Topic 14 - CNS/PNS
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
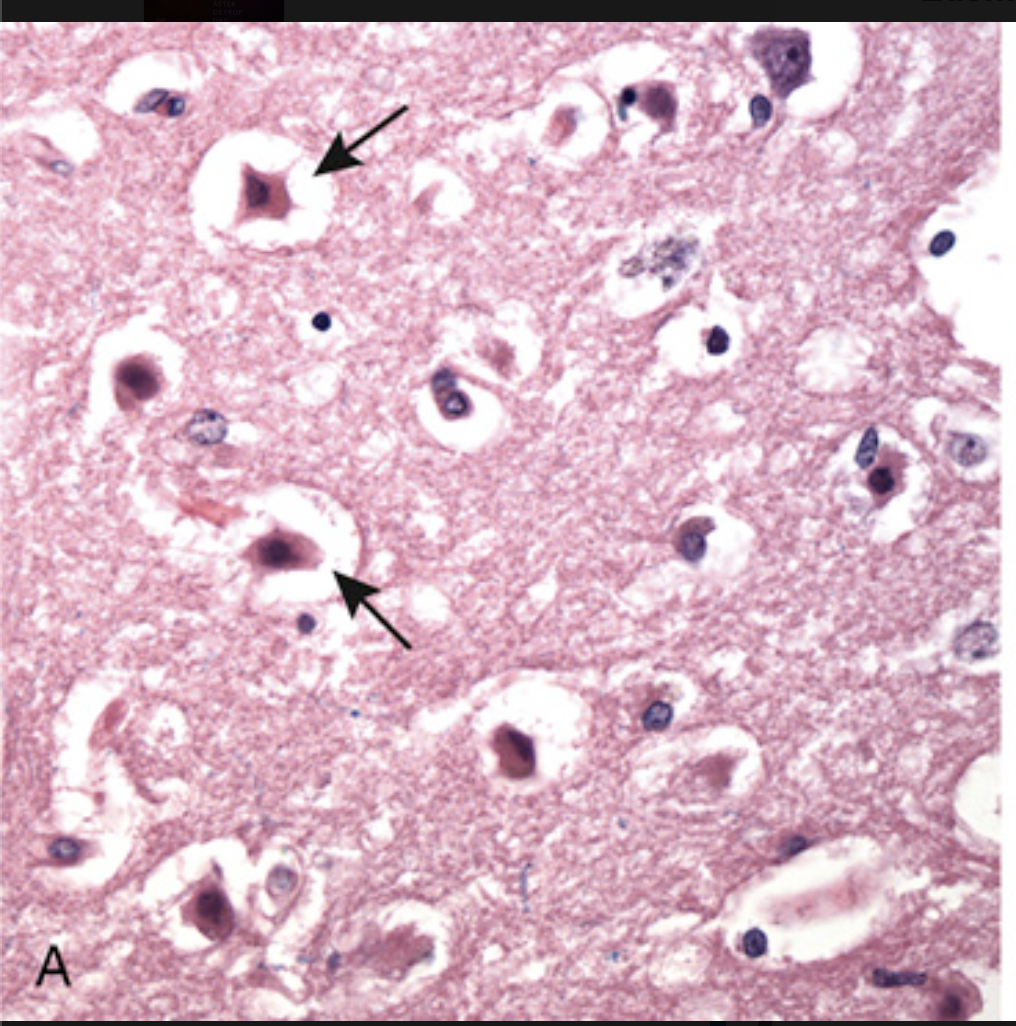
Patterns of neuronal injury. (A) Acute hypoxic-ischemic injury in the cerebral cortex. The cell bodies are shrunken and eosinophilic (“red neurons,” arrows), and the nuclei are pyknotic.
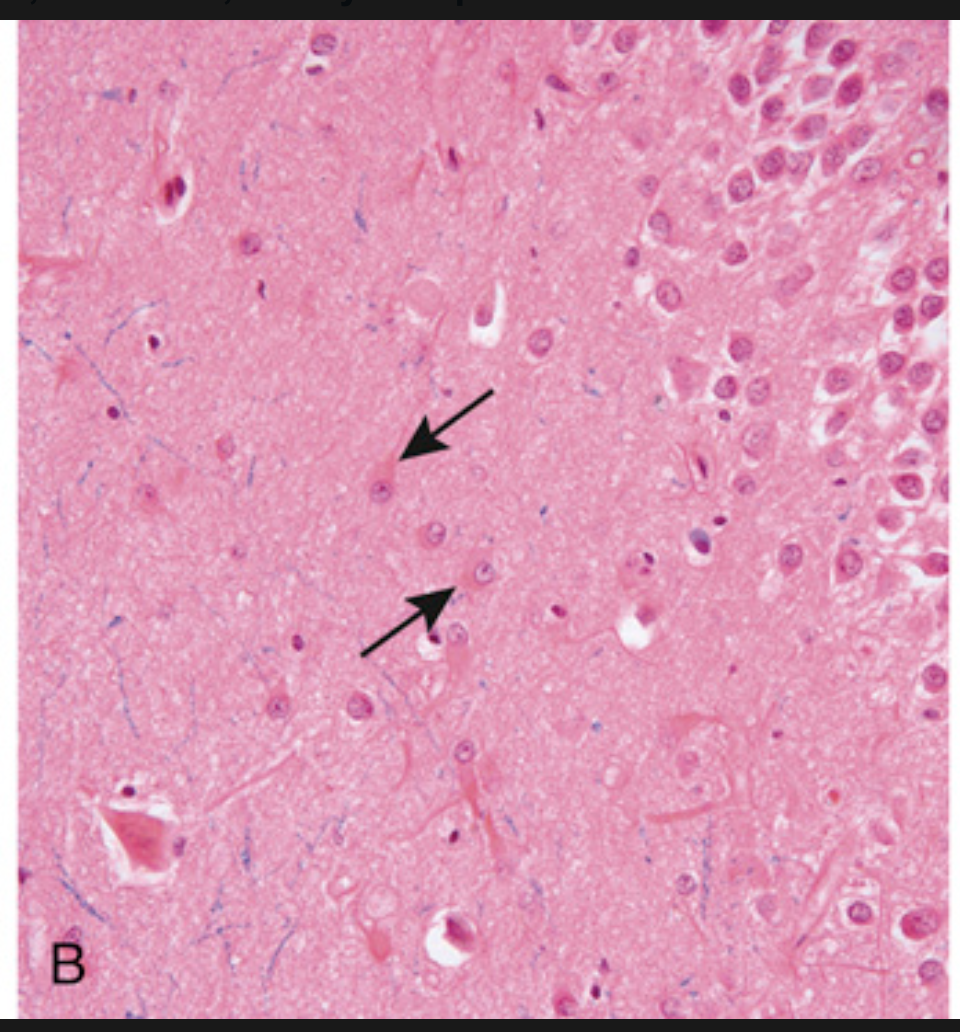
Patterns of neuronal injury. (B) Reactive astrocytes (arrows), with eosinophilic cytoplasm and multiple radiating processes.
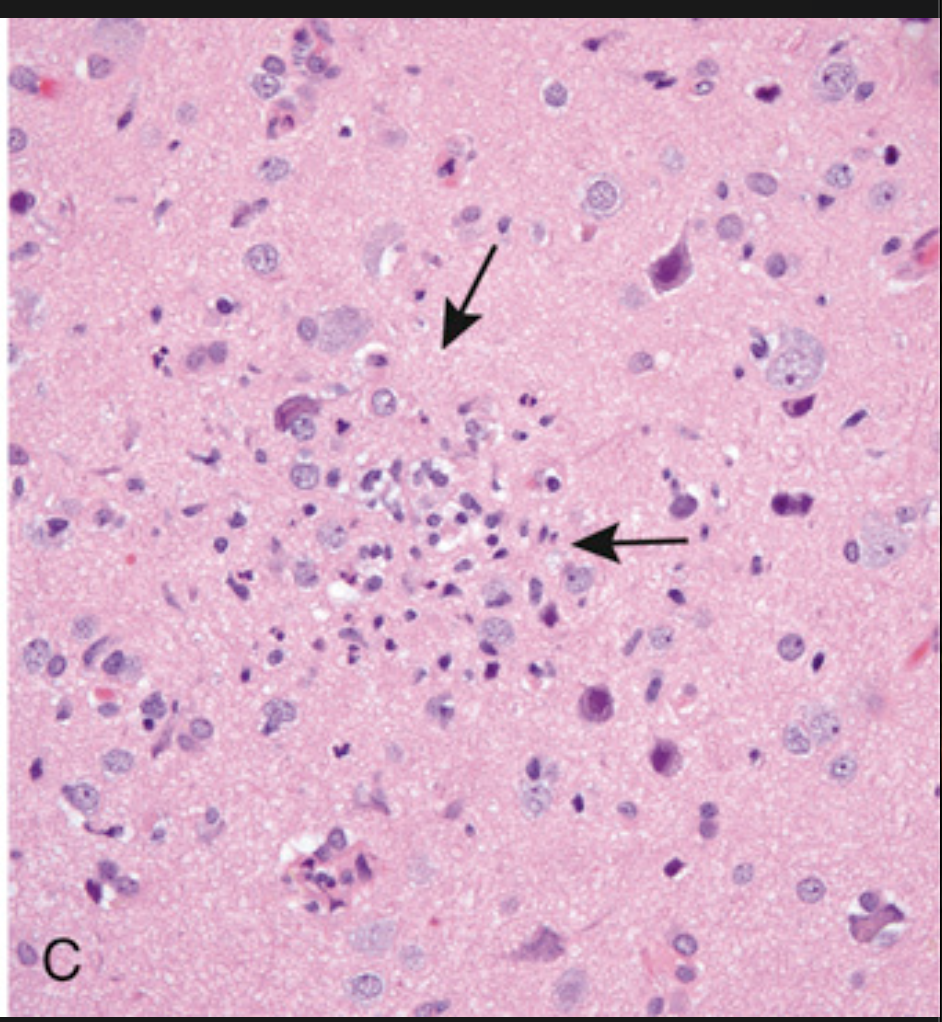
Patterns of neuronal injury. (C) Collection of microglial cells forming a poorly defined nodule (arrow), a common finding in viral infections
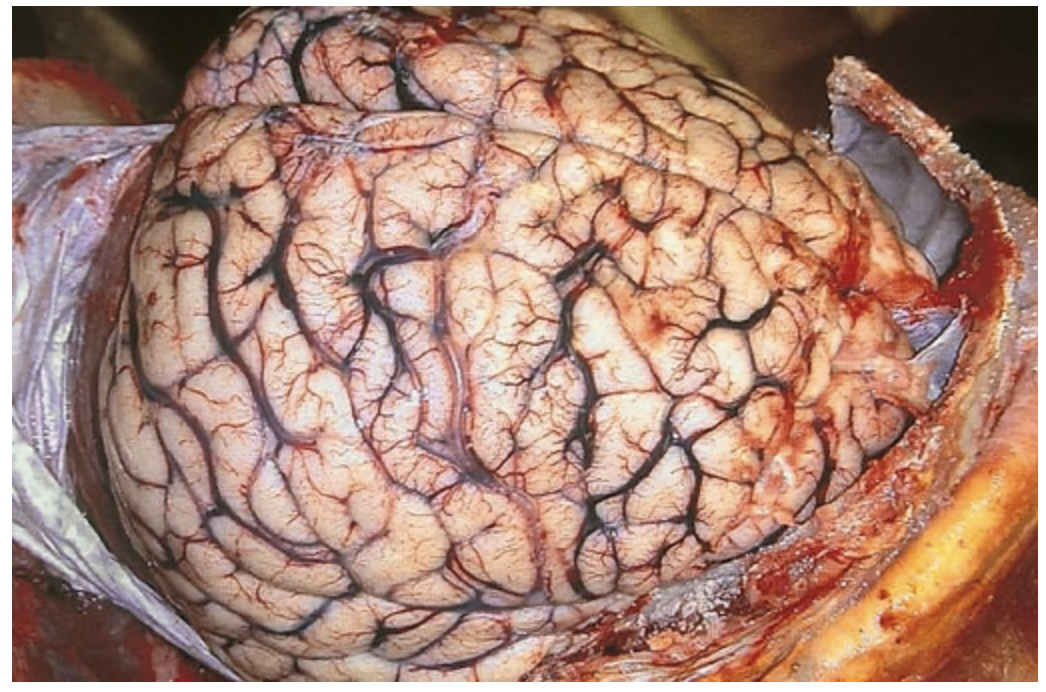
Cerebral edema. The surfaces of the gyri are flattened as a result of compression of the expanding brain by the dura mater and inner surface of the skull. Such changes are associated with a dangerous increase in intracranial pressure
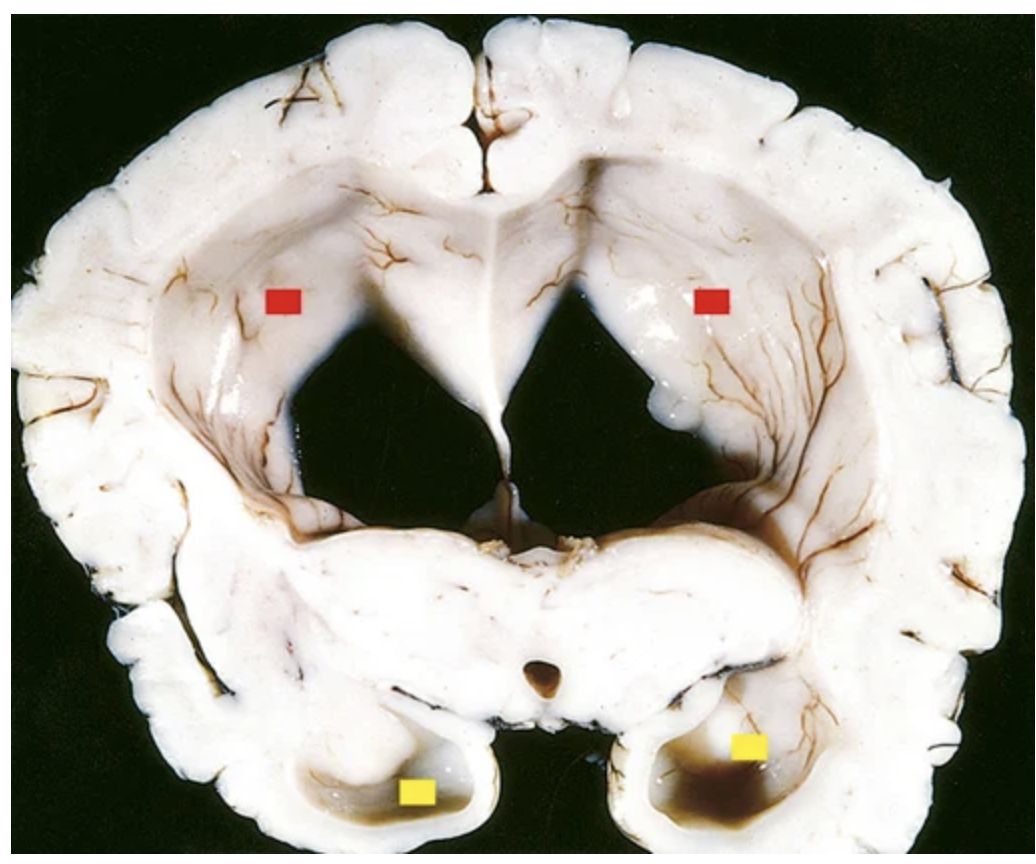
Hydrocephalus. Dilated lateral ventricles (red boxes, bodies of lateral ventricles; yellow boxes, posterior horns of lateral ventricles) seen in a coronal section through the mid-thalamus
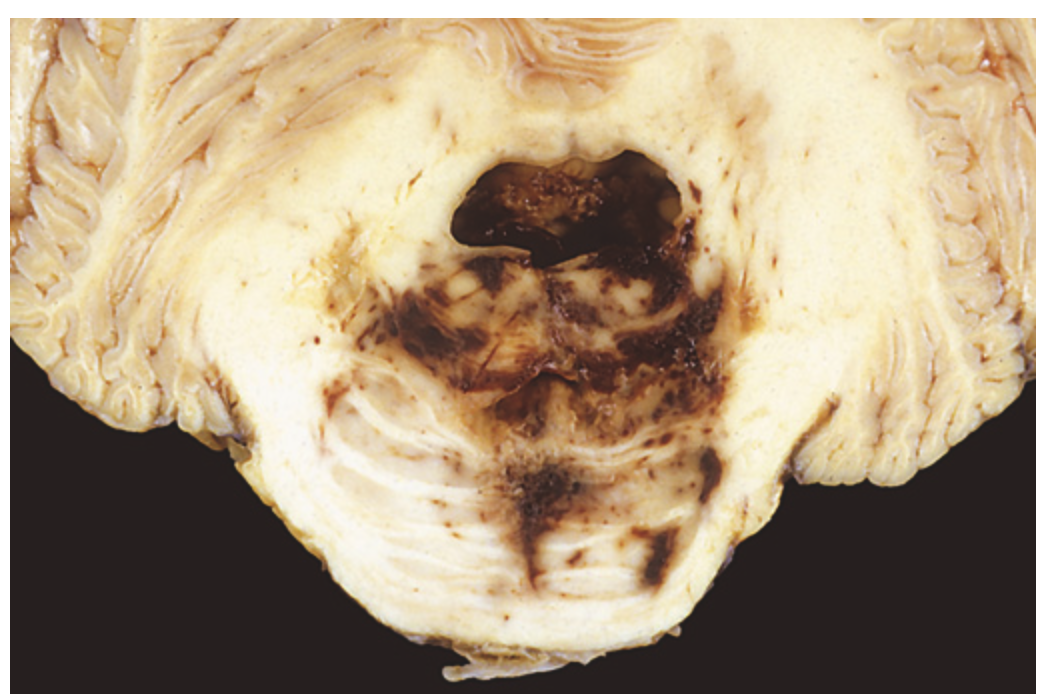
Duret hemorrhage. As mass effect displaces the brainstem downward, there is disruption of the vessels that enter the pons along the midline, leading to hemorrhage.
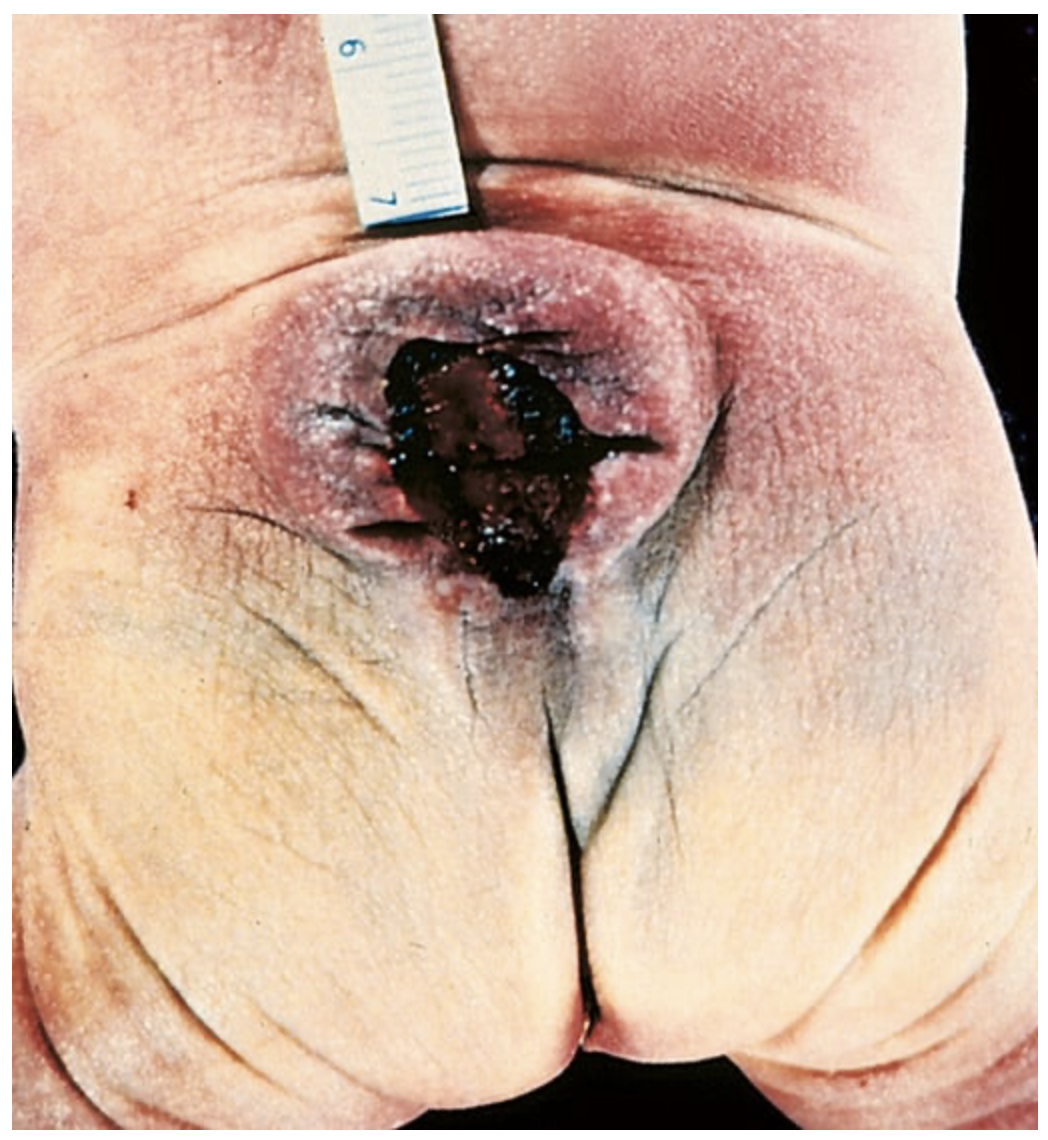
Myelomeningocele. Both meninges and spinal cord parenchyma are included in the cystlike structure visible just above the buttocks.
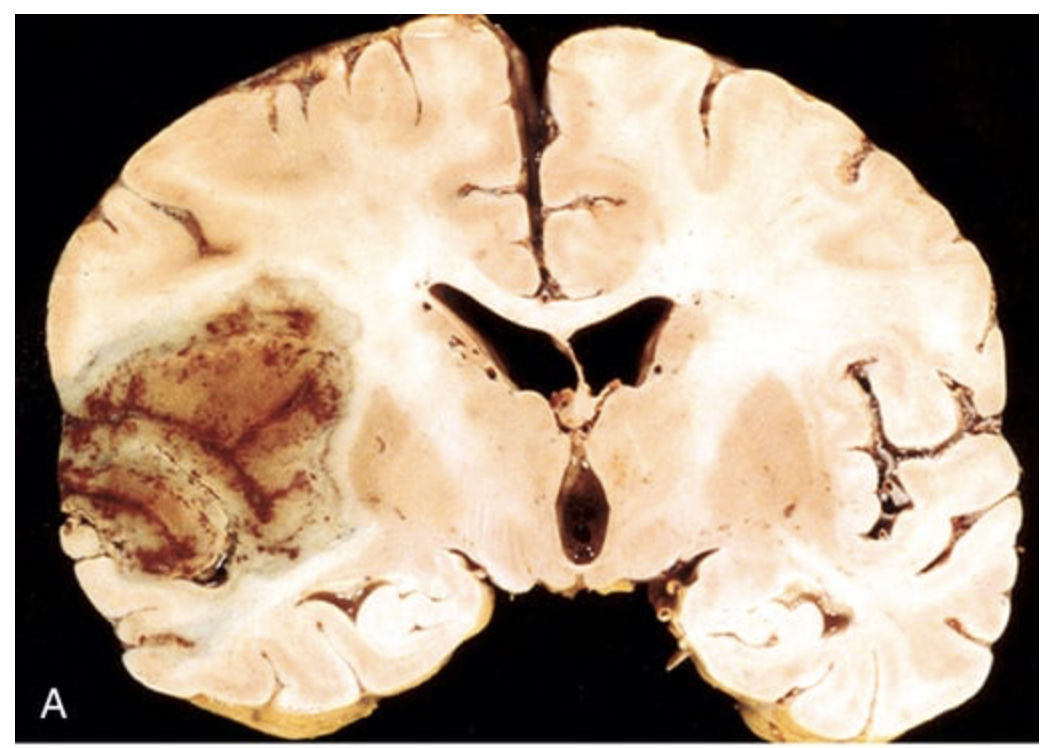
Cerebral infarction. (A) Section of the brain showing a large, discolored, focally hemorrhagic infarct in the distribution of the left middle cerebral artery distribution.
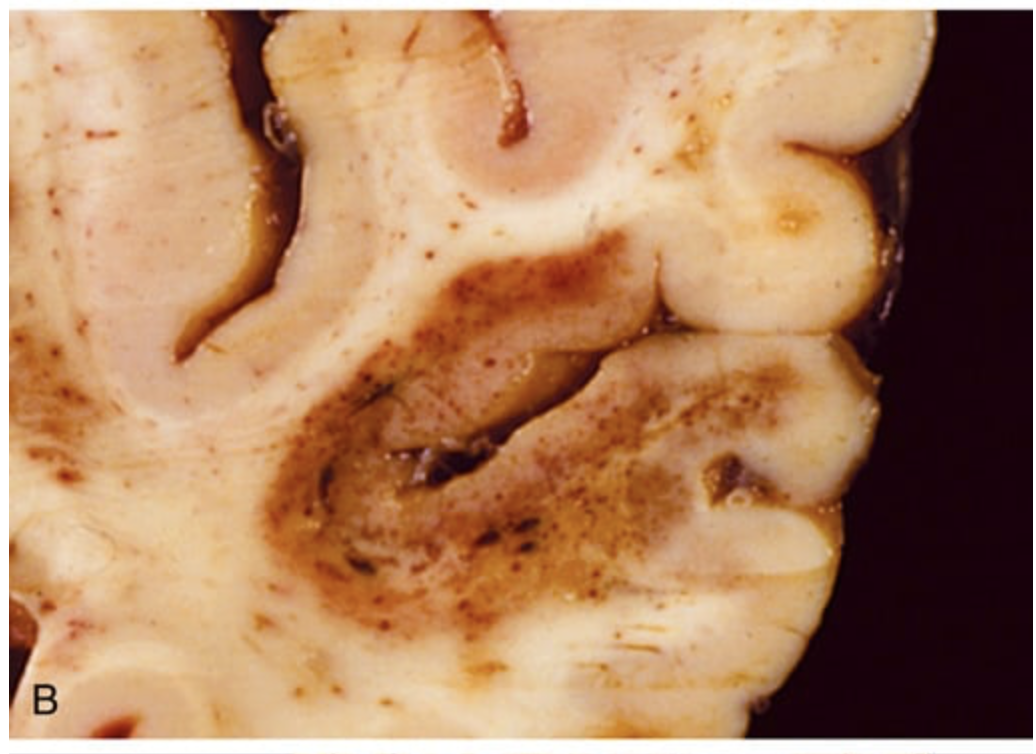
Cerebral infarction. (B) An infarct with punctate hemorrhages, consistent with ischemia-reperfusion injury, is present in the temporal lobe.
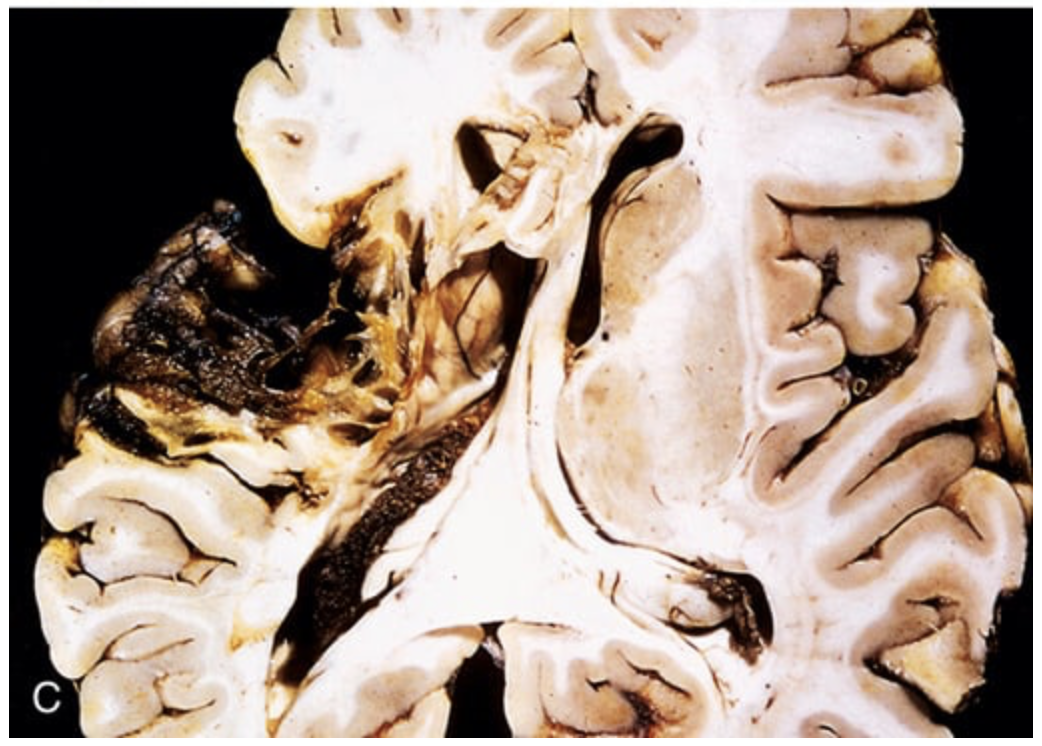
Cerebral infarction. (C) Old cystic infarct shows destruction of cortex and surrounding gliosis
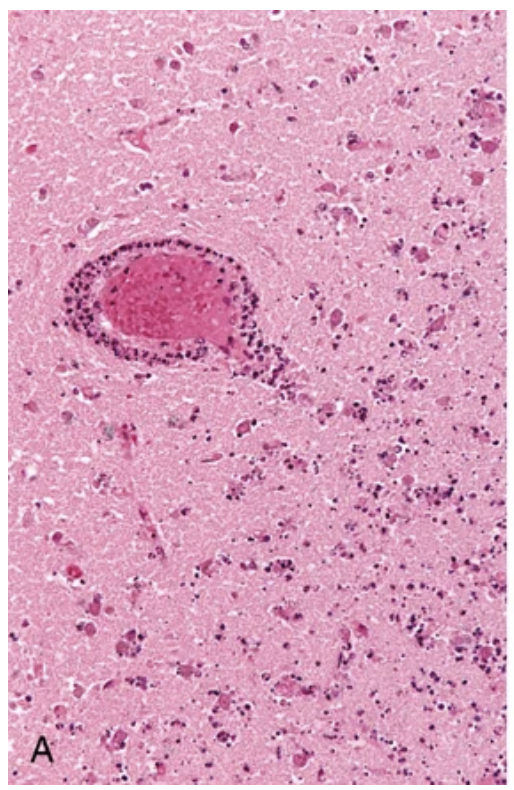
Cerebral infarction. (A) Infiltration of a cerebral infarct by neutrophils begins at the edges of the lesion, where the vascular supply is intact.
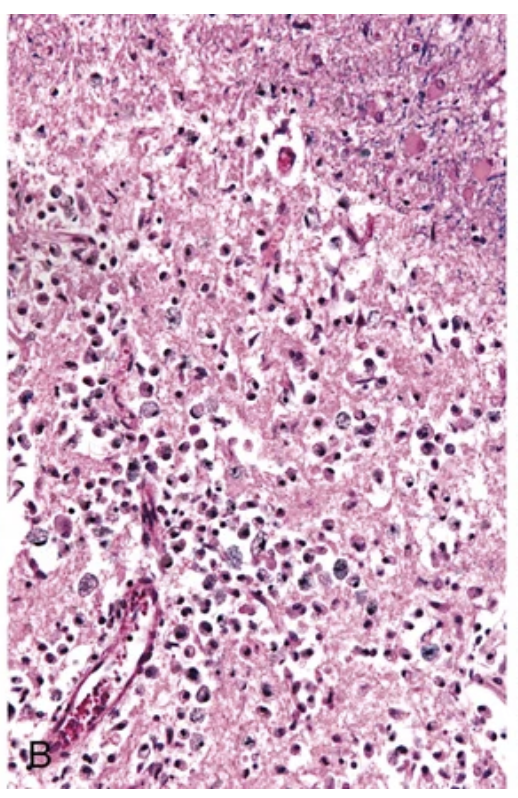
Cerebral infarction. (B) By day 10, an area of infarction shows the presence of macrophages and surrounding reactive gliosis.
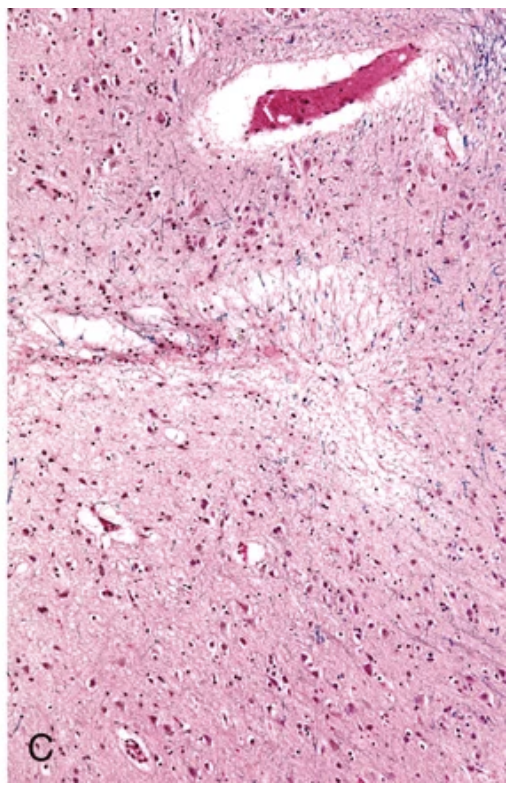
Cerebral infarction. (C) Old intracortical infarcts are seen as areas of tissue loss and residual gliosis
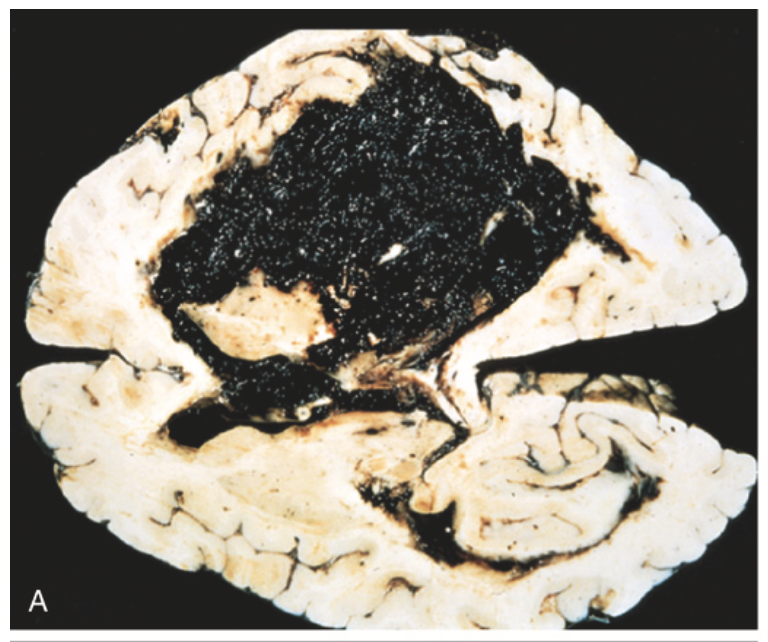
Cerebral hemorrhage. (A) Massive hypertensive hemorrhage of the basal ganglia rupturing into a lateral ventricle.
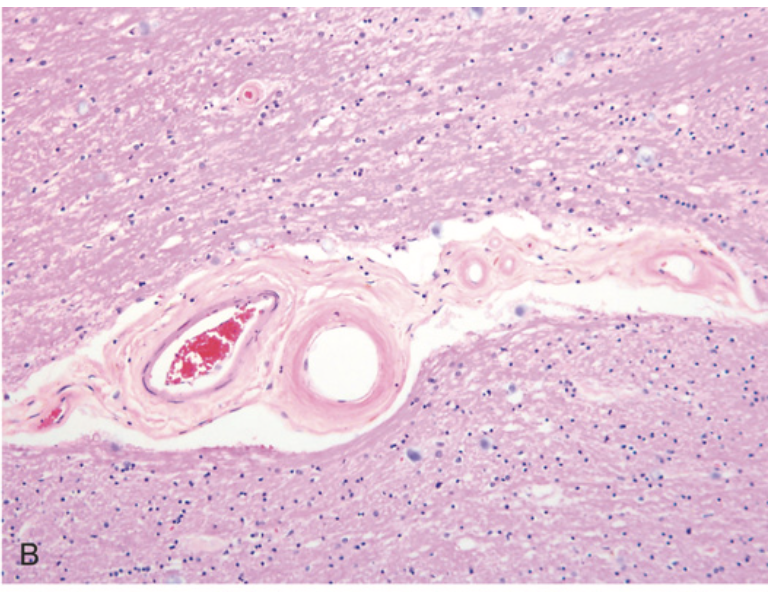
Cerebral hemorrhage. (B) Hyaline arteriolosclerosis (fibrosis and thickening of the arteriolar walls) develops in the basal ganglia and subcortical white matter of patients with long-standing hypertension; it is a risk factor for hypertensive hemorrhages as well as lacunar infarcts.
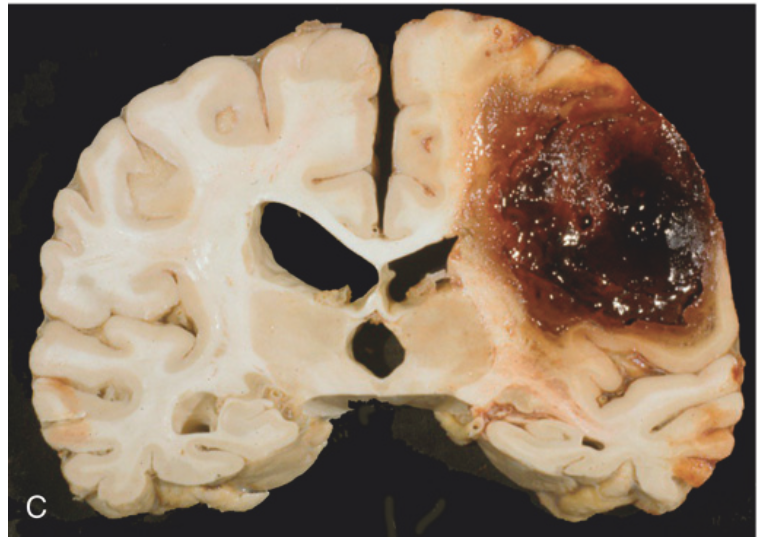
Cerebral hemorrhage. (C) Large lobar hemorrhage due to cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
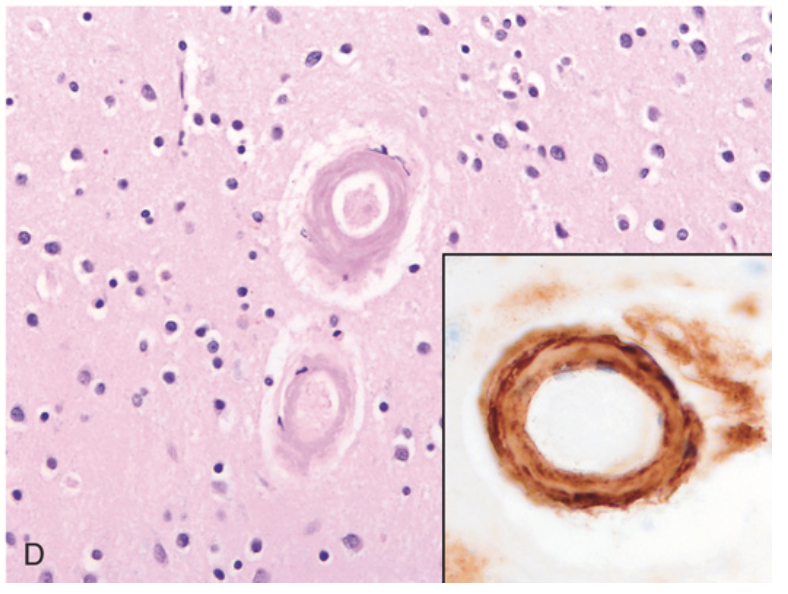
Cerebral hemorrhage. (D) Amyloid deposition in cortical arterioles in cerebral amyloid angiopathy; inset, immunohistochemical staining highlights the deposited amyloid Aβ protein in the vessel wall
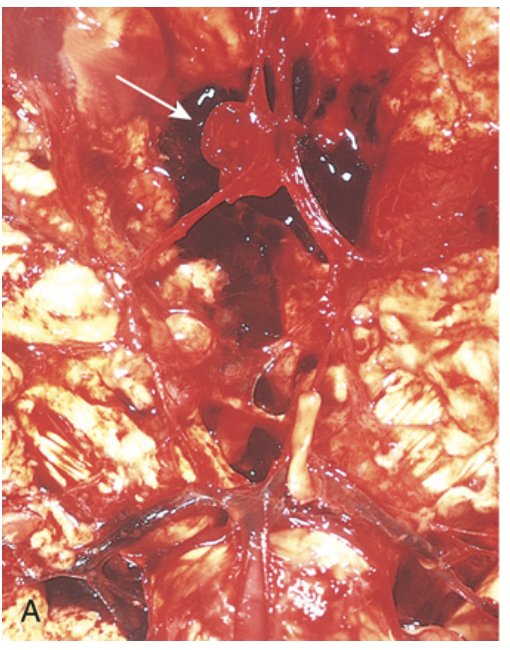
Saccular aneurysm. (A) View of the base of the brain, dissected to show the circle of Willis with an aneurysm of the anterior cerebral artery (arrow).
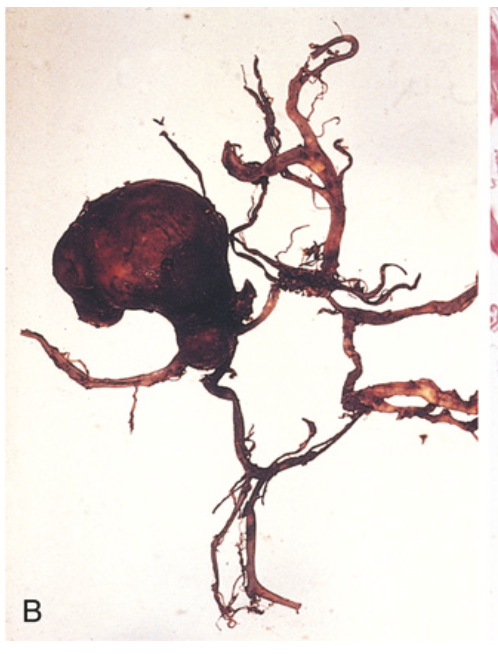
Saccular aneurysm. (B) The circle of Willis is dissected to show a large aneurysm.
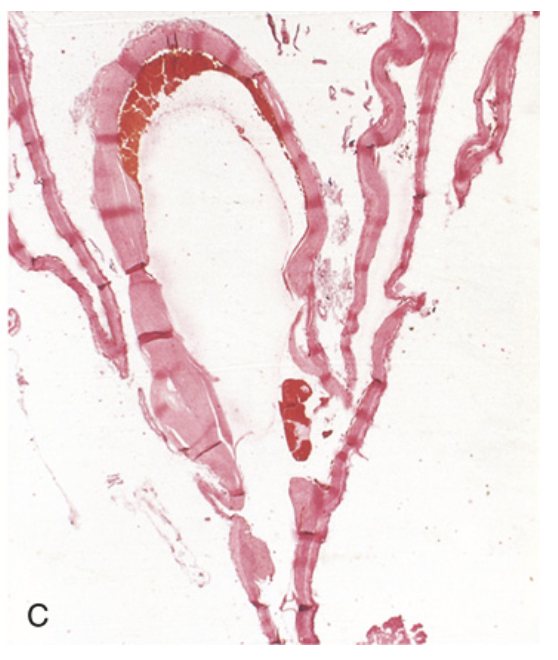
Saccular aneurysm. (C) Section through a saccular aneurysm showing the hyalinized fibrous intima forming the vessel wall. Hematoxylin-eosin stain
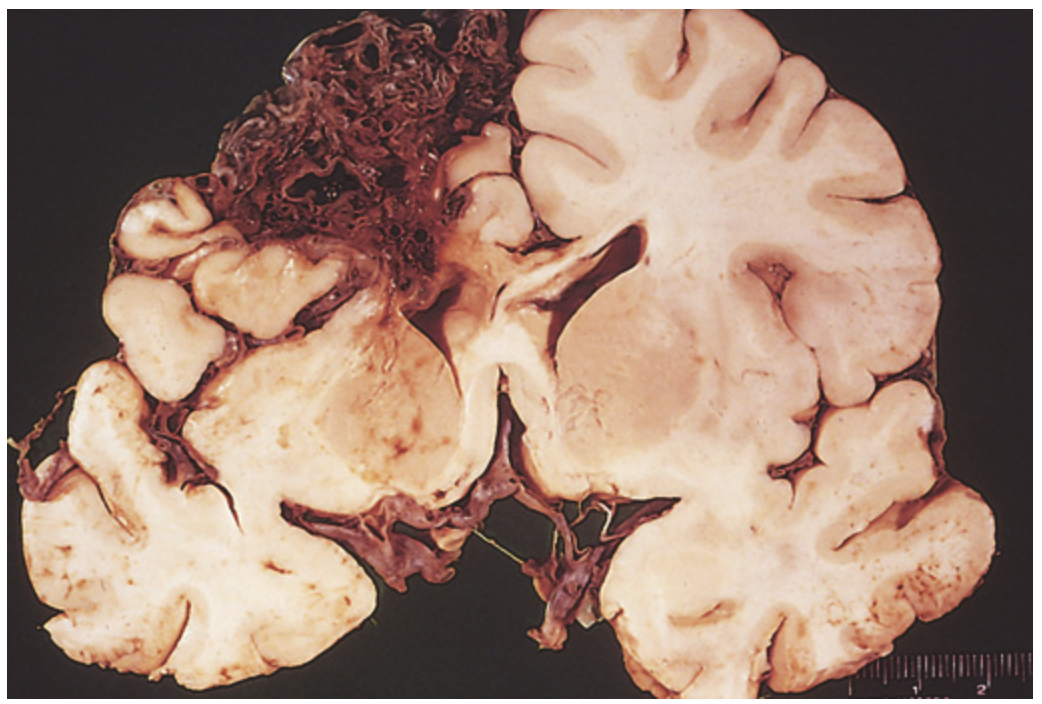
Arteriovenous malformation
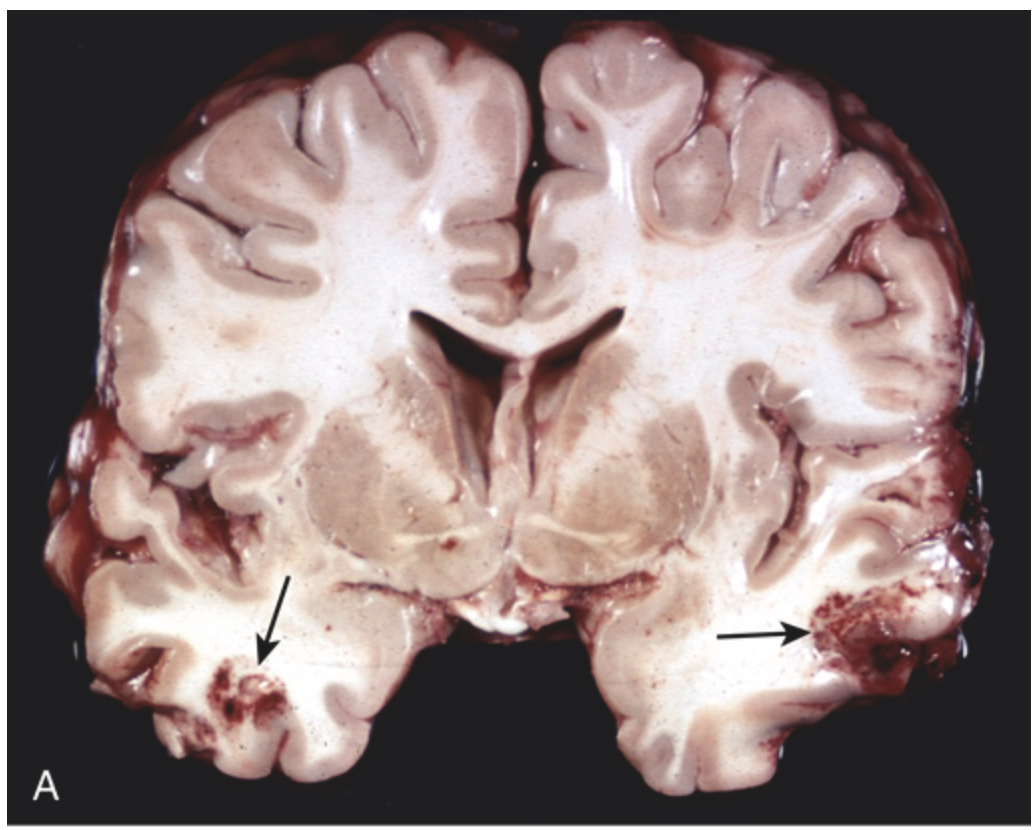
Contusions. (A) Acute contusions are present in both temporal lobes, with areas of hemorrhage and tissue disruption (arrows).
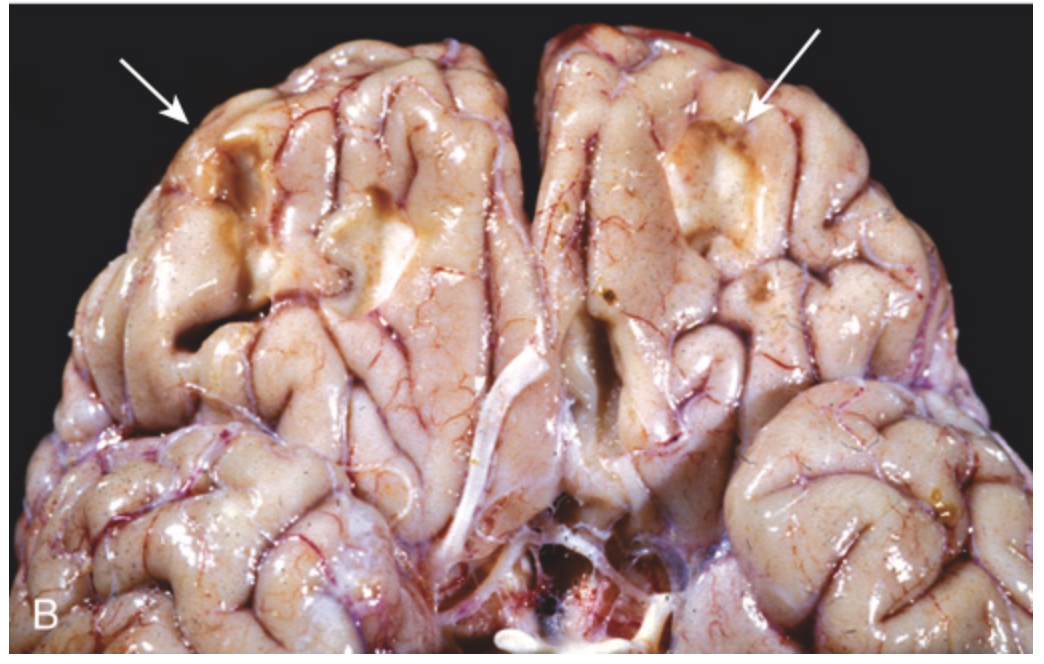
Contusions. (B) Remote contusions, seen as discolored yellow areas (arrows), are present on the inferior frontal surface of this brain.
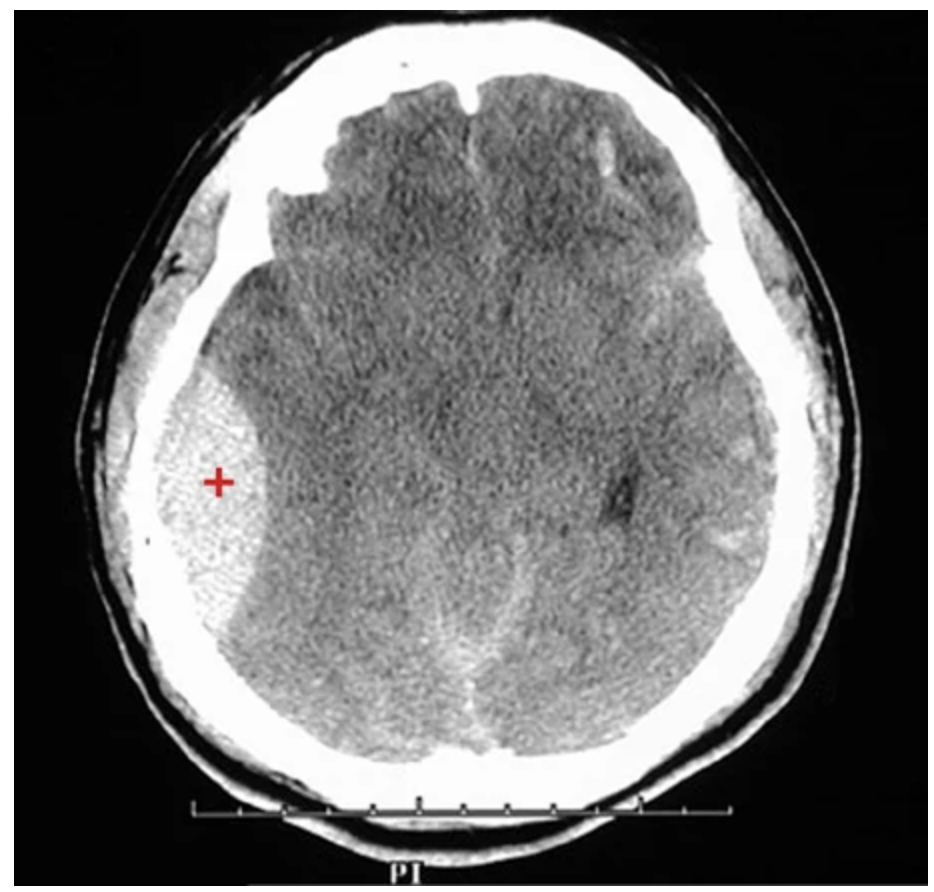
Epidural hematoma (CT image). Note the large right epidural hematoma with a lens-shaped outline (red plus sign), bounded by cranial sutures, where the dura is firmly adherent to the skull. severing the middle meningeal artery.
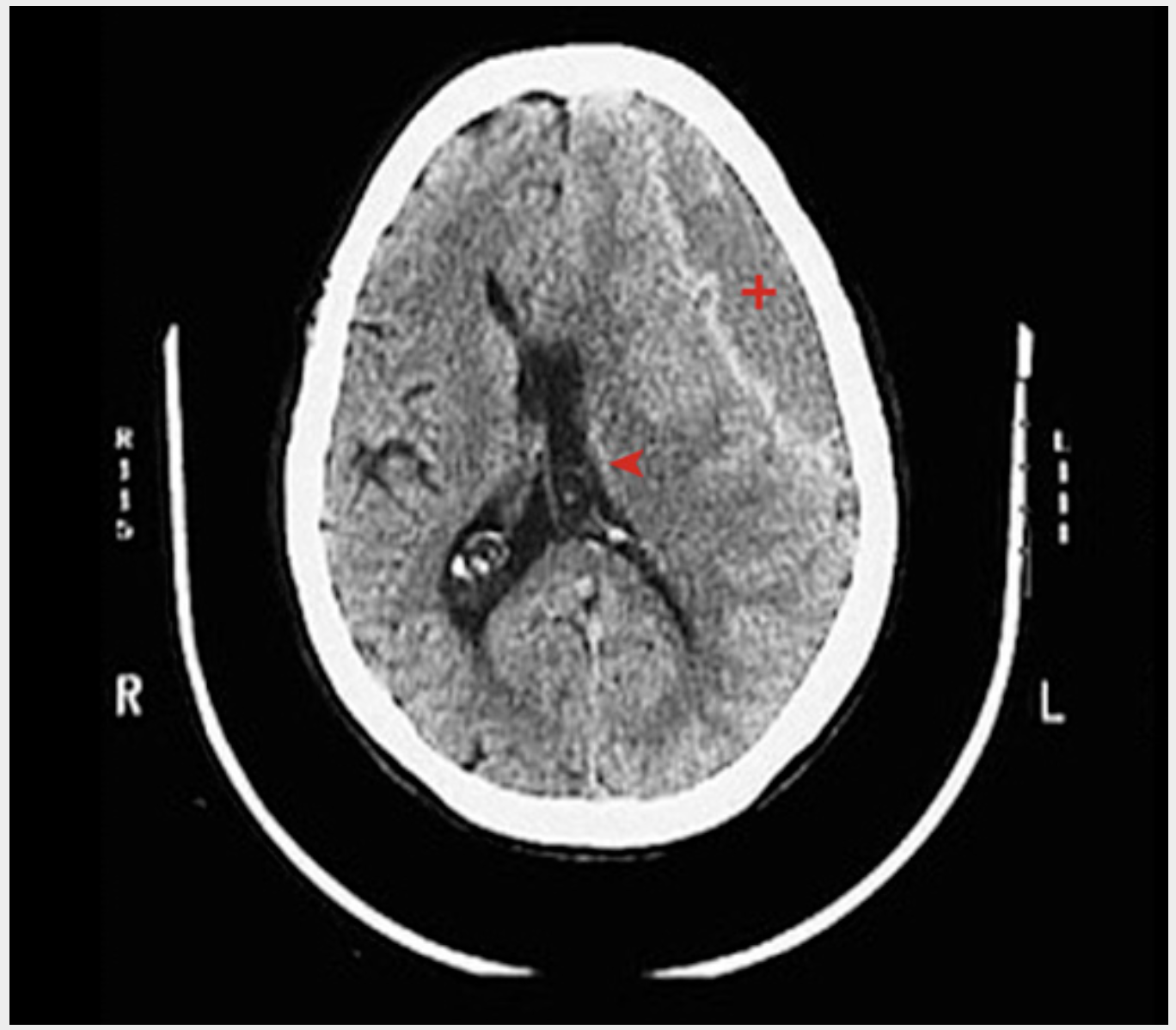
Subdural hematoma (CT image). A large left subdural hematoma (red plus sign) with left-to-right shift (red arrowhead) and ventricular narrowing interdigitates with the adjacent gyri and sulci but compresses the brain.
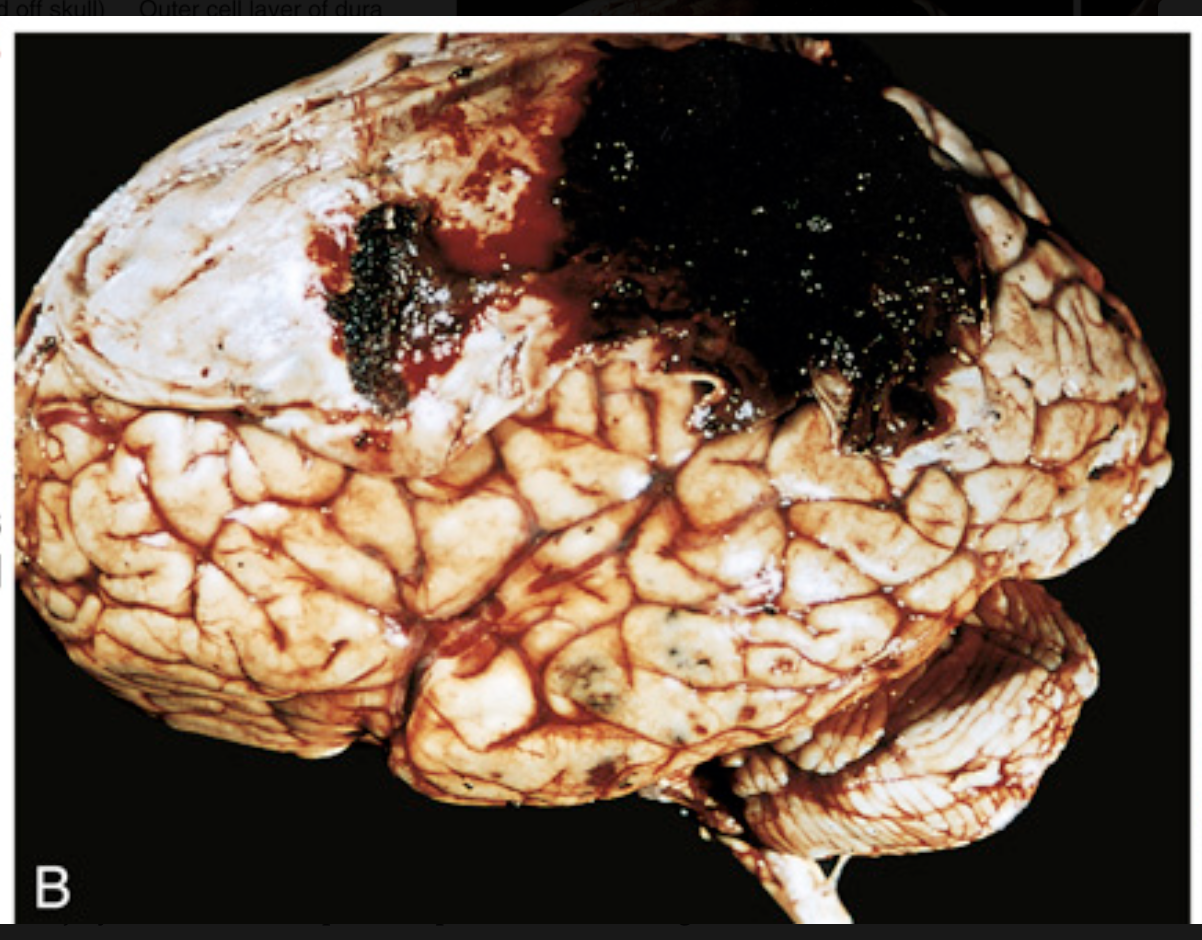
Traumatic intracranial hemorrhages. (B) Epidural hematoma covering a portion of the dura.
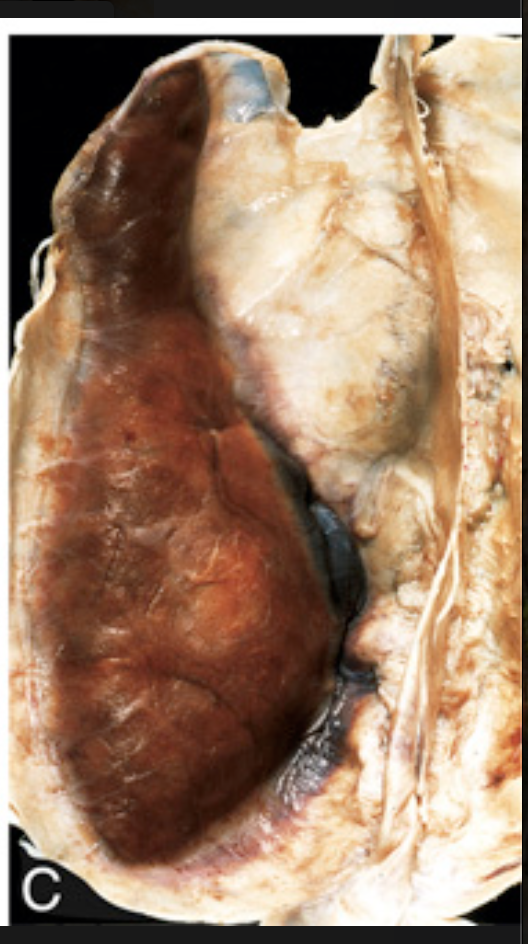
Traumatic intracranial hemorrhages. (C) Large organizing subdural hematoma attached to the dura
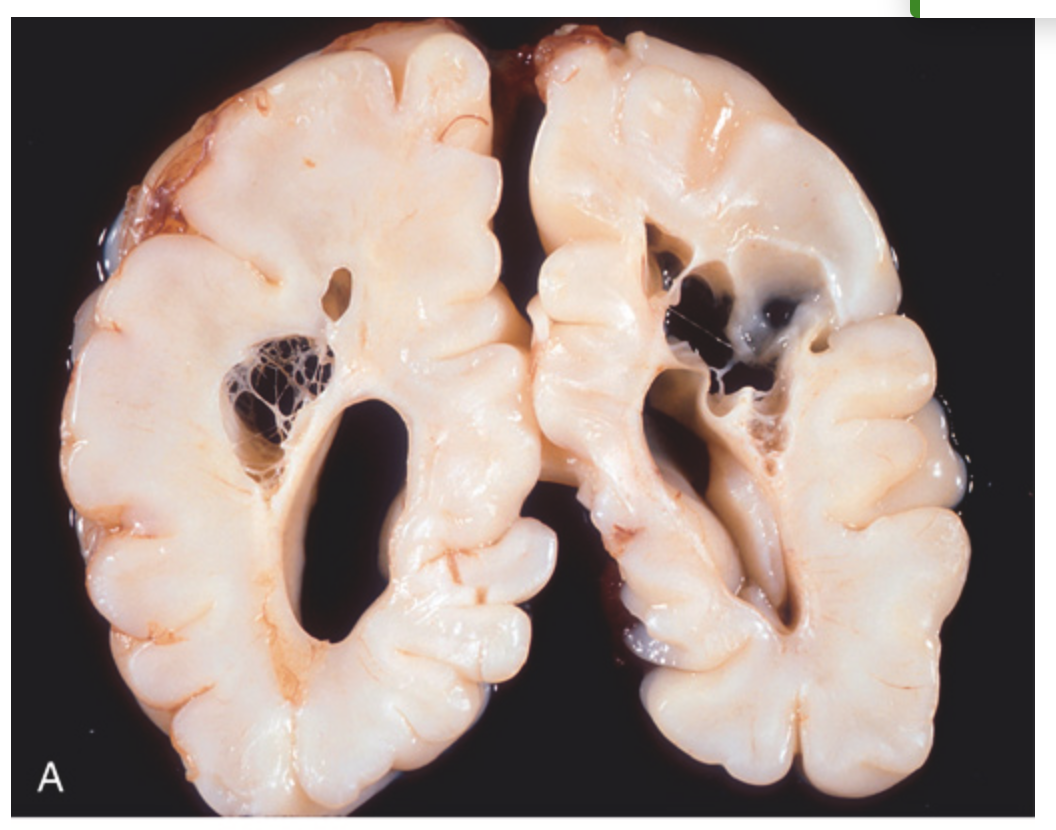
Perinatal brain injury. (A) Chronic stage of periventricular leukomalacia. Large cystic spaces in the periventricular white matter (seen in both hemispheres of the brain) are the long-term sequelae of severe prenatal or perinatal ischemic injury.
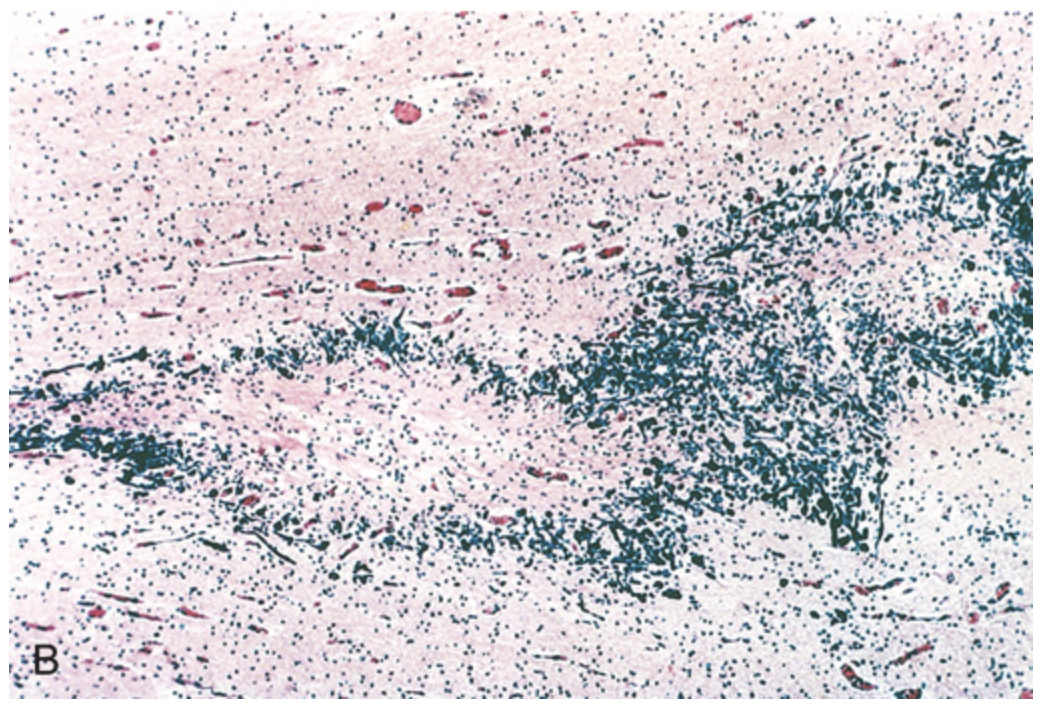
Perinatal brain injury. (B) Histologic section of periventricular leukomalacia shows a central focus of white matter necrosis with a peripheral rim of mineralized axonal processes
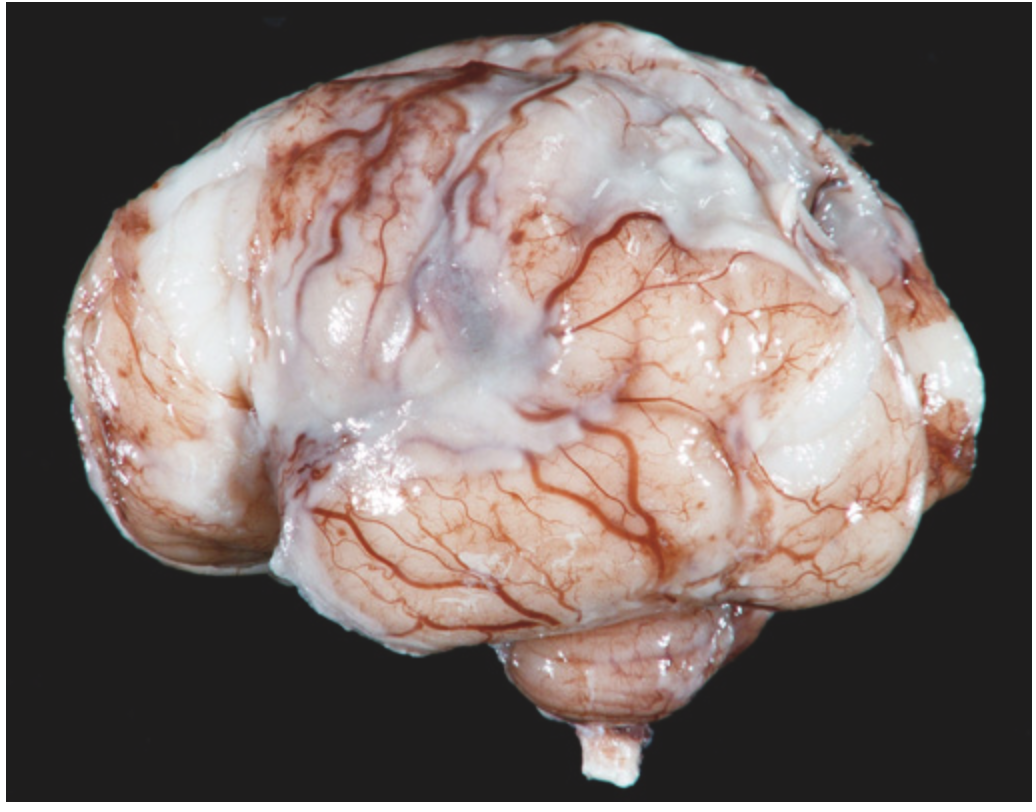
Pyogenic meningitis. A thick layer of suppurative exudate covers the brain stem and cerebellum and thickens the leptomeninges
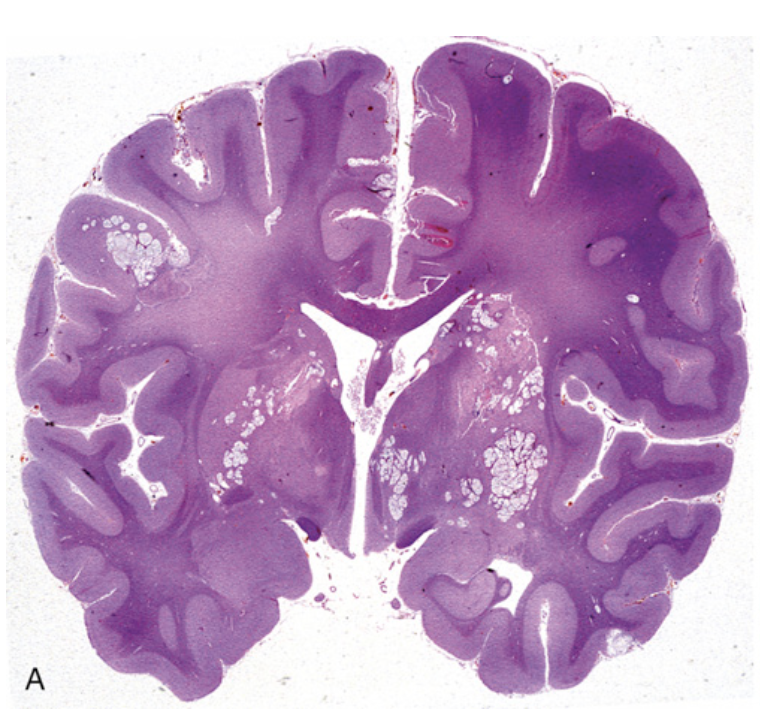
Cryptococcal infection. (A) Whole-brain section showing the numerous areas of tissue destruction associated with the spread of organisms in the perivascular spaces.
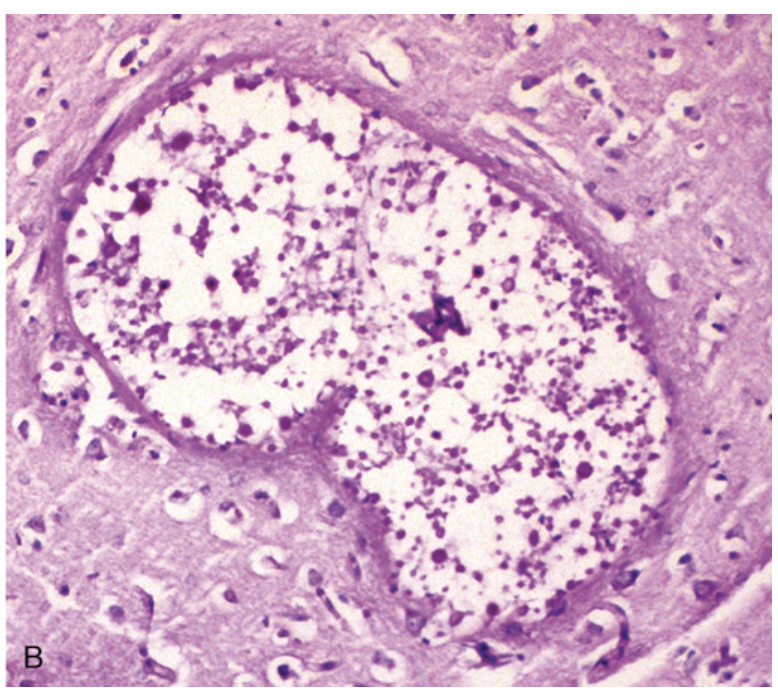
Cryptococcal infection. (B) At higher magnification, it is possible to see the cryptococci in the lesions
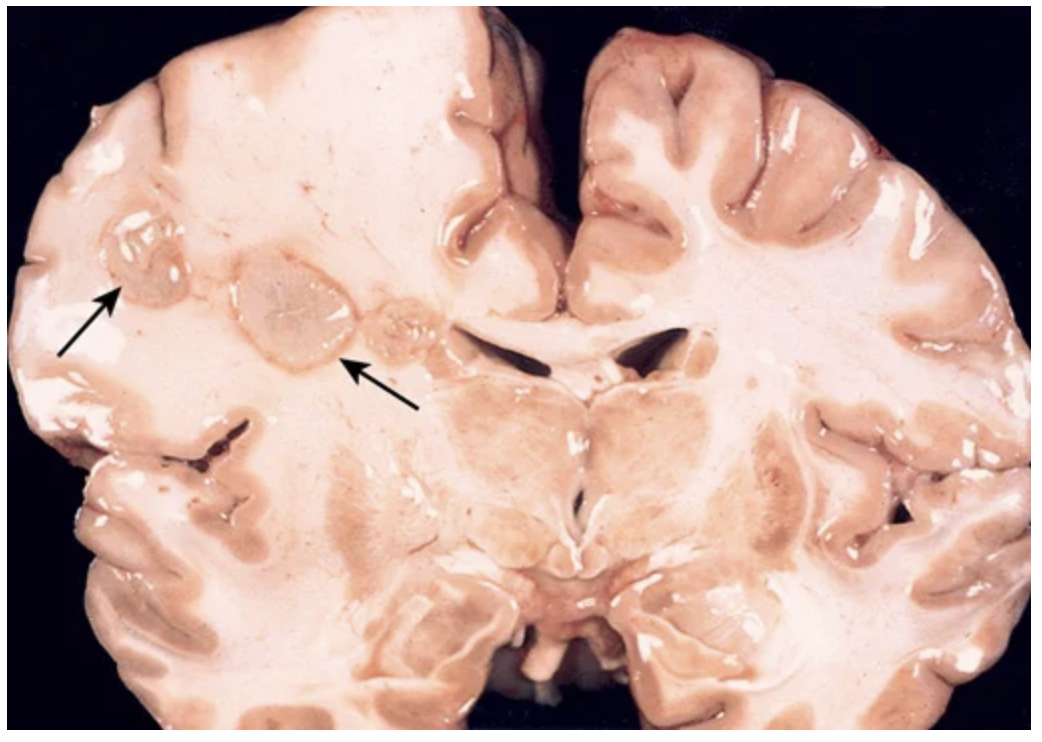
Cerebral abscesses in the frontal lobe white matter (arrows).
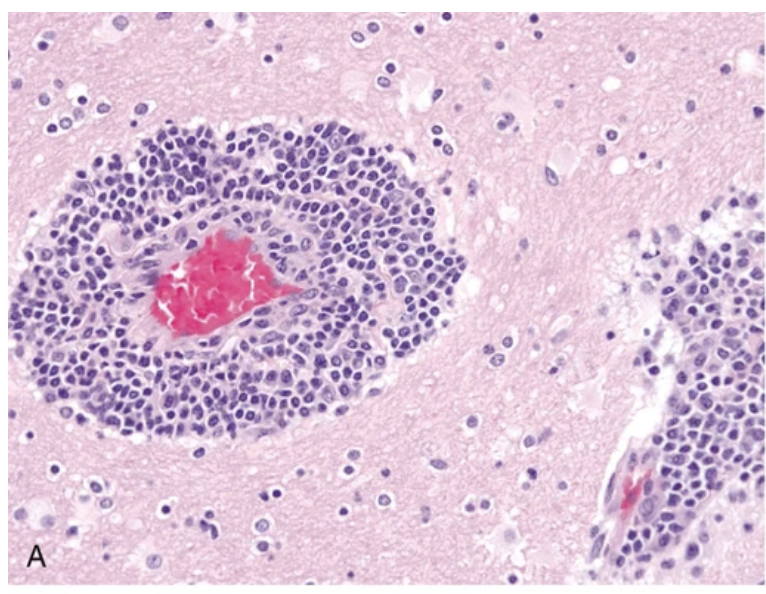
Viral infections. (A, B) Characteristic findings in many forms of viral encephalitis include perivascular cuffs of lymphocytes (A) and microglial nodules (B).
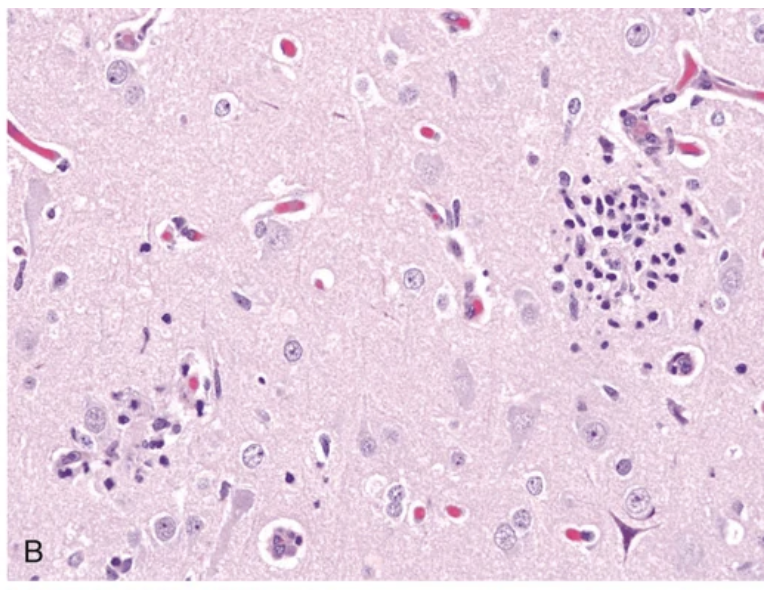
Viral infections. (A, B) Characteristic findings in many forms of viral encephalitis include perivascular cuffs of lymphocytes (A) and microglial nodules (B).
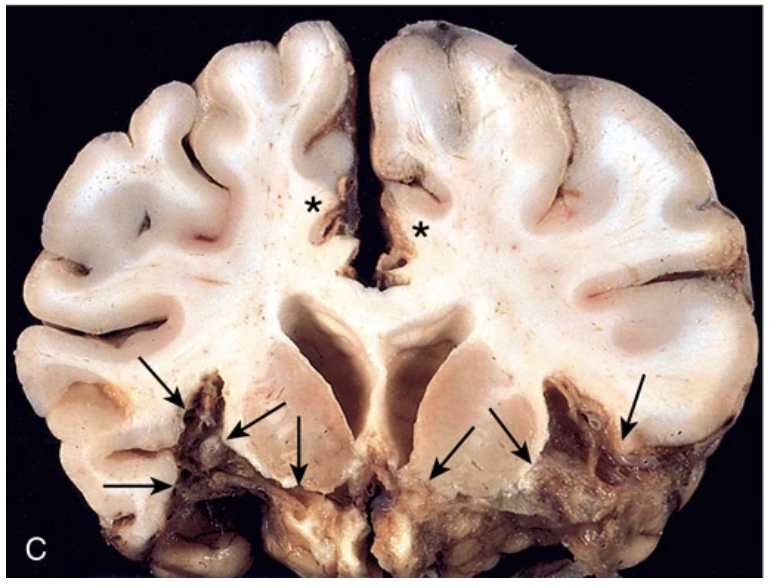
Viral infections. (C) Herpes encephalitis showing extensive destruction of inferior frontal and anterior temporal lobes (arrows) and cingulate gyri (asterisks).
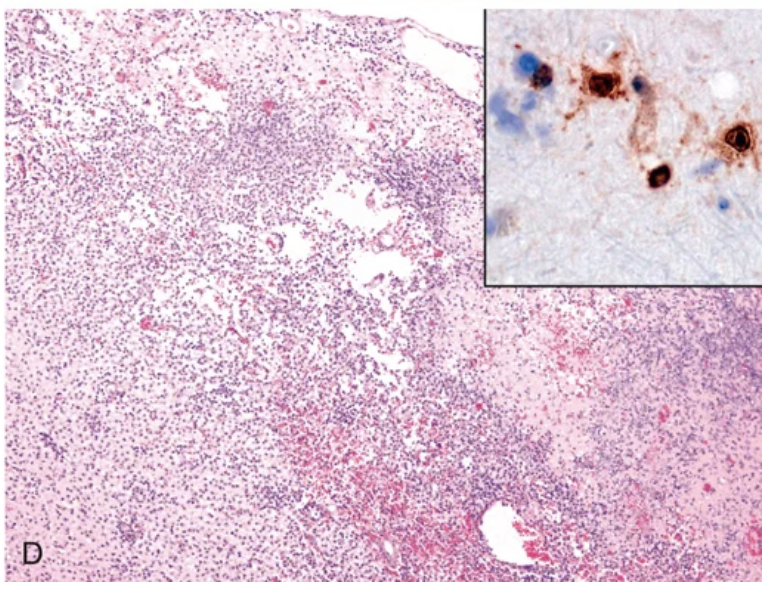
Viral infections. (D) Necrotizing inflammatory process characterizes acute herpes encephalitis; nuclear viral inclusions can be highlighted by immunostaining (inset).
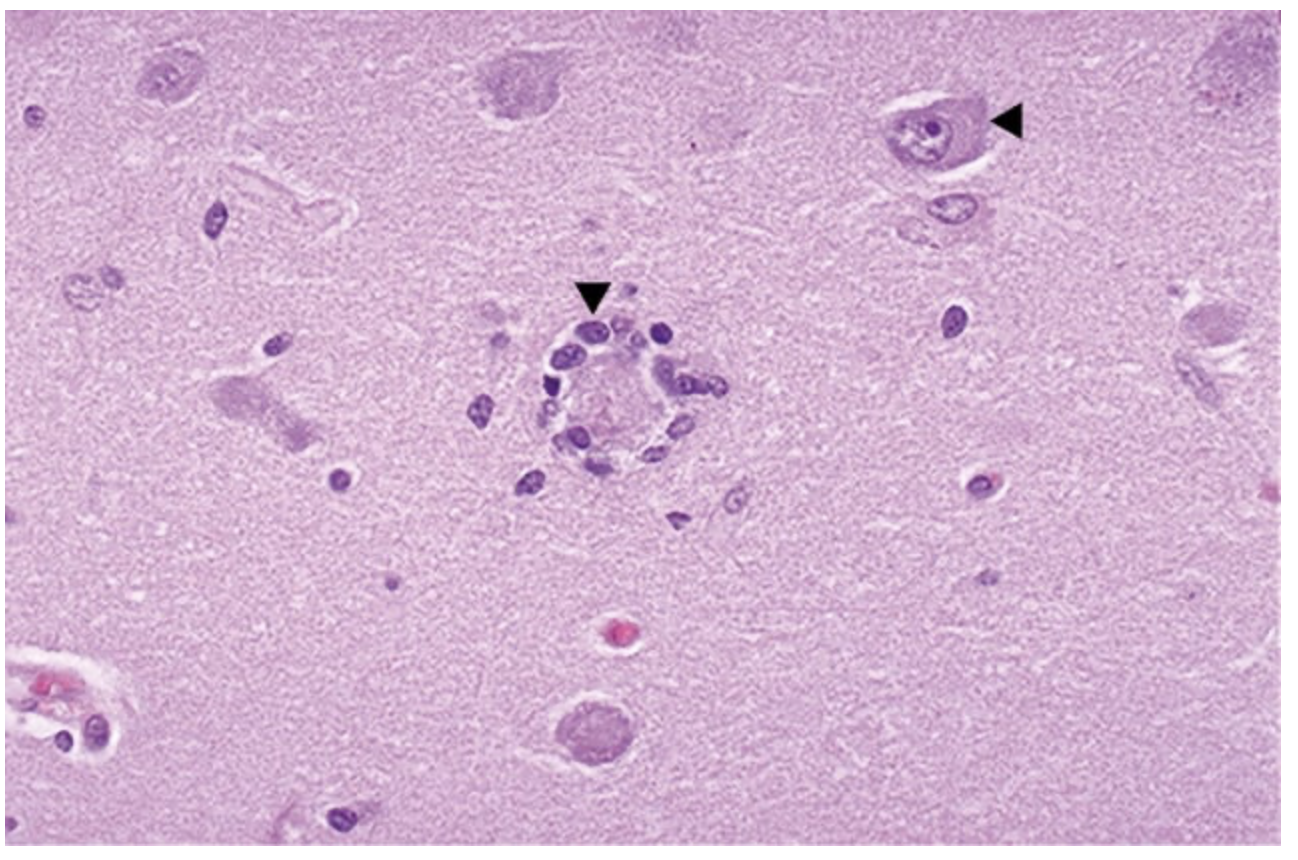
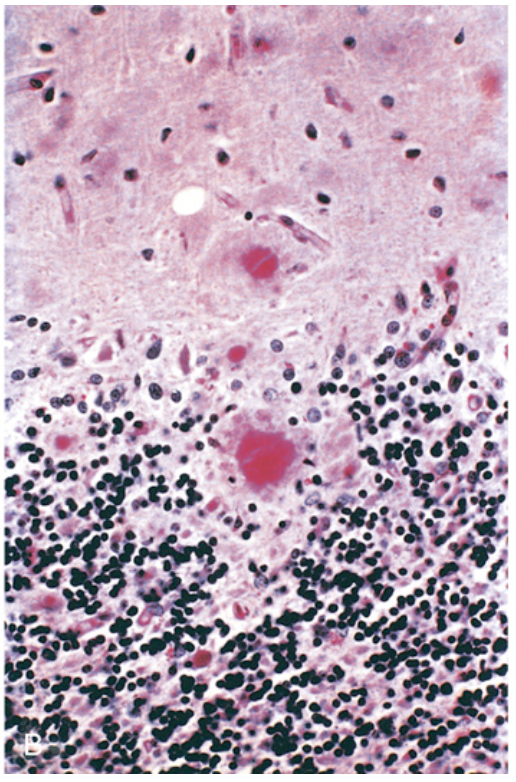
Neuronophagia is a process in which the neuron dies and becomes surrounded by microglial cells (left arrowhead). Compare with an intact neuron (right arrowhead). can be from viral infections or paraneoplastic antineuronal encephalomyelitis (with polyclonal IgG anti-Hu antibodies or type 1 antineuronal nuclear antibodies seen in some cases). In either case, it is probably mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes
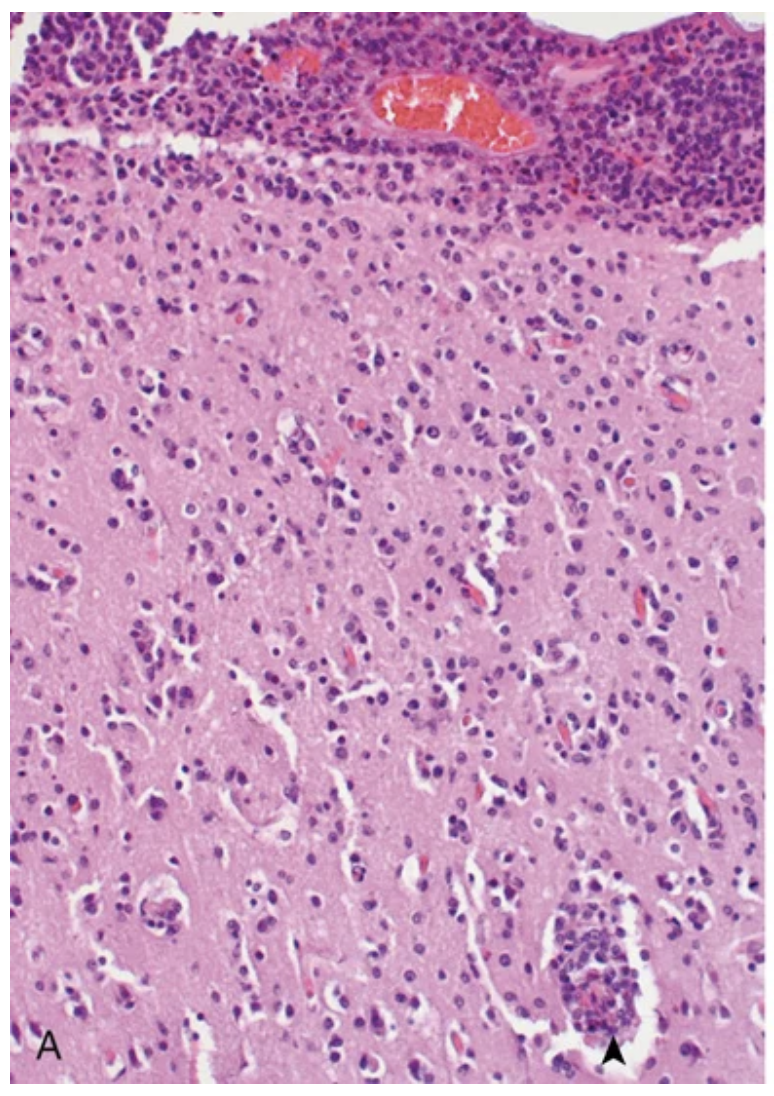
Cytomegalovirus meningoencephalitis. (A) Intense lymphocytic infiltrate in the meninges and underlying cerebral cortex, including perivascular (arrowhead).
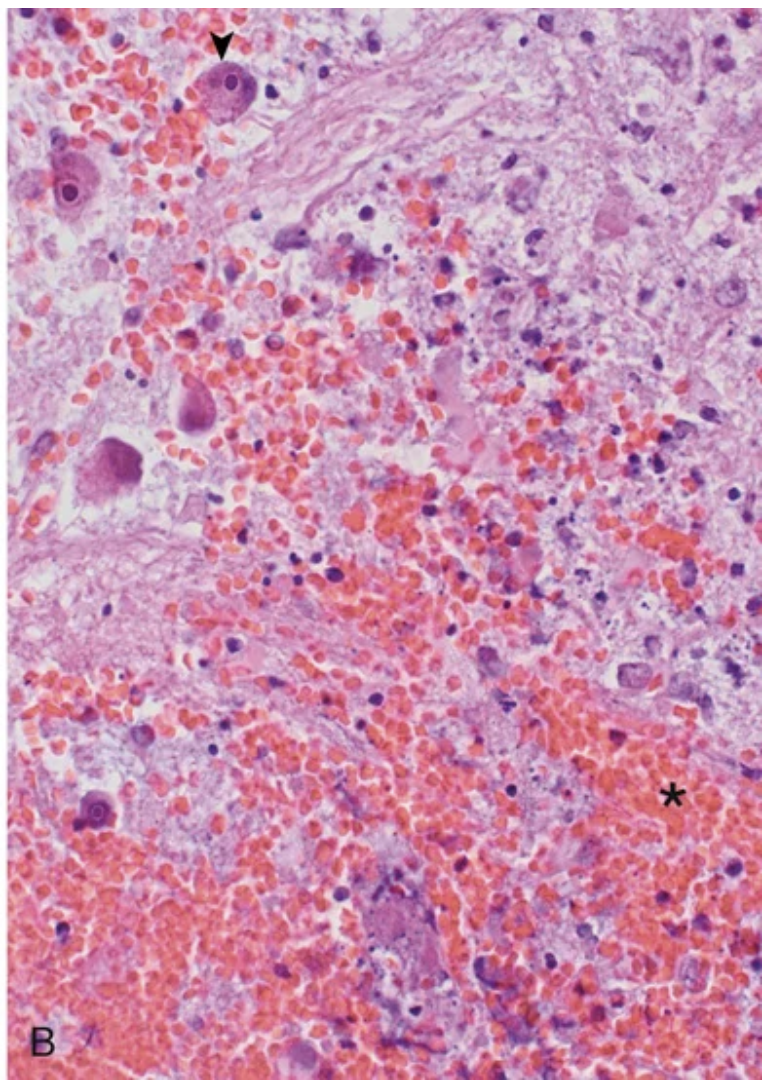
Cytomegalovirus meningoencephalitis. (B) Areas of necrosis and hemorrhage (asterisk) and infected glial cells containing intranuclear viral inclusions (arrowhead)
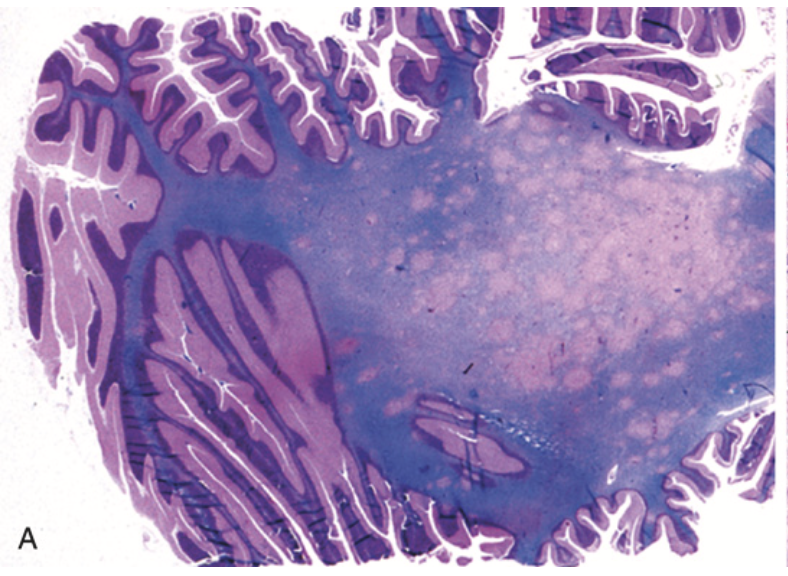
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. (A) Section stained for myelin showing irregular, poorly defined pale areas of myelin loss, which become confluent in places.
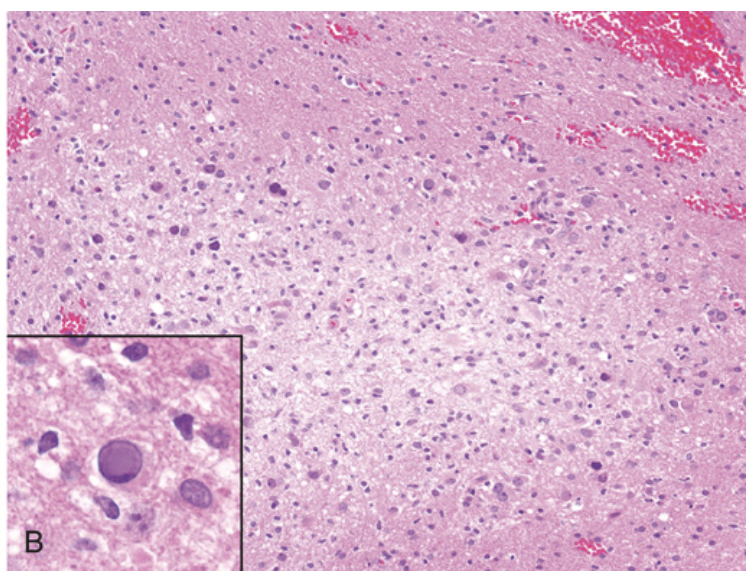
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. (B) Microscopically, the lesions consist of areas of demyelination. Inset, Enlarged oligodendrocyte nucleus containing viral inclusion characteristic of virus-infected cell
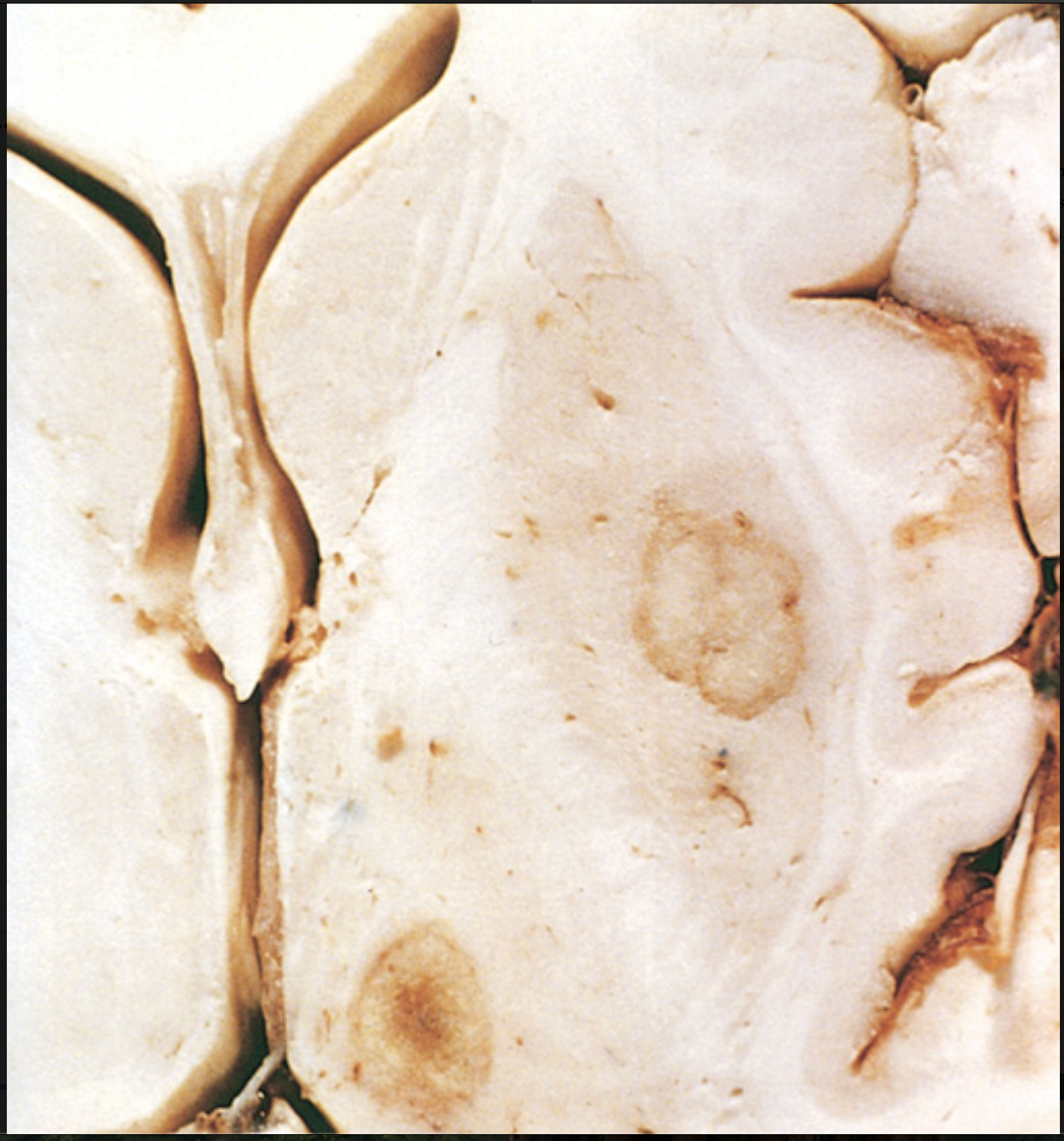
Toxoplasma infection. Abscesses in the putamen and thalamus
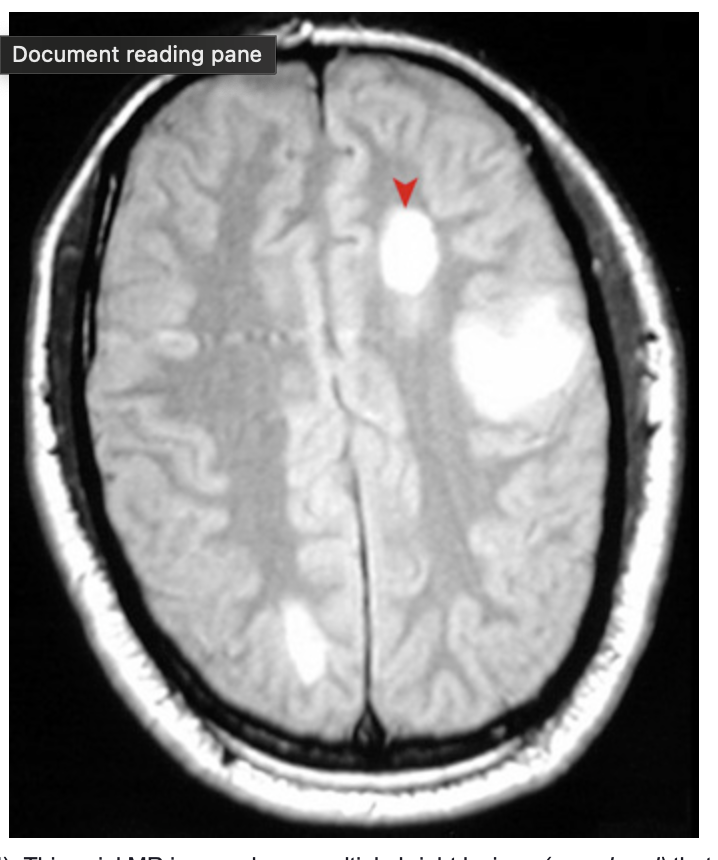
Multiple sclerosis (MRI). This axial MR image shows multiple bright lesions (arrowhead) that represent areas of demyelinating plaque formation in a patient with an exacerbation of multiple sclerosis
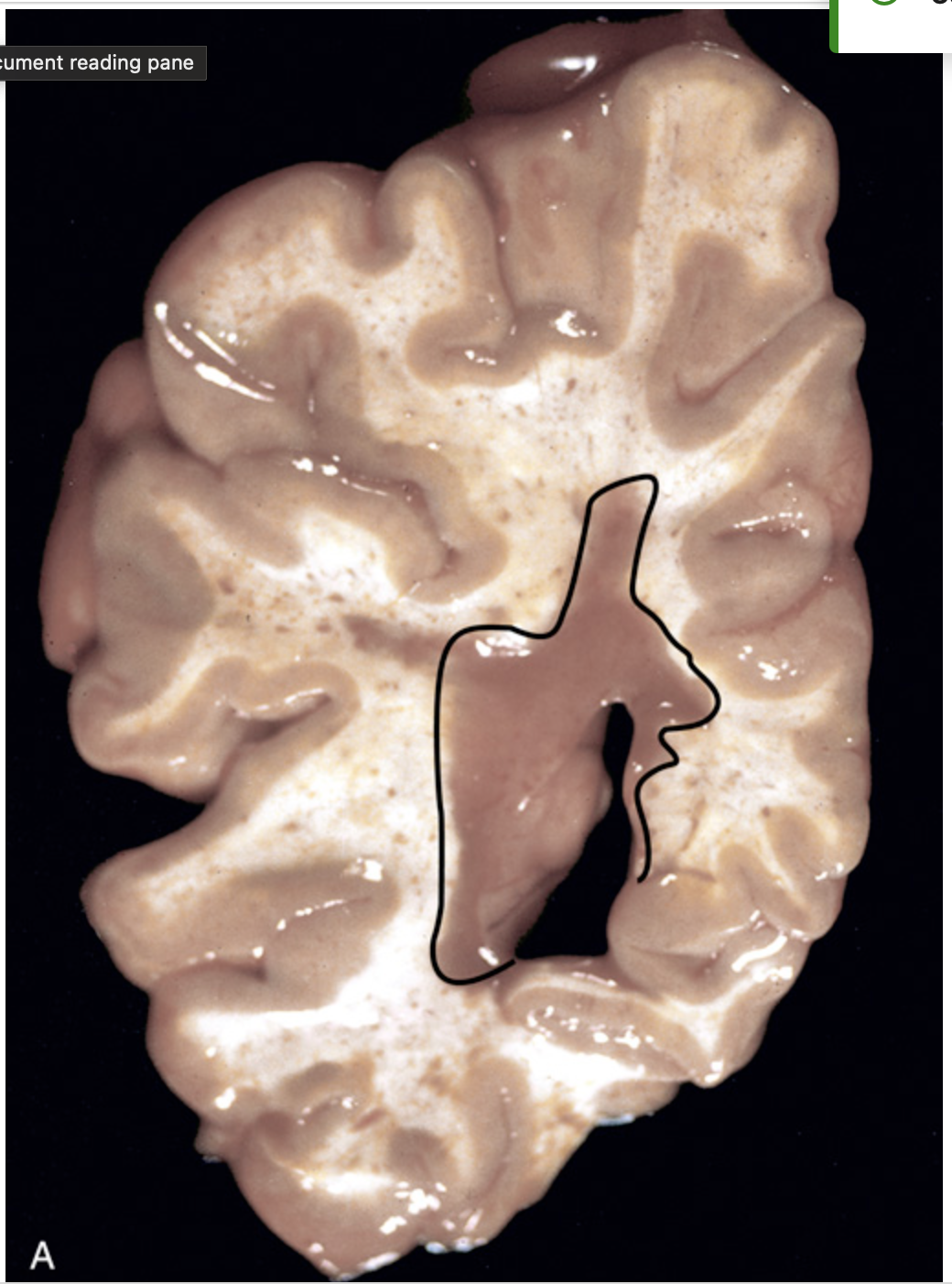
Multiple sclerosis (MS). (A) Section of fresh brain showing a gray-brown plaque around the occipital horn of the lateral ventricle (outlined).
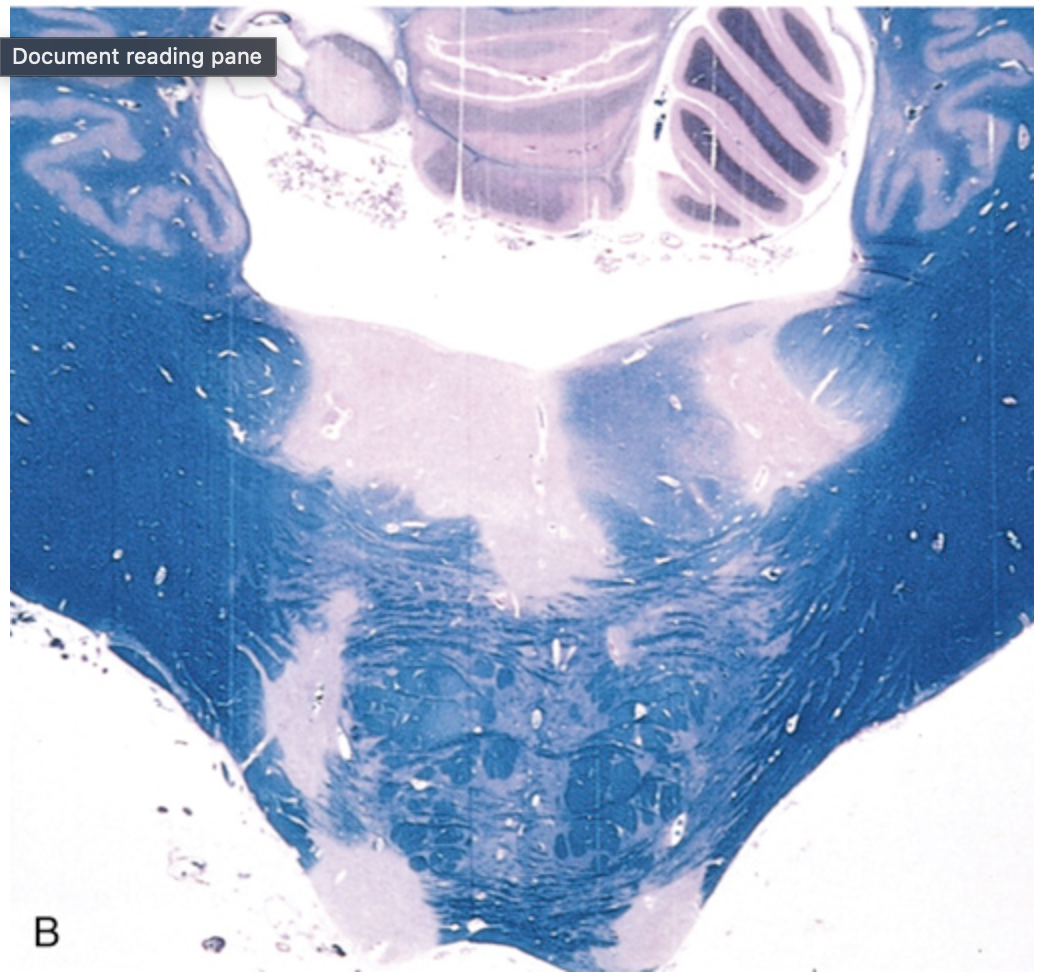
Multiple sclerosis (MS). (B) Unstained regions of demyelination (MS plaques) around the fourth ventricle. Luxol fast blue–periodic acid–Schiff stain for myelin
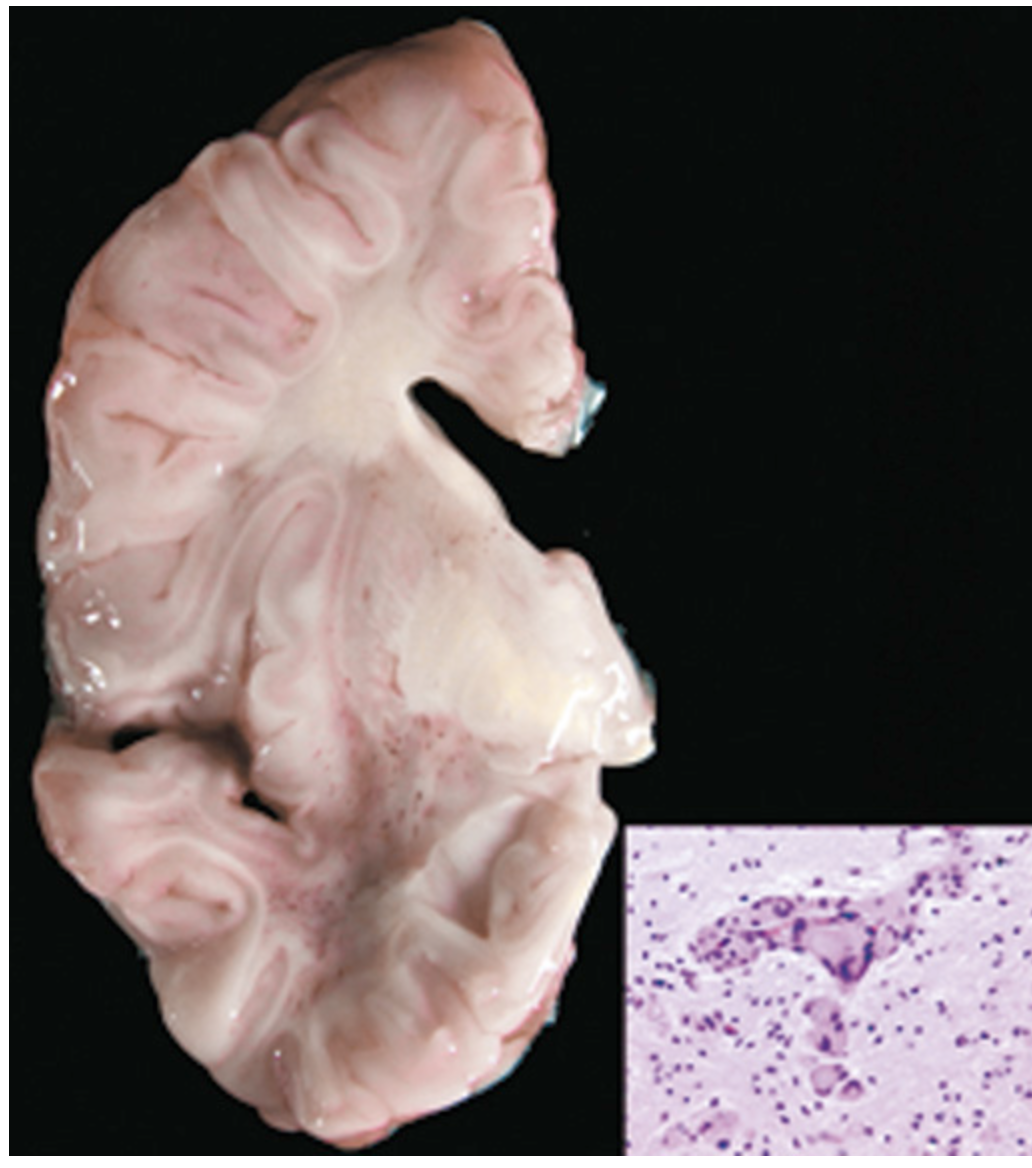
Krabbe disease. Much of the white matter is gray/yellow because of the loss of myelin. Inset, Multinucleate cells, sometimes filled with lipid, called globoid cells are the hallmark of the disease
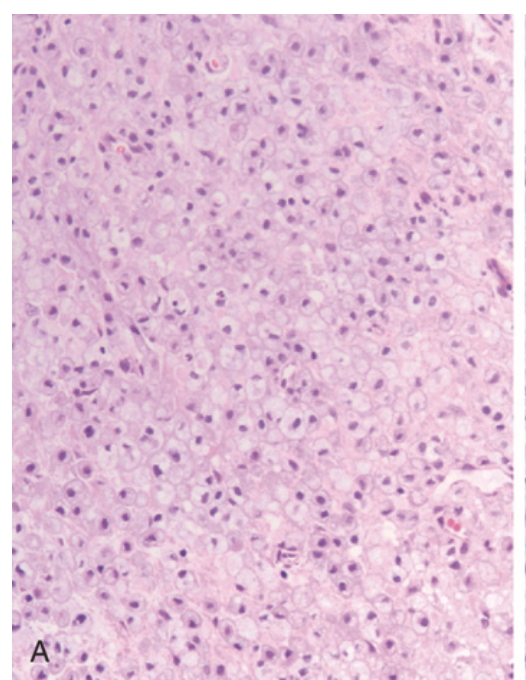
Multiple sclerosis. (A) Active demyelinating plaques appear very cellular due to the presence of numerous lipid-laden macrophages.
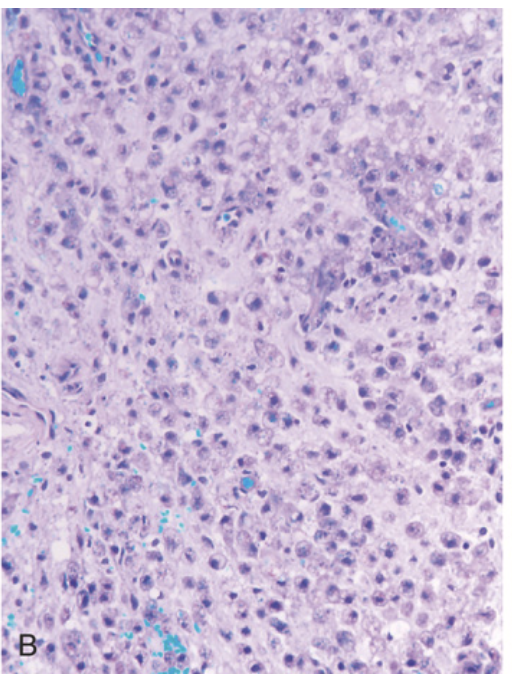
Multiple sclerosis. (B) The same lesion stained with the Luxol fast blue periodic acid–Schiff stain shows a complete absence of myelin.
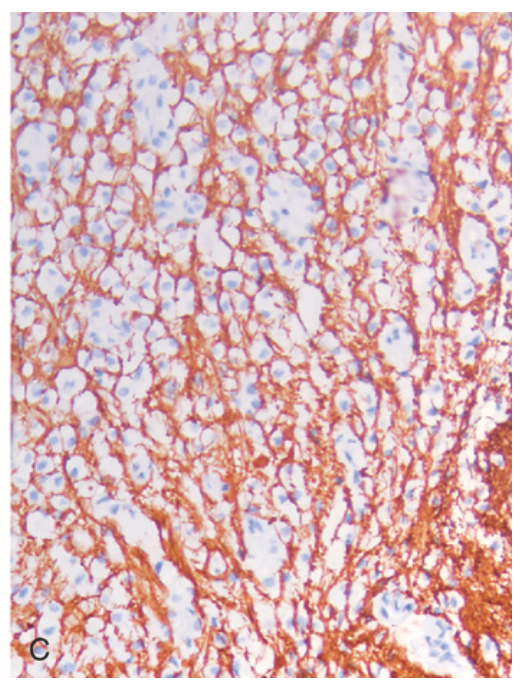
Multiple sclerosis. (C) Relative preservation of axons is seen on the neurofilament immunostain (brown).
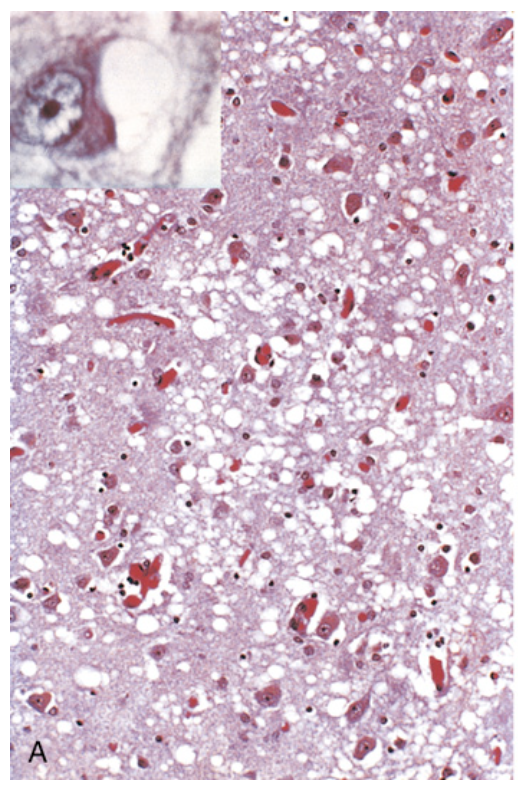
Prion disease. (A) Spongiform change in the cerebral cortex. Inset, High magnification of neuron with vacuoles.
Prion disease. (B) Cerebellar cortex showing kuru plaques (periodic acid–Schiff stain) that consist of aggregated PrPsc.
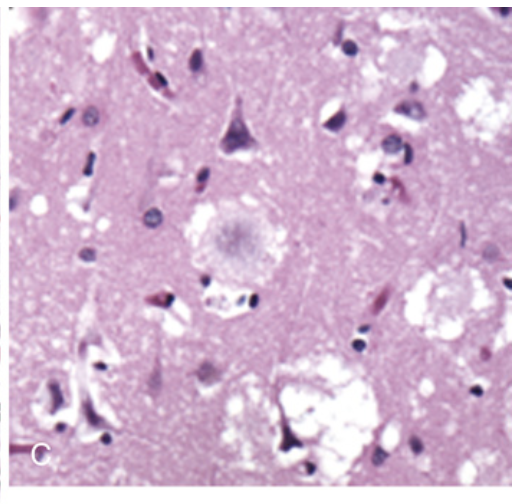
Prion disease. (C) Cortical kuru plaques surrounded by spongiform change in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
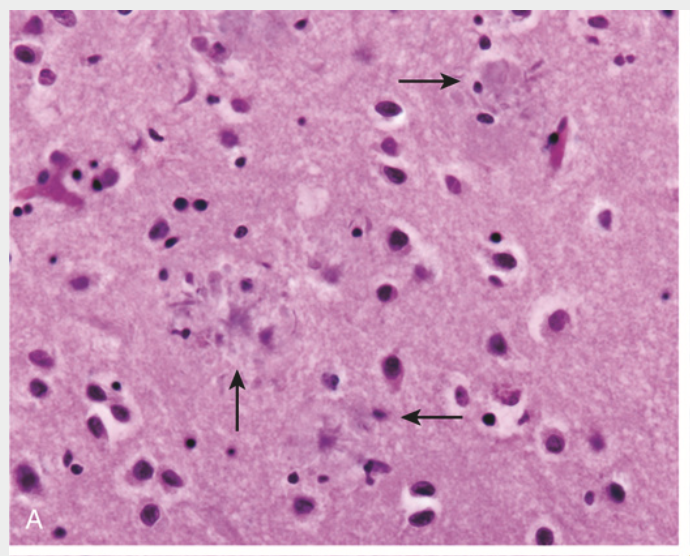
Alzheimer disease. (A) Plaques with dystrophic neurites surrounding amyloid cores are visible (arrows).
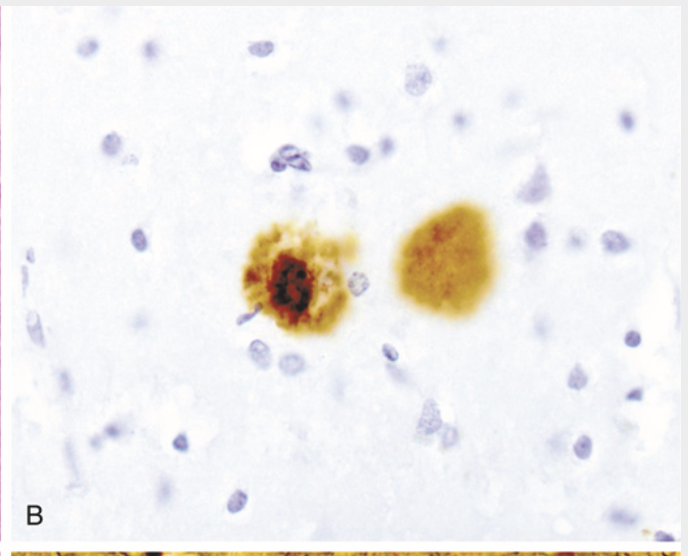
Alzheimer disease. (B) Plaque core and surrounding neuropil are immunoreactive for Aβ.
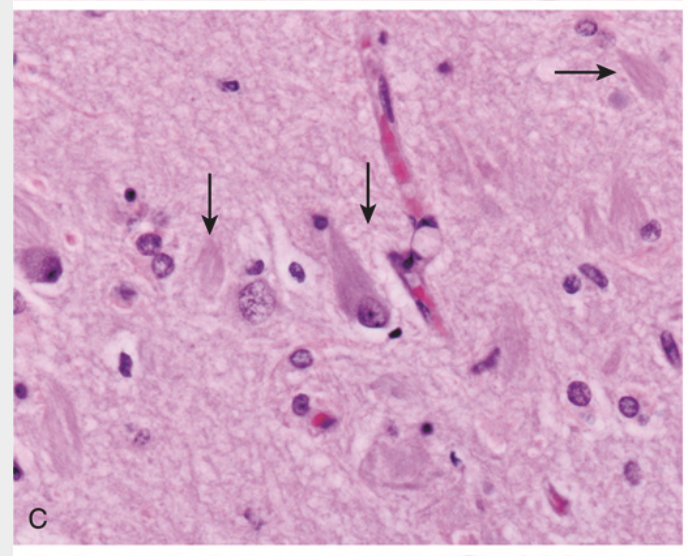
Alzheimer disease. (C) Neurofibrillary tangle is present within one neuron, and several extracellular tangles are also present (arrows).
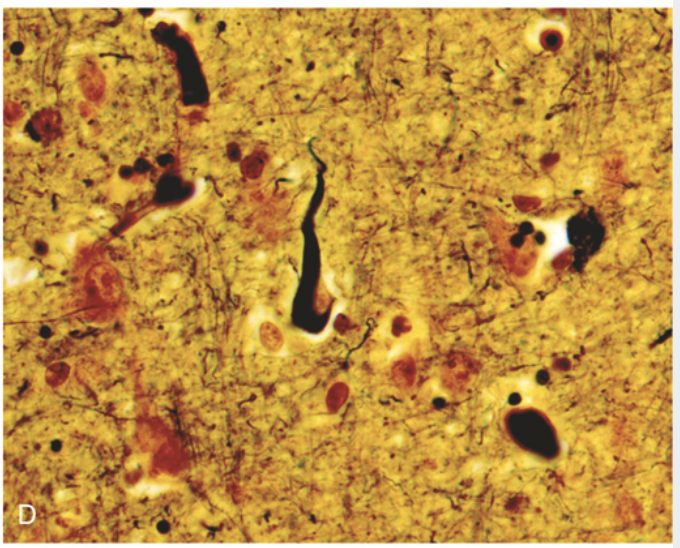
Alzheimer disease. (D) Silver stain highlights a neurofibrillary tangle (black) within the neuronal cytoplasm.
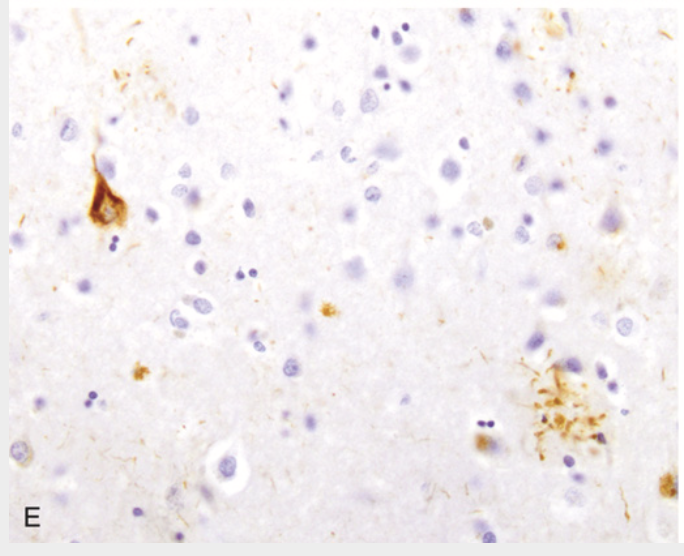
Alzheimer disease. (E) Tangle (upper left) and neurites around a plaque (lower right) contain tau, demonstrated by immunohistochemistry
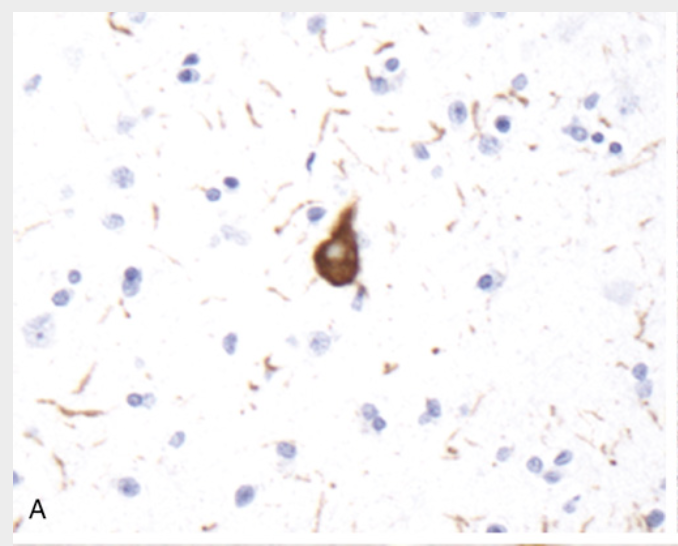
Frontotemporal lobar degenerations (FTLDs). (A) FTLD-tau. A tangle is present along with numerous tau-containing neurites (immunohistochemical stain for tau).
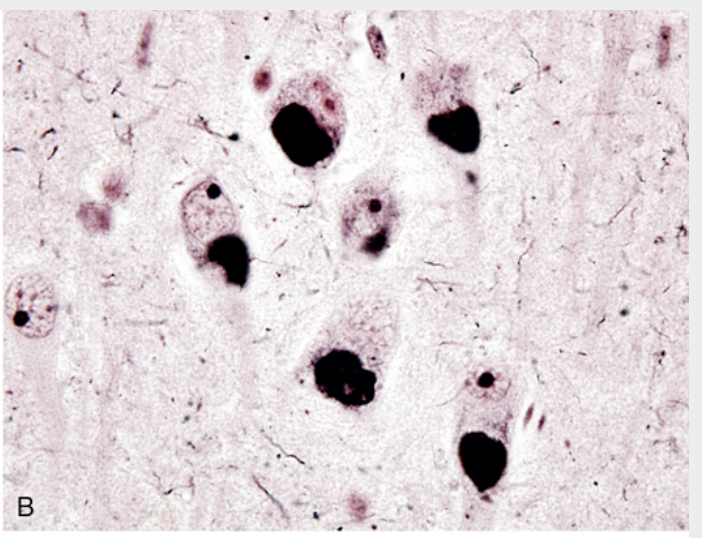
Frontotemporal lobar degenerations (FTLDs). (B) Pick disease. Pick bodies are round, homogeneous neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions that stain intensely with silver stains.
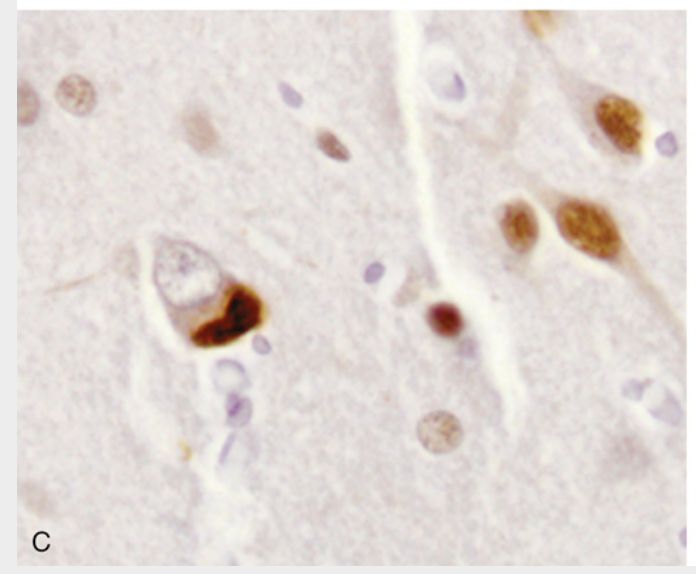
Frontotemporal lobar degenerations (FTLDs). (C) FTLD-TDP. Cytoplasmic inclusions containing TDP43 are seen in association with loss of normal nuclear immunoreactivity (immunohistochemical stain for TDP43).
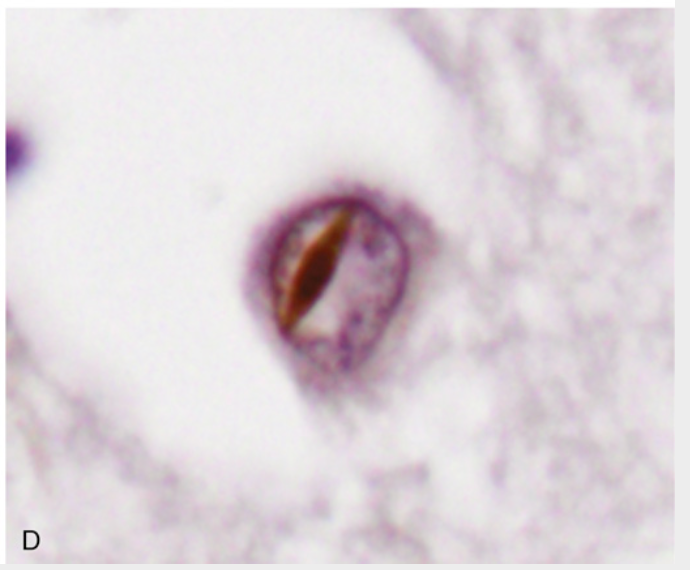
Frontotemporal lobar degenerations (FTLDs). (D) FLTD-TDP. With progranulin mutations, the TDP43–containing inclusions are commonly intranuclear
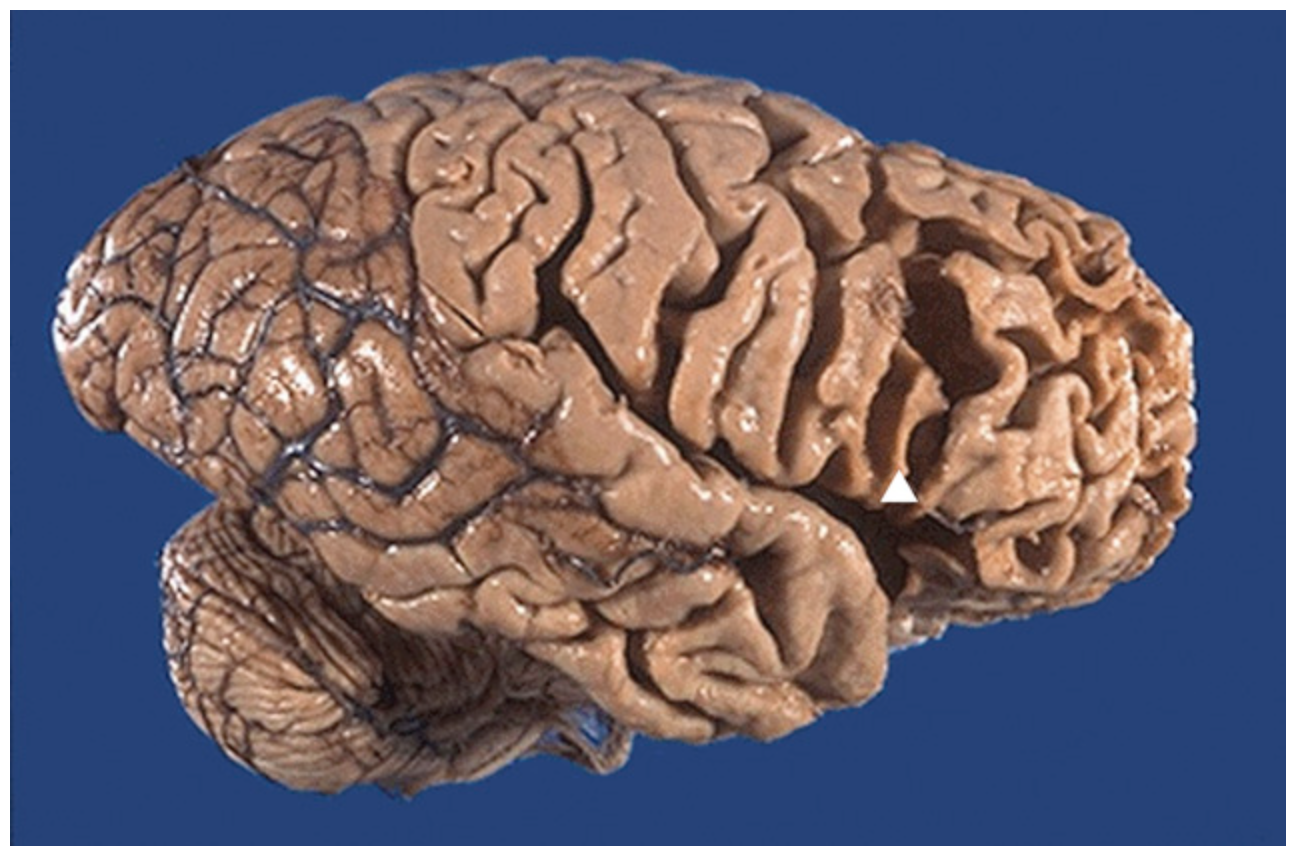
Pick disease, gross. The marked frontal and temporal lobe (lobar) atrophy with knifelike thinning of the gyri (arrowhead) is seen here in a sagittal view of the brain
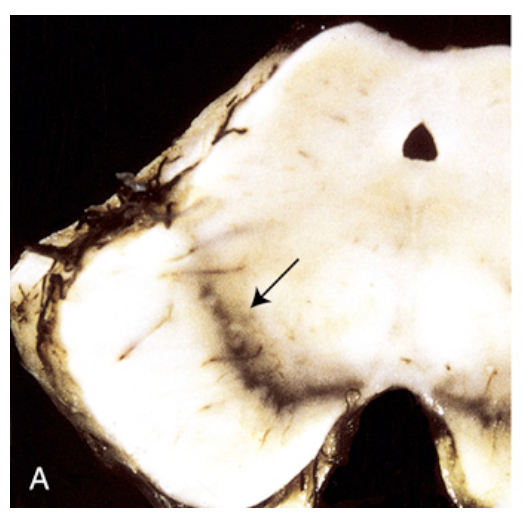
Parkinson disease. (A) Healthy substantia nigra (arrow).
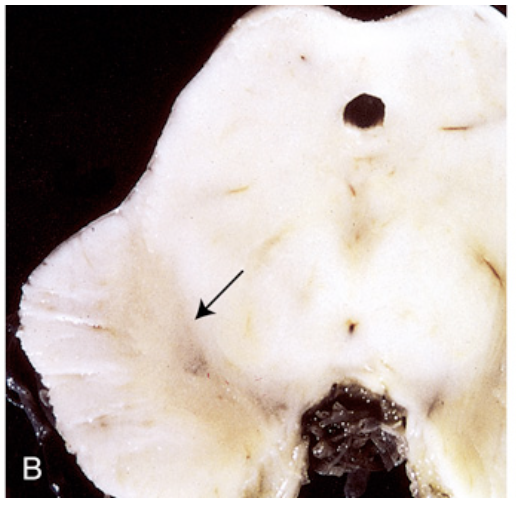
Parkinson disease. (B) Depigmented substantia nigra (arrow) in idiopathic Parkinson disease.
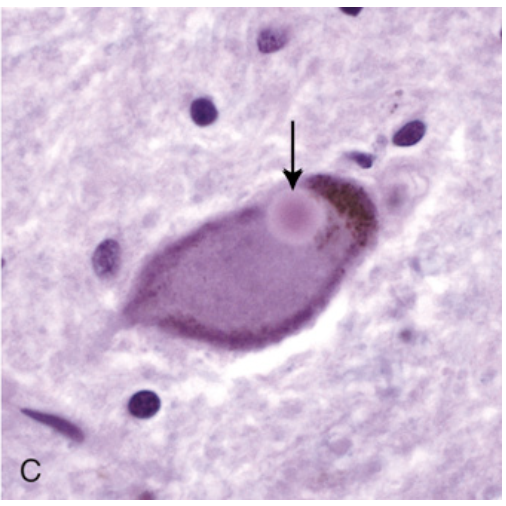
Parkinson disease. (C) Lewy body in a neuron from the substantia nigra stains pink (arrow).
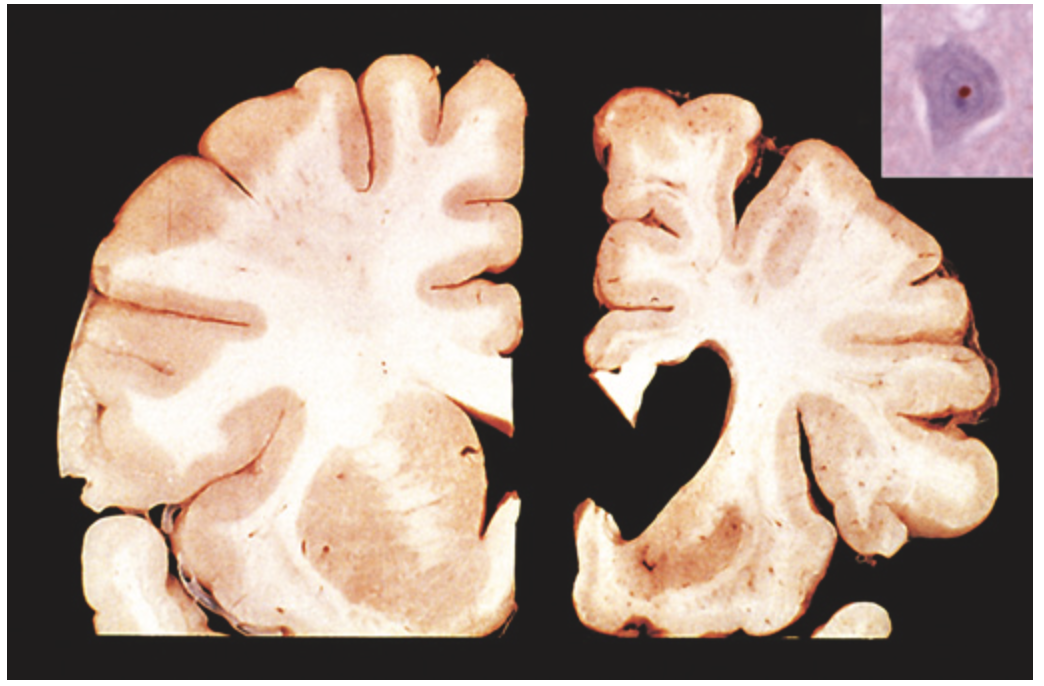
Huntington disease. Healthy hemisphere (left) compared with a hemisphere with Huntington disease (right) showing atrophy of the striatum and ventricular dilation. Inset, An intranuclear inclusion in a cortical neuron is strongly immunoreactive for ubiquitin.
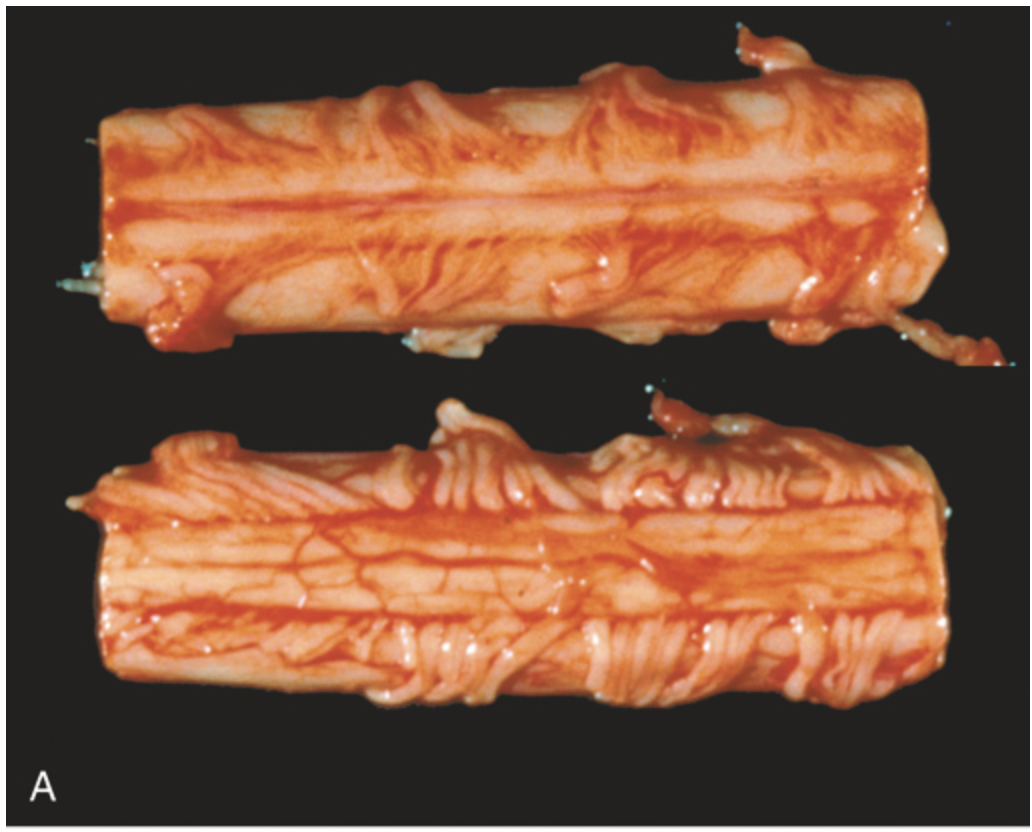
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. (A) Segment of spinal cord viewed from anterior (upper) and posterior (lower) surfaces showing attenuation of anterior (motor) roots compared with posterior (sensory) roots.
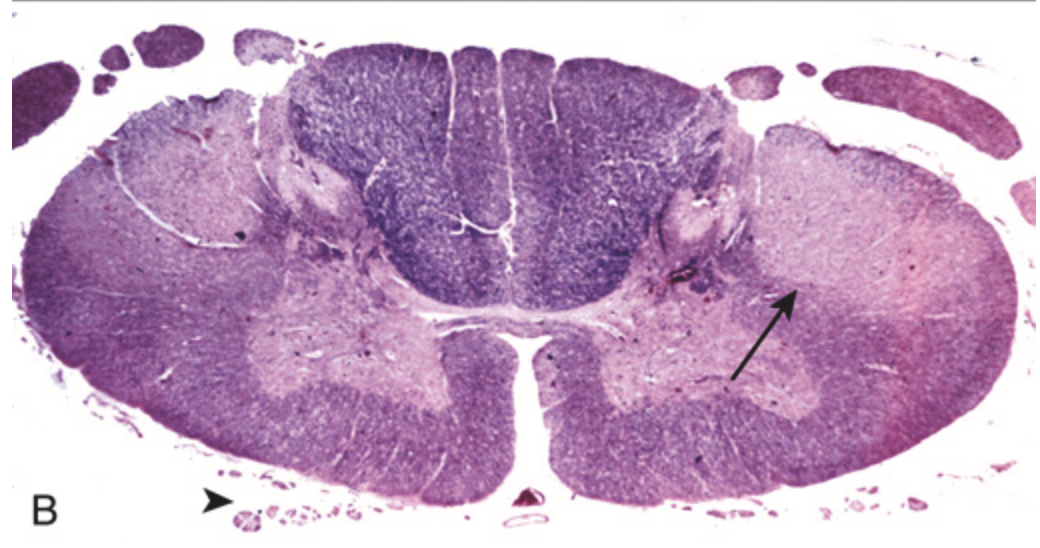
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. (B) Spinal cord showing loss of myelinated fibers (lack of stain) in corticospinal tracts (best seen on the right side of this specimen; arrow) as well as degeneration of anterior roots (arrowhead)
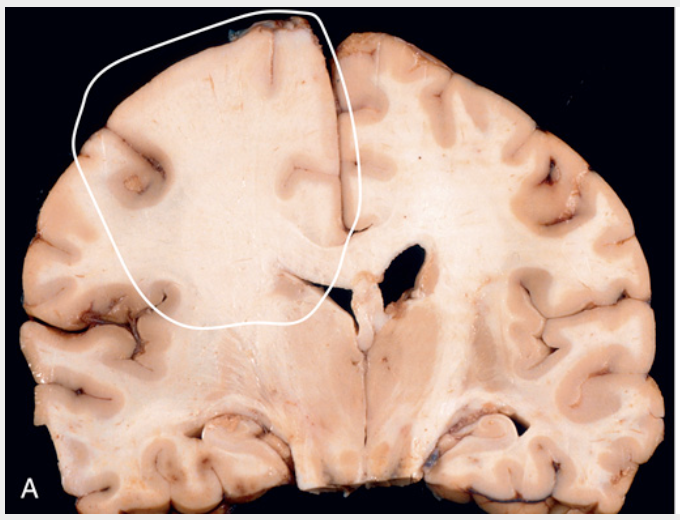
Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, grade 2. (A) On coronal section, the left frontal white matter is expanded, and there is blurring of the corticomedullary junction due to infiltrative tumor (circled region).
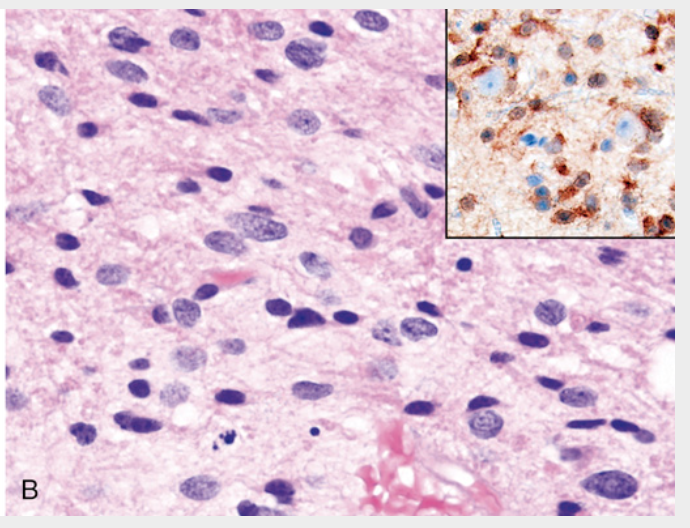
Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, grade 2. (B) A histologic section of the tumor shows enlarged, irregular, large nuclei embedded within the native fibrillar matrix of the brain; the smaller round and oval nuclei are benign oligodendrocytes and reactive astrocytes, respectively. Inset, An immunostain for mutant IDH1 is positive in tumor cells, some of which surround unstained cortical neurons
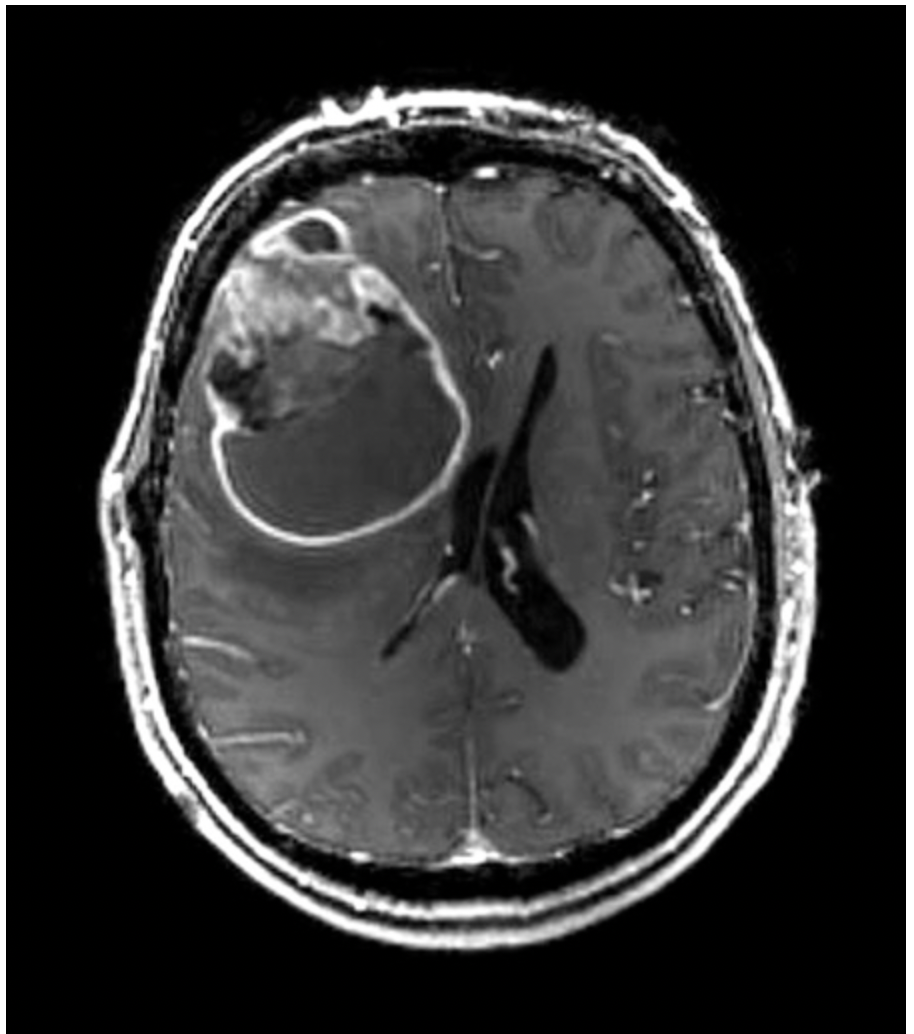
MRI image of glioblastoma (axial postcontrast, T1-weighted) showing a rim-enhancing right frontal mass
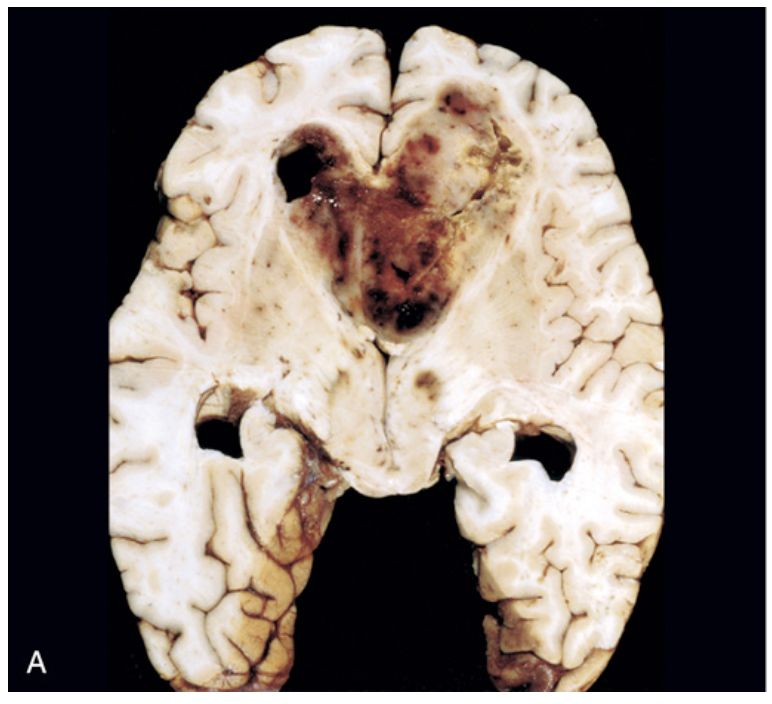
Glioblastoma. (A) The tumor forms a necrotic, hemorrhagic, infiltrating mass.
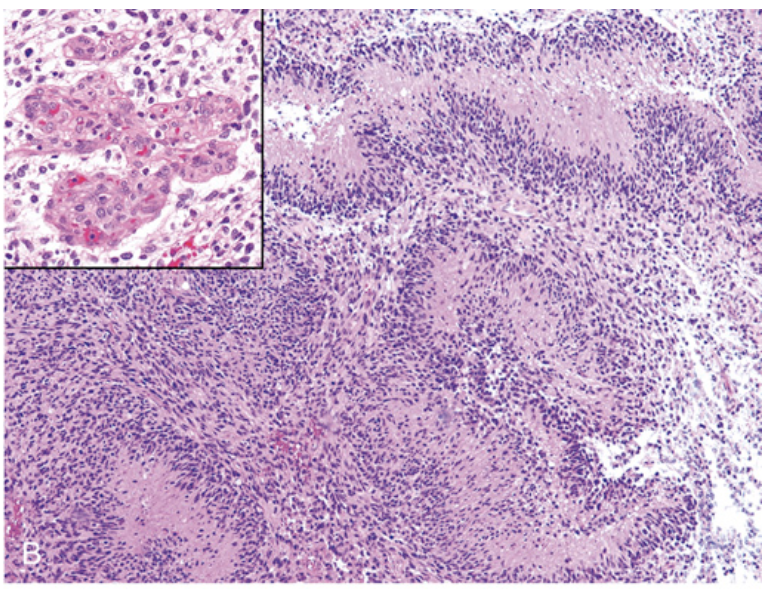
Glioblastoma. (B) Serpiginous foci of palisading necrosis (tumor nuclei lined up around the red anucleate zones of necrosis).
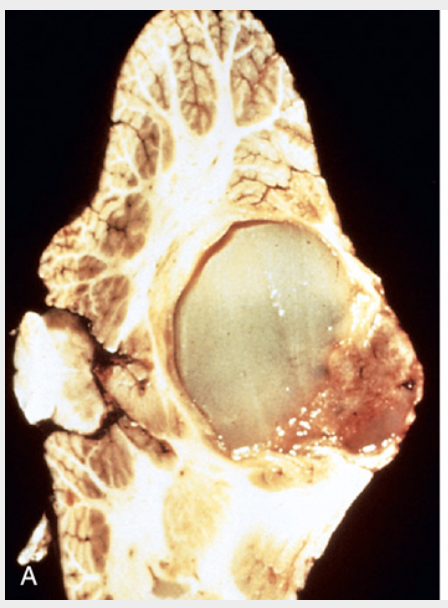
Pilocytic astrocytoma. (A) Grossly, this cerebellar tumor forms a mural nodule within a cyst.
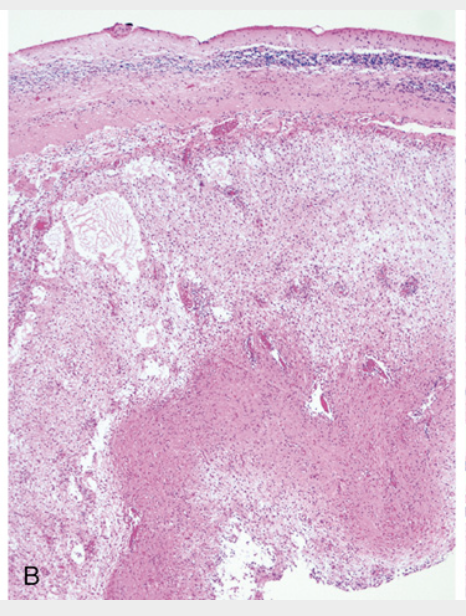
Pilocytic astrocytoma. (B) At low magnification, one can appreciate atrophic cerebellar cortex (top), sharp circumscription, and a biphasic pattern with alternating loose (middle) and compact (bottom) regions of tumor growth.
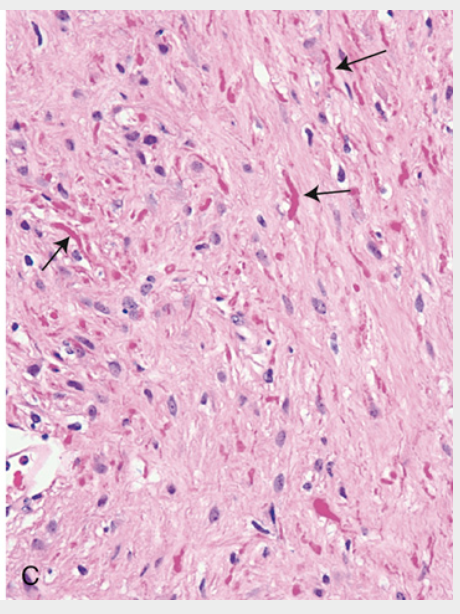
Pilocytic astrocytoma. (C) Higher magnification reveals oval to irregular tumor nuclei resembling those of diffuse astrocytoma, but with numerous Rosenthal fibers (brightly eosinophilic corkscrew-shaped inclusions, arrows) in the background
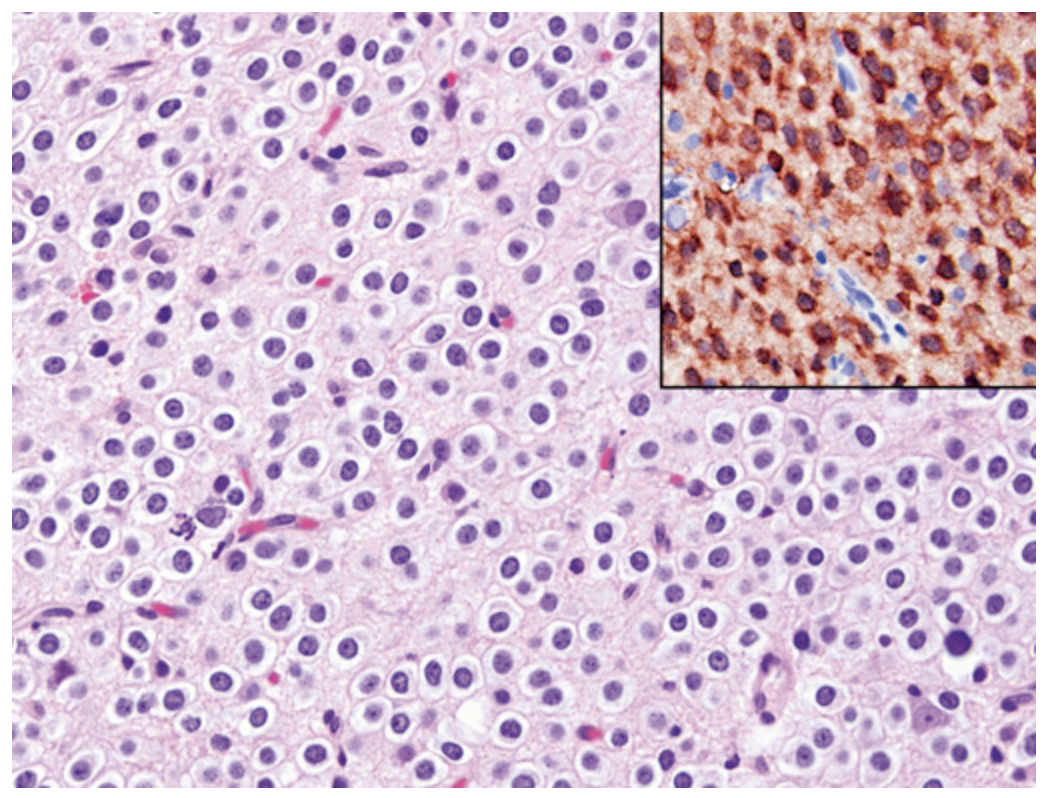
Oligodendroglioma. Tumor cells have round nuclei, often with a clear cytoplasmic halo. Blood vessels in the background are thin and can form an interlacing pattern. Inset, Similar to diffuse astrocytomas, tumor cells are positive for mutant IDH1.
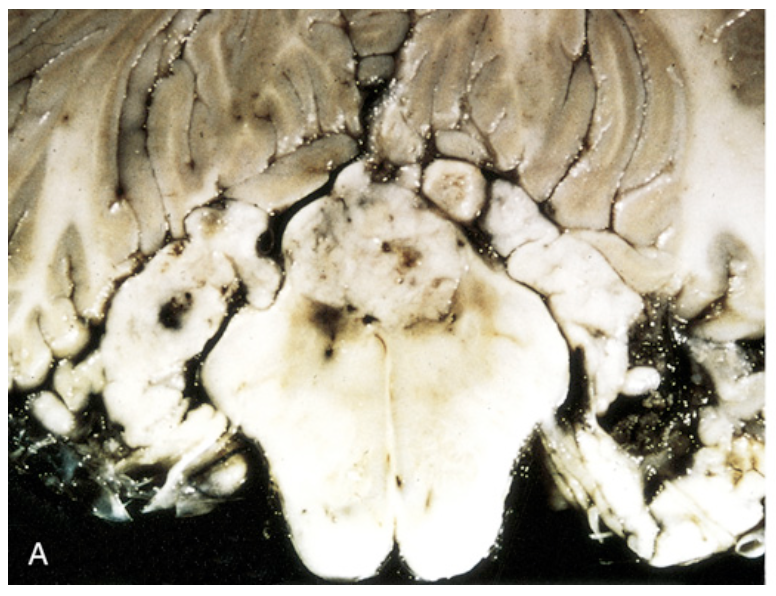
Ependymoma. (A) Tumor of the fourth ventricle, distorting, compressing, and infiltrating surrounding structures.
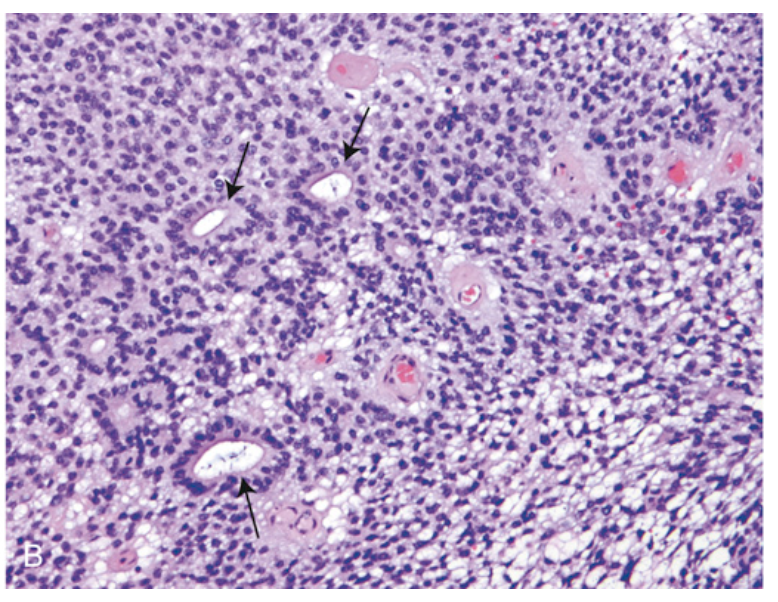
Ependymoma. (B) The microscopic appearance includes both true rosettes (with a glandlike central lumen, arrows) and perivascular pseudorosettes (nuclear-free zone composed of fibrillary processes radiating toward a central blood vessel).
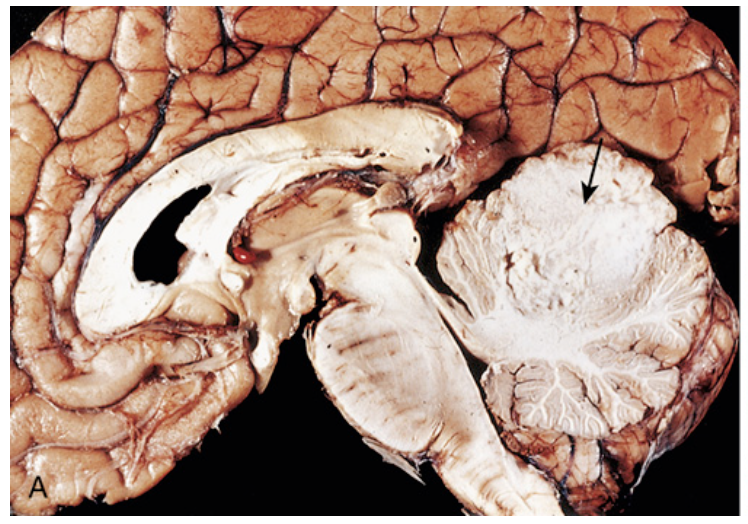
Medulloblastoma. (A) Sagittal section of a brain showing medulloblastoma involving the superior vermis of the cerebellum (arrow).
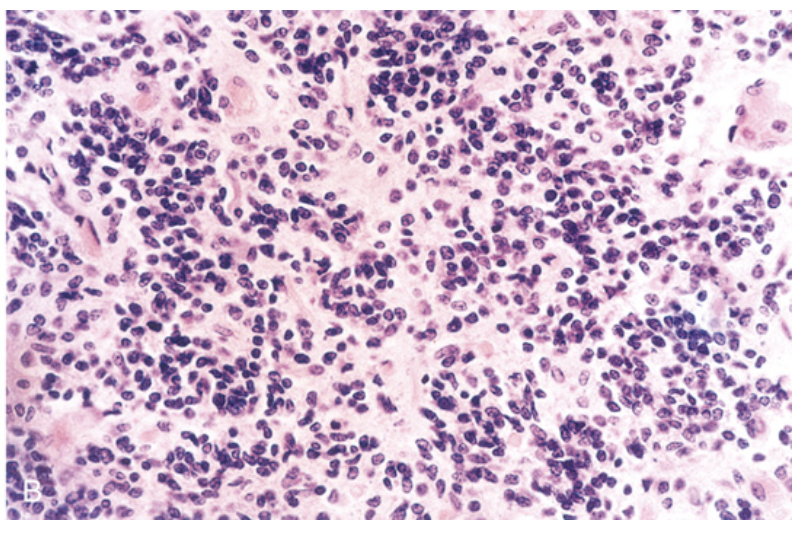
Medulloblastoma. (B) Microscopic appearance of medulloblastoma, showing mostly small, blue, primitive-appearing tumor cells

Meningioma (MRI). This MR image in coronal view shows bright enhancement of a meningioma (red diamond) arising in the parasagittal region and compressing the underlying right frontal lobe.
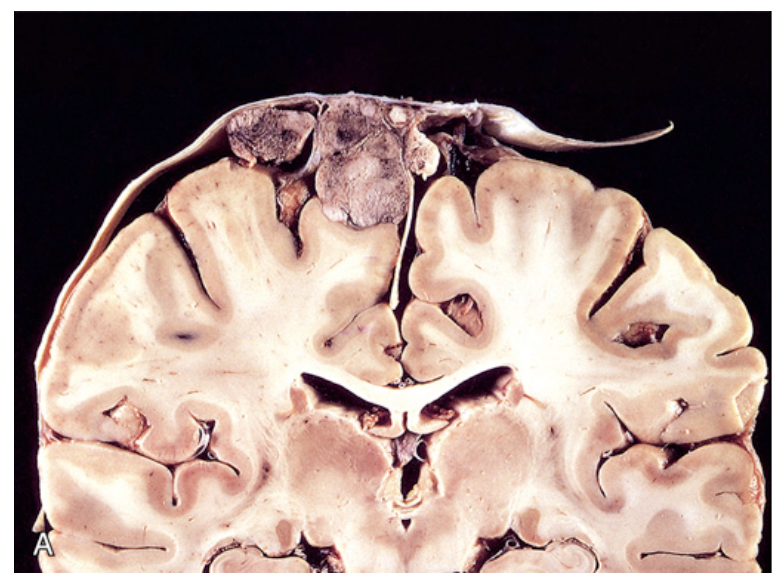
Meningioma. (A) Parasagittal multilobular meningioma attached to the dura with compression of underlying brain.
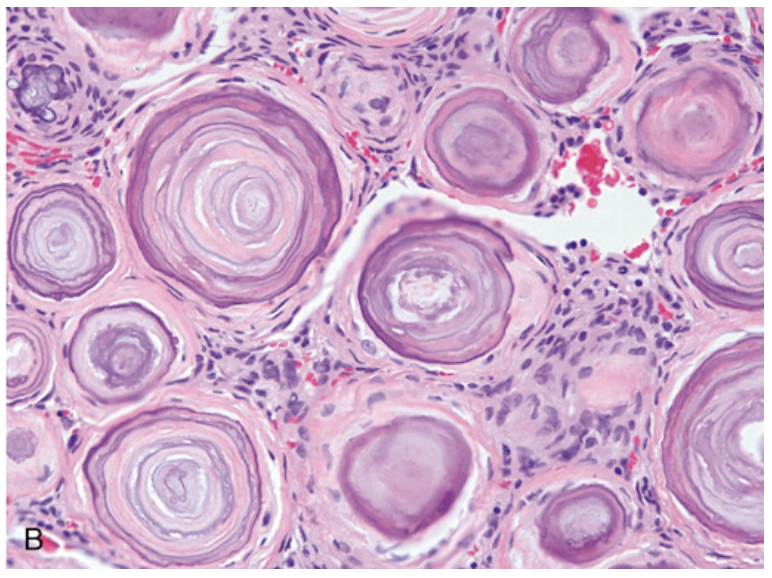
Meningioma. (B) Meningioma with a whorled pattern of cell growth and psammoma bodies (calcifications with concentric rings).
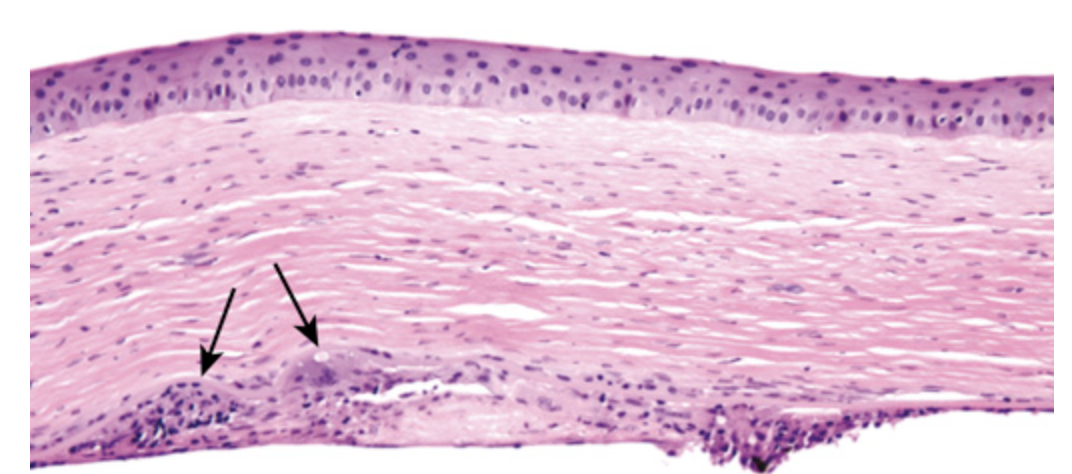
Chronic herpes simplex keratitis. The cornea is thin and scarred (note the increased number of fibroblast nuclei). Granulomatous reaction in the Descemet membrane (arrows) is a histologic hallmark of chronic herpes simplex keratitis