30°C, 50-100cm rain)
Dominated by grasses and grazers, often converted into farmland
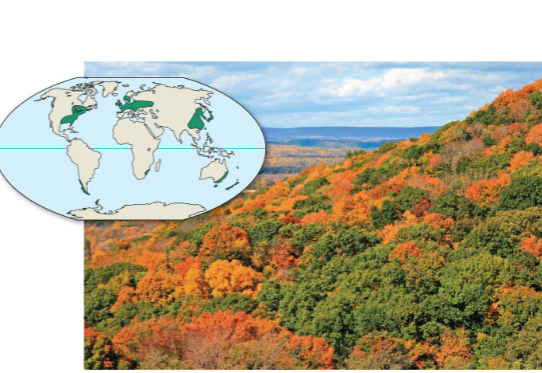
Temperate broadleaf forest
Summer: 30-35°C
Winter: 0-10°C
Consistent precipitation (70-200cm/year)
Organisms go dormant or migrate in winter
Features vertical layers: canopy, understory, shrubs, and floor
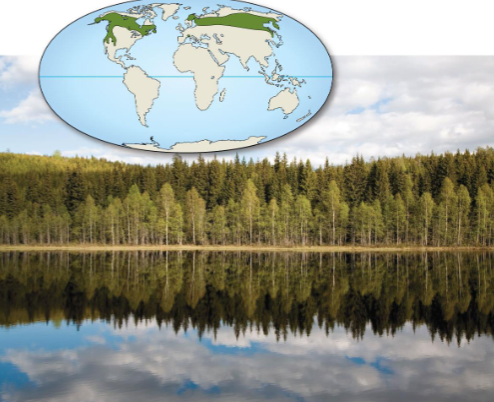

Northern coniferous forest
The largest terrestrial biome
Cold winters (-50°C)
Snowy precipitation
Summers are warmer (10-20°C)
Variable precipitation supports conifers that resist cold or go dormant in winter

Tundra
The coldest biome with short, wet summers and long, dry winters
Permafrost (permanent ice layer)
Mostly herbaceous plants
Aquatic biomes
Oceanic pelagic zone
Marine benthic zone
Freshwater biomes
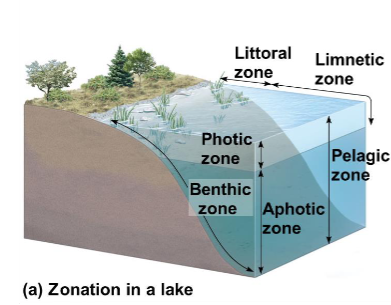
Zonation
The distribution of plants or animals into specific zones
Aquatic layering
Pelagic zone:
Photic zone
Aphotic zone
Benthic zone
Abyssal zone (only in oceans)
Pelagic zone
Photic zone & aphotic zone
Benthic zone
The ocean floor
Lakes from the shore
Littoral Zone: Shallow, rich in life near the shore
Limnetic Zone: Open water, farther from shore, with less life
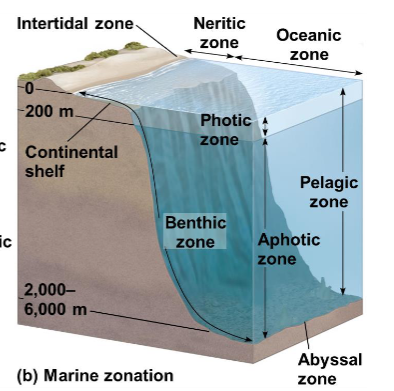
Oceans from the shore
Intertidal Zone: Organisms adapted to tides
Neritic Zone: Rich in life, close to shore
Oceanic Zone: Deep water, less life, more open
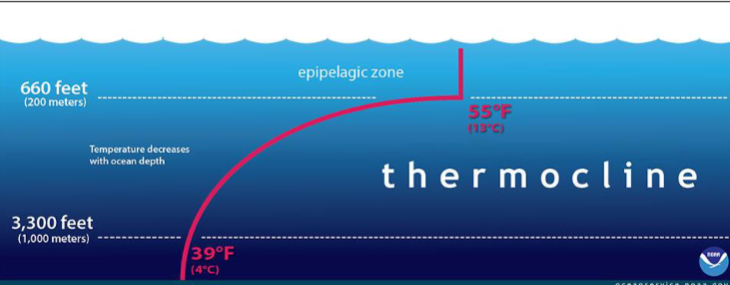
Thermocline
Gradual decrease in temperature due to increasing in depth
Oceanic pelagic zone
Covers ~70% of Earth; largest biome
Most life is in the photic zone (phytoplankton & zooplankton), with mixing from ocean currents

Hydrothermal vents
Hot spots due to Earth’s core heat, fostering chemoautotrophs and creatures that feed on them

Coral reefs
Found in the neritic and benthic zones
High biodiversity and thrive in waters between 20-30°C
Intertidal zone
Area that’s submerged in water part of the time, with organisms adapted to both water and air
Freshwater biomes
Lakes:
Eutrophic
Oligotrophic
Wetlands
Estruaries
Streams & Rivers

Eutrophic lakes
Lakes with high nutrients, much life, and low oxygen levels

Oligotrophic lakes
Lakes with low nutrients, little life, and high oxygen levels

Wetlands
Areas that are waterlogged for part of each day

Estruaries
Where freshwater mixes with salty seawater, creating a unique, brackish environment

Streams & rivers
Flowing water that starts fast and narrow (headwaters) and becomes wider and slower downstream
Altitudinal biomes
Biomes that mimic the latitudinal biomes based on altitude