✅ [A] COLOR THEORY
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
Color
A phenomenon of light and visual perception that may be described in terms of an individual’s perception of hue, saturation, and lightness
(1) Observer
(2) Object
(3) Sufficient Light
Color is a mental sensation that can only occur if these three requirements are fulfilled
Visible Spectrum
The narrow band of wavelengths that the human eye can view
Color Effect
What we actually see as color is known as its
True
True or false: The entire electromagnetic spectrum is not perceivable to humans
True
True or false: All light travels at the same speed but waves of light energy are emitted at different distances apart
Frequencies
What do you call the varying distances emitted by waves of light energy?
Wavelength
The physical difference between radio waves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays
Wavelength
The distance between peaks of light energy emissions
Spectral Color
Light of a specific wavelength
Hue
Color perception of a specific wavelength
True
True or false: Color only exists in the brain
Red
Color having the longest wave length in the visible spectrum
Violet
Color having the shortest wave length in the visible spectrum
Nanometers
Wavelengths of light are measured in
Psychological
Physical events that affect the conscious, subconscious, and unconcious
Physiological
Lightwave frequencies that “describe the effects stimuli have upon us”
Chromotherapy
The healing of color. Light is used in the form of color to balance energy
True
True or false: Color connotations and associations differ among men to women, children to adults, as well as professions and cultures
Light Quality
A factor in perception that is concerned with the spectral energy distribution of the light including the conditions under which the color is perceive
Metamerism
Two objects that appear to match under one light source but not under another exhibit
Metameric Pair
The objects that appear to match under one light source but not under another
False
True or false: If the colorants of two things are different, they can be made to match under all light conditions
Color Constancy
The perception that the colors of familiar objects remains the same no matter what the illumination (light sources) may be
Media and Techniques
Spectral characteristics of the object, with respect to absorption, reflection and transmission of light
True
True or false: Colors may be different according to the media, support employed, brands of paint
Eye and Brain
Body parts that allow certain colors to be perceived more easily than others
True
True or false: Most of what we see is based on the memory of a color — when and how we have experienced it before
Synesthesia
A neurological condition in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway
Grapheme-color Synesthesia
An individual's perception of numbers and letters is associated with the experience of colors
False
True or false: Grapheme-color synesthesia is not involuntary, consistent, and memorable
Sound-to-Color Synesthesia or Chromesthesia
Color is experienced as a result of a musical sound such as sound, pitch, key, tone, key, or timbre. Synesthetes that perceive color while listening to music experience the colors in addition to the normal auditory sensations that would be triggered in the average person
Color Blindness
It is the inability or decreased ability to see color, or perceive color differences, under normal lighting conditions. For the vast majority of people with deficient color vision the condition is genetic and has been inherited from their mother, although for some is a result of other diseases such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis or they acquire the condition over time due to the aging process, medication etc.
Color Vision Deficiency or CVD
Color blindness is also known as
Ishihara Color Blindness Test
Most well known color vision deficiency test all around the world
Dr. Shinobu Ishihara
Japanese doctor that produced three different test sets which are widely used and which all are based on the same pseudoisochromatic plates
True
True or false: Memories, experiences, intelligence and cultural background all affect the way a color’s impact can vary from individual to individual
Eye Training
Learning to distinguish in every color sample three objective attributes
Color Competence
The ability to predict and control, to the extent possible, color effects and the ability to select and use colors that will enhance every product and page
Color Control
The instability of colors cannot be eliminated, but with awareness and kill it can be minimized, even utilized
Hue
Undiluted colors. The true colors of the spectrum. Attribute of colors that permits them to be classed as red, yellow, green, blue or an intermediate
Chromatic
Having hue
Achromatic
Without hue. There is no discernable hue or color
Polychromatic
Having many hues (usually 3-4)
Monochromatic
Having one hue only
Prismatic
Use of pure hues only
Chromatic Scale
Any linear series of hues in spectrum order. This can illustrate pure saturated colors or more complex, diluted colors. Its defining characteristic is that each step in the progression is a change in hue
Broken Hue
A combination of unequal proportions of all the primaries. Russet, gold, ecru are some examples found in nature, sometimes known as earth colors
Color Wheels
Color arrangements or structures that enable us to organize and predict such color reactions and interactions
Pigment Wheel
The basis for working with subtractive color, it imparts information about the reactions colors have when they are actually mixed
Mixing Wheel
The pigment wheel is also known as
False
True or false: When using the pigment wheel, red and yellow, and blue can be obtained by mixing pigments
True
True or false: When using the pigment wheel, mixing red, yellow, and blue creates a muddy black
Primary Colors
Colors that cannot be created by combining other colors
(1) Red
(2) Yellow
(3) Blue
The three primary colors
Secondary Colors
Produced from the mixing of one primary color with another
(1) Orange
(2) Green
(3) Violet
The three secondary colors
Tertiary Colors or Intermediate
These colors are created when mixing one secondary and one primary colors
Process Wheel
This primary arrangement is the standard employed in color printing and photography as well as pigment (ink) manufacture
(1) Cyan
(2) Magenta
(3) Yellow
The three basic primaries of the process wheel
True
True of false: In the process wheel, mixing the three primaries together will result to gray-black
Light Wheel
It is based on the additive color system and provides information concerning light rays and transparent color. It is now used for theatrical lighting and projection and is now the basis for video and computer graphics as well
False
True or false: In the light wheel, since these are combinations of colored light, when all the primaries (red, green and blue) are combined, black is the result
Black
The total absence of light results in
True
True or false: Because light is being added to light, the more color rays are mixed or fused with other color rays, the lighter they become
(1) Cool Hues
(2) Warm Hues
Two major types of color temperature
Cool Hues
Usually related to blue. This color temperature recede and suggest sky, water, distance, foliage, shadows. It is quiet, restful, far, airy, and light
Blue-green
The coolest hue
Warm Hues
Usually related to red. This color temperature advance and suggest aggression, sunlight, heat, blood, arousal and stimulation. They appear heavier than cool ones and when placed side by side, these differing visual weights influence their surroundings
Red-orange
The warmest hue
Hot
Color temperature that is intense and attention-grabbing, these schemes often include bright shades of red
Cold
Color temperature that can be powerful, frigid or austere, these palettes include bright shades of blue
Intensity
Also called chroma or saturation and is the brightness or dullness of a color
True
True or false: Orange appears heavy and is warmer than yellow
Value
The relative lightness and darkness of a color sample
Tint
Color with the presence of white. Lighter shade of a color
True
True or false: Pink is a tint of red
Shade
A color with the presence of black. Darker shade of a color
True
True or false: Navy is a shade of blue
Saturation
Intensity, brightness or dullness of a color. Also known as the brilliance, purity, or chroma
Tone
Addition of gray to pure hue
True
True or false: A saturated hue can be reduced in saturation by the addition of achromatic gray or by the addition of its complement
False
True or false: Saturated color is not a good way to compare color value
True
True or false: Some colors, such as yellow and orange, have a much lighter value at their highest saturation point, while other colors have a darker value (such as blues and purples)
Dilution
Changing a pure hue by lightening, darkening or muting by the use of additives such as white, black, gray or its complement. When the descendant of any two colors is arranged as if the parent colors were crossing one another, it creates an illusion
Intervals
An ______ is a step of change between color samples. Most design situations involving this involve three elements: The “parents” (samples on either side) and the “descendant”, a visual step between two parents
Transparence
The impression of transparency can be achieved when two sets of color are joined by a third that is perfectly balanced between them
Gradient
Series of progressive intervals that are so close that individual steps cannot be distinguished. It is a seamless transition between color differences
Threshold
The point at which an individual can no longer detect a difference between two close samples
Visual acuity for color
The ability to detect differences between wavelengths (colors) of light
True
True or false: Each individual's visual acuity for color determines his or her threshold of color vision
Colorway
Any of a range of combinations of colors in which a style or design is available
Dissonance
Use of conflicting, unrelated colors
Advancing
Colors lower in value (darker), more highly saturated, and warmer in hue are considered to be
Receding
Colors higher in value (lighter), lower in saturation, and cooler in hue are considered to be
Color Harmony
Refers to the visual agreement of all parts of a work. These are time-tested combinations that work well together
Color Chords
Color harmony is also known as
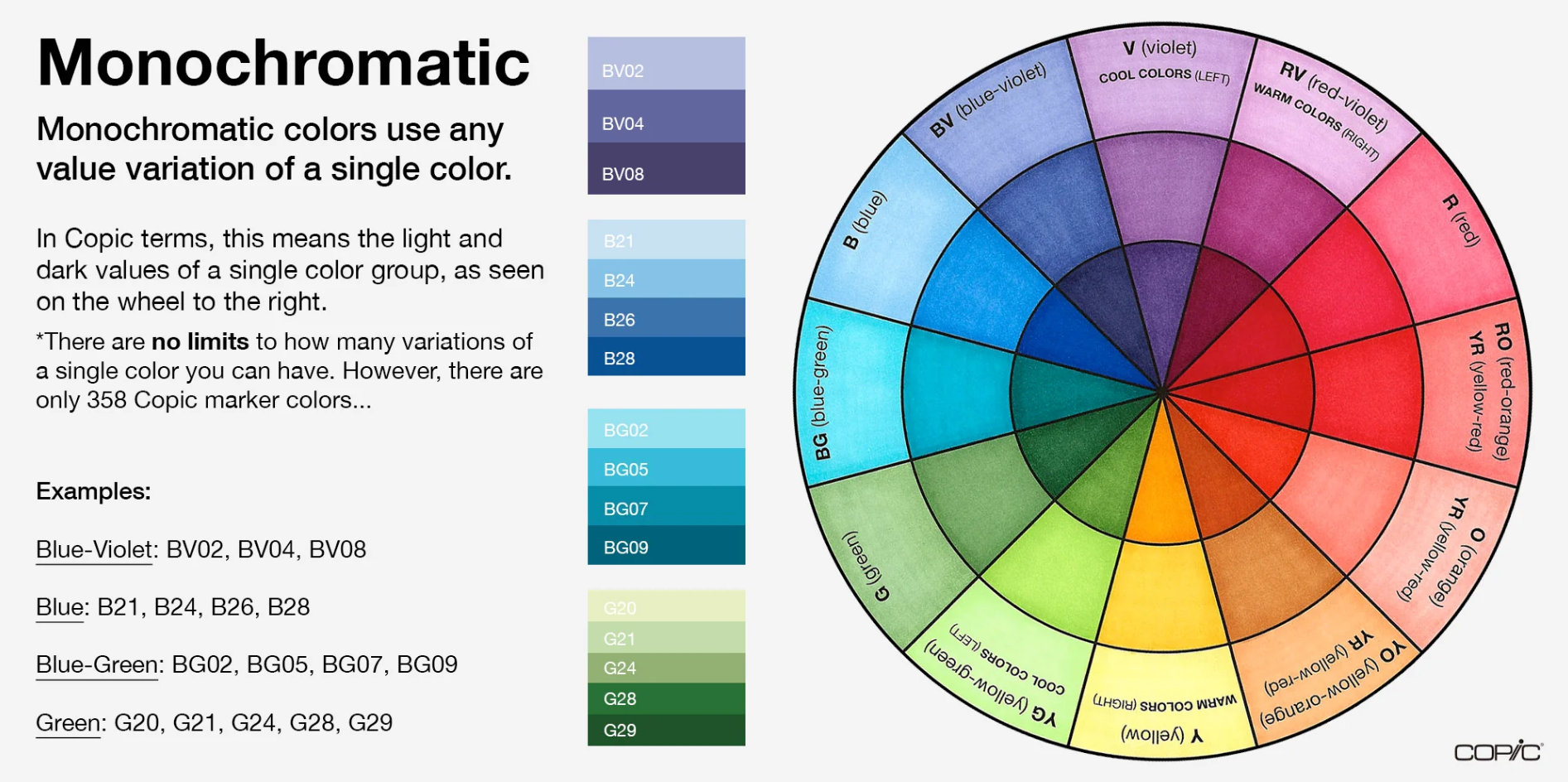
Monochromatic
Containing or using only one hue
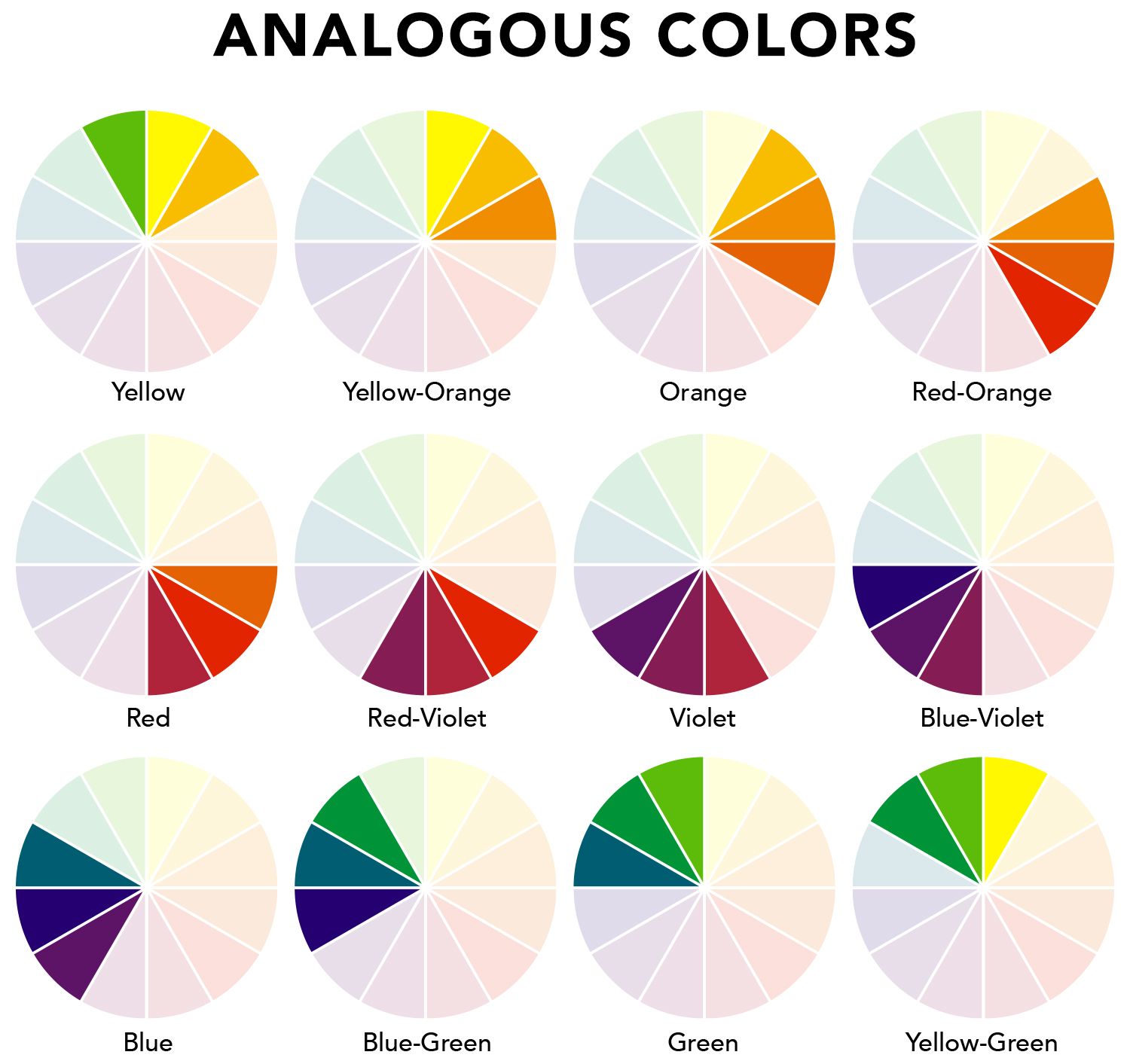
Analogous
Groups of colors (3 colors) that are next to each other on the color wheel
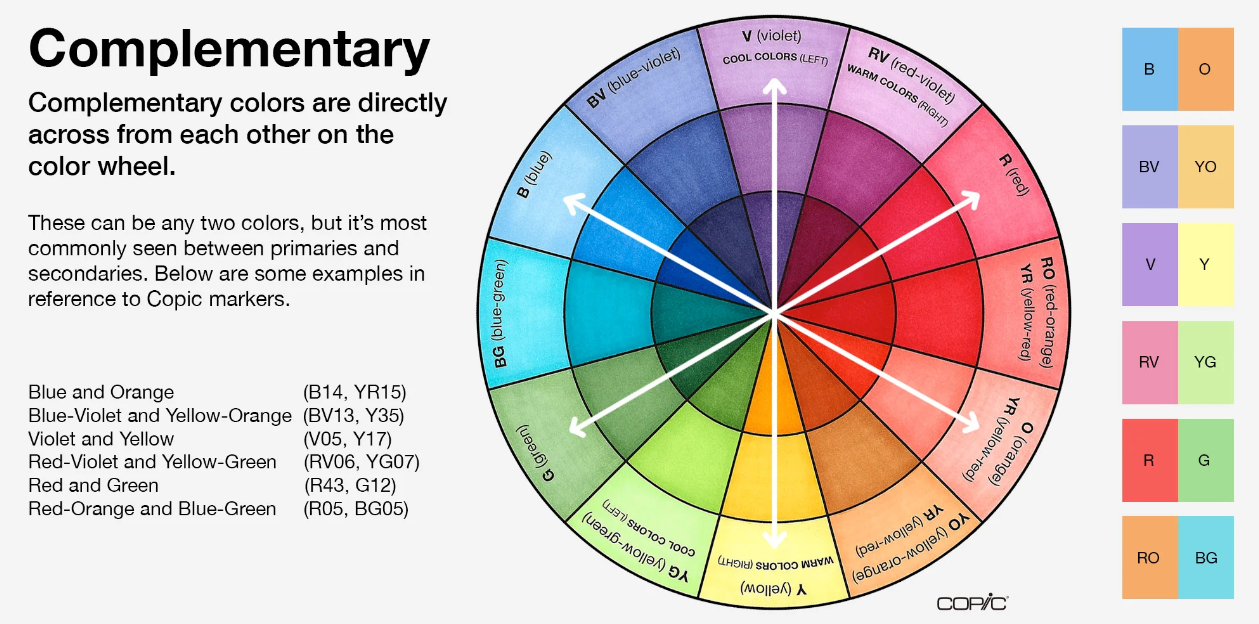
Direct Complementary
A color scheme that lies directly across the color wheel from each other