tooth developmental defects
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
anodontia
total lack of tooth development
ankylosis
cessation of eruption after emergence, fusion of cementum w bone, unknown pathogenesis
concrescence
union of two teeth by cementum alone
dens in dente
“a tooth within a tooth”, developmental anomaly that results when the enamel organ invaginates into the crown of a tooth before mineralization
dentinogenesis
formation of dentin
dilaceration
an abnormal bend or curve in reference to the root of a tooth
fusion
two tooth buds try to join and create a single enlarged/joined tooth resulting in a missing tooth count
gemination
one tooth bud tries to divide in which the tooth count is normal
hypodontia
a few missing teeth, 1-5; associated w ectodermal dysplasia; teeth present are usually abnormal in shape
impacted teeth
embedded teeth that cannot erupt into the oral cavity bc of a physical obstruction
macrodontia
abnormally large teeth
microdontia
abnormally small teeth
oligodontia
a subcategory of hypodontia in which 6 or more teeth are missing
supernumerary
excess number of teeth; associated w Gardener’s Syndrome and Cleidocranial Dysplasia
are permanent or primary teeth more affected by hypodontia
permanent- 3rd molars
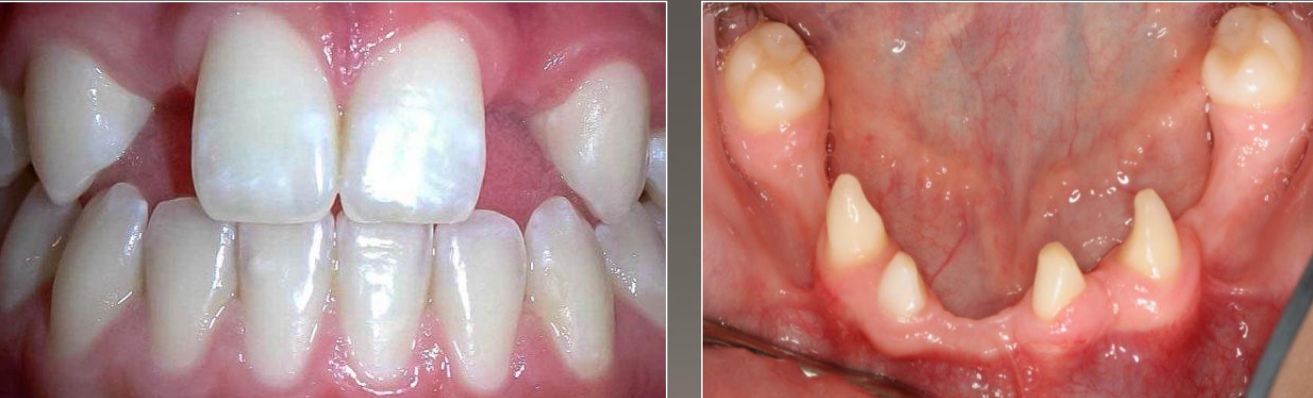
dx
hypodontia
origin of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
inherited condition via AD, AR, X-linked, where 2 or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop
clinical manifestations of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
heat intolerance
fever
hypodontia
fine, sparse hair
reduced eyebrows and eyelashes
periocular skin shows wrinkling and
hyperpigmentation
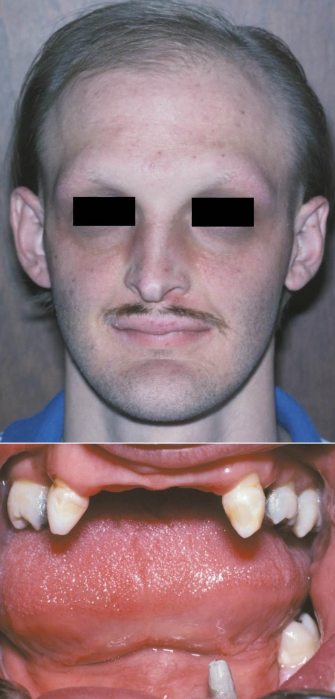
what are the most common teeth you will see in hyperdontia
max incisor > max 4th molar > mand 4th molar
what is mesiodens
type of hyperdontia referring to maxillary incisors (most common)
what is distomolar/distodens
type of hyperdontia referring to accessory 4th molar
what is paramolar
type of hyperdontia referring to situated lingually or buccally to a molar
what syndromes should be assessed if a pt have hyperdontia
Gardener’s Syndrome and Cleidocranial Syndrome
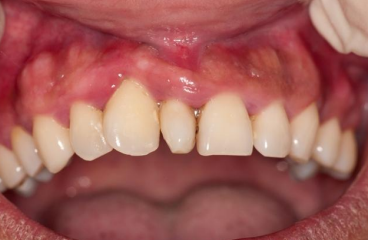
type of hyperdontia
mesiodens
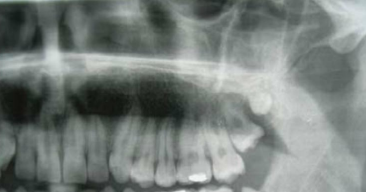
type of hyperdontia
distomolar/distodens
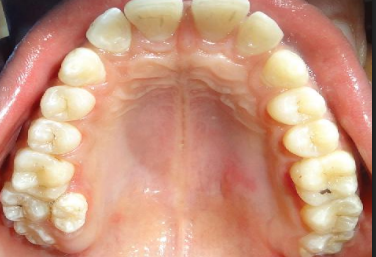
type of hyperdontia
paramolar
what are natal teeth
teeth present at birth
what are neonatal teeth
teeth present within the first 30 days
mode of inheritance for cleidocranial dysplasia
AD
clinical manifestations of cleidocranial dysplasia
prolonged retention of deciduous teeth
delay or failure or eruption of permanent teeth
abnormally shaped teeth
numerous unerupted permanent and supernumerary teeth
clavicle abnormalities
Gardener Syndrome mode of inheritance
AD, mutation in chromosome 5 (APC)
clinical manifestations in Gardener Syndrome
colorectal polyps (can become malignant)
multiple osteoma (bone tumor in head)
epidermoid cysts of skin
supernumerary teeth
thyroid carcinoma
pigmented ocular fundus (90%)

is hyperdontia more commonly found in gardeners syndrome or cleidocranial dysplasia
cleidocranial dysplasia
is microdontia often associated w hypodontia or hyperdontia
hypodontia
what tooth is most affected by microdontia
lateral incisors- peg laterals
microdontia can be associated w what syndromes
down syndrome
hypopituitarism (dwarfism)
is isolated or generalized macrodontia more common, which tooth/teeth
isolated; incisors and canines
if macrodontia is generalized, this is rare, but it may be associated w…
systemic conditions
what are where is the cusp of carabelli
accessory cusp on ML of maxillary molars that may contain pulp tissue
what and where are talon cusps
accessory cusp on lingual of maxillary (lateral) incisor that may contain pulp tissue
what is dens evaginatus/occlusal pearl
elongated cusp extending from central occlusal surface that usually contains pulp tissue
what teeth are most common in dens evaginatus
mandibular premolars, then maybe molars
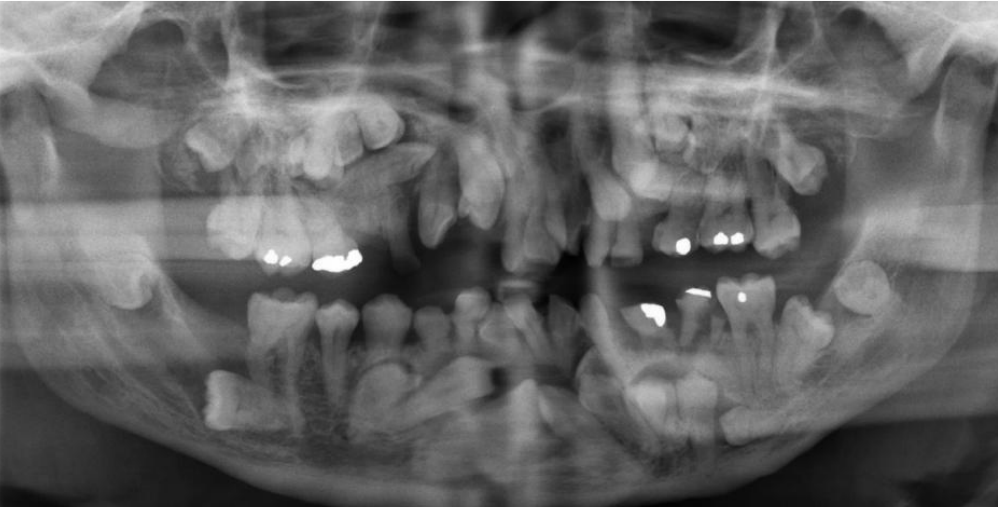
dx
hyperdontia/supernumerary
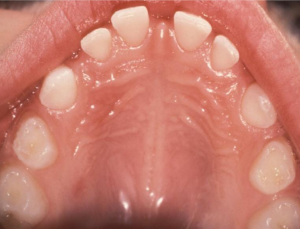
dx
microdontia
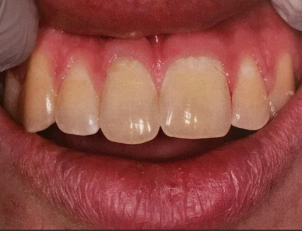
dx
macrodontia
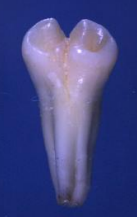
dx
gemination
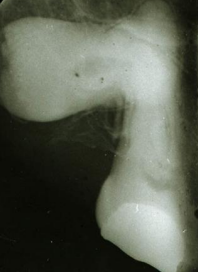
dx (by cementum only)
concrescence
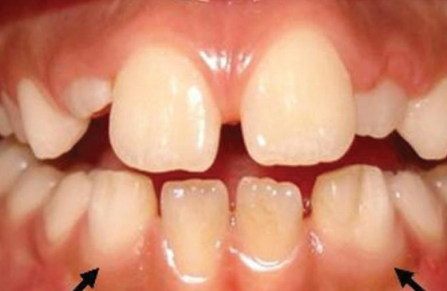
dx (two teeth join together)
fusion
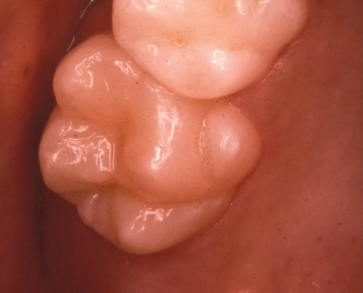
dx
cusp of carabelli
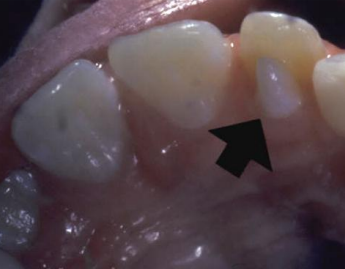
dx
talon cusp
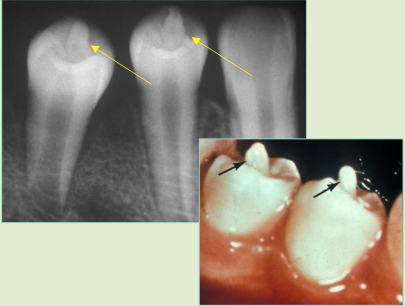
dx
dens evaginatus/occlusal pearl
des invaginatus, AKA, dens in dente, can be coronal or radicular, what are the three types
type I: invagination is confined to crown
type II: invagination extends below the CEJ
type III: invagination may extend through the root
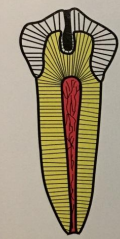
dx
type I dens in dente/dens invaginatus
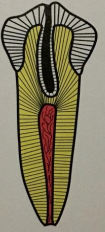
dx
type II dens in dente/dens invaginatus
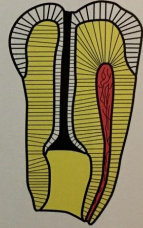
dx
type III dens in dente/dens invaginatus
what are shovel shaped teeth
prominent marginal ridges on maxillary incisors- especially centrals
shovel shaped teeth can be associated w…
dens evaginatus/occlusal pearls
is shovel teeth usually uni- or bilateral
bilateral
shovel teeth are most common in ..
Asians
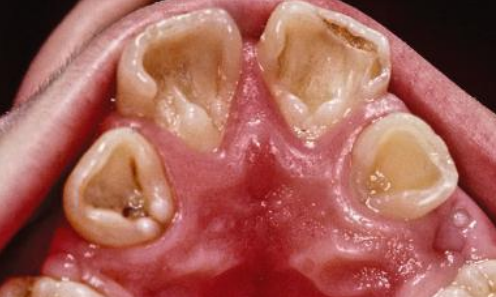
dx
shovel teeth
what are enamel pearls
enamel nodules at furcations of multi-rooted teeth that contain pulp tissue but no dentin
where are enamel pearls most common
maxillary molars
what problems can present w enamel pearls
perio defects and pulp exposures
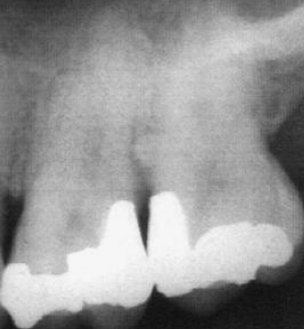
dx
enamel pearl
what is taurodontism
enlargement of the body and the pulp chamber of a tooth; is associated w many syndromes
where is taurodontism most common
mandibular molars and premolars
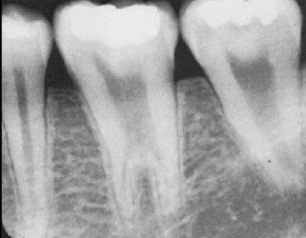
dx
taurodontism
where is dilaceration is most common
3rd molars
what problems can present w dilaceration
if endo or ext is needed
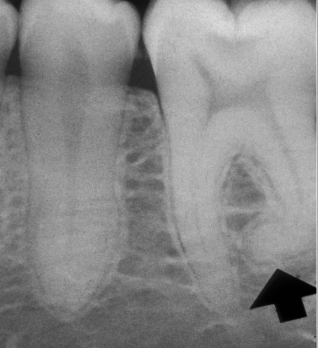
dx
dilaceration
what can hypercementosis be caused by
local factors (localized)
systemic factors (generalized)
what local factors can cause hypercementosis
abnormal occlusal trauma
adjacent inflammation
unopposed teeth (super eruption)
repair of vital root fx
what are some systemic factors that can cause generalized hypercementosis
paget disease of bone
Gardener syndrome
what teeth are most affected by hypercementosis
mandibular molars, then 2nd premolars
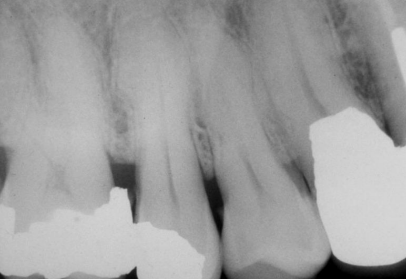
dx- only #4
localized hypercementosis
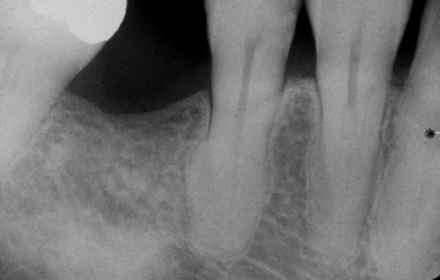
dx- #27, 28, 29
generalized hypercementosis
what is a supernumerary root
inc in number of roots in either primary or secondary teeth
what teeth are most common in supernumerary roots
mandibular 3rd molars > cuspids and bicuspids
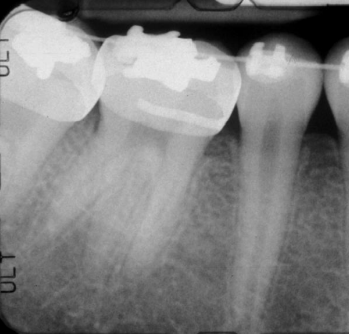
dx
supernumerary root of #30
mode of inheritance of amelogenesis imperfecta
AD, AR, X-linked
what is amelogenesis imperfecta
affects the enamel making it soft and thin, easily damaged, and susceptible to decay and will leave dentin exposed; can show has yellow-brown to white pitted lesions and open bite/loss of contacts
what are the types of amelogenesis imperfecta
hypoplastic (pitted)
hypomaturation/hypocalcification (snow capped)
amelogenesis imperfecta w taurodontism
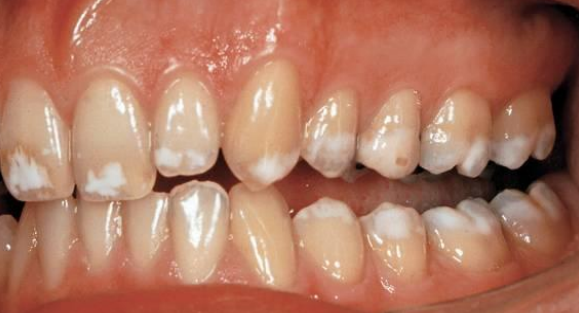
dx
hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta- snow capped
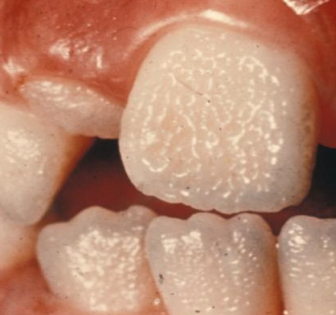
dx
hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta- pitted pattern
what are the two types of enamel dysplasia
hypoplasia and hypomineralization
is hypoplasia a quantitative or qualitative defect
quantitative defect
is hypomineralization a quantitative or qualitative defect
qualitative defect
what is hypoplasia
thickness deficit in the quantity of minerals
what is hypomineralization
mineral deficit
what other two conditions branch off hypomineralization
hypomaturation and hypocalcification
what is hypomaturation
amelogenin-rich
what is hypocalcification
amelogenin-poor
what condition branches off of hypocalcification
molar hypomin
what is molar hypomin
albumin rich
amelogenin poor
acquired defect
what are the three shields classifications of dentinogenesis imperfecta
DGI I
DGI II
DGI III
what is the witkop classification for DGI I
dentinogenesis imperfecta
what is the witkop classification for DGI II
hereditary opalescent teeth
what is the witkop classification for DGI III
brandywine teeth
DGI I clinical presentation
osteogenesis imperfecta (for boards)
opalescent teeth
bone fractures
DGI II clinical presentation
isolated opalescent teeth
MOST COMMON