Science Module 1 - Solar System I
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Information for uhhhh 😁
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Universe
Contains everything that is known to exist in this world, including objects such as galaxies, planets, stars, celestial bodies, etc. Our galaxy, known as the Milky Way galaxy, is one of the billion galaxies in the universe.

Solar System
Contains the sun, the eight planets, dwarf planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, and many other celestial bodies such as those in the Kuiper belt and interplantary dust. The Solar System is located within the Milky Way galaxy.
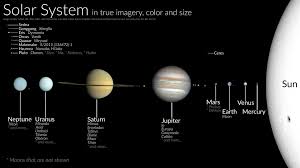
Outer Gaseous Planets
Called gas giants because of their larger size along with the high presence of gases in their composition. The gas giants rotate faster, have thicker atmospher, lower densities, more moons, and fluid interiors that are rich in hydrogen, helium, and ices (water, ammonia, methane).
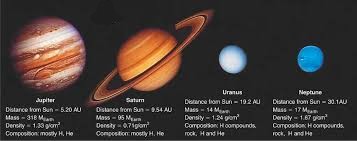
Mercury - Fun Fact
Smallest and fastest revolving planet in the Solar System

Venus - Fun Fact
The hottest planet in our Solar System

Earth - Fun Fact
Isn’t actually round; revolves around the sun in counter clockwise direction

Mars - Fun Fact
Has two moons, with their names being Phobos and Deimos

Jupiter - Fun Fact
Famous for its stripy appearance, along with the Great Red Spot

Saturn - Fun Fact
Rings aren’t solid; the rings are made of pieces of ice, dust, and rock

Uranus - Fun Fact
An ice giant (instead of gas giant); made mostly of flowing icy materials above a solid core

Neptune - Fun Fact
Furtherst planet from the sun, more than 30 times farther away from the Earth

Comets - Fun Fact
Called “dirty snowballs” because they are primarly composed of ice (snowball part), but are also mixed with dust and rock particles (dirty part).

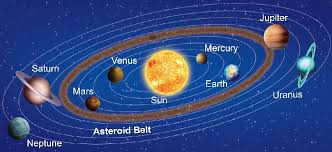
Asteroid Belt
Region of space between Mars and Jupiter that contain millions of asteroids
Meteoroid
A rock, usually an asteroid fragment, that revolves around the sun, traveling through space. Only called this before it has entered Earth’s atmosphere.

Meteor
A meteoroid that enters Earth’s atmosphere; burns up as it travels through the atmosphere.

Meteorite
A meteor that doesn’t completely burn up and has landed on the Earth’s surface.

Large Features of the Solar System
More of the mass of the Solar System is concentrated at the center (the Sun) while angular momentum (measure of how much an object rotates) is held by the outer planets.
Orbits of the planets are oval shaoed and are all on the same plane.
All planets revolve around the Sun.
The periods of revolution of the planets increase with distance from the Sun. The innermost planets revolve the fastest whereas the outermost revolve the slowest.
All planets are located at regular intervals from the Sun.
Small Features of the Solar System
Most planets rotate prograde (spins in the same direction as its orbit).
Inner Terrestrial Planets
Made of materials with high melting points (silicates, iron, nickel, etc)
Rotate slower, have thin or no atmosphere, higher densities
Lower contents of volatiles (hydrogen, helium, and noble gases)

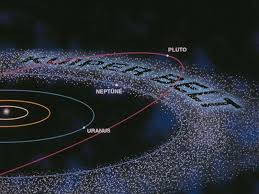
Kuiper Belt
Region of the Solar System beyond the orbit of Neptune that is filled with icy rocky bodies. Pluto lives here.
BL’s Pocket
A small region located near the Sun. The closer region near the Sun generate what scientists call “Spicy BL,” whereas the outer region of BL’s Pocket generate “Shounen AI BL.” Once formed, the BL orbit the Sun and travel throughout space in which they will occasionally enter Earth’s atmosphere and land on the surface.
