Chemistry 20 acids and bases 5.1/5.2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
matter - 2
pure substances and mixtures
pure substance
substance with one type of particle
mixture
substances with more than one type of particle
mixtures consist of - 2
homogeneous mixtures
heterogeneous mixtures
homogeneous mixture
particles are uniformly mixed; same properties throughout
heterogeneous mixture
particles are NOT uniformly mixed; different properties in small samples
Solutions are ________ mixtures or __________ solutions.
homogeneous
aqueous
solutions composed of
at least one solute and one solvent (can be solid, liquid, or gas)
aqueous solutions
the solute is dissolved in water (water is the solvent)
(aq)
aqueous solutions - precipitation reactions
require dossolving reactants in water before you can produce precipitate (one product is a solid)
acidic aqueous solutions - 2
included solutions with hydrogen bonded to an anion
starts with H or ends with COOH
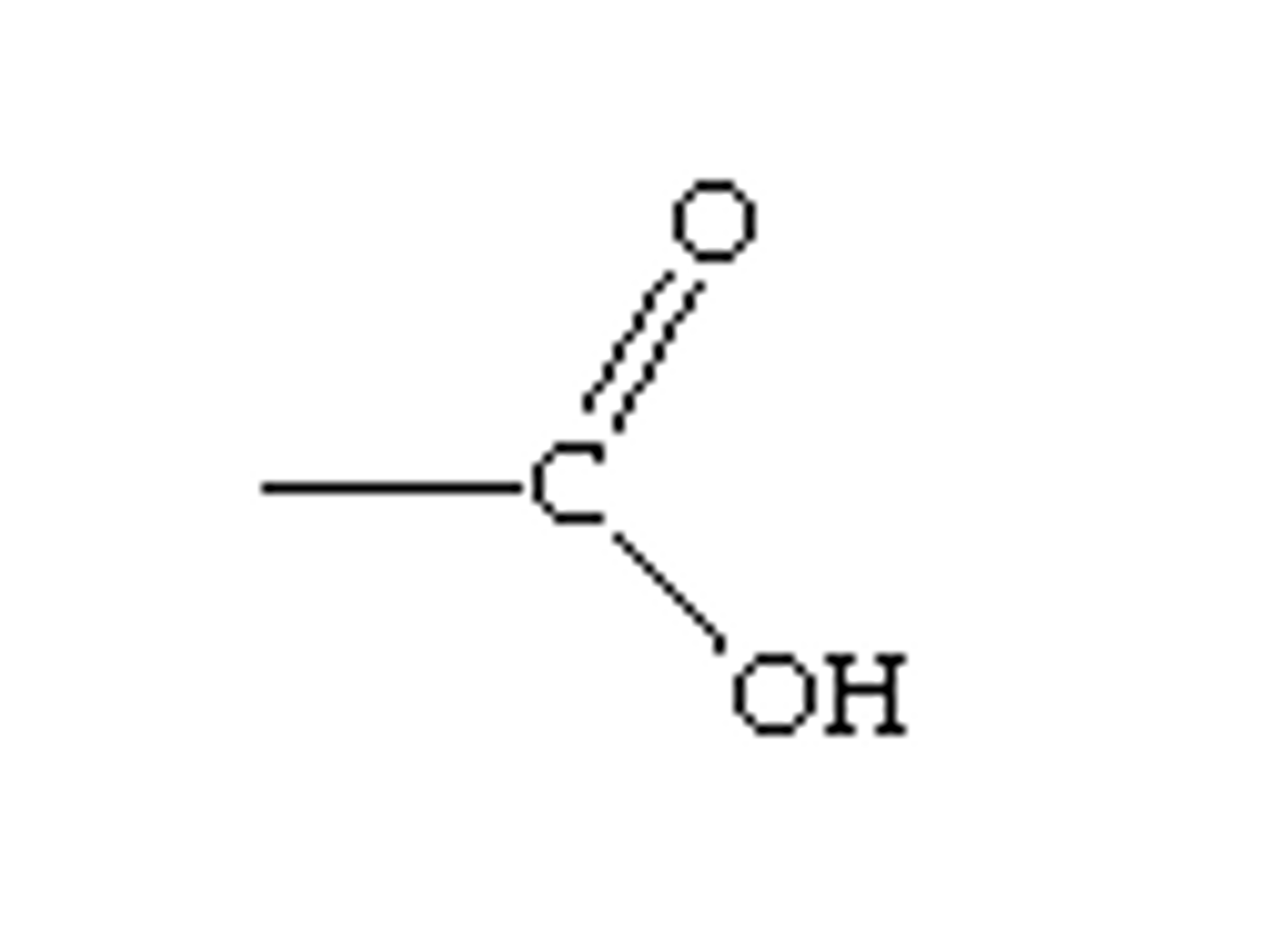
acidic solution diagnostic test
blue litmus -> red
red litmus stays red
pH < 7
conducts electricity
basic aqueous solution
includes ionic compounds containing the hydroxide (OH^-) ion and ammonia gas (NH3) in solution
basic solution diagnostic test
red litmus -> blue
blue litmus stays blue
pH > 7
conducts electricity
neutral aqueous solution
may be neutral ionic
may be neutral molecular
neutral solution diagnostic test
no change in litmus colour
pH = 7
ionic conducts electricity
molecular DOES NOT conduct electricity
electrolytes
IONIC COMPOUND
aqueous solution that conducts electricity
electrolytes have ions in the solution
ex/ soluble ionic compounds, acids and bases
form ions in solutions
ionic particles "dissociate"
strong acids "ionize"
nonelectrolytes
MOLECULAR
aqueous solution that does NOT conduct electricity
ex/ solution with a molecular substance
form electrically neutral particles in solution
particles "dissolve/disperse"
entities list - elements have low solubility
leave them in original state
add water as second entity
ex/ nitrogen gas mixed in water -> N2 (g), H2O (l)
entities list - ionic compounds with low solubility
check solubility table for low/high solubility
ions will stay together when mixed with water - do not break compound apart
ex/ solid dilver sulfate in water -> Ag2SO4 (s), H2O (l)
entities list - ionic compounds with high solubility
check solubility table for high/low solubility
ions will dissociate when mixed with water - seperate compound and add charges (aq cuz mixed w water)
ex/ solid magnesium chloride in water -> Mg2+ (aq), Cl- (aq), H2O (l)
entities list - molecular substances with low solubility
non-polar compounds have LOW SOLUBILITY in water
keep them in original state - add water as second entity
ex/ octane (C8H18 (l)) in water -> C8H18 (l), H2O (l)
entities list - molecular substances with high solubility
polar compounds have HIGH SOLUBILTY (sugars, proteins, vitamins)
molecules dissolve/disperse when mixed with water - show as dissolved by changing state to (aq) - keep compound together
ex/ solid sucrose (C12H22O11 (s)) in water -> C12H22O11 (aq), H2O (l)
entities list - strong acids (top six)
full ionize/react with water to form ions
break them apart into H+ (aq) and anion - include water as another entity
ex/ nitric acid (HNO3 (aq)) -> H+ (aq), NO3- (aq), H2O (l)
entities list - weak acids (everything below top six)
do not fully ionize (leave them as molecules) - change state to (aq)
ex/ acetic acid (CH3COOH) in water -> CH3COOH (aq), H2O (l)
dissociation equations show as an equation what happens to
ionic compounds (all solid at room temp) when added to water
do dissociation equations include water?
no, but entities do
dissociation product states are
aqueous (aq)
dissociation of soluble ionic compounds
start with solid, seperate into ions
ex/ NaCl (s) -> Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
(NH4)3PO4 (s) -> 3NH4 + (aq) + PO4 3- (aq)
dissociation of not soluble ionic compounds
show that it has dissolved, but do not break apart into ions
( (aq) all ionic compounds are soluble to a degree)
ex/ CaSO4 (s) -> CaSO4 (aq)
2 diagnostic tests - aqueous solution of a molecular substance
doesnt conduct
no change in litmus paper
2 diagnostic tests - aqueous solution of a neutral ionic compound
conducts electricity
no change in litmus paper
2 diagnostic tests - aqueous solution of an acid
conducts electricity
red litmus
2 diagnostic tests - aqueous solution of a base
conducts electricity
blue litmus
what is believed to happen when ionic compund dissolves in water
- cations of compound surrounded by negative ends of water and pulled away from crystal
- anions of compound surrounded by positive ends of water and pulled away from crystal
all reactancts of dissociation equations start as (state)
solid
when do you write charges for products/entities?
dissociaion products
entities of ionic with high solubulity
strong acids
when do you balance entities?
don't balance entities (balance compound tho if it does not break down)
aqueous means
it has water + very soluble
for entities, does water have a charge?
no charge on water (so its H2O (l))
for entities, elements -
have low solubilty so they stay in original state
don't add charge