5- normal occlusion vs malocclusion & Andrew’s keys
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Why is normal occlusion desirable?
allows oral functions to occur, best esthetics and helps prevent disease
What can malocclusion have an effect on?
Dental diseases
Chewing
Speech
Aesthetics
Why can malocclusions occur?(4)
Heredity
Trauma
Disease
Habits
What is Edward H Angle’s definition of normal occlusion?
1st upper molar mesiobuccal cusp over lower 1st molar mesiobuccal groove
Occlusion line
No missing teeth
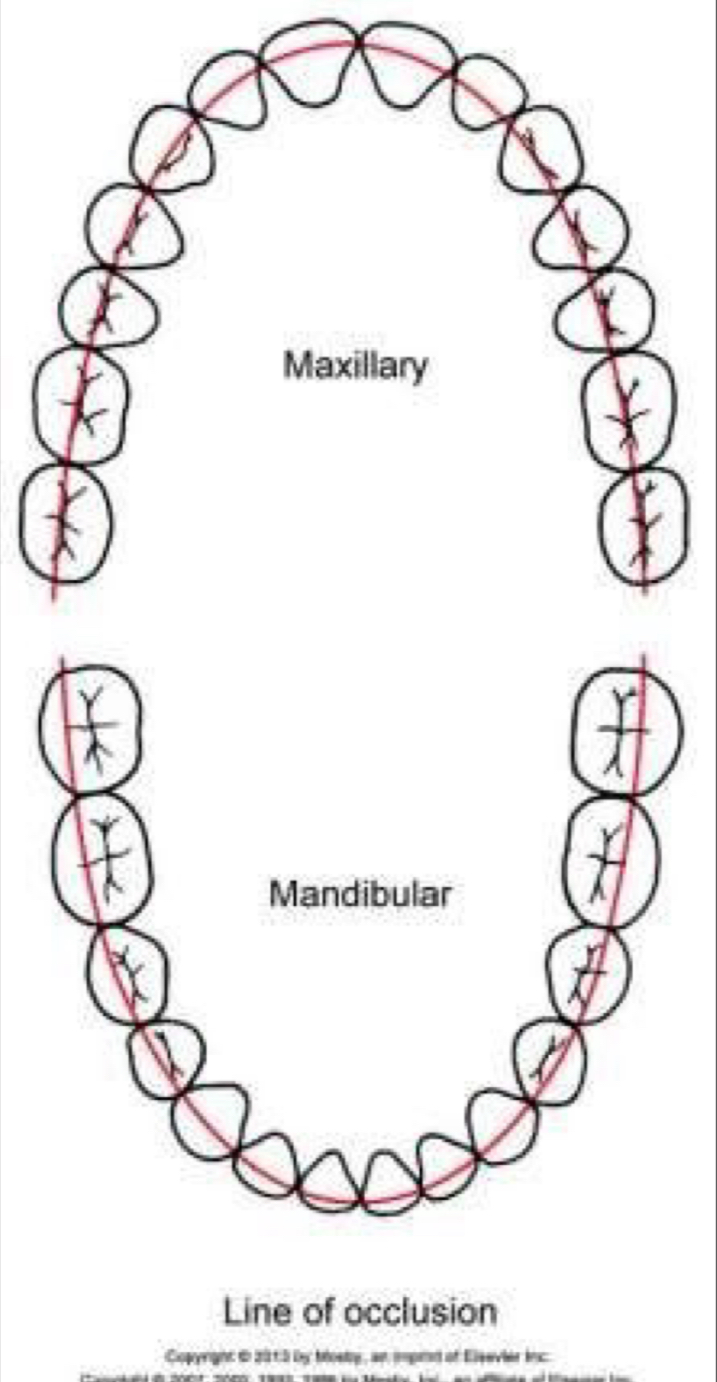
What is the line of occlusion?
Upper arch- smooth curve through central fossae of posterior and cingulums of anterior
Lower- through buccal cusps of posterior, incisal edges of anterior
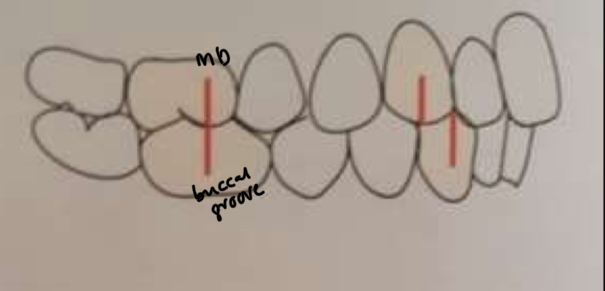
What is a Class 1 malocclusion?
1st upper molar mesiobuccal cusp occludes with 1st lower Buccal groove
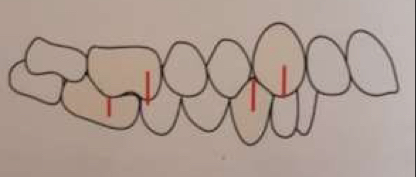
What is a class 2?
1st lower molar Buccal groove occludes distally with 1st upper mesiobuccal
What is a class 3 malocclusion?
1st lower molar Buccal groove occludes mesially to 1st upper molar mesiobuccal
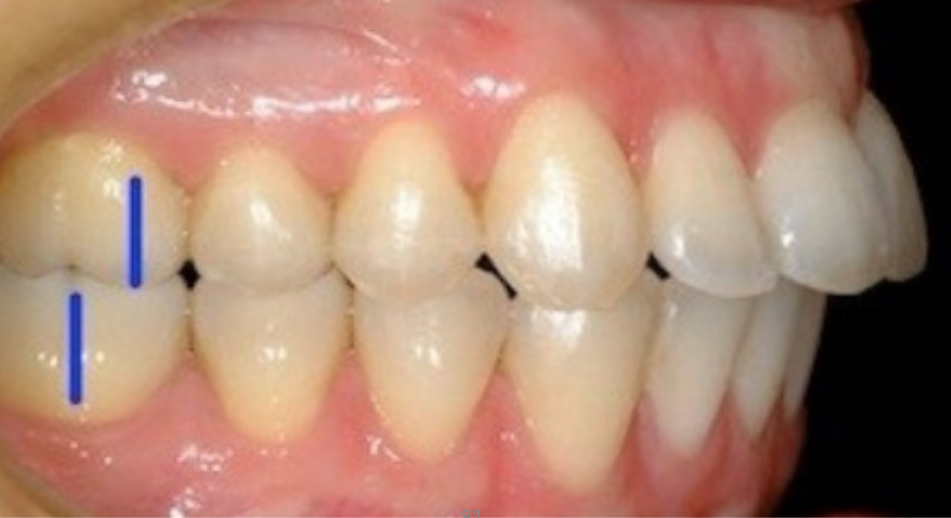
What is a class 2 division 1?
Proinclined upper central incisors
increase in overjet
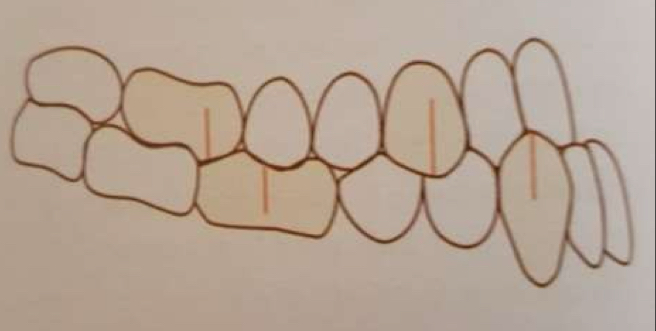
What is a class 2 division 2?
Retroclined upper central incisors- lateral can be proinclined or normal
Overjet minimal or increased
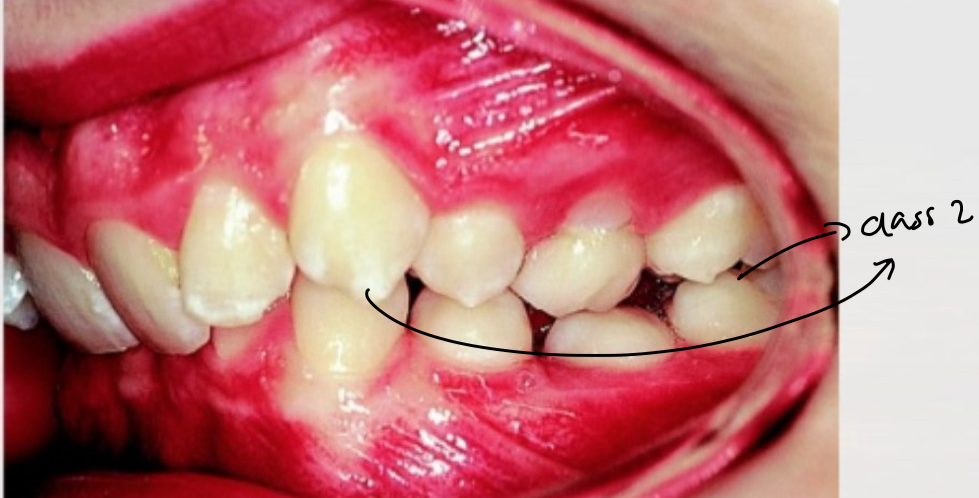
What is a class 2 subdivision?
When class 2 molar relationship exists on only one side, normal relationship on other

What is a pseudo class 3 malocclusion?
Due to occlusal premature contact, when mandible moves from rest position to occlusion, it slides forward into pseudo class 3
What is a class 3 subdivision?
Unilateral class 3 malocclusion
If can move mandible back, it means it’s pseudo class 3
What are the 4 clinical types of class 1 malocclusion?
Transversal or vertical dentoalveolar anomalies and asymmetries
Volumetric anomalies
Eruptive anomalies
Anomalies in inclination of incisors
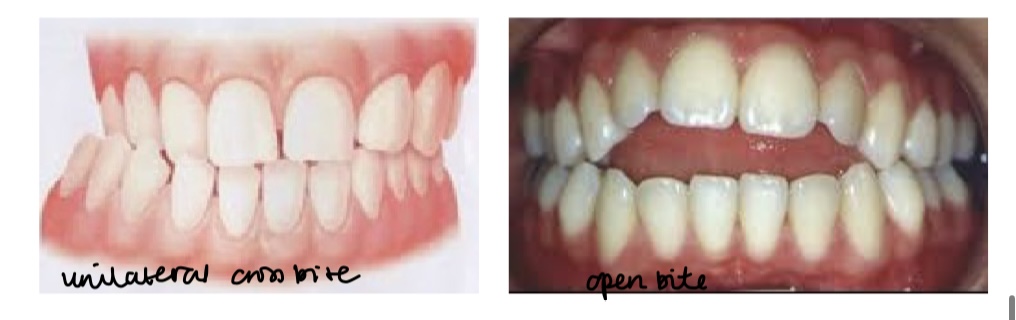
What are the transversal vs vertical dentoalveolar anomalies?
Unilateral cross bite vs anterior open bite
What are volumetric anomalies?
Crowding- negative discrepancy- between sum of mesiodistal diameter of each tooth and length of arch
Diastemas- positive
What are eruptive anomalies?
Transpositions
Impactation
Ectopias
Gryoversion
Ankylosis
What do anomalies in the inclination of incisors cause?
Dentoalveolar protrusion or retrusion
Overjet
Anterior cross bite
What are the important points regarding crowding?
Expressed as either overlap or protrusion
Teeth may not all erupt causing retention or ectopic tooth position
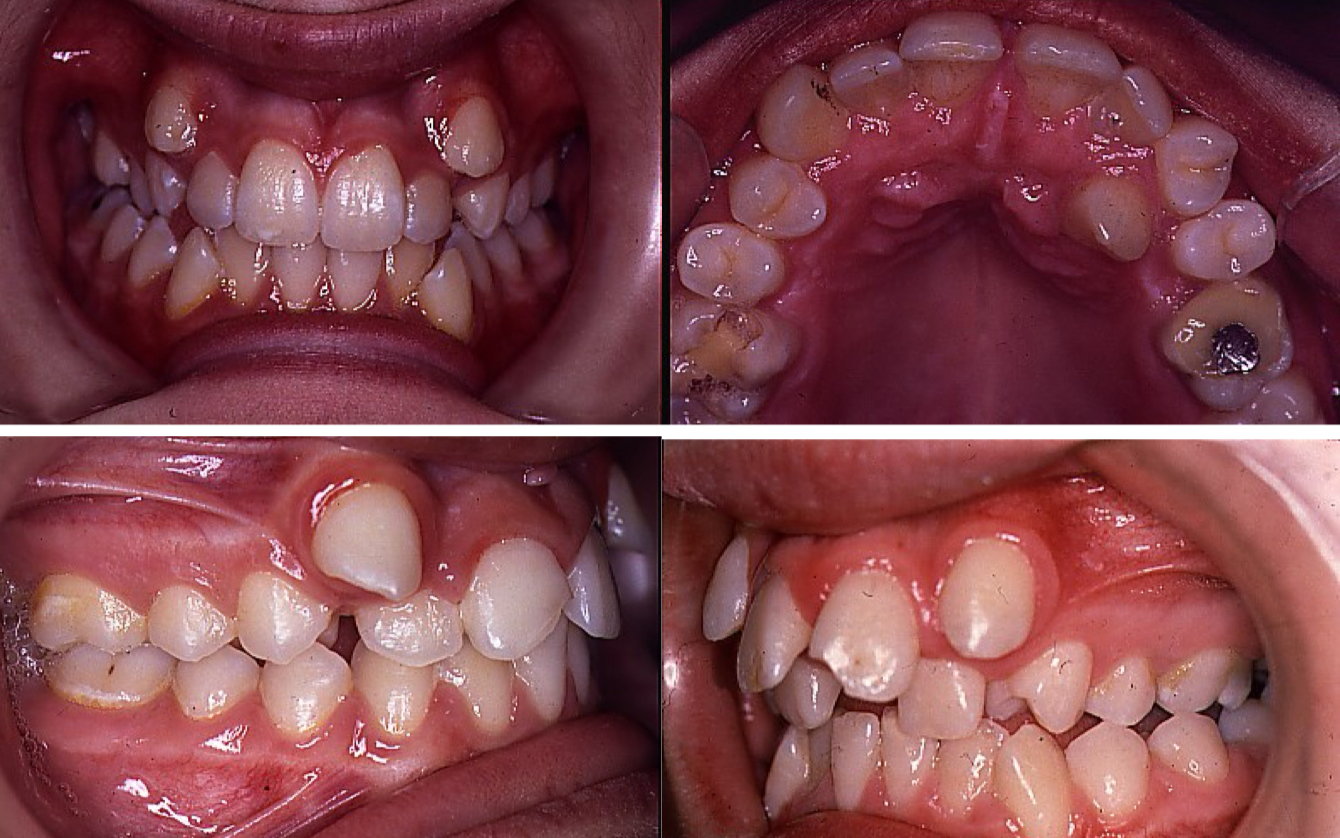
What is the Van der linden classification based on?
Moment of eruption and etiological factors
When is there primary vs secondary vs tertiary crowding based on the van de Linden classification?
General factors
Early loss of temp teeth, oral habits
Eruption of 3rd molars, delayed facial growth
What are examples of general factors that cause primary crowding?
Genetic bone-tooth discrepancy
Volumetric conflict between the size of the teeth (large) and the size of the bony bases (small)
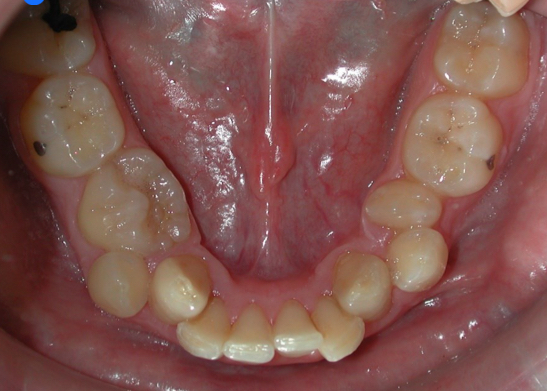
What is secondary crowding caused by?
Environmental factors shorten the arch length, no tooth bone discrepancy
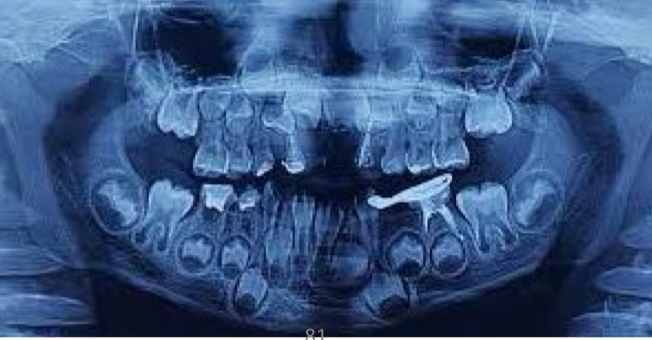
What does the early loss of temporary teeth which leads to secondary crowding depend on and how do you prevent it?
Cusp occlusion
Age of temp teeth missed
Degree of primary crowding
Type of tooth
Prevent with space maintainers
How can oral habits lead to secondary crowding?
Oral breath- affects the length of upper arch- causes open bite
Finger/lip/object sucking- retrusion then crowding of lower incisors
When does tertiary crowding appear, in who does it present and we must…?
18-25
Lower incisors crowding in people without previous crowding or an aggravation in patient with malocclusion
Must differentiate from relapse of treatment
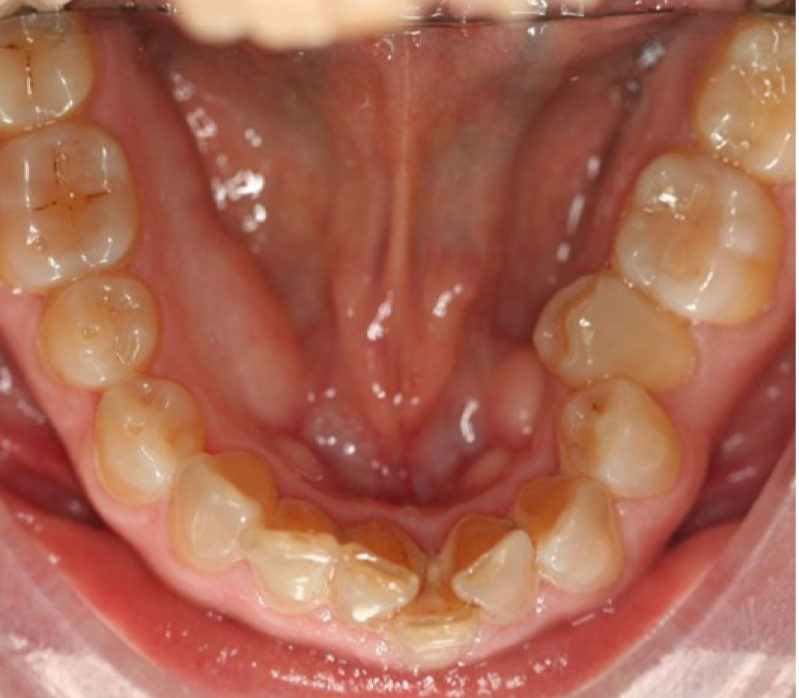
What are advantages of angles classification?
Easy practical method
Quick
No instruments
Easy to communicate and teach
What are disadvantages of angles classification?
Only considers sagittal dimension
Not for temp teeth or when 1st molars missing
Doesn’t consider skeletal problems
Incorrect hypothesis
What do the 6 keys to normal occlusion evaluate?
Why good class 1 occlusion failed to be achieved at the end of treatment
What are the 6 keys of Andrew?
Correct-
Molar relationship
Crown angulation
Crown inclination
No rotations
No spaces
Flat occlusal plane
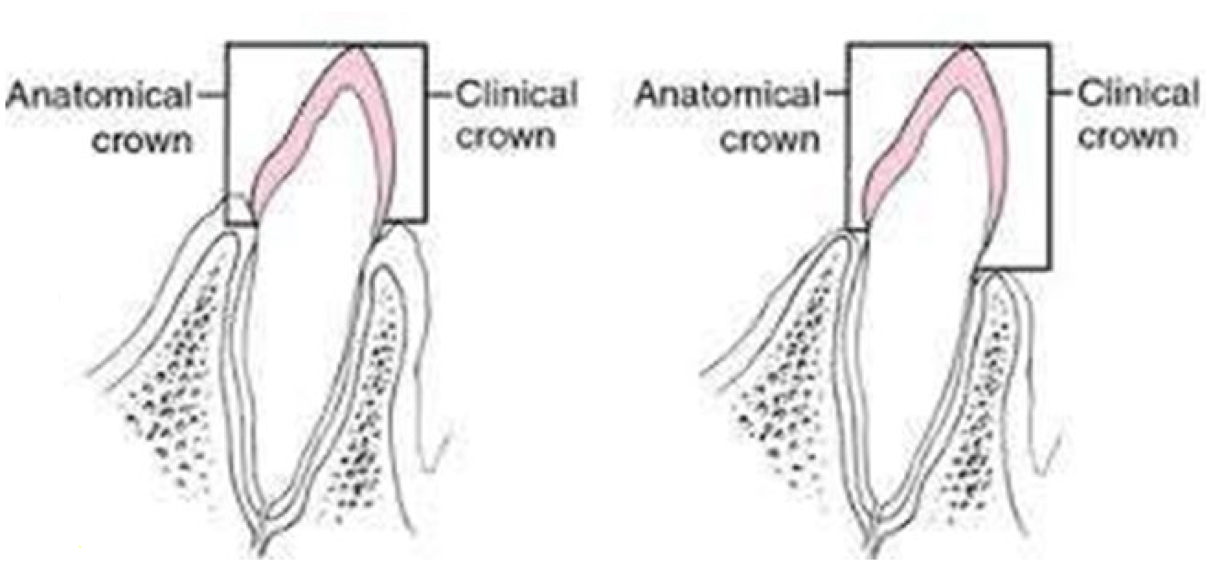
What is the clinical crown and how can you calculate it?
Amount of tooth visible above the gum line, doesn’t recess
Anatomical crown minus 1.8mm
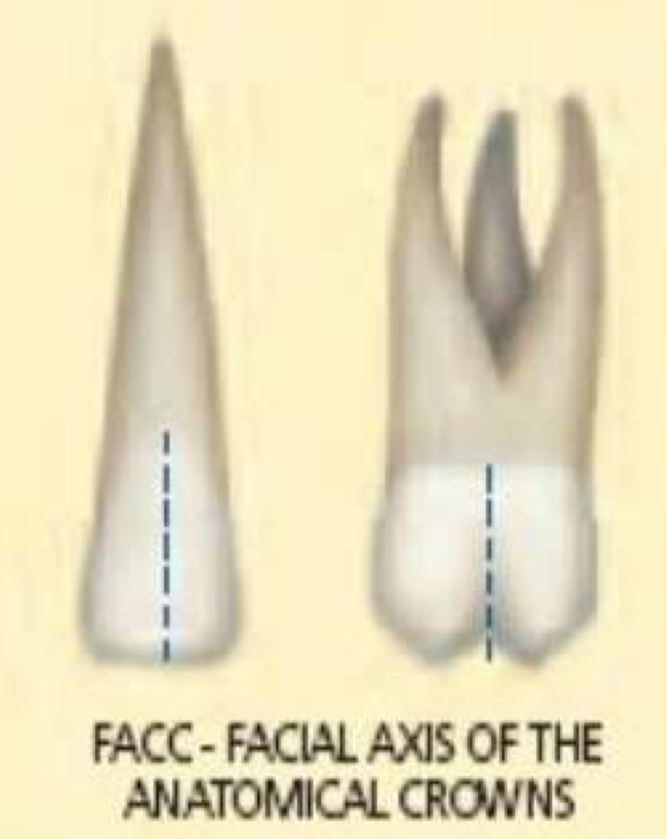
Where is the facial axis clinical crown (FACC) on all the teeth except molars?
On prominent portion of central lobe on facial surface vs Buccal groove that separates the facial cusp
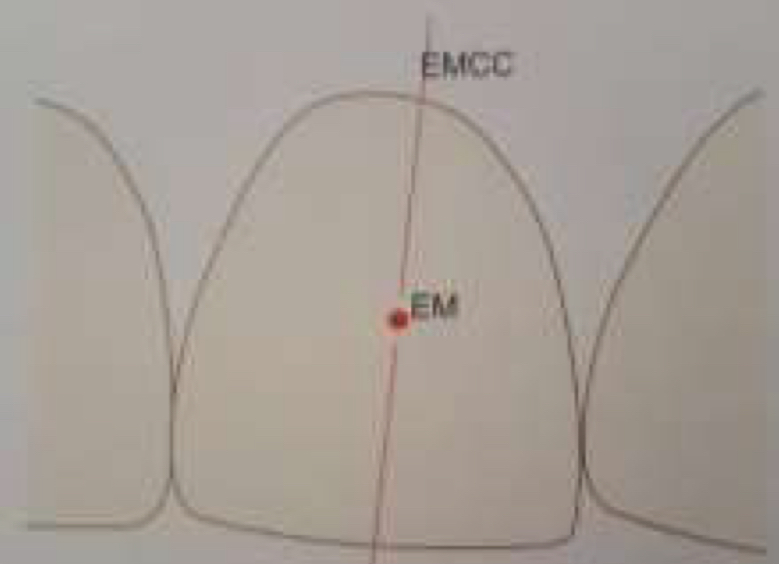
What is the facial axis point (EM)?
Point in facial axis that separates the gingival half of the clinical crown from occlusal
What’s the Andrew’s plane?
Mid transverse plane of every crown will ideally be consistent when every tooth in the arch is aligned
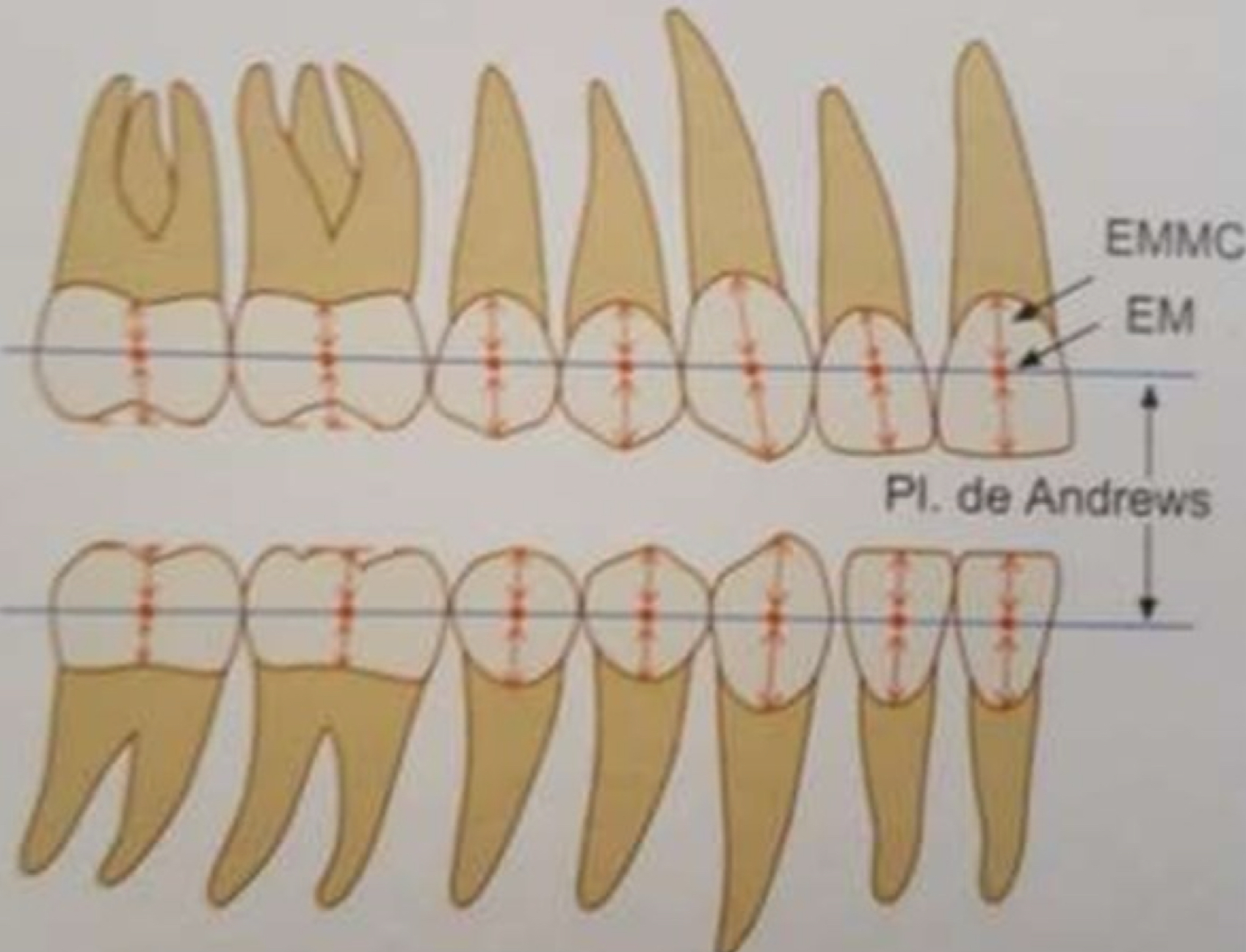
What is the correct molar relationship?
MB cusp of 1UM occludes with grove between 1LM
What is the correct crown angulation?
Gingival portion of long axis of each crown should be distal to incisal portion
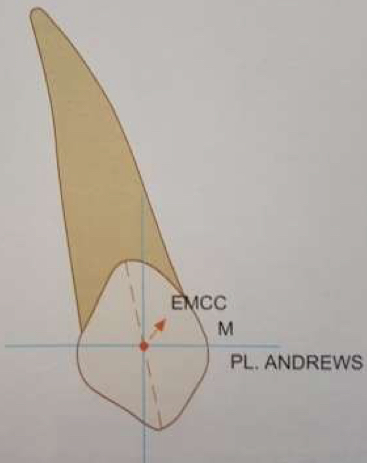
How is correct crown inclination measured?
Draw perpendicular line from Andrew’s plane passing through em point
inclination is the angle formed between this perpendicular line and the FACC
If correct more MD space needed
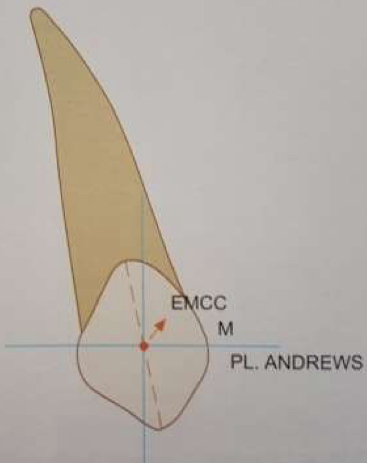
What does crown inclination refer to and what is the difference between positive and negative torque?
Buccolingual inclination of long axis of crown
Upper incisors inclined towards buccal (positive torque)
Upper buccal teeth and lower incisors towards lingual (negative torque)
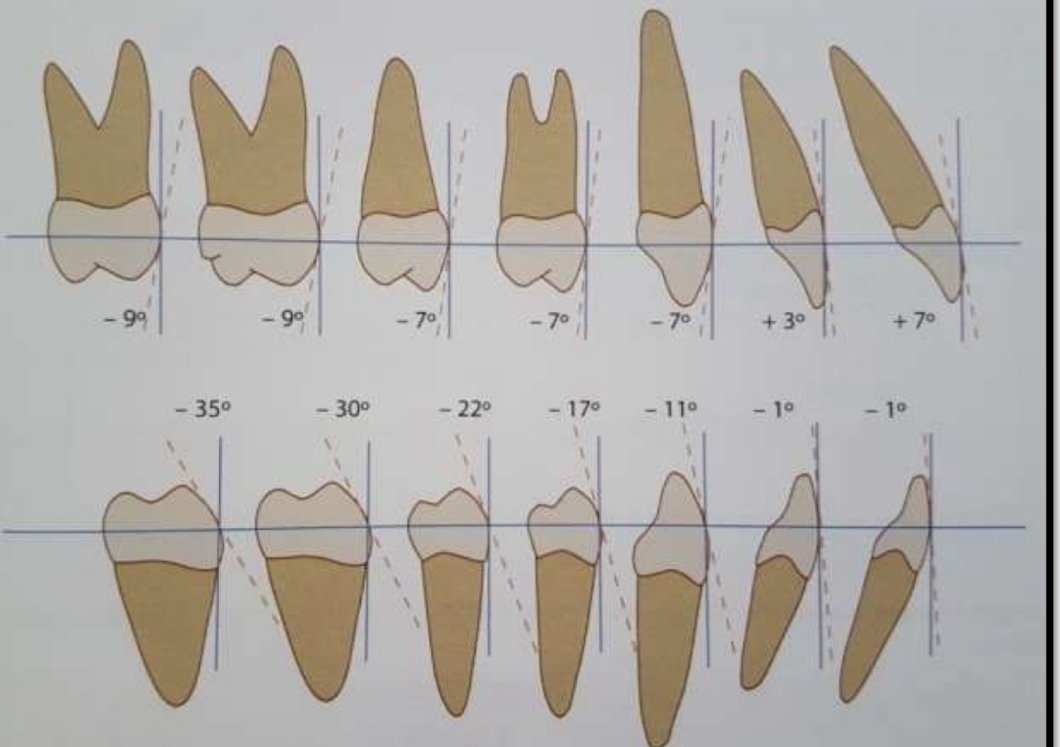
What does the degree of angulation depend on?
Type of tooth
How much space does each tooth occupy if rotated?
Molars and premolars- more
Incisors- less
Canines- adversely affect aesthetics, occlusal interference
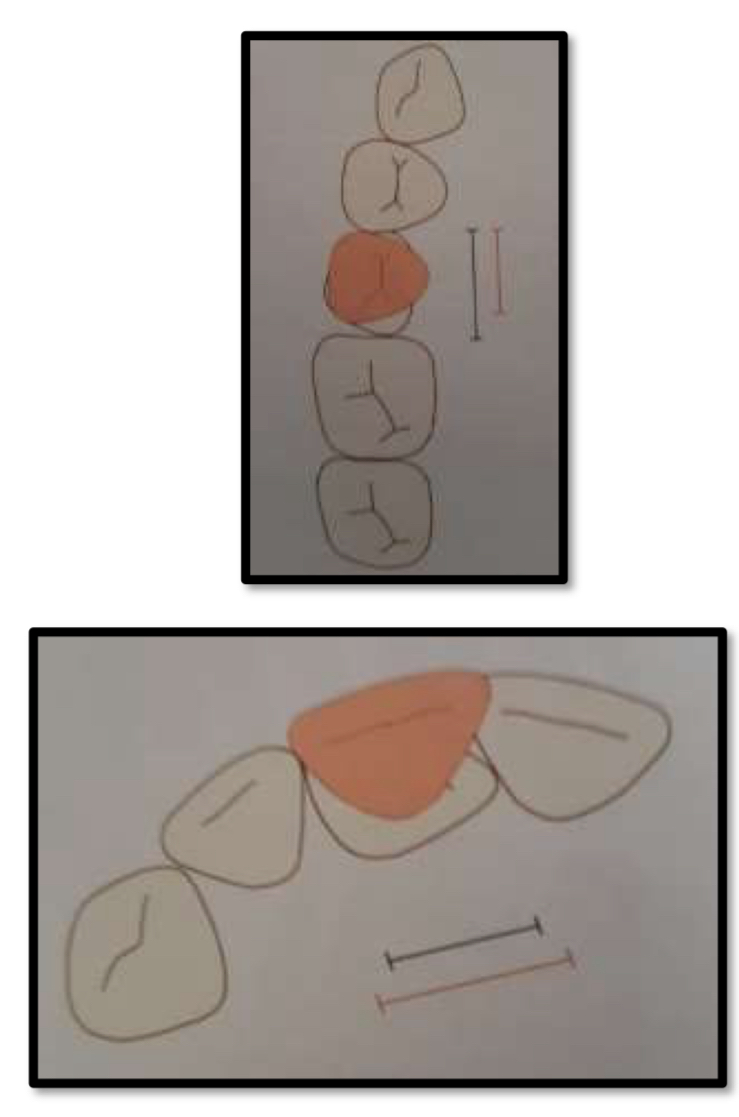
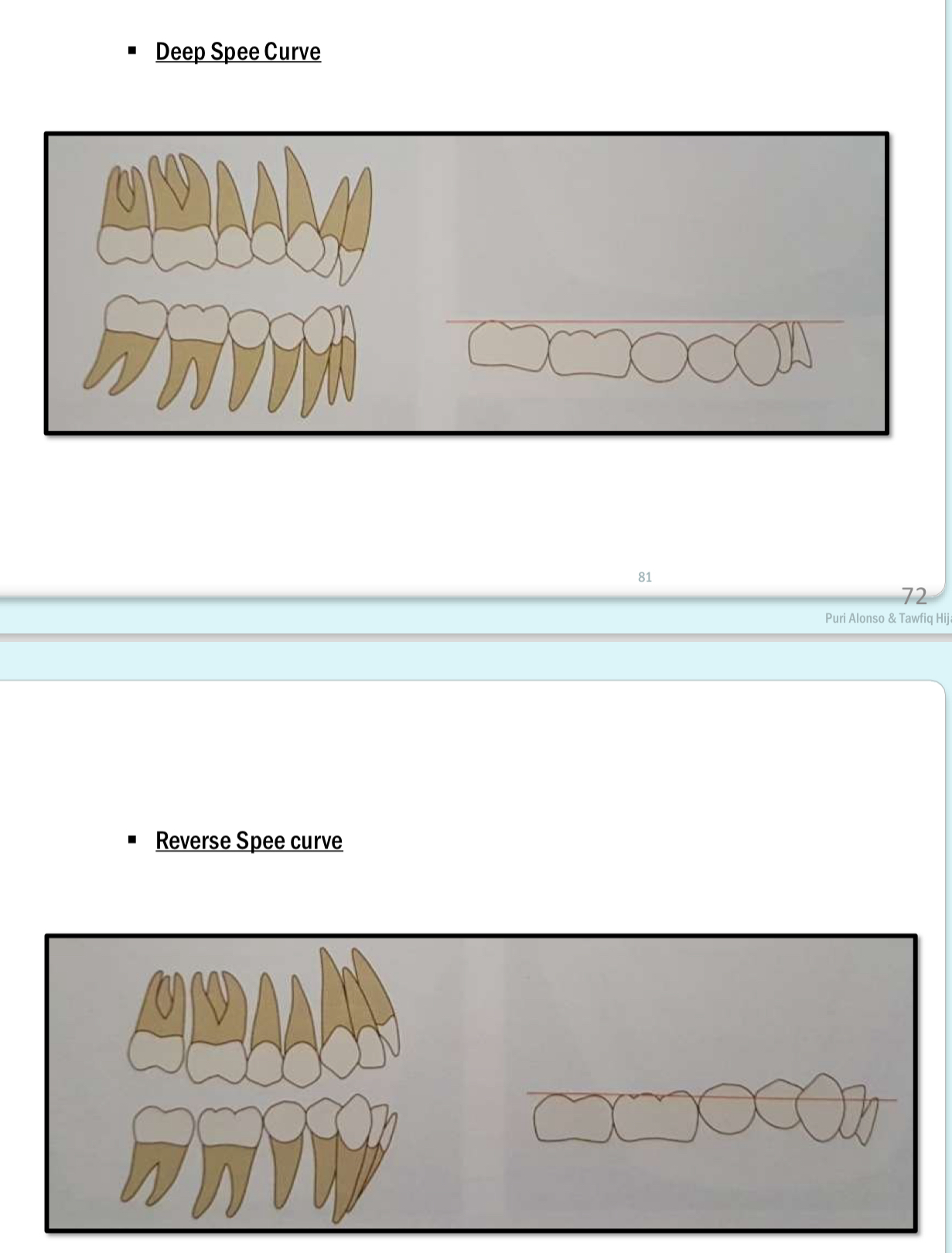
The curve of spee shouldn’t be…
Deeper than 1.5 mm