Cell Bio Test #3: Intracellular Transport 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Cytosol
metabolic pathways, protein synthesis
nucleus
contains nuclear genome, DNA/RNA synthesis
mito
ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation
chloroplasts
ATP synthesis and carbon fixation via photosynthesis
Golgi apparatus
proteins and lipid modification and sorting
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
mem synthesis, protein distribution
main site of lipid synthesis
Rough: ribosomes attached
Smooth: Ca2+ sequestration
lysosomes
intracell. degradation
endosomes
sorting of endocytosed material
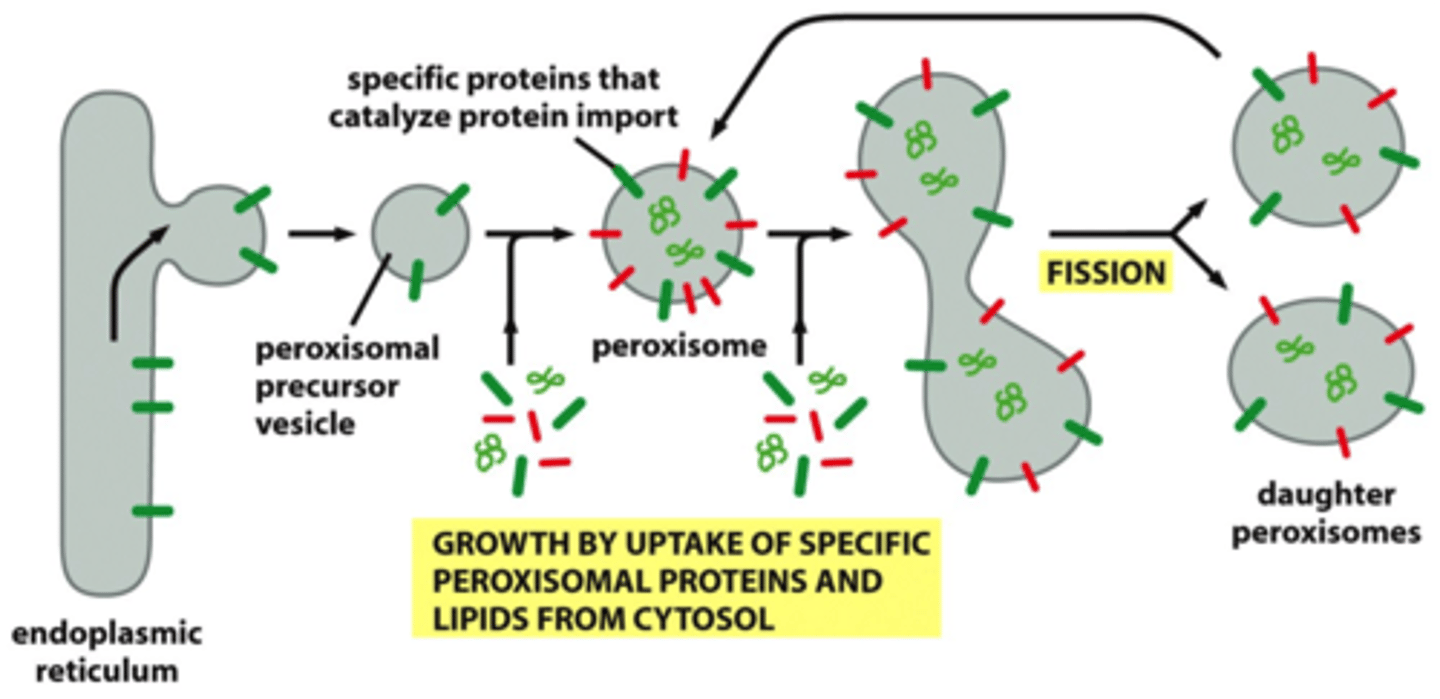
peroxisomes
contain enzymes that produce H2O2, proteins don't need to unfold to enter perox.
contains protein transolcator that aids in transport
oxidation of toxic molecules
Endomembrane system
ER, Golgi app, peroxisomes, endosomes, lysosomes
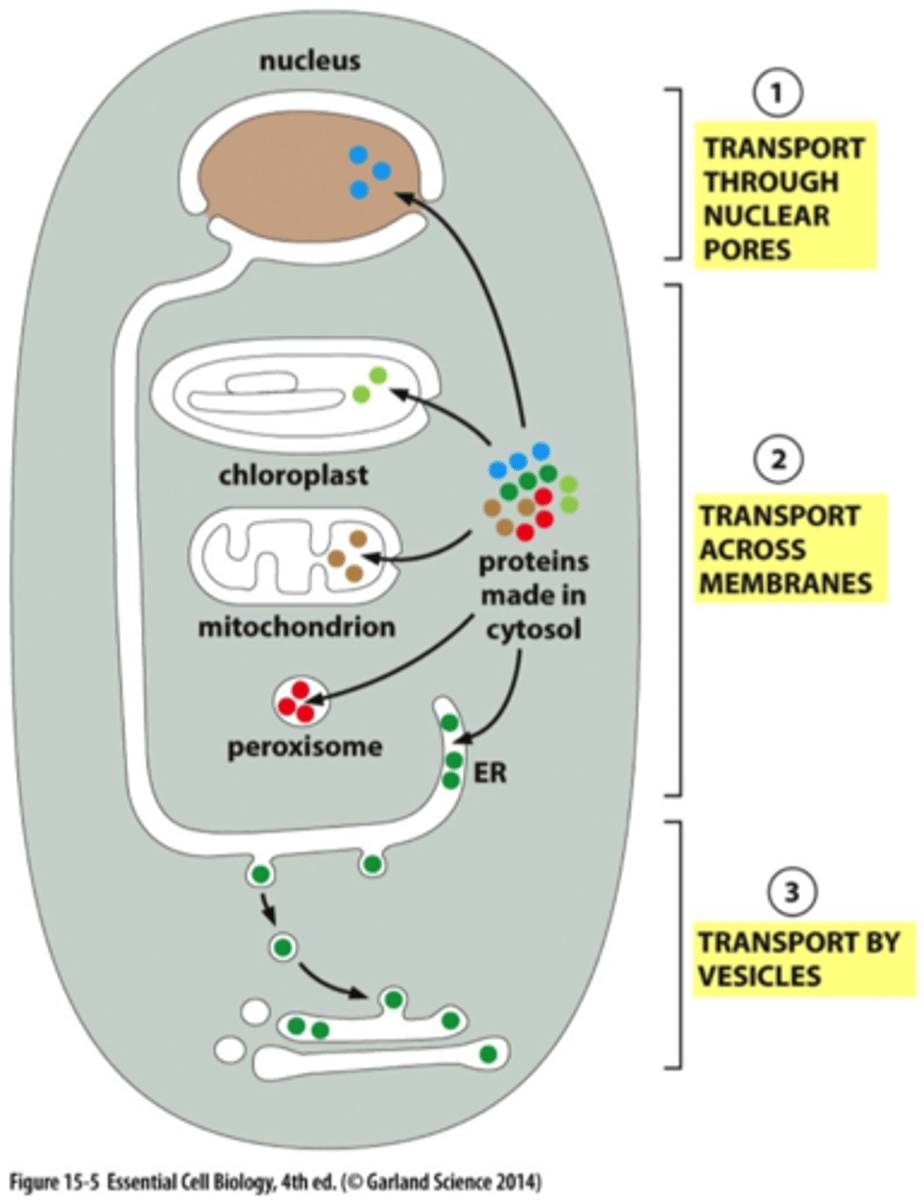
What are the 3 mechanisms of protein transport for an imported water-soluble protein into organelles?
All of these processes require energy
2) needs to be unfolded
1) Transport through nuc. pore: folded proteins enter via nuc pores
2) Transport across mem: unfolded proteins enter organelles via protein translocators (must unfold to get across mem)
3) Transport by vesicles: folded proteins move via transport vesicles that fuse w/ other mem (pinches off mem to form vesicle that fuses w/ another part of a mem)
nuclear pores
selective gates but allow free passage of small, water-soluble mol
penetrates outer and inner mem
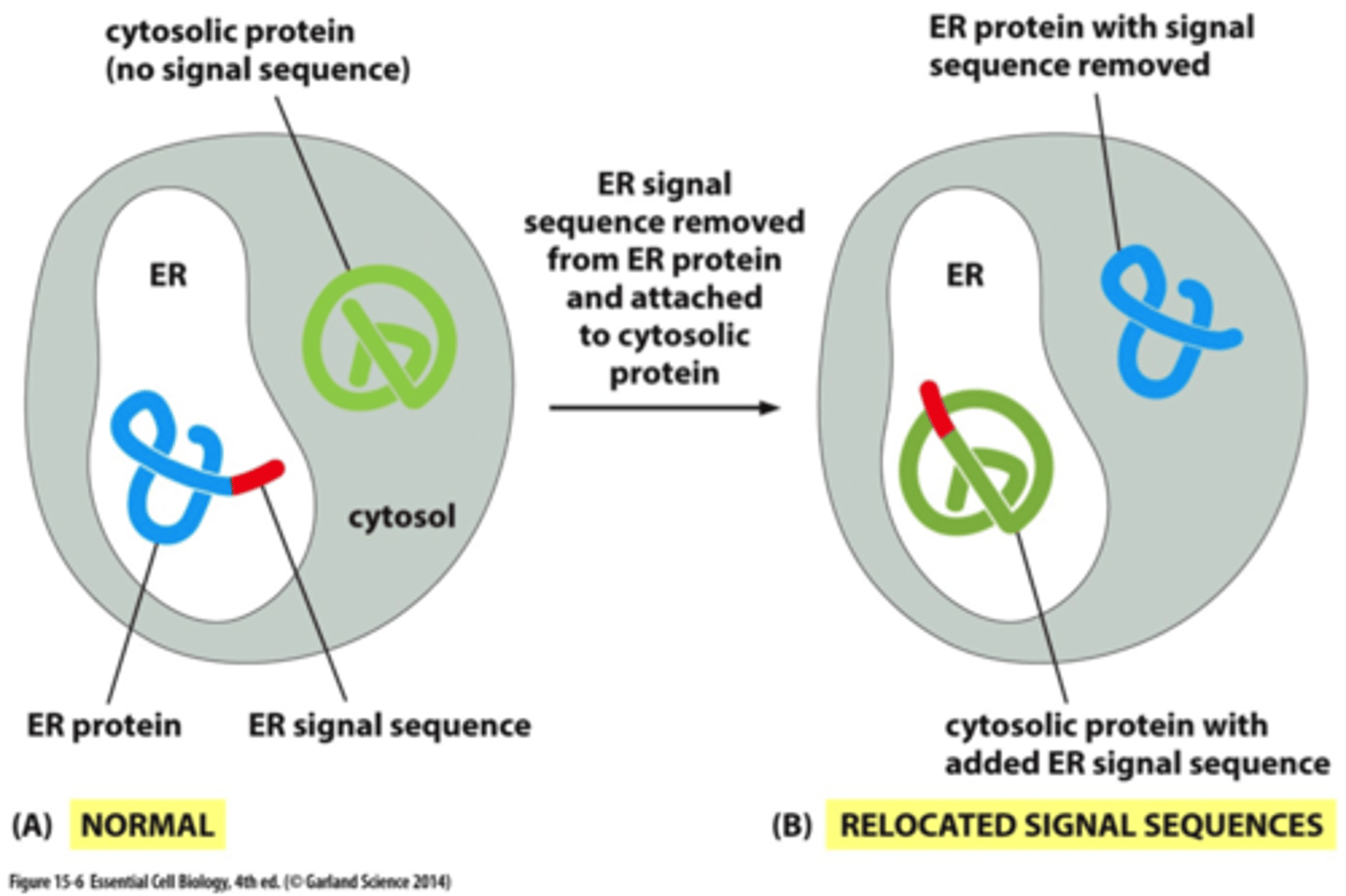
What do signal sequences do?
direct proteins to the correct organelle
What are ss comprised of?
a stretch of 3-60 aa
The final destinations have the same or different signal seq?
-If there is no signal sequence on the protein, where does it stay?
they have diff ss;
it stays in the cytosol
structure of nucleus
Folded proteins w/ nuclear localization siganls (NLS) are bound by what type of receptors?
-What crosses the nuclear envelope via the nuclear pore?
bound by nuclear import receptors;
Nuclear import receptors and cargo(prospective nuclear protein) to be able for the protein to get delivered to the nucleus
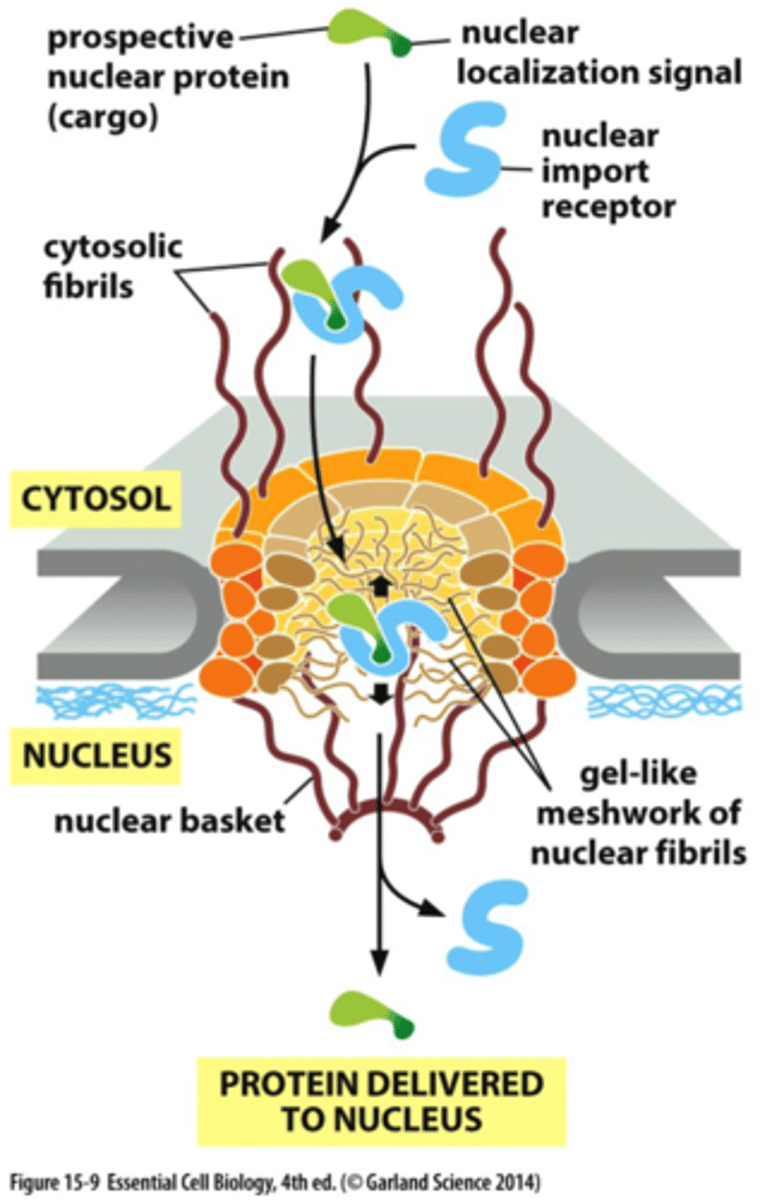
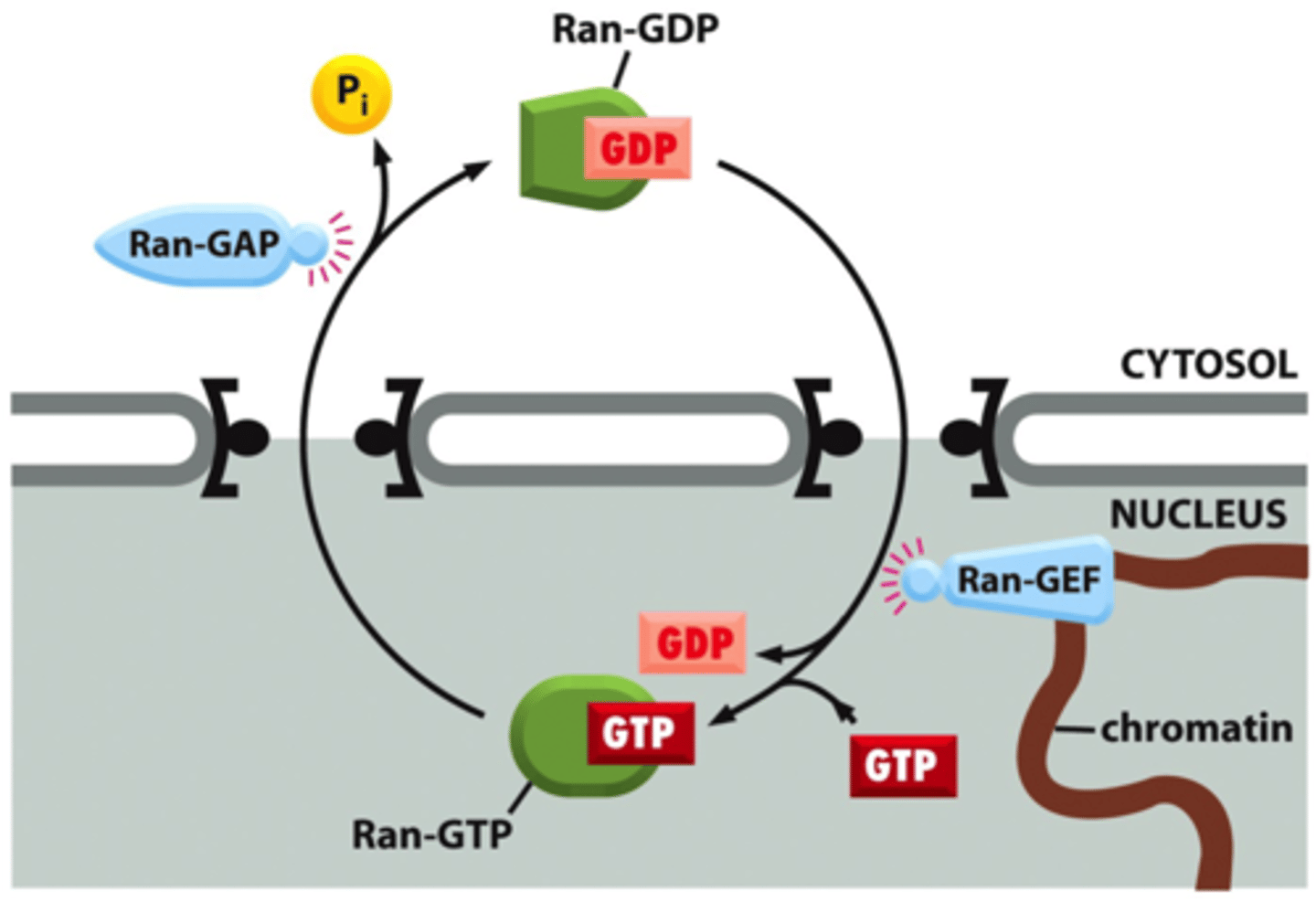
What does Ran-GTP do?
it binds to the nuclear import receptor in the nucleus and then returns it to the cyto.
once in nuc, Ran-GTP binds to receptor and exits via nuc pore into cyto, ran hydrolyzes the bound GTP. Ran-GDP dissociates from receptor
What two things mediate the activity of Ran?
Ran-GAP (GTPase activating protein) and RAN-GEF(guanine exchange factor)
How are unfolded proteins able to enter the mito and chloroplasts?
via protein translocators
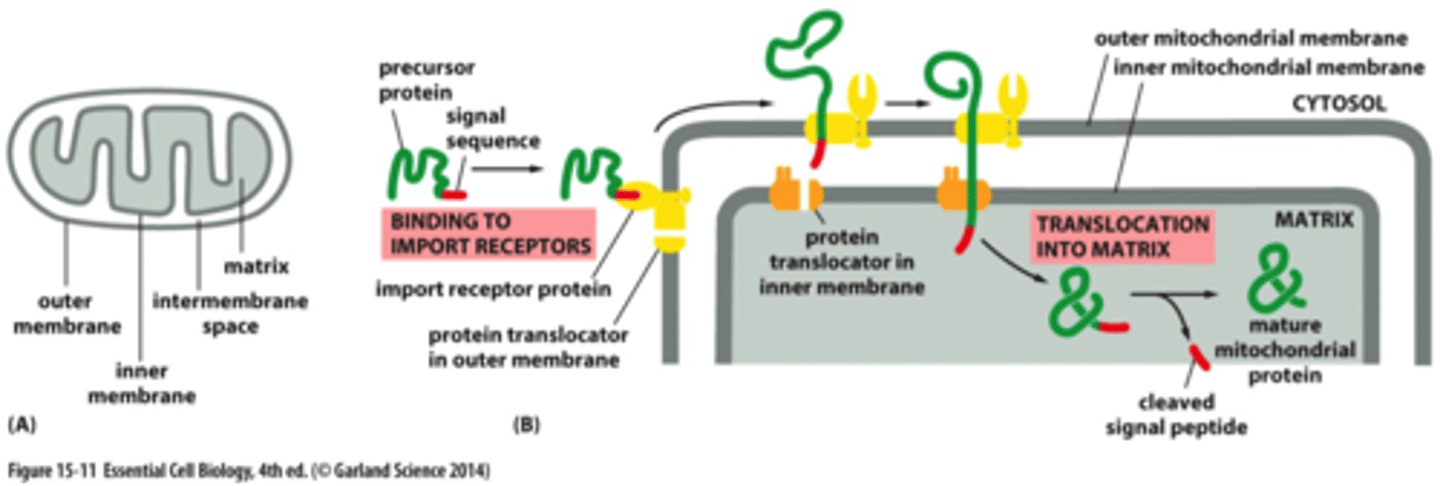
What two things help drive import into the mito?
Chaperons and mem potential
Peroxisomes use what two things to remove protons?
What do perox do?
What are perox involved in the formation of?
O2 and H2O2;
break down F.A, toxins, alch
plasmalogen: phospholipid that is needed for neuron function
How do peroxisomes import proteins?
via peroxins that use ATP as energy source
Rough ER
When translating proteins that have an ER ss, ribosomes that attach to it, are targeted where?
The free ribosomes that have no SS attached, go where?
to the ER
they remain free in the cytosol
ER protein targeting depends on what?
ER proteins are threading through what?
the signal recognition particle (SRP) and the SRP receptor;
through protein translocator (to get into the ER)
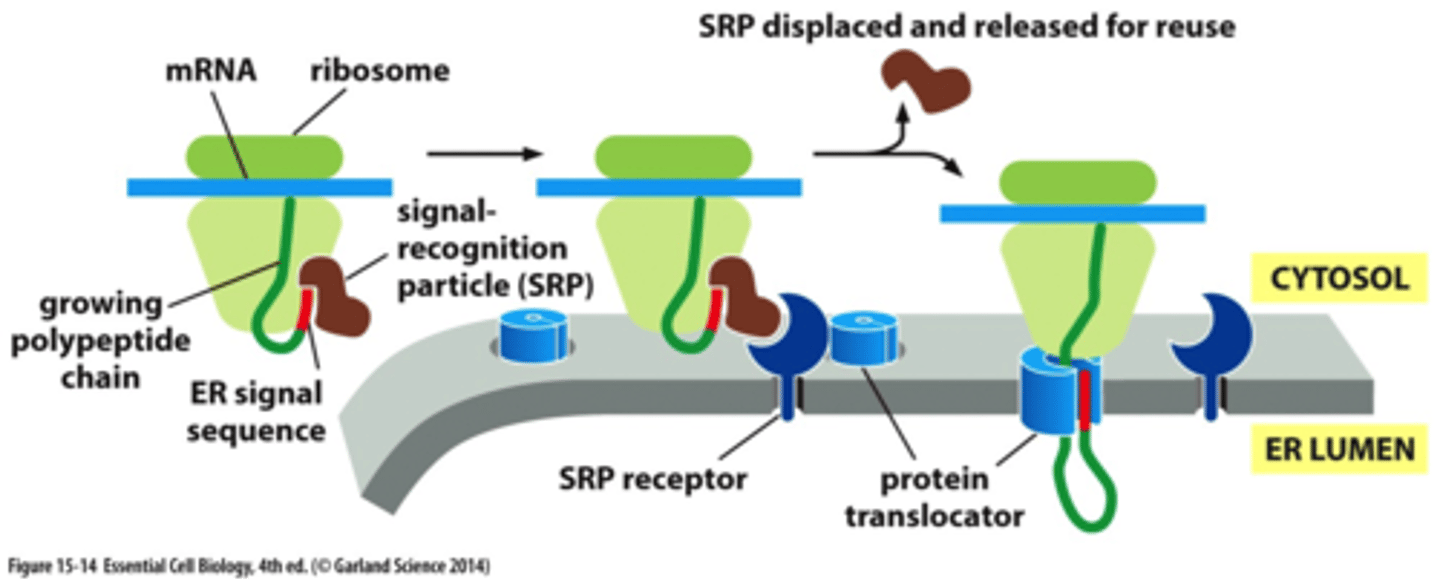
SRP and SRP receptor bind and hydrolyze what?
GTP
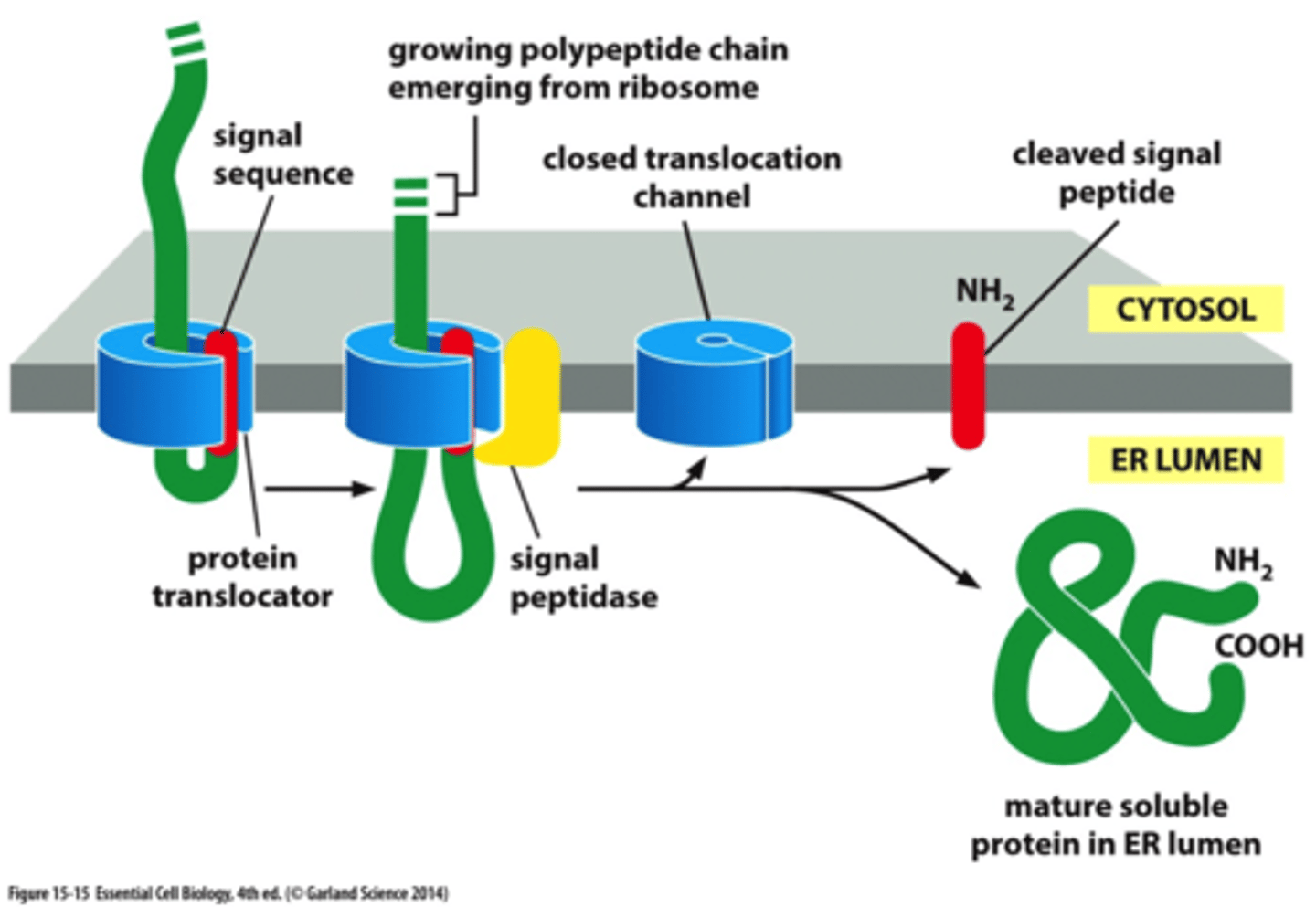
After the ss is cleaved from the proteins, what happens to the soluble proteins?
the mature soluble protein is released into the ER lumen
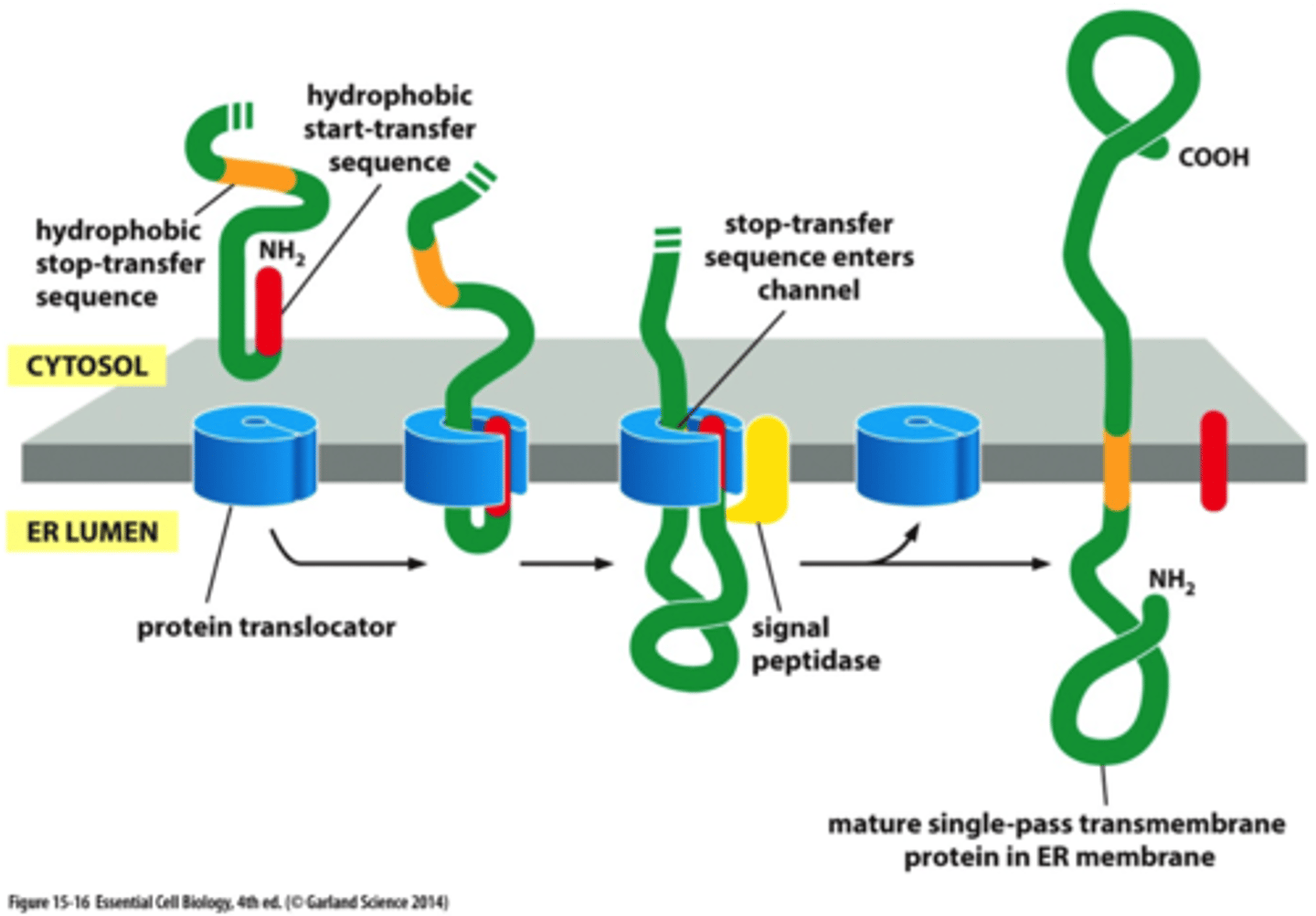
What determines the arrangement of the ER mem protein?
they hydrophobic start transfer and stop transfer sequences
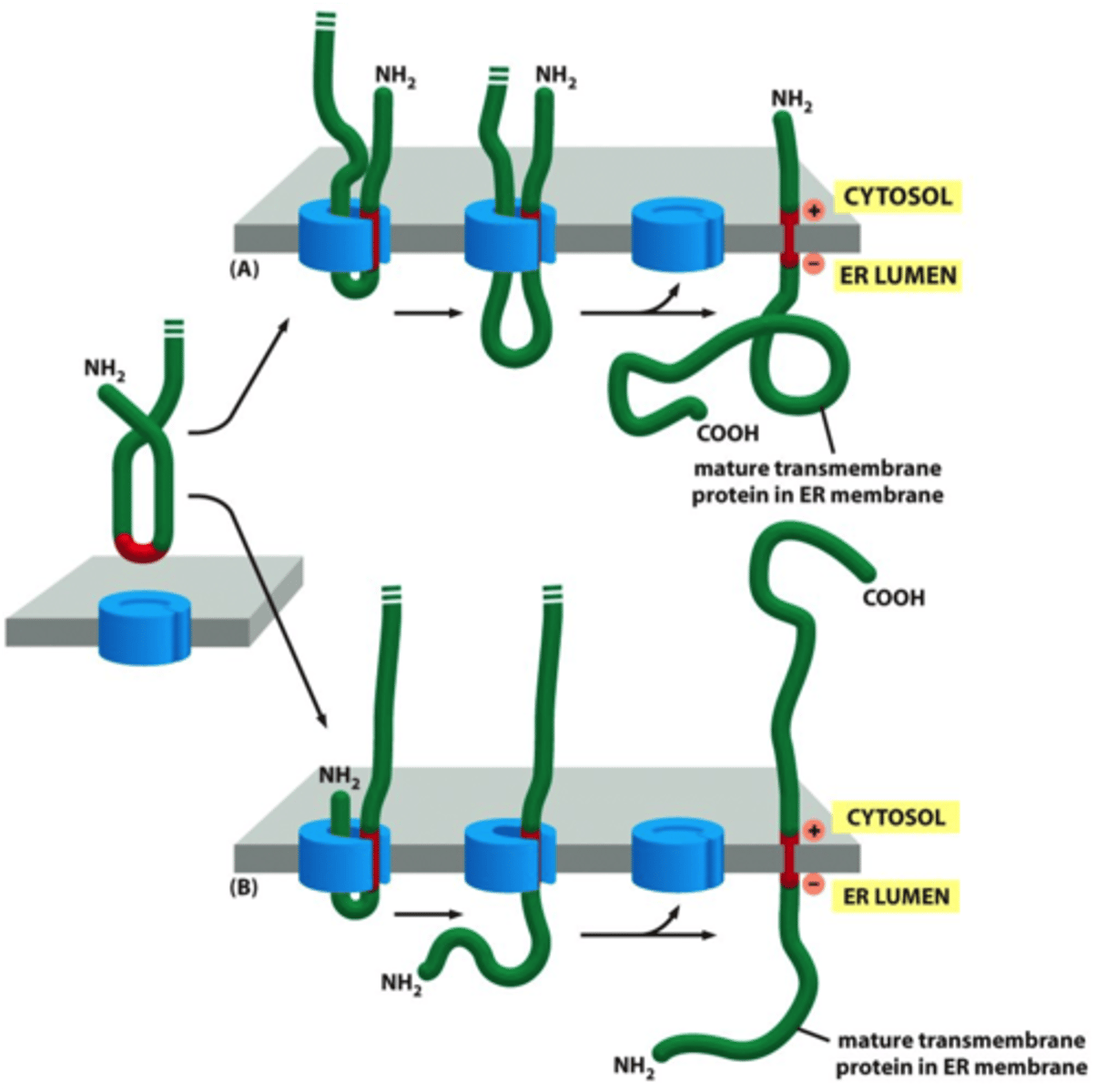
What determines the orientation of protein insertion?
Before the start transfer, what is N terminus?
After the start transfer, N terminus is what?
the location of positively charged aa;
cytosolic;
lumenal
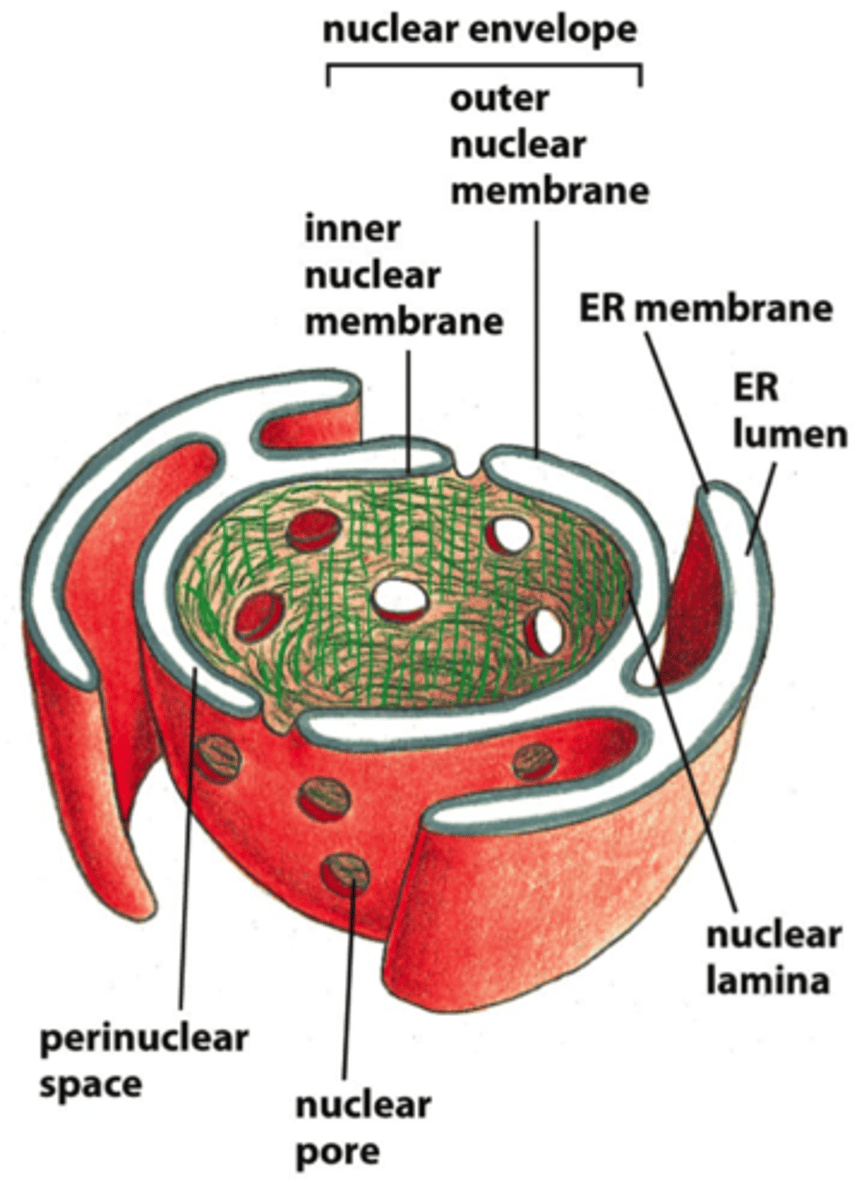
The outer nuclear mem is continuous w/ what?
b/c of this what does outer nuc mem have on it?
the ER.
ribosomes
Many organelles are held in their locations by what?
by their attachment to the cytoskeleton
When is the ss removed from finished protein?
once it has been sorted
Deleting a ss from an ER protein does what?
converts it to a cytosolic protein
inner nuc mem
contains proteins that act as binding site for chromo, and proteins that provide anchorage for nuc lamina
ribosomes are bound to which surface of ER mem?
cytosolic surface
nuclear pore complex
forms a gate in which selected macromolecules and larger complexes enter or exit the nucleus
What is the ss that directs a protein from the cytosol into the nucleus?
nuclear localization signal.
What energy drives nuclear transport?
the energy supplied by GTP hydrolysis
nuclear import receptors interact w/ what?
cytosolic fibrils that extend from the rim of the poe
What happens after a nuclear import receptor picks up a prospective nuclear protein in the cytosol and then enters the nucleus?
Then the nuclear import receptor encounters GTPase (Ran), which carriers a mol of GTP. This ran GTP binds to the import receptor=nuclear protein is released in the nucleus.
-Receptor is still carrying Ran-GTP, so goes back to cytosol, and some protein triggers Ran to hydrolyze the GTP that is bound to it. Ran-GDP falls off the receptor which makes it free to bind another protein that needs to go to nuc.
What do chaperons helps to do inside the organelles?
They help to pull the protein across the 2 mem and fold it once inside
Transport initiation outside the outer mem
The precursor protein is recognized by a receptor in the outer mem. This receptor is associated w/ a protein translocator. Then the receptor, precursor protein, and translocator diffuse across outer mem till it reaches 2nd translocator in inner mem. The 2 translocators transport protein across both mem, unfolding protein in process. ss cleaved off by peptidase and chaperons help to refold these
What organelle serves as an entry point for proteins that are destined for other organelles, as well as this organelles itself?
ER
Proteins destined for where all enter the ER first from the cytosol?
What happens once these are inside the ER lumen?
golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes;
proteins will be transported via vesicles from organelle to organelle or to plasma mem. They will NOT re-enter cytosol
What 2 types of proteins are transferred from the cytosol to the ER?
water-soluble proteins: completely transported across ER and then enter ER lumen
prospective transmem proteins: partially transported and then become embedded in it
ER ss is?
hydrophobic
Why is it necessary for the ribosome protein to be attached to the ER mem?
What do all of theses ribosomes make up ?
b/c most proteins that enter the ER are threaded across the ER mem before the polypeptide chain has been completely synthesized. So the ribosome is synthesizing the protein while it is going through ER mem;
Rough ER
mem-bound proteins
Free ribosomes
attached to the cytosolic face of ER
-make proteins that are being translocated in ER
unattached to any mem
make proteins that are encoded by nuclear DNA
Why do mem bound ribosomes need no additional energy required for transport?
b/c the elongation of each polypep provides the thrust needed to push it through the ER mem
As an mRNA molecule is being translated, what happens? What is this called?
many ribosomes bind to it, forming a polyribosome
Soluble proteins that are made on the ER are released where?
Some of these remain embedded in the ER mem as what?
in ER lumen;
as transmem proteins
SRP is present where?
What does it bind to?
cytosol;
both ribosome and ER ss
SRP receptor is embedded where?
ER mem;
it recognizes SRP
SRP binds to ribosomes w/ ER ss, protein synthesis slows until SRP binds to SRP receptor. After binding, What happens?
the SRP is released. Receptor gives ribosome to protein translocator in ER mem, protein synthesis resumes, polypep chain is threaded across channel in translocator, translocator transfers growing polypep across lipid bilayer
Where is ss located on soluble proteins?
at N-terminus
In addition to direction protein to correct organelle, what does the ss also do?
it functions to open the channel in the protein translocator, ss remains bound to channel while chain is threaded through. After, the ss is released from channel and degraded in lipid bilayer
When is the protein released into the ER lumen?
after the C-terminus of a soluble protein has passes through the translocation cahnnel
N- terminal ss OR internal signal sequence (start-transfer)
stop transfer seq
initiates translocation;
additional seq of hydrophobic aa
When the stop transfer seq remains in bilayer after N-term is cleaved what happen?
the stop transfer seq forms an a-helical mem spanning segment that anchors protein to mem
What is special about the internal signal sequence (start-transfer seq)
it is NEVER removed from the polypep) unlike the N-term that is cleaved off in some mol
single-pass transmembrane protein
N-terminal ER ss initiates transfer,
contains 2nd hydrophobic seq that acts as stop-transfer seq. After goes through channel, N-terminal is cleaved off and the transmem protein is anchored in mem. Then protein syntheisis on cytosolic side finishes
double-pass transmembrane protein
internal sequence (start transfer) acts as start signal and helps to anchor to final protein in mem. Eventaully, when stop-transfer enters translocation channel, coth seq are discharged into bilayer. NEITHER seq are cleaved. polypep chain stays anchored in mem
Proteins go from ER-->G.A-->?
How is this carried out?
to other organelles. This is carried out by vesicular transport. Routes of comm between interior of cell and around it
Secretory pathway
starts w/ synthesis of proteins in ER mem, ER, G.A, side branch leads off thorugh endosomes and lysosomes
Endocytic pathway
responsible for ingestion/degradation
-moves mol from plasma mem through endosomes to lysosomes