APHG Unit 1 Vocab
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Absolute Location
Position on Earth's surface using the coordinate system of longitude (that runs from North to South Pole) and latitude (that runs parallel to the equator).
Cartography
The theory and practice of making visual representations of Earth's surface in the form of maps.
Climate
The composite or generally prevailing weather conditions of a region, as temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, averaged over a series of years.
Concentration (Of Population)
The concentration of population refers to the spatial pattern or arrangement of people within a particular areas.
Conservation
The sustainable use and management of Earth's natural resources to meet human needs such as food, medicine, and recreation is conservation.
Contagious Diffusion
Involves a form of expansion in which people near the point of origin become adopters of a cultural fad.
Cultural Landscape
The visible reflection of a society, including their cultural beliefs and practices, on the physical environment.
Culture
A total way of life held in common by a group of people, including learned features such as language, ideology, behavior, technology, and government.
Density (Of Population)
Refers to the number of people who live in a defined land area (usually square miles or square kilometers).
Diffusion
The spread of an idea or characteristic over time.
Distance Decay
The theory that states that as the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases.
Enclave
A state that is completely surrounded by another state.
Exclave
A region of a country that is completely separated from the main body of that country, usually by the borders of another country.
Expansion Diffusion
When innovations spread to new places while staying strong in their original locations.
Formal/Uniform Region
Homogenous areas where everyone in that region shares common attributes or traits like language, climate, or political system.
Functional/Nodal Region
Defined by a social or economic function that occurs between a node or focal point and the surrounding areas.
Geographic Information Science (GIScience)
The basic research field that seeks to redefine geographic concepts and their use in the context of geographic information systems.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
A computer system that analyses and displays geographically referenced information.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A space-based radio-navigation system consisting of a constellation of satellites broadcasting navigation signals and a network of ground stations and satellite control stations used for monitoring and control.
Globalization
Refers to the homogenizing impact on local culture and economics caused by increased interaction between geographically distinct regions.
Hearth
The region from which innovative ideas originate.
Hierarchical Diffusion
The spreading of culture via a hierarchy "vertically" either from the top to the bottom or vice versa.
Infrastructure
The basic physical and organizational structures needed for a society to function.
Interdependence
Collective actions by people within a territory to gain political freedom and sovereignty, typically from a larger political entity.
Local Scale Analysis
Geographers describe the distinctive site or physical character of each place on earth.
Map
A symbolic representation of selected characteristics of a place, usually drawn on a flat surface.
Map Projection
The representation on a plane surface of any part of the surface of the Earth or a celestial sphere.
Metropolitan Area
Includes an urbanized area with a high population of at least 50,000 with high density adjacent countries where the majority of inhabitants work in nonagricultural jobs.
National Scale Analysis
Examining geographic phenomena and issues at the level of an entire nation or country.
Pattern
The arrangement of objects on Earth's surface in relation to other objects.
Preservation
The maintenance of resources in their present condition, with as little human impact as possible.
Region
Any area differentiated from surrounding areas by at least one characteristc.
Regional Scale Analysis
Involves analysis geographic data within distinct areas characterized by certain unifying features which as climate, culture, language, etc., which could be part of one country or span multiple countries.
Relative Location
A description of how a place is related to other places.
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of an idea or characteristic over time. When people move, or relocate, they spread ideas along with them.
Remote Sensing
The process of taking pictures of the Earth's surface from satellites to provide a greater understanding of the Earth's geography over large distances.
Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
A type of expansion diffusion in which ideas spread from area to area by ways of small towns, temporarily bypassing urban areas.
Scale
The ratio between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole.
Scale Of Analysis
Includes global, regional, national, and local. Patterns and processes at different scales reveal variations in, and different interpretations of data.
Sense Of Place
A way to characterize the relationship between people and their spatial settings.
Site
The physical characteristics of an absolute location.
Situation
Where something is in relation to other locations/areas.
Spatial Patterns
An analytical tool used to measure the distance between two or more physical locations/items.
Stimulus Diffusion
The alteration of a characteristic as it spreads from one location to another; the alteration often occurs to better fit the new culture.
Sustainability
The use of Earth's resources in ways that ensure their availability in the future.
Time Distance Decay
The effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions; the interaction between two locations declines as the distance between them increases.
Time Space Compression
The reduction in the time it takes for something to diffuse to a distant location because of improved communication, technology, and transportation.
Toponym
The name given to a specific location on Earth's surface.
Transnational Corporation
A company that conducts research, operates factories and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located.
Vernacular/Perceptual Region
An area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity.
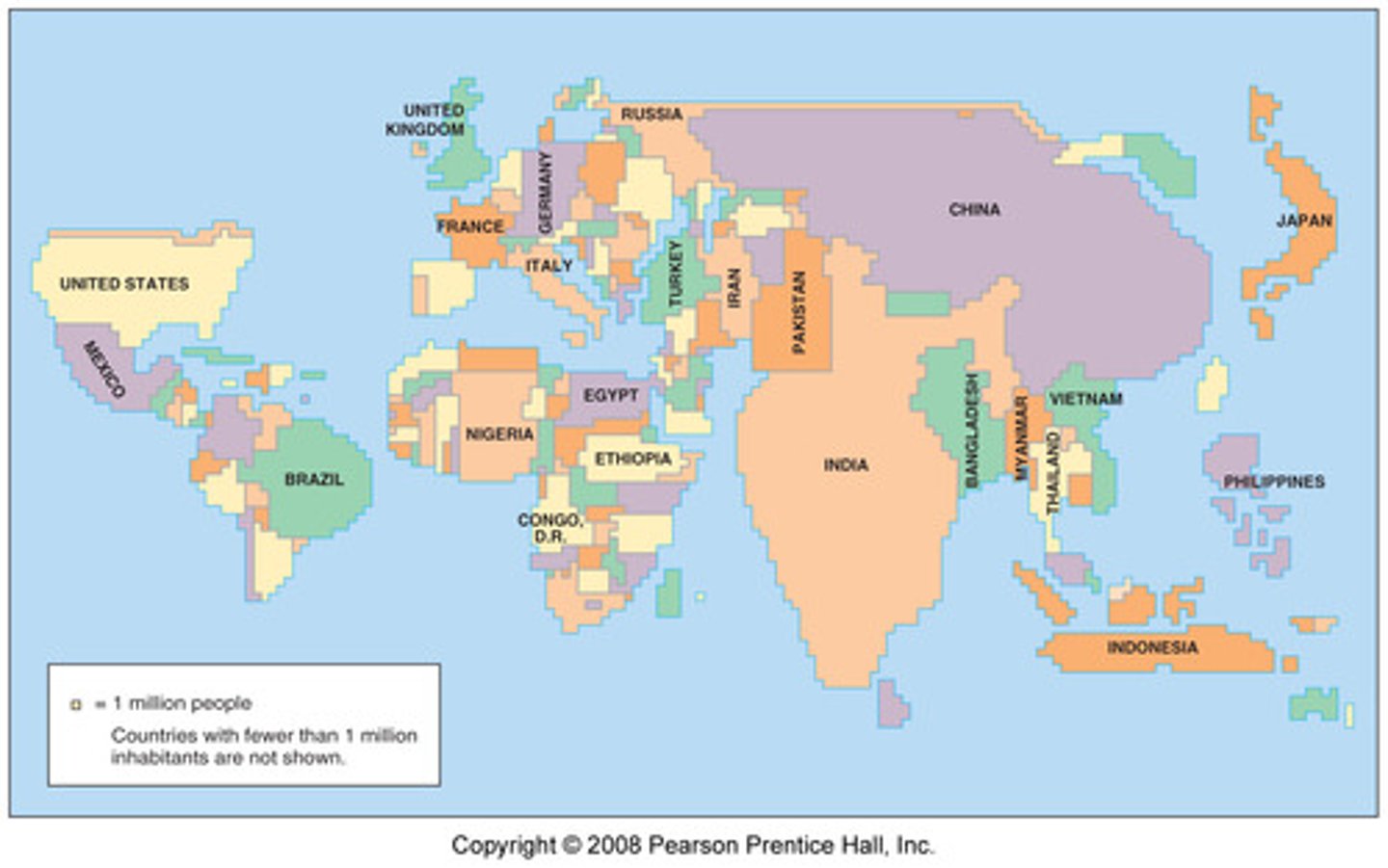
Cartogram
Size of a country is determined by its total population.
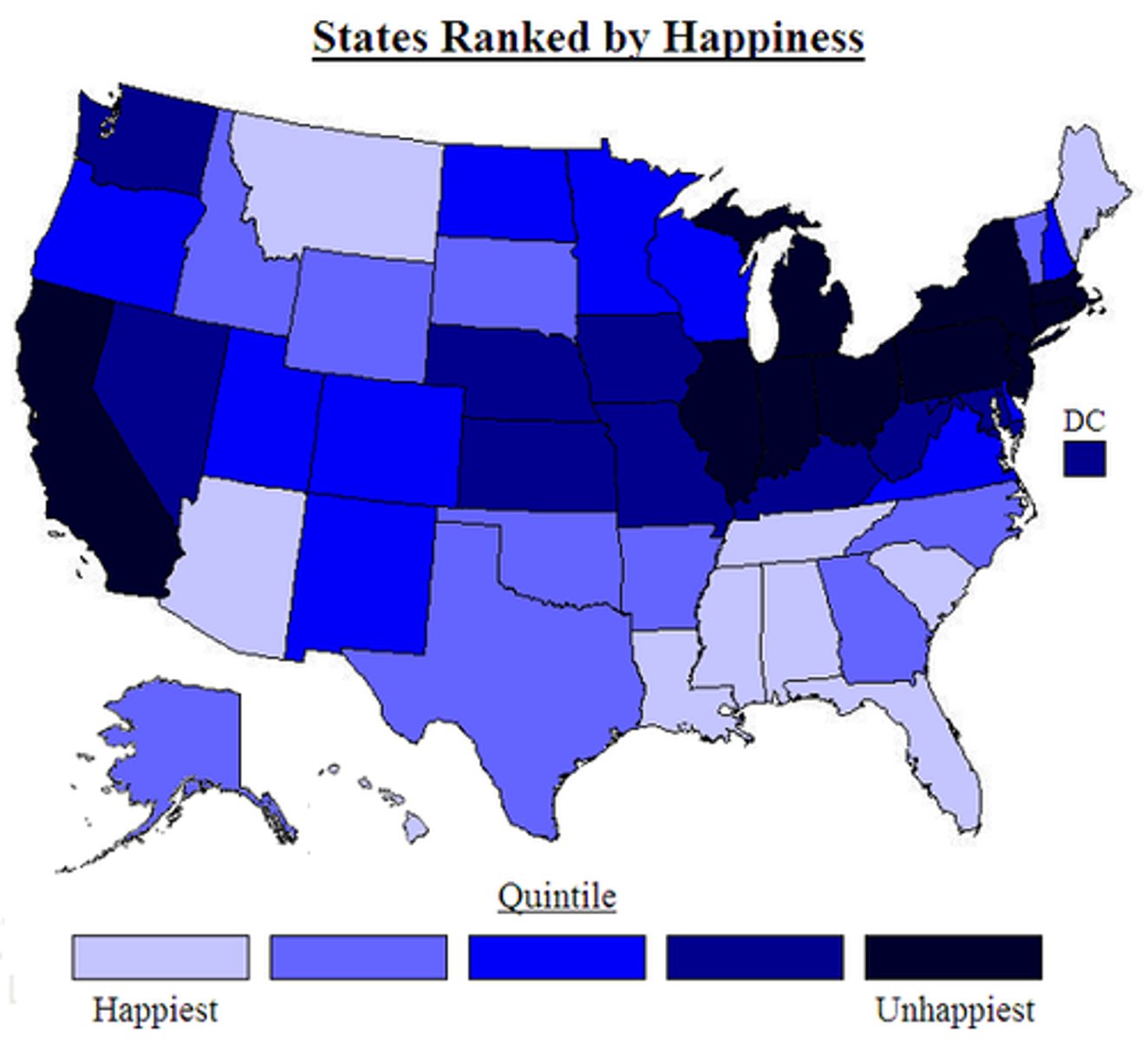
Choropleth Map
Gradient of color helps determine the intensity of whatever is being measured/observed.
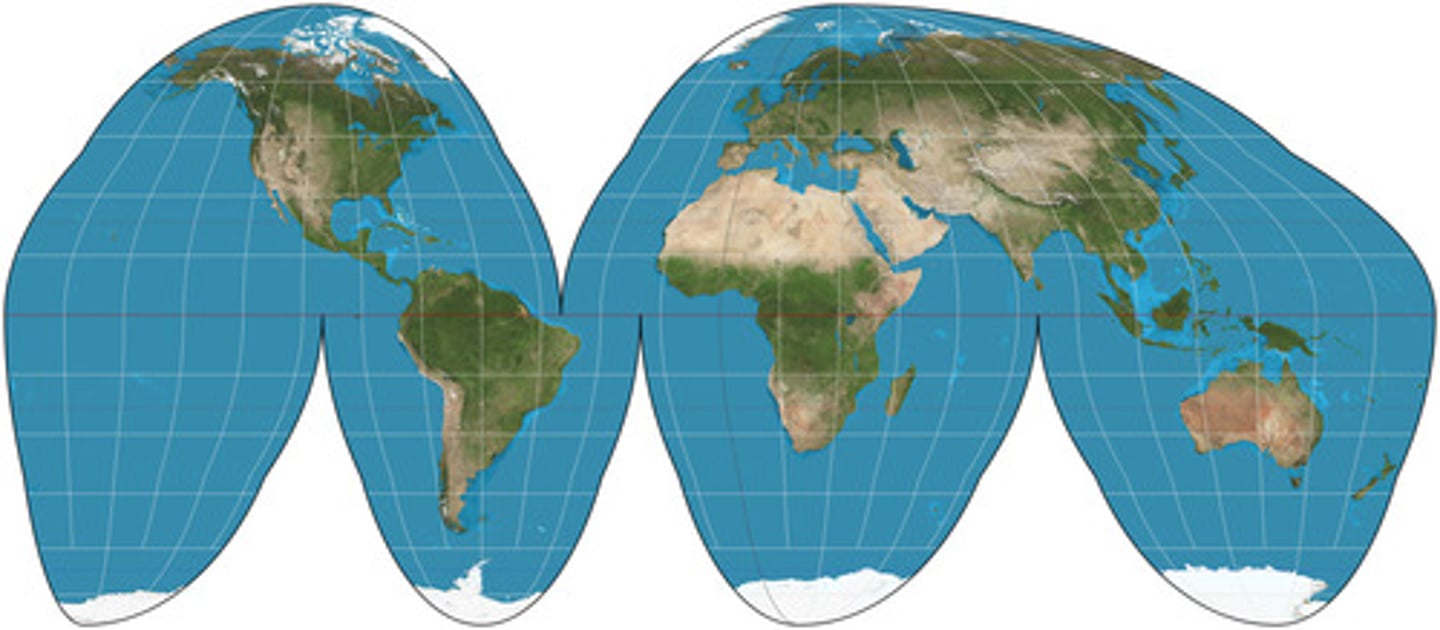
Goode-Homolosine Projection
Equal area map projection useful for showing spatial phenomenon across continents/around the world.
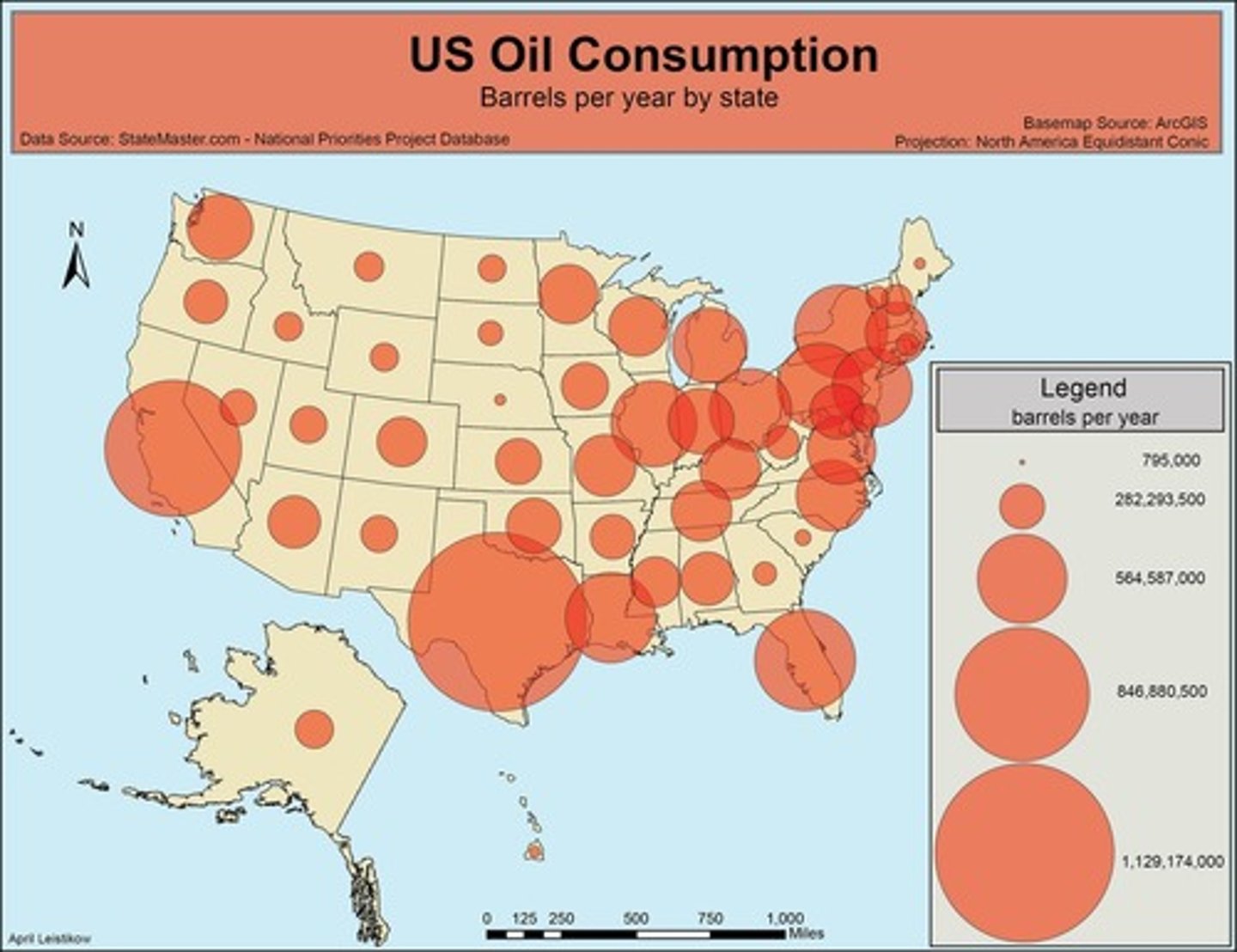
Graduated Circle Map
Circles that vary in size depending on the increased/decreased prevalence of a characteristic.
Dot Density/Distribution Maps
Dots used to show how close together/far apart items being measured are placed.
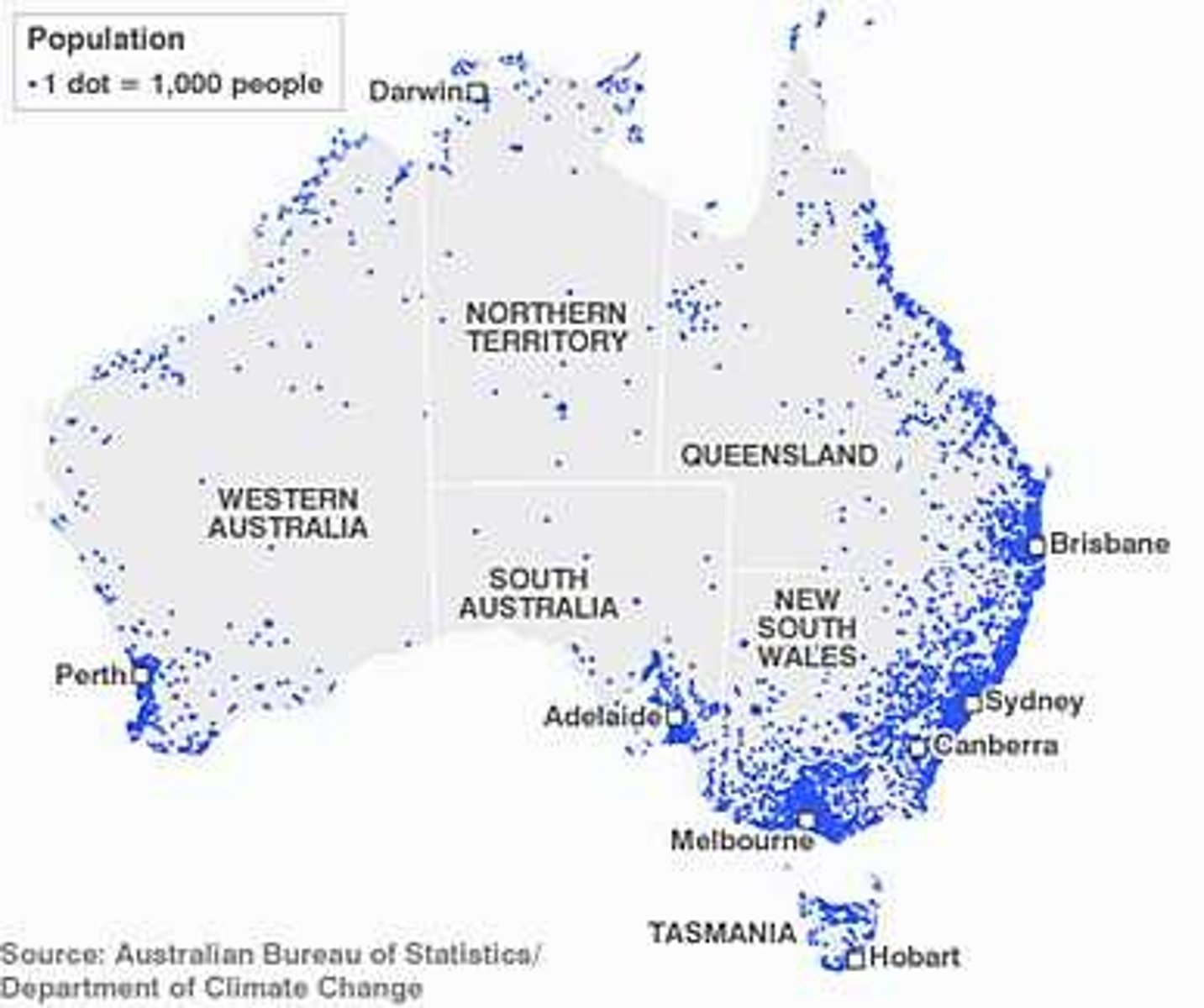
Large Scale Map
A map that covers a small geographic space in large amounts of detail.
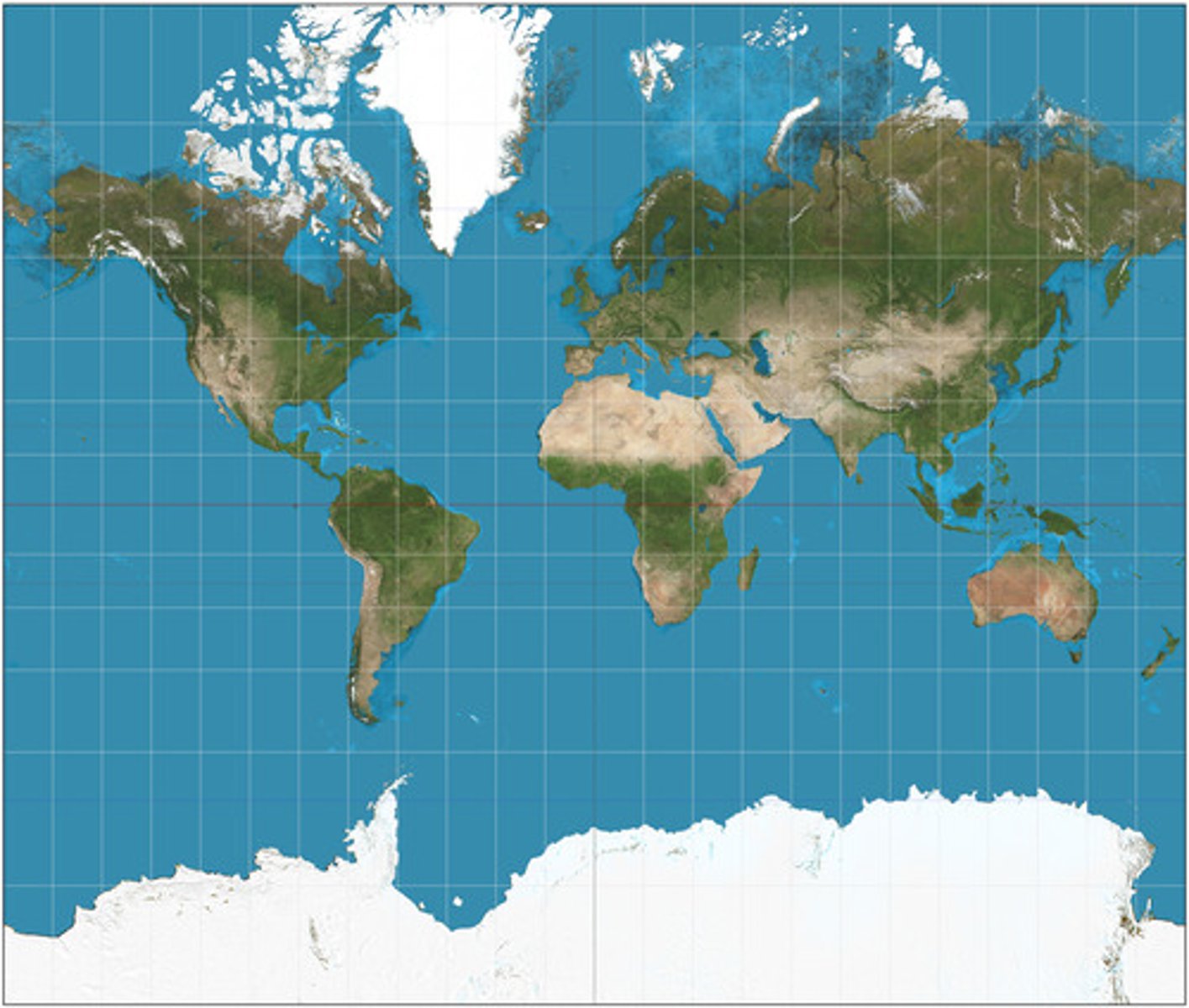
Mercator Projection
90 degree angles where all latitude and longitude lines meet.
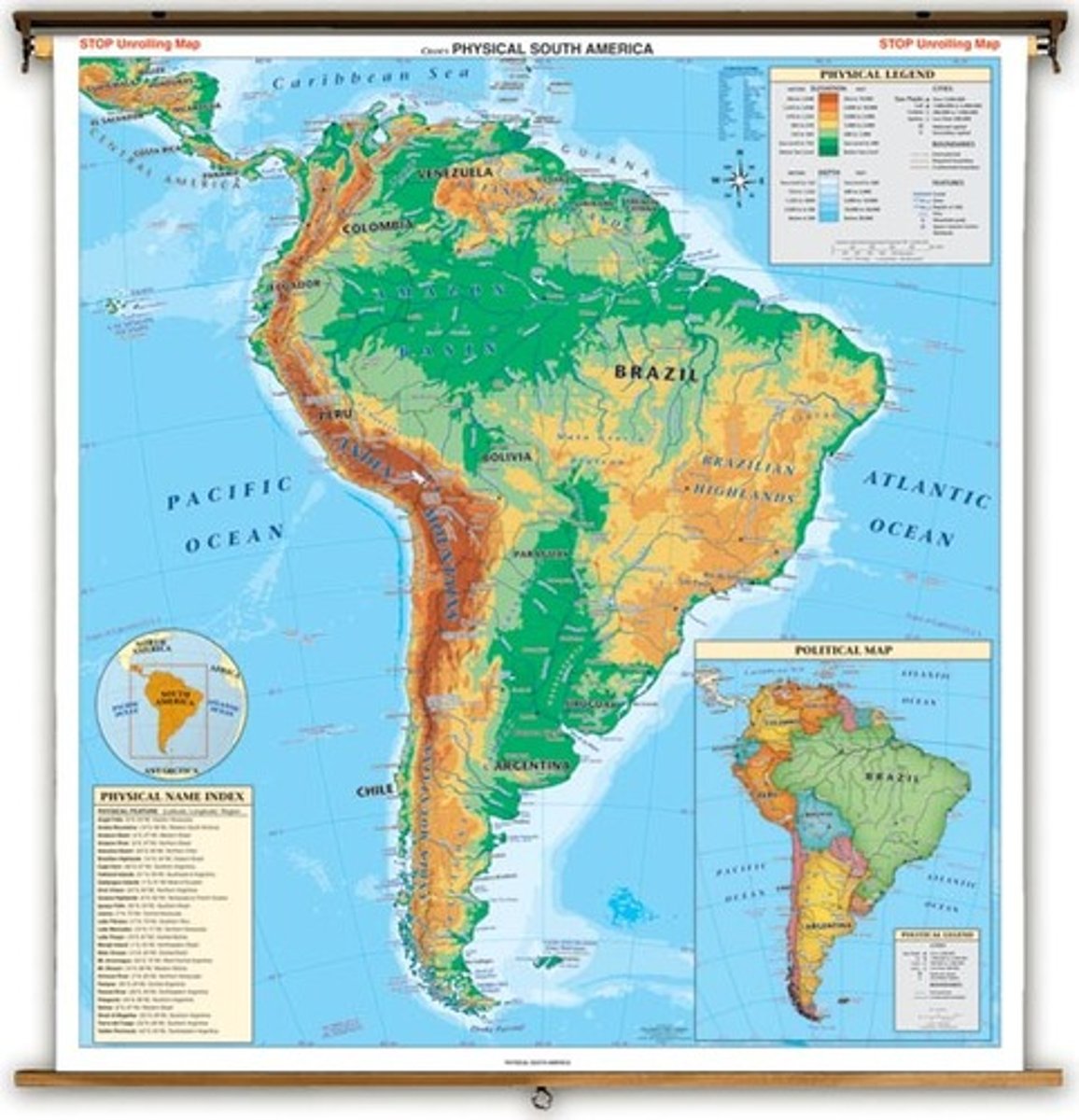
Physical Map
Highlights the physical features of specified pieces of geography.
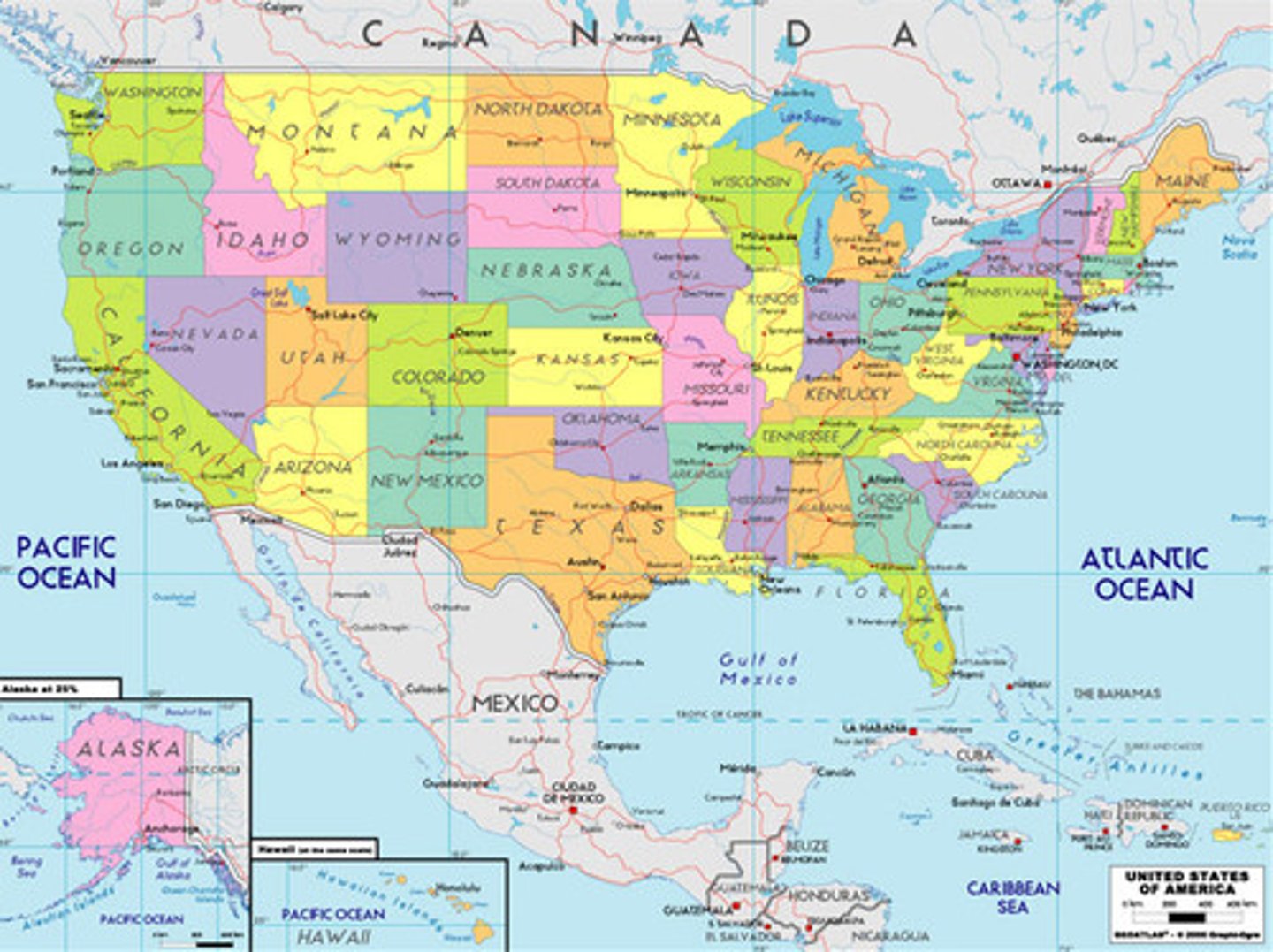
Political Map
Shows the borders between different political entities.
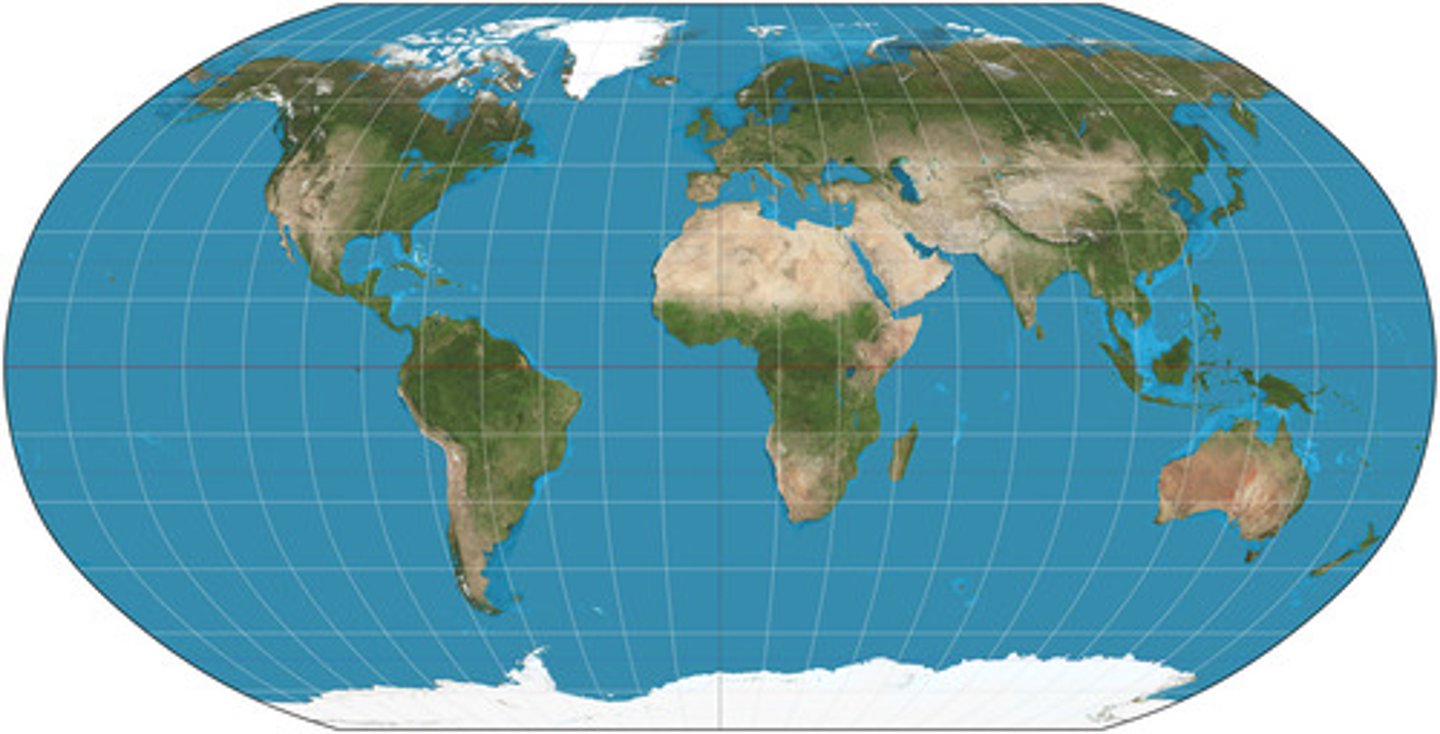
Robinson Projection
Known as a "compromise projection" because it slightly distorts size, shape, area, and direction to give a more "balanced" projection of the world.
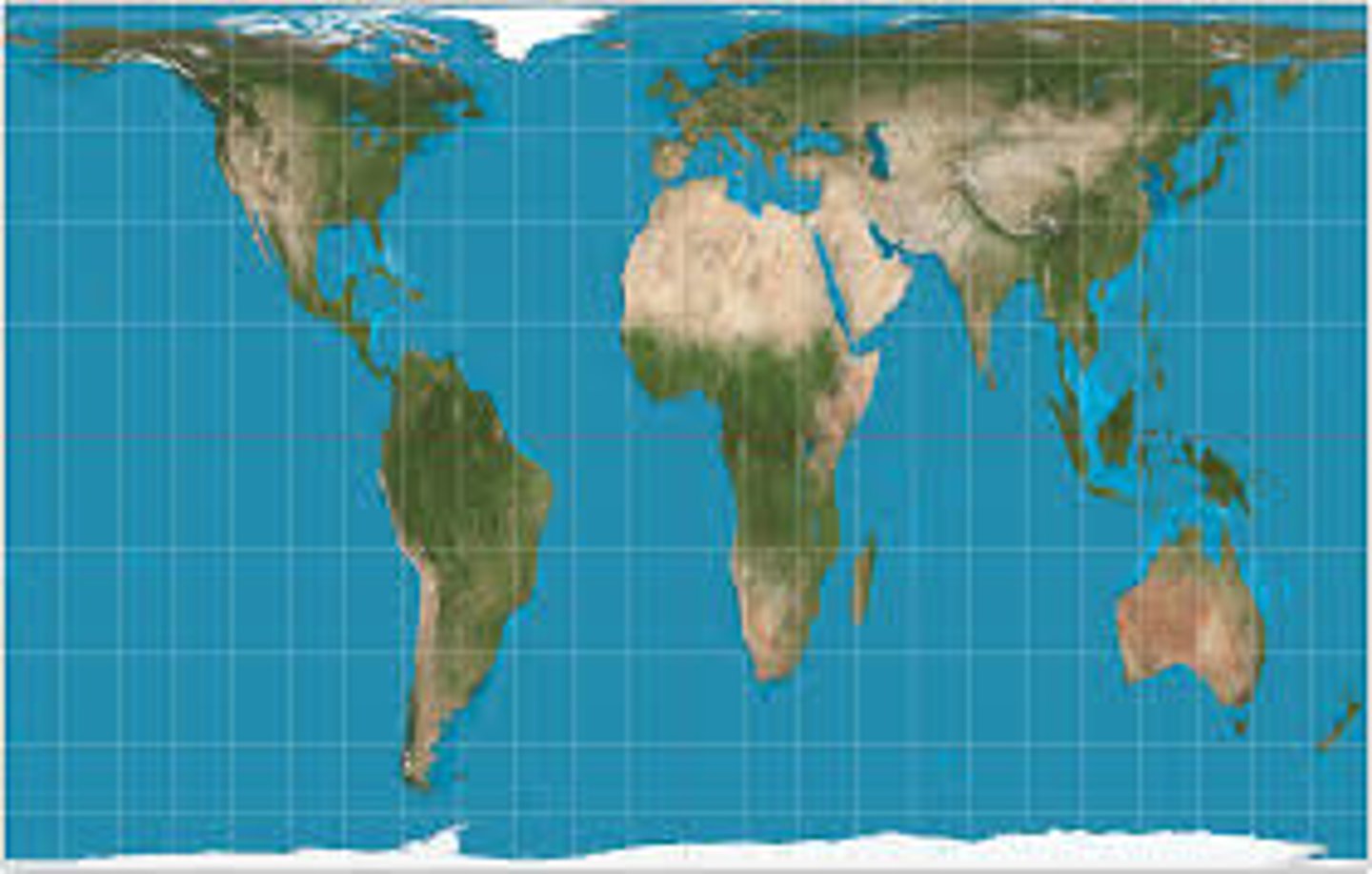
Peters Projection (Gall-Peters)
Distorts areas near the equator so that they appear smaller than they actually are.
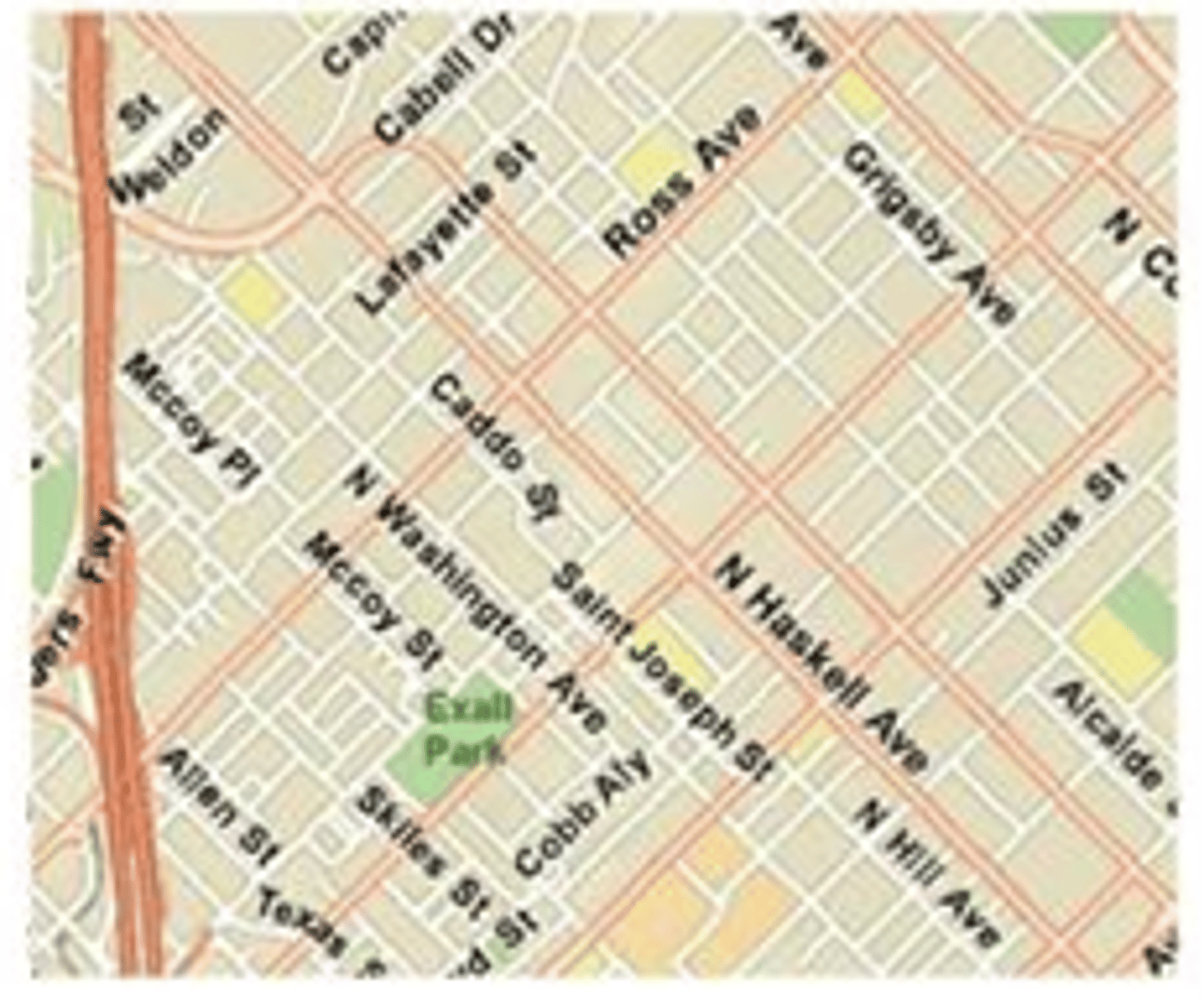
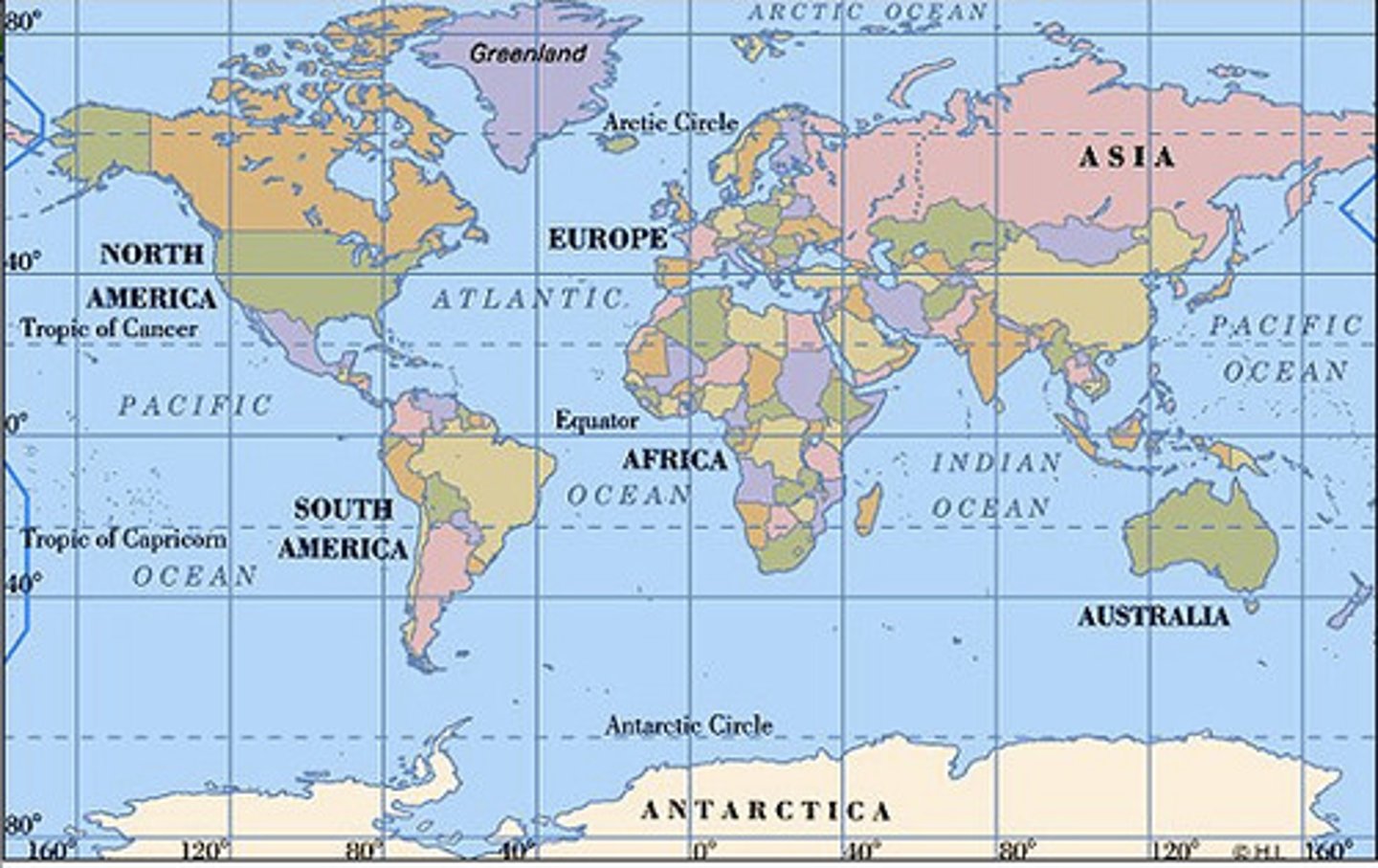
Small Scale Map
A map that covers a large geographic space in small amounts of detail.
Topographic Map
Maps with lines measuring "relief features" of a piece of land. Relief features are details about elevation.