164 EKG
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
wk 1-7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
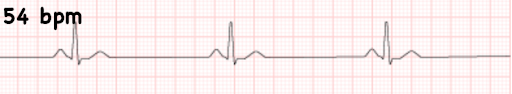
sinus bradycardia
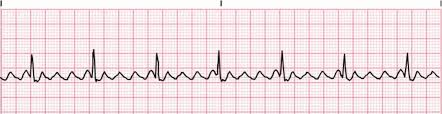
atrial flutter
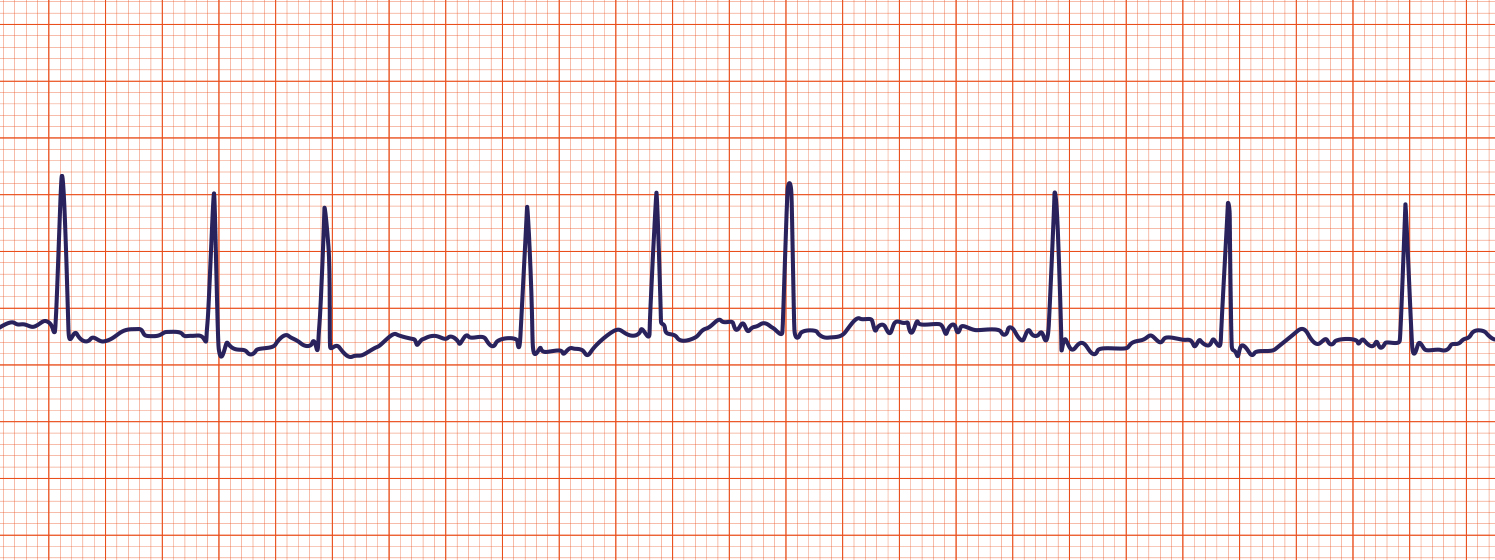
Afib
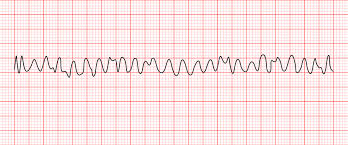
Vfib
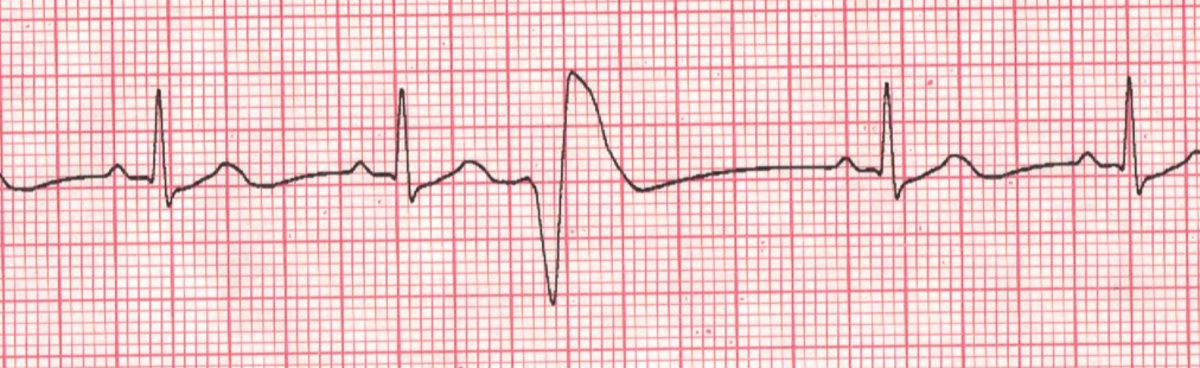
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
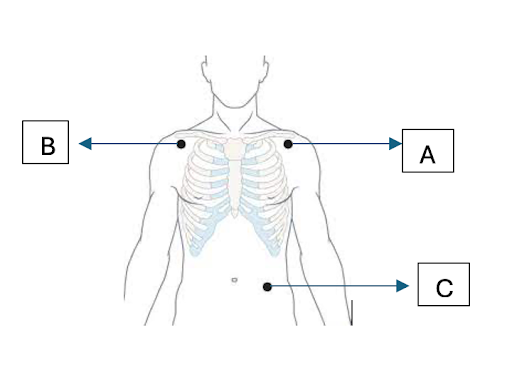
A: LA (modified)
B: RA (modified)
C: LL (modified)
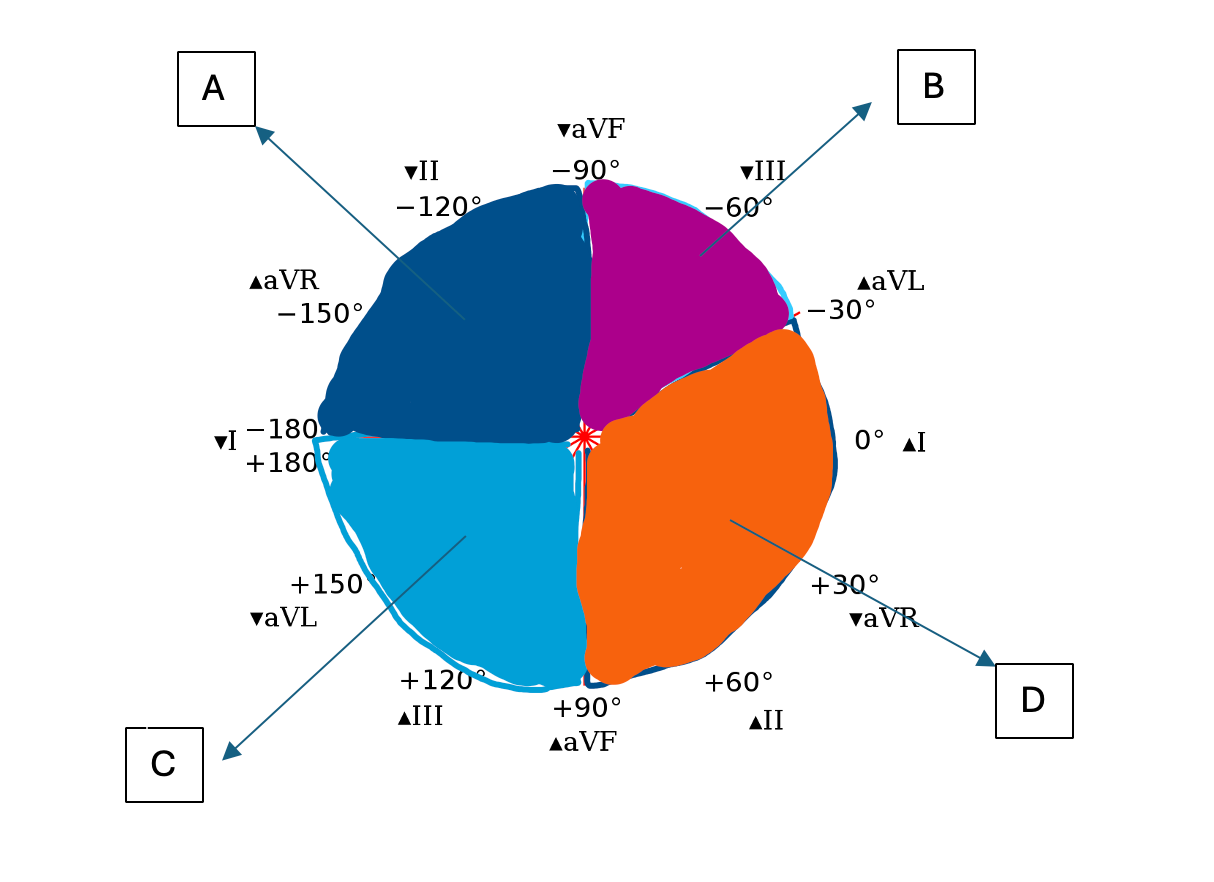
A: Extreme axis deviation
B: Left axis deviation
C: Right axis deviation
D: Normal electrical axis
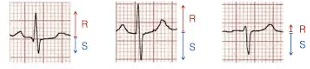
A. Positive
B. Equiphasic
C. Negative
1. True or False: Conduction blocks can occur anywhere from the SA node to the Purkinje fibers.
TRUE
What percentage of conduction blocks are associated with ischemia?
40%
How many types of conduction blocks are there?
4
Which conduction block is known to be a "complete heart block"?
Third-degree AV block
True or False: "Hay Block" is also known as Mobitz I?
FALSE
Left bundle branch block is associated with which ventricle?
LV
Right bundle branch block is most likely observed in which ECG leads?
V1 and V2
How does one determine first-degree AV block from normal sinus rhythm?
Measuring the PR interval
What is the common treatment for third degree AV block?
External or internal pacemaker
True or False: Patients will have symptoms with first degree AV block
FALSE
What are the three major types of cardiomyopathies?
Dilated, Hypertrophic, or Restrictive
True or False: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is another term used to describe left ventricular hypertrophy?
FALSE
A common ECG finding for dilated cardiomyopathy is?
Atrial Flutter
Atrial Fibrillation
Tachy-arrhythmias
Inverted T-waves
Small QRS wave heights
What are the five types of restrictive/infiltrative cardiomyopathy?
Amyloidosis, Sarcoidosis, Hemochromatosis, Pompe disease, and endomyocardial fibrosis
What is the most common type of restrictive/infiltrative cardiomyopathy?
Amyloidosis
Which cardiomyopathy is the least common?
Restrictive / Infiltrative Cardiomyopathy (R/I CM)
The S-wave in V1 added to the R wave in V5-V6 should be greater than _____ to be considered hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
35 mm
Which part of the myocardium is most commonly affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
he intraventricular septum
Which part of the ECG complex is most commonly affected by atrial enlargement?
P wave
True or False: A large QRS amplitude is the only finding to confirm left ventricular hypertrophy?
FALSE
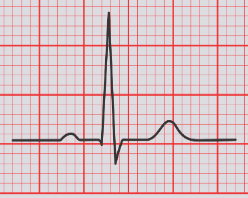
normal
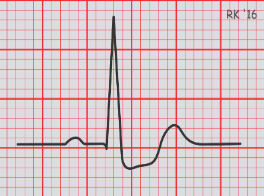
ischemia
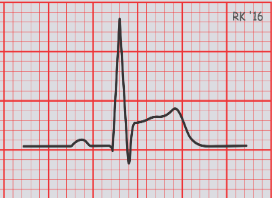
MI
True or False: A denervated heart loses its conduction system and cannot generate impulses?
FALSE
Which group of cells initiates the heartbeat under normal conditions?
SA node
A troponin blood test is most commonly used to evaluate:
Heart attack (myocardial infarction)
Which phase corresponds to ventricular depolarization on the ECG (QRS complex)?
Phase 0
The plateau phase (Phase 2) of ventricular action potential is maintained by:
Calcium influx balanced by potassium efflux
In transplanted hearts, the loss of vagal tone leads to a _____ resting heart rate
fast
Pacemaker cells begin at approximately ____ and slowly drift upward toward threshold due to funny currents
-60 mV
Which protein does calcium bind to in order to initiate contraction?
Troponin
The long refractory period of cardiac muscle prevents ___________?
tetanic contractions (tetany)
Pacemaker cells lack a true resting potential because of:
Funny currents (slow sodium leak)
The process by which calcium entry triggers more calcium release from the SR is called ___________?
calcium-induced calcium release (CICR)
Why is stress echo especially useful in transplant patients?
They lack angina symptoms due to denervation
In contractile myocytes, the resting membrane potential is about _____?
-90 mV
True or False: The relative refractory period means the heart cannot fire again under any circumstance
FALSE
segment
end to beginning
interval
beginning to end