ANSC 230 Exam 3 Practice MC
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Which of the following is NOT a function of the skeletal system?
a. Support
b. Storage of minerals and lipids
c. regulation of body temperature
d. blood cell production
regulation of body temperature
Yellow bone marrow primarily functions in:
a. blood cell production
b. lipid storage for energy reserves
c. calcium regulation
d. formation of synovial fluid
lipid storage for energy reserves
Which skeletal function allows bones to act as levers for movement?
a. protection
b. support
c. leverage
d. mineral storage
leverage
A ligament connects:
a. muscle to bone
b. bone to bone
c. tendon to cartilage
d. bone to muscle
bone to bone
Which connective tissue covers the ends of bones and joints to reduce friction?
a. ligament
b. tendon
c. articular cartilage
d. periosteum
articular cartilage
The structural frame made of bones and joints is called the:
a. skeleton
b. periosteum
c. endosteum
d. trabeculae
skeleton
Tendons connect:
a. bone to bone
b. muscle to bone
c. cartilage to cartilage
d. joint to joint
muscle to bone
The femur is classified as a:
a. flat bone
b. irregular bone
c. long bone
d. sesamoid bone
long bone
The patella is an example of a:
a. short bone
b. flat bone
c. irregular bone
d. sesamoid bone
sesamoid bone
Vertebrae are classified as:
a. long bones
b. flat bones
c. irregular bones
d. sesamoid bones
irregular bones
Which is part of the axial skeleton?
a. femur
b. radius
c. sternum
d. metacarpal
sternum
The neurocranium houses:
a. the digestive tract
b. the brain
c. the lungs
d. the pelvic organs
the brain
Vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs for what type of joint?
a. synovial
b. symphysis (slightly movable)
c. immovable fibrous
d. hinge
symphysis
The annulus fibrosus of an intervertebral disc is composed of:
a. collagen only
b. fibrocartilage
c. hyaline cartilage
d. elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
Ribs that do not attach to the sternum at all are called:
a. true ribs
b. false ribs
c. floating ribs
d. accessory ribs
floating ribs
Which domestic mammal has a clavicle?
a. horse
b. dog
c. cat
d. cow
cat
The os coxae is formed by the fusion of which bones?
a. Ilium, ischium, and sacrum
b. ilium, ischium, and pubic
c. sacrum, pubis, and coccyx
d. femur, tibia, and fibula
ilium, ischium, and pubis
In horses, the main metacarpal/metatarsal bone is called the:
a. splint bone
b. cannon bone
c. pastern bone
d. coffin bone
cannon bone
The acetabulum is found in the:
a. scapula
b. pelvis
c. femur
d. tibia
pelvis
The human wrist and quadruped forelimb "knee" joint contains which bones?
a. metacarpals
b. carpals
c. tarsals
d. phalanges
carpals
The cylindrical shaft of a long bone is the:
a. epiphysis
b. metaphysis
c. diaphysis
d. periosteium
diaphysis
Compact (cortical) bone makes up approximately what percentage of bone tissue?
a. 20%
b. 50%
c. 70%
d. 80%
80%
Spongy bone contains a scaffold of mineralized tissue called:
a. osteons
b. lamellae
c. trabeculae
d. canaliculi
trabeculae
The periosteum contains:
a. only blood vessels
b. an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer
c. cartilage and synovial fluid
d. osteons exclusively
an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer
The Haversian system consists of concentric lamellae surrounding a:
a. trabecula
b. Haversian canal
c. canaliculus.
d. Lacuna
Haversian canal
Which bone cells are most abundant and maintain bone structure?
a. osteoblasts
b. osteocytes
c. osteoclasts
d. chondrocytes
osteocytes
Osteoblasts are responsible for:
a. bone resorption
b. ossification
c. producing cartilage
d. forming marrow
ossification
Osteoclasts function by:
a. producing osteoid
b. recycling calcium salts
c. dissolving bone matrix
d. creating trabeculae
dissolving bone matrix
Approximately what percentage of bone is mineral by composition?
a. 25%
b. 30%
c. 45%
d. 60%
45%
The vascular inner lining of bone is the:
a. Endosteum
b. Periosteum
c. Epiphysis
d. metaphysis
endosteum
Which process replaces hyaline cartilage with bone during fetal development?
a. intramembranous ossification
b. endochondral ossification
c. appositional growth
d. bone remodeling
endochondral ossification
The epiphyseal growth plate is the site of:
a. Post-natal longitudinal growth
b. bone width increase
c. compact bone remodeling only
d. bone resorption exclusively
post-natal longitudinal growth
Which hormone primarily stimulates IGF-1 production for longitudinal bone growth?
a. Calcitonin
b. Parathyroid hormone
c. growth hormone
d. estrogen
growth hormone
Closure of the growth plate at puberty is mediated largely by:
a. testosterone
b. estrogen
c. parathyroid hormone
d. cortisol
estrogen
In the zone of proliferation, chondrocytes:
a. die in a calcified matrix
b. divide and push the epiphysis away from the diaphysis
c. hypertrophy and enlarge lacunae
d. are replaced by osteoblasts
divide and push the epiphysis away from the diaphysis
Apposition growth refers to:
a. bone lengthening
b. cartilage replacement by bone
c. bone fracture repair
d. bone widening
bone widening
Which cells are quiescent stem cells in the periosteum that differentiate into osteoblasts?
a. osteogenic progenitor cells
b. osteoclasts
c. chondrocytes
d. osteocytes
osteogenic progenitor cells
Which process enlarges the medullary cavity during appositional growth?
a. osteoblast deposition from periosteum
b. osteoclast resorption from endosteum
c. osteocyte entrapment
d. calcitonin activity
osteoclast resorption from endosteum
The first stage of bone fracture repair involves formation of a:
a. spongy bone callus
b. compact bone matrix
c. hematoma
d. osteon
hematoma
During bone repair, the cartilage callus is converted into bone by:
a. intramembranous ossification
b. calcitonin
c. periosteal ossification
d. endochondral ossification
endochondral ossiication
Which vitamin-derived hormone increases intestinal calcium absorption?
a. calcitonin
b. calcitriol
c. parathyroid hormone
d. aldosterone
calcitriol
Which hormone is released when blood calcium is too low?
a. parathyroid hormone
b. calcitonin
c. growth hormone
d. cortisol
parathyroid hormone
Which hormone reduces osteoclast activity to lower blood calcium levels?
a. parathyroid hormone
b. calcitriol
c. calcitonin
d. vitamin D3
calcitonin
Which muscle type is voluntary and striated?
a. skeletal
b. cardiac
c. smooth
d. all of the above
skeletal
Cardiac muscle cells are distinguished by:
a. multinucleation at the periphery
b. intercalated discs
c. spindle-shaped fibers
d. lack of striations
intercalated discs
Smooth muscle is primarily responsible for:
a. voluntary body movement
b. blood vessel constriction
c. shivering thermogenesis
d. postural control
blood vessel constriction
The connective tissue surrounding an entire muscle is the:
a. endomysium
b. perimysium
c. epimysium
d. sarcolemma
epimysium
The contractile organelle of skeletal muscle is the:
a. sarcolemma
b. myofilament
c. sarcoplasmic reticulum
d. myofibril
myofibril
The basic contractile unit of striated muscle is the:
a. sarcomere
b. myofiber
c. fascicle
d. Z-line
sarcomere
Which protein blocks myosin binding sites on actin?
a. troponin
b. tropomyosin
c. titin
d. dystrophin
tropomyosin
Which protein binds calcium during contraction?
a. actin
b. tropomyosin
c. troponin
d. myosin
troponin
The sarcoplasmic reticulum's primary role is to:
a. store glycogen
b. store and release calcium
c. transmit nerve impulses
d. form cross-bridges
store and release calcium
The site where a motor neuron communicates with a muscle fiber is the:
a. sarcomere
b. T-tubule
c. Myofibril
d. Neuromuscular junction
Neuromuscular junction
Which neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction?
a. norepinephrine
b. acetylcholine
c. dopamine
d. serotonin
acetylcholine
What enzyme degrades acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft?
a. acetylcholinesterase
b. monoamine oxidase
c. lactate dehydrogenase
d. create kinase
acetylcholinesterase
According to the sliding filament theory, which band remands the same length during contraction?
a. I-band
b. A-band
c. H-zone
d. Z-line
A-band
Which structure moves closer together during contraction?
a. A-bands
b. M-lines
c. Z-lines
d. H-zones
Z-lines
Cross-bridge detachment requires binding of:
a. Calcium
b. ADP
c. ATP
d. Phosphate
ATP
Hydrolysis of ATP during muscle contraction serves to:
a. Release calcium from SR
b. expose actin binding site
c. detach acetylcholine
d. re-cock the myosin head
re-cock the myosin head
During relaxation, calcium is returned to the SR by:
a. passive diffusion
b. sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase pump
c. voltage-gated Na+ channels
d. Troponin-tropomyosin
Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase pump
A muscle twitch is defined as:
a. continuous contraction of a whole muscle
b. a contraction from a single action potential in one motor unit
c. tetanus caused by bacterial toxins
d. multiple motor units firing together
a contraction from a single action potential in one motor unit
The latent phase of a muscle twitch corresponds to:
a. immediate contraction after stimulation
b. passive relaxation fibers
c. ATP depletion
d. Time for Ca2+ to diffuse from SR and bind to troponin
Time for Ca2+ to diffuse from SR and bind to troponin
During the contraction phase of a twitch:
a. Cross-bridge cycling actively generates force
b. troponin releases Ca2+
c. the muscle lengthens passively
d. no ATP is required
cross-bridge cycling actively generates force
The relaxation phase occurs when:
a. ATP stores are depleted
b. the muscle continues force generation
c. Ca2+ returns to the SR and muscle returns to resting length
d. troponin is permanently bound to calcium
Ca2+ returns to the SR and muscle returns to resting length
Wave summation occurs when:
a. a second action potential arrives before relaxation of the first twitch
b. multiple motor units fire at the same time
c. Ca2+ is completely removed from cytosol
d. ATP is exhausted
A second action potential arrives before relaxation of the first twitch
Tetanus (not the disease) refers to:
a. sudden random spasms
b. fusion of individual twitches into a sustained contraction
c. a bacterial infection of the muscles
d. loss of neuromuscular junction function
fusion of individual twitches into a sustained contraction
In tetanus, force reaches:
a. zero tension
b. only half the normal force
c. below twitch levels
d. a plateau at maximal contraction
a plateau at maximal contraction
Red skeletal muscle fibers are specialized for:
a. endurance
b. power
c. rapid fatigue
d. low oxygen usage
endurance
White skeletal muscle fibers are specialized for:
a. endurance
b. strength and power
c. fatigue resistance
d. slow contraction
strength and power
Red muscle has high levels of:
a. glycolytic enzymes
b. fast twitch isoforms
c. myoglobin and mitochondria
d. fatigability
myoglobin and mitochondria
White muscle fibers have:
a. few mitochondria, high glycolytic activity
b. high oxidative enzyme levels
c. abundant myoglobin
d. slow contraction
few mitochondria, high glycolytic activity
Which factor primarily determines red vs. white muscle color?
a. collagen
b. capillary density
c. myoglobin concentration
d. ATP concentration
myoglobin concentration
The number of muscle fibers in an individual is:
a. fixed at birth
b. increased by training
c. doubled after puberty
d. controlled only by diet
fixed at birth
Postnatal skeletal muscle growth occurs by:
a. hyperplasia (increase in fiber number)
b. hypertrophy (increase in fiber size0
c. addition of new stem cells
d. none of the above
hypertrophy (increase in fiber size)
Muscle wasting from disuse or disease is due to:
a. hyperplasia
b. atrophy of existing fibers
c. loss of muscle cell nuclei
d. formation of new small fibers
atrophy of existing fibers
Which twitch phase corresponds to Ca2+ binding troponin?
a. latent
b. relaxation
c. recovery
d. contraction
contraction
A marathon runner would rely more heavily on:
a. red fibers
b. white fibers
c. equal mix
d. neither
red fibers
A sprinter would rely primarily on:
a. Red fibers
b. white fibers
c. slow twitch only
d. none of the above
white fibers
Increased mitochondrial density is most associated with:
a. White fibers
b. atrophied muscle
c. hyperplasia
d. red fibers
red fibers
A key reason white fibers fatigue quickly is:
a. lack of ATP production
b. reliance on glycolytic metabolism
c. poor neuromuscular junctions
d. weak cross-bridge
reliance on glycolytic metabolism
Disuse atrophy occurs because:
a. existing fibers shrink
b. muscle cells die
c. myoglobin is lost
d. fiber number decreases
existing fibers shrink
Tetanus provides greater force than a twitch because:
a. Ca2+ accumulates, maintaining cross-bridge cycling
b. ATP is more abundant
c. fibers become longer
d. myosin heads detach more rapidly
Ca2+ accumulates, maintaining cross-bridge cycling
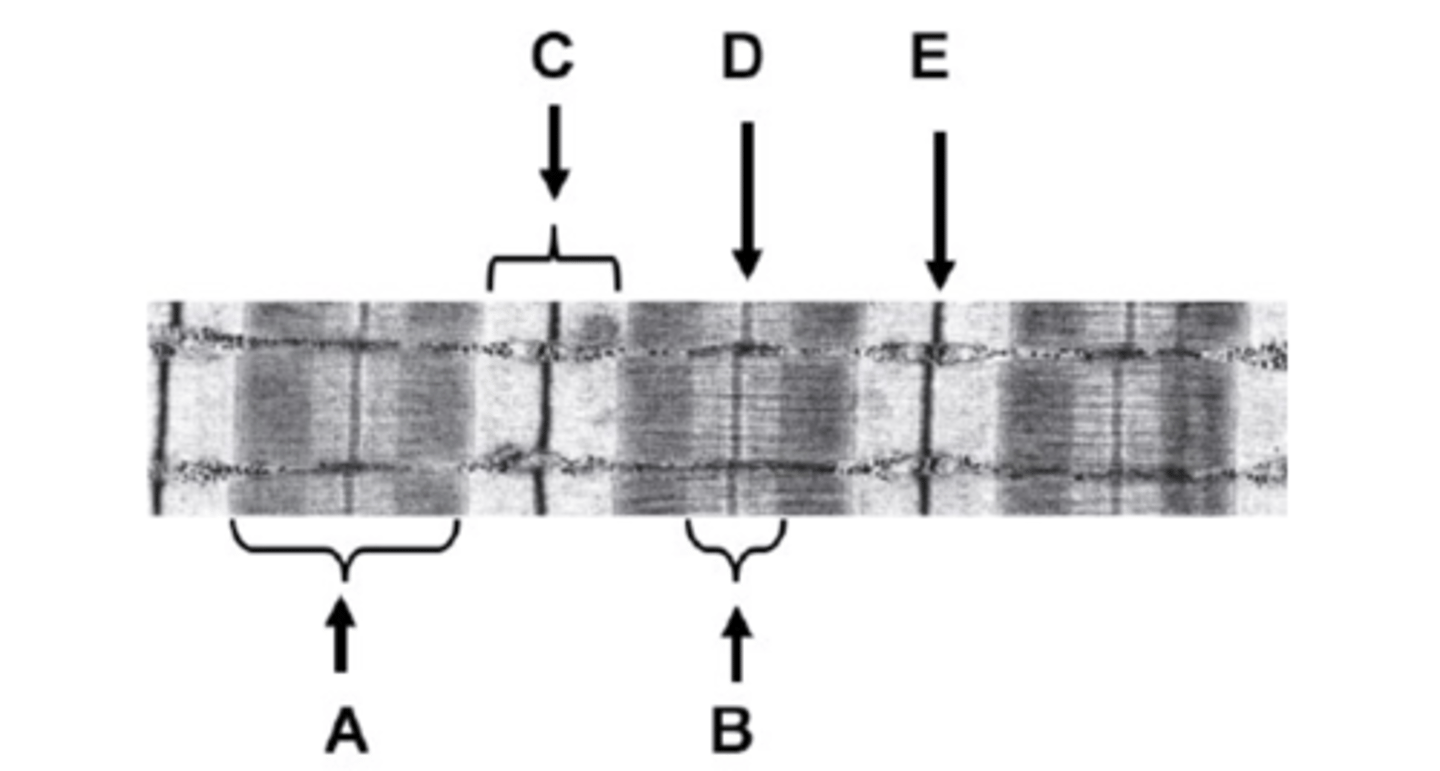
What is A on the diagram?
A-band
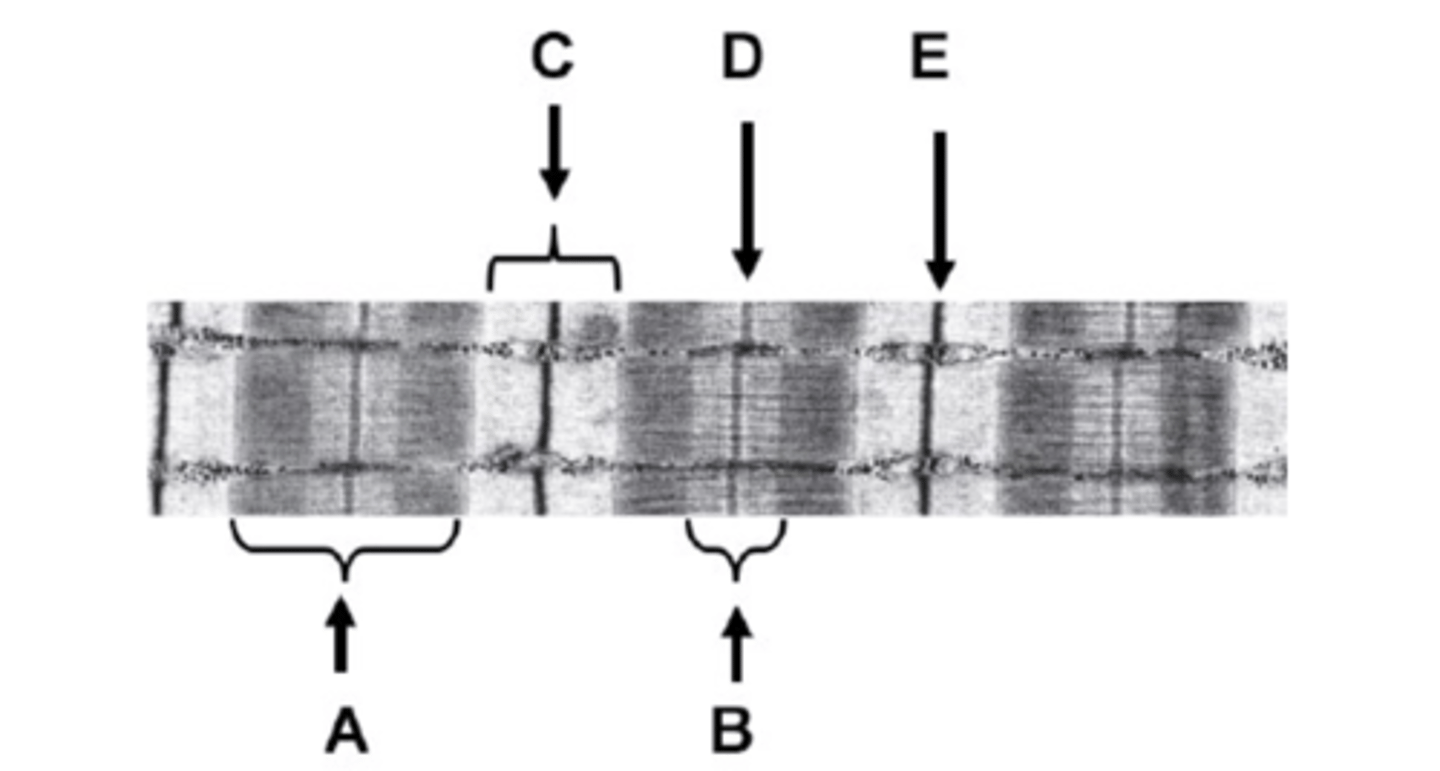
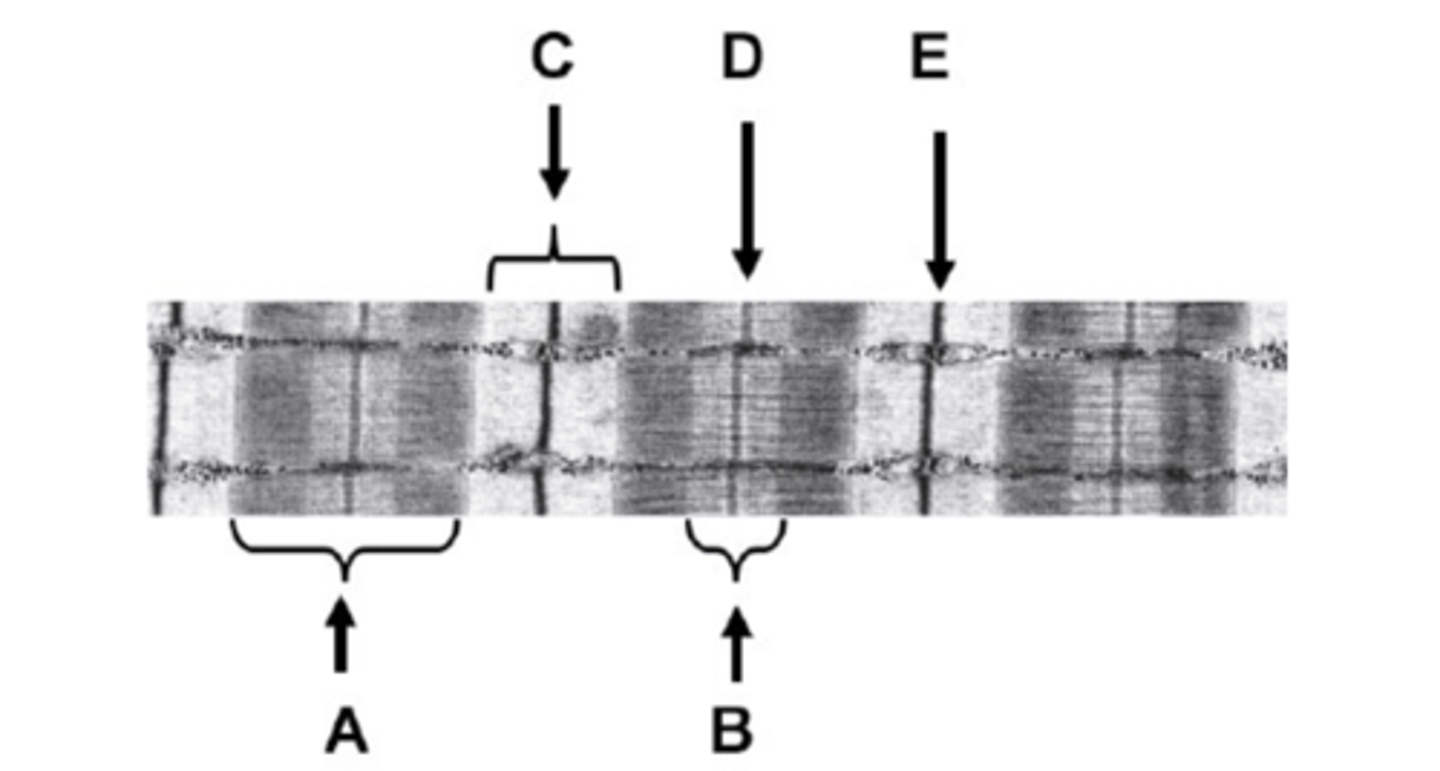
What is B on the diagram?
H-zone
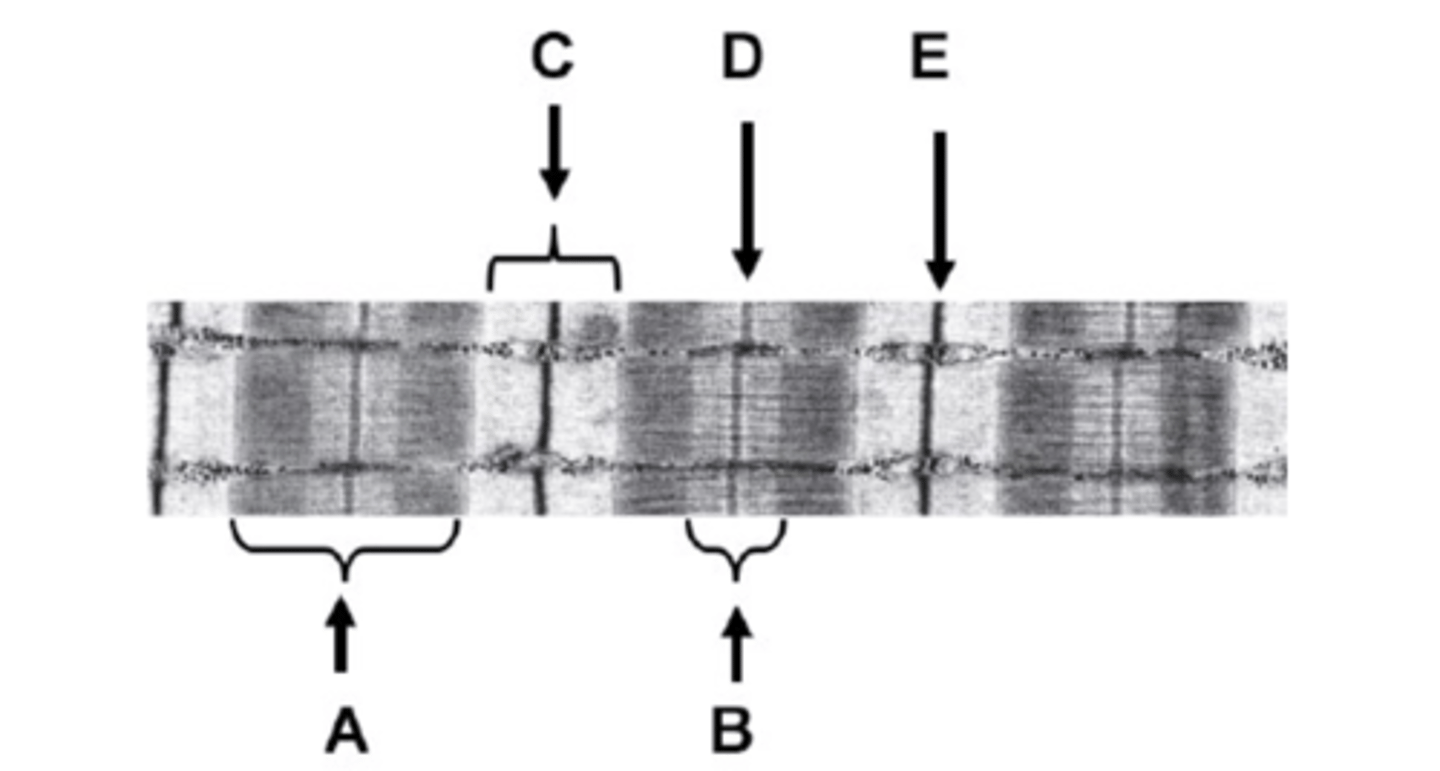
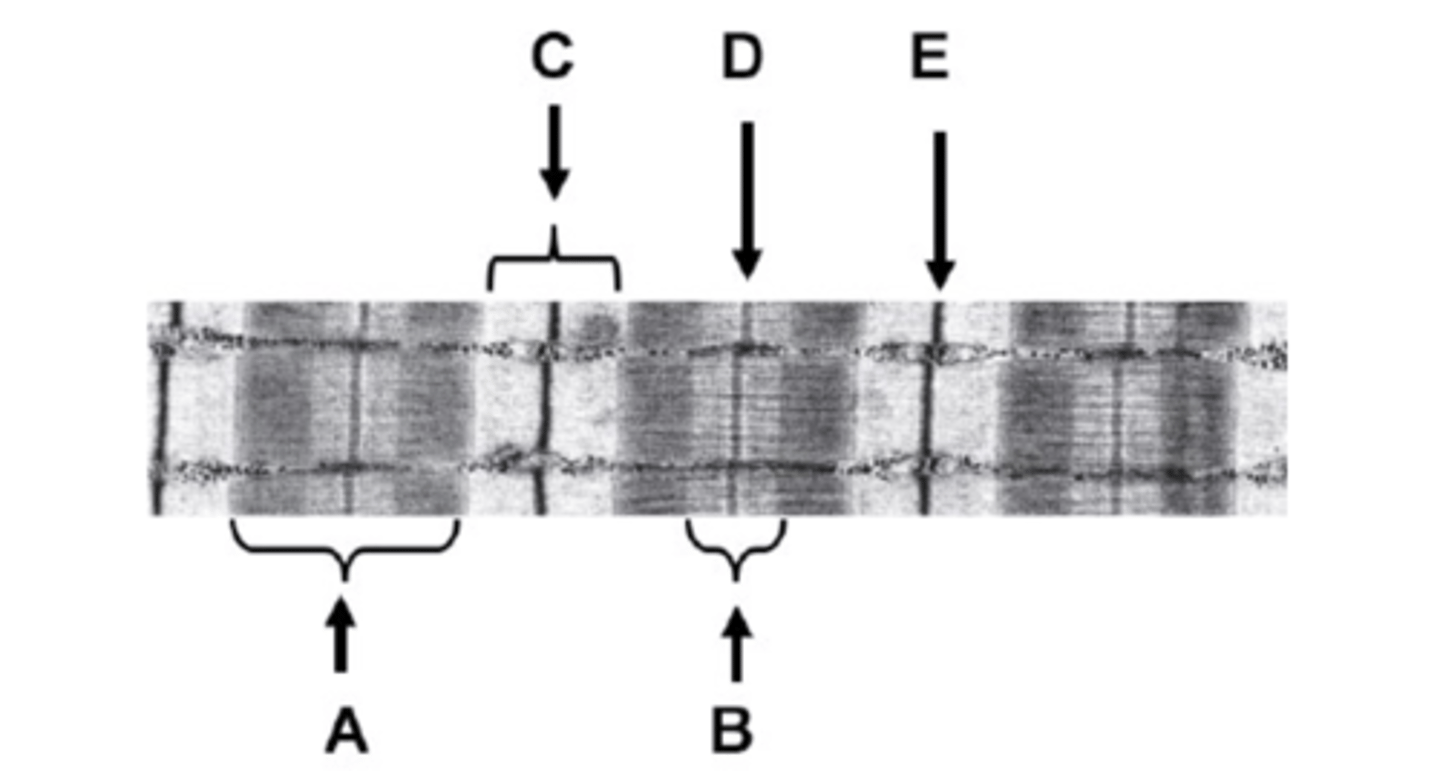
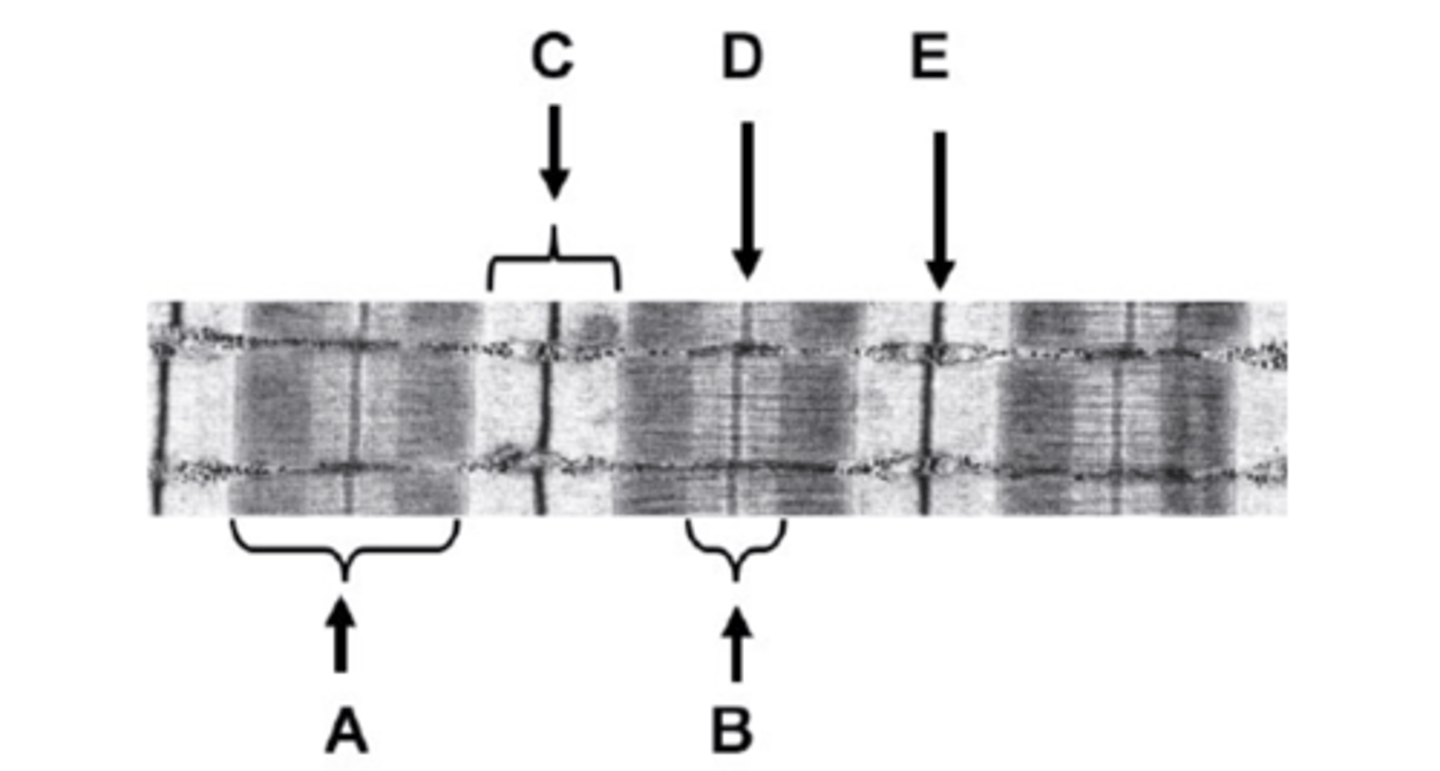
What is C on the diagram?
I-band
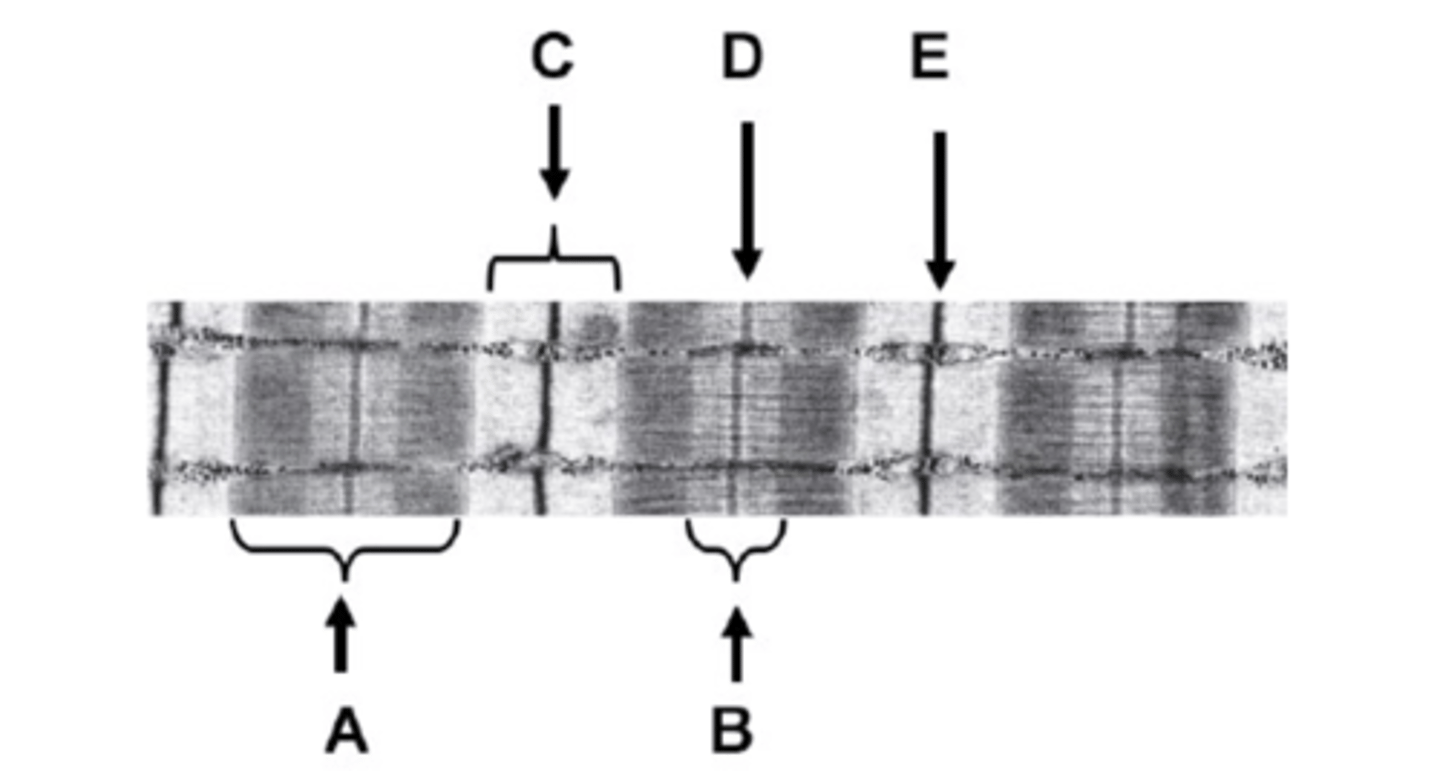
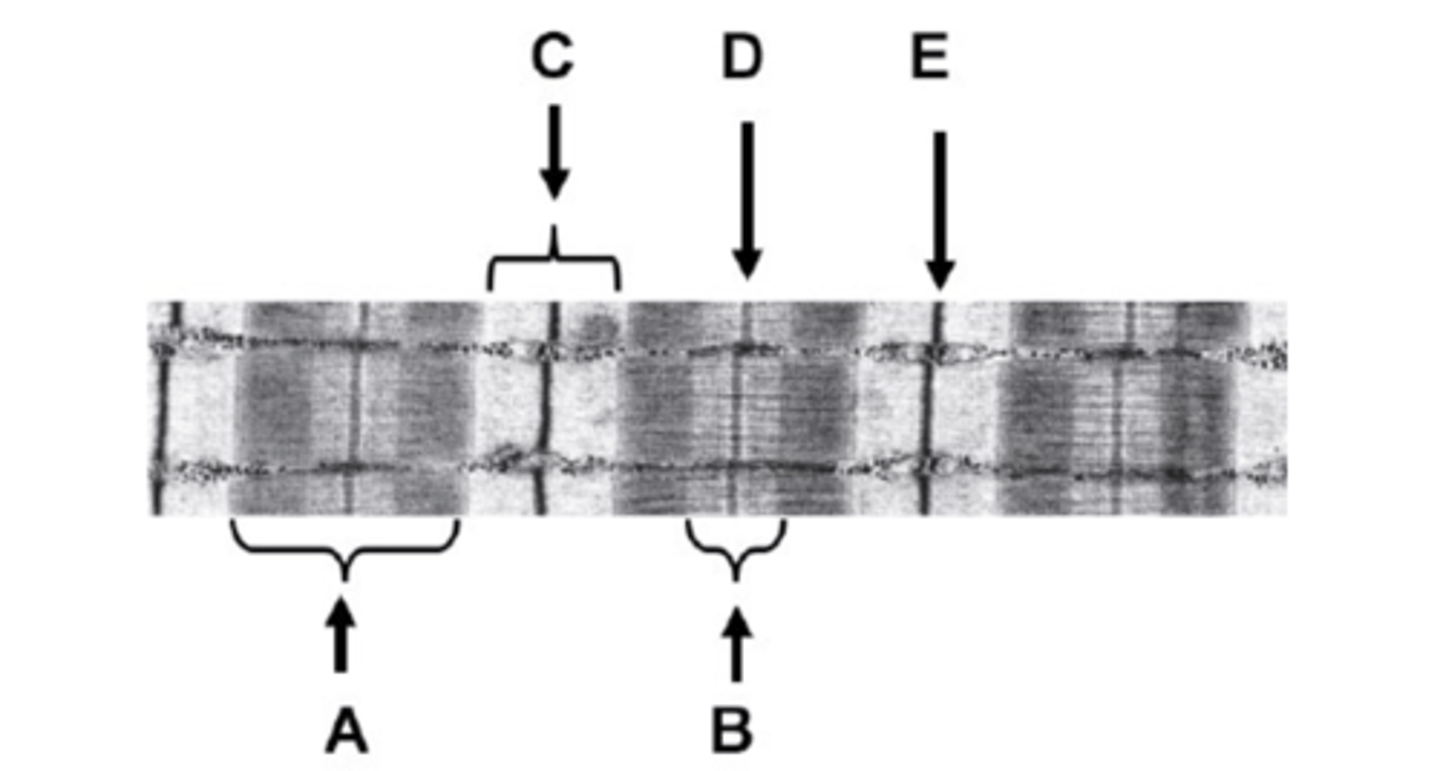
What is D on the diagram?
M-line
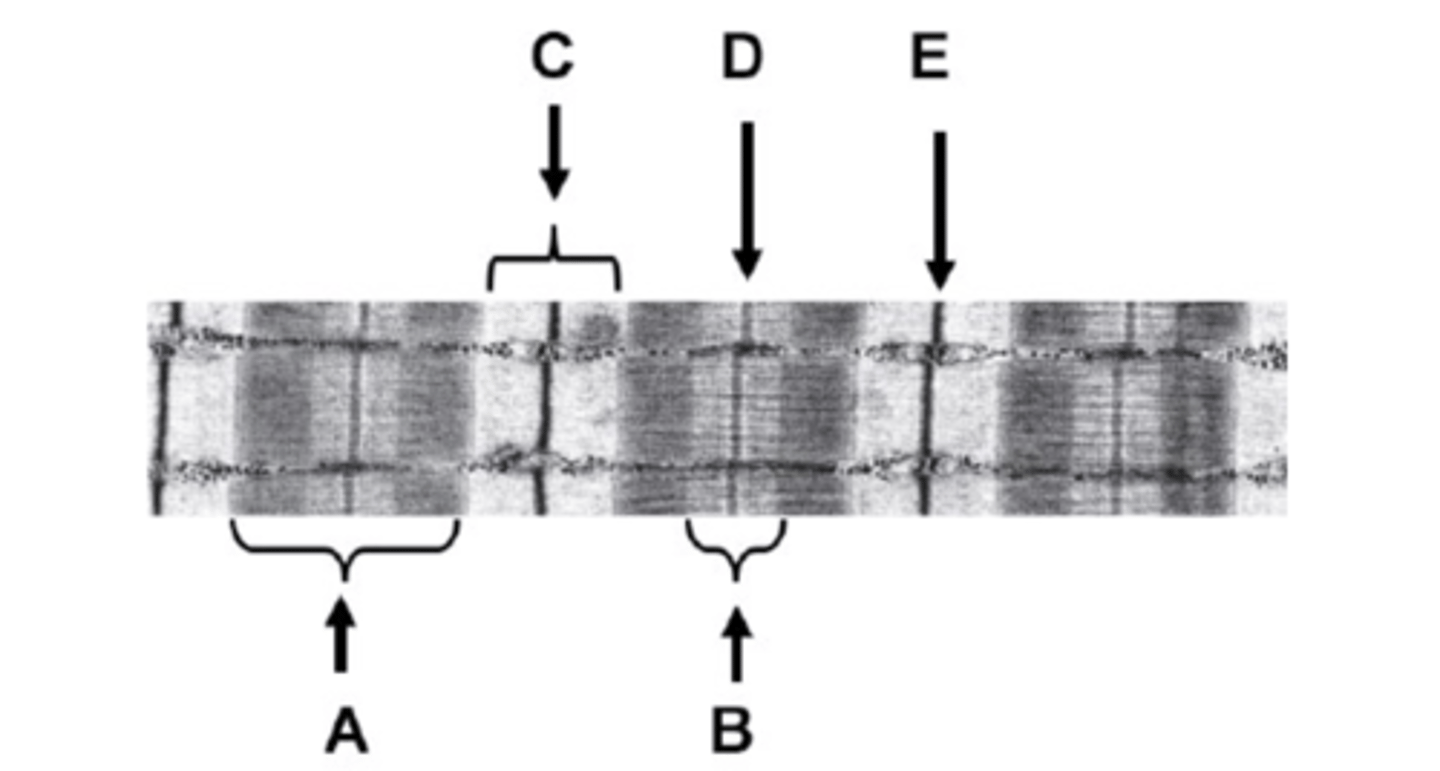
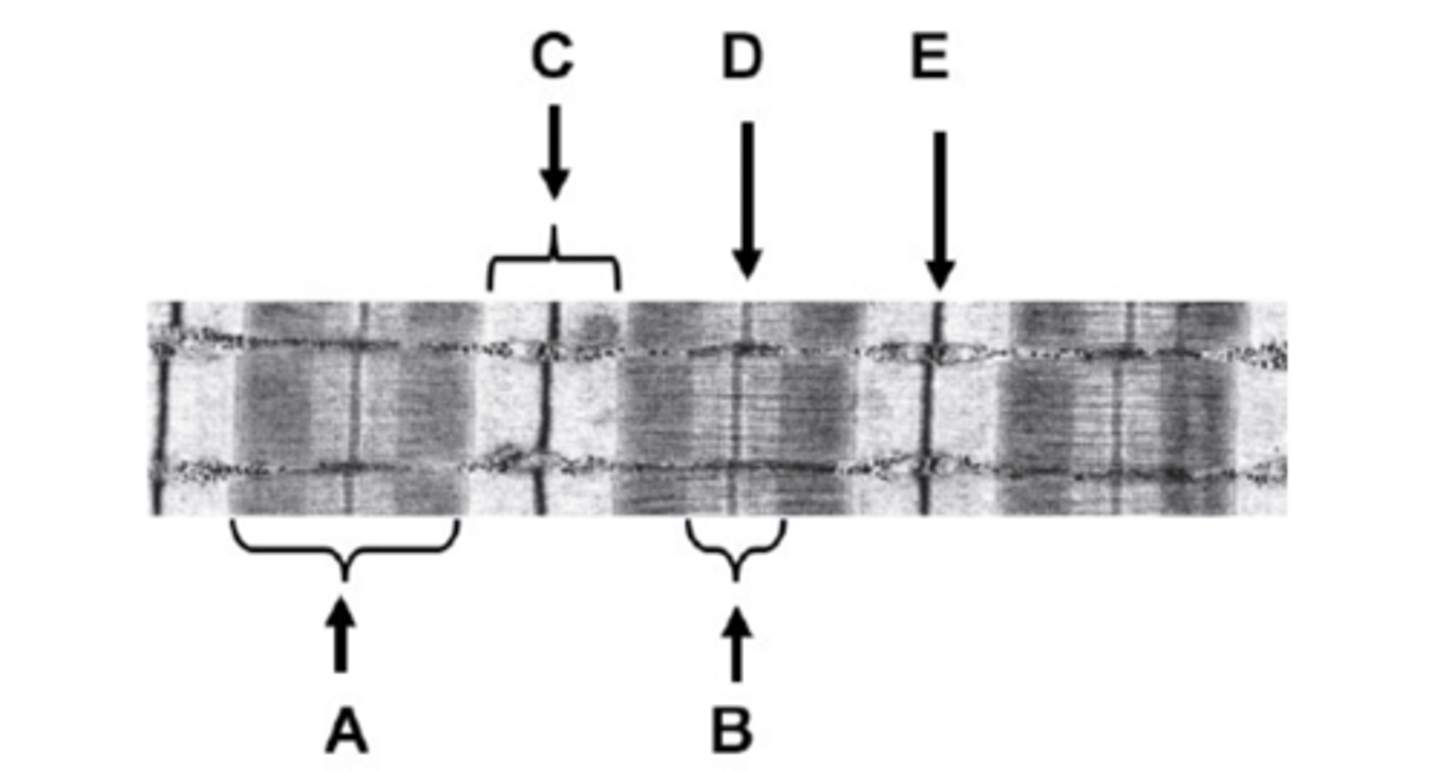
What is E on the diagram?
Z-line