Physics 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
which statement is NOT true about electrons?
electrons cannot move from one object to another by friction
The rough comparison of metric system charge -1.00 Coulomb to one electron’s charge is this:
one electron is a tiny fraction of -1.00 Coulomb
Charles Coulomb measured very small electrical forces with high precision using a torsion balance which
twists a set amount for each Newton of force
The first electron is the nearest neighbor to the target proton. In what direction is the force of this nearest neighbor on the proton?
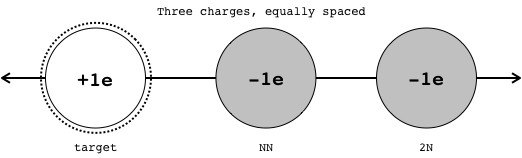
right
If the size of the nearest neighbor force on the proton is 200 nanoNewtons, then how large is the force from the second neighbor (2N) on the proton?
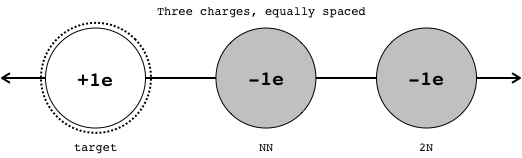
50nN
The unit of electric charge is called a
Coulomb
When you double the distance between the proton and electron, to 2 nanometers from 1 nanometer, the force of attraction is
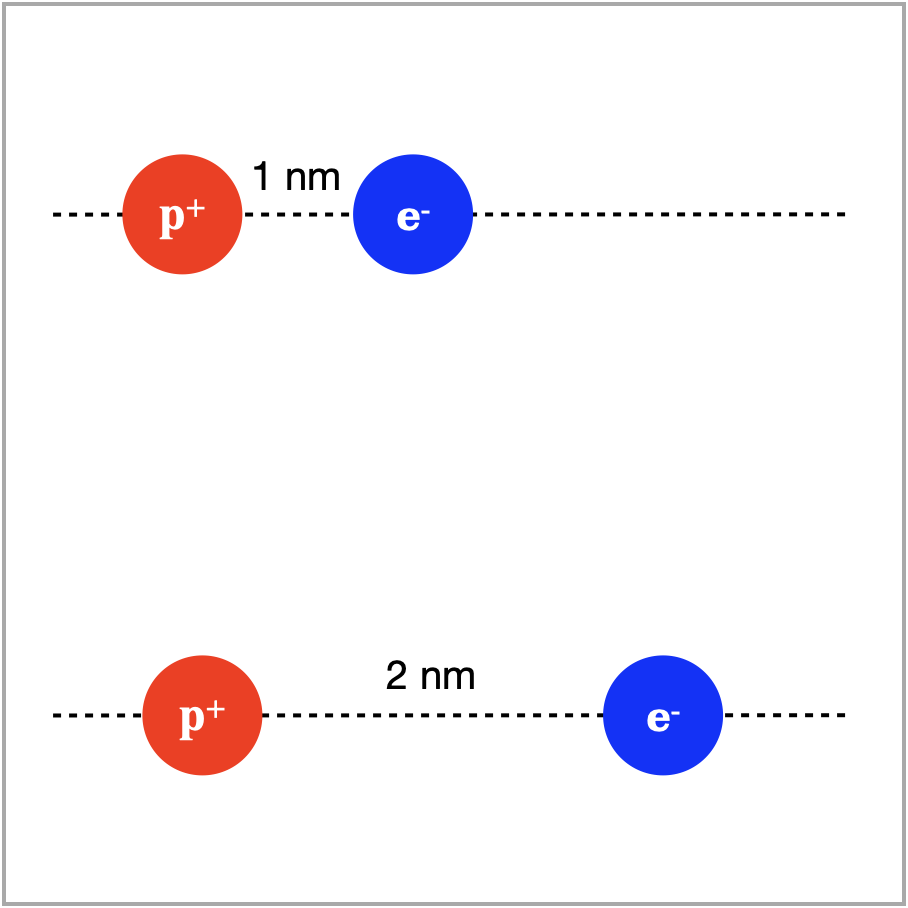
Smaller, 0.0577 nN
If 1.51 x 1020 electrons move through a pocket calculator during a full day’s operation, how many coulombs of charge moved through it?
-24.4
A certain lightning bolt moves +28.0 C of charge. How many fundamental units of charge e is this?
1.75

The nearest neighbor interaction force is 279 nanoNewtons.
Calculate the size of the net force on the leftmost proton.
379.8
As you move positive charges further and further apart, their potential energy?
decreases
What is an electron-Volt?
the energy acquired by an electron across a potential difference of 1 volt
In a region of space, the electric potential decreases uniformly from east to west, and does not vary in any other direction. The electric field:
points west and is uniform
Which is the correct description of electrons and protons?
protons are positively charges, and electrons are negatively charged
For a Feynman diagram, where is time located?
vertical axis
What does the blue line represent in a Feynman diagram?
motion of electrons
Who determined protons were positive?
Ben Franklin
All of quantum field theory is based on?
Feynman diagram
what is the correct description of electrons and protons?
protons attract electrons and repel protons
V=kQ/r
electric potential V of a point charge
V for a point charge decreases with
distance
E for a point chrage decreases with
distance squared
What is the voltage 5.00 cm away from the center of a 1-cm diameter metal sphere that has a -3.00nC static charge?
-539 V
electric potential is
scalar
electric field
vector
additional voltages as numbers gives…
the voltage due to a combination of point charges
addition of individual fields as vectors gives
the total electric field
green lines represent
places where electric potential is constant
electric field lines point where?
radially away from the charge, and are perpendicular to equipotential lines
When is work zero?
force is perpendicular to motion
When is a conductor an equipotential surface?
in static situations
there can be no voltage difference across the surface of a conductor, or charges will flow
TRUE
an equipotential line
a line along which the electric potential is constant
what is a equipotential surface?
a 3D version of equipotential lines
process by which conductor can be fixed at zero volts by connecting it to the earth with a good conductor
grounding
1 N/C equals
1 V/m
voltage points btwn A nd B
Vab= Ed
E=Vab/d
general relationship btwn voltage and electric field is
E= -deltaV/delta s
magnitude of the force on a charge in an electric field is obtained from
F=qE
electric potential per unit charge
V=PE/q
1V=
1 J/C
C x V
J
most common energy unit for submicroscopic processes
electron volt
electrical potential energy will decrease radially inward
kinetic energy increases outward
proton electron (lines of force
electric potential energy will decrease radially outward
proton proton lines of force
arrows are outward, q>0
proton towards proton
arrows point inward q<0
proton towards electron
what is inversley proportional to distance btwn two objects squared?
force
separation of positive and negative charges in a neutral object
polarization
What allows transfer of charge to and from the earth’s large reservoir?
grounding
can objects be charged by contact with another charged object and obtain the same sign charge
yes
what happens if an object is temporarily grounded?
it can be charged by induction and obtain opposite sign charge
polar molecules
have an inherent separation of charge
What is induction?
process by whivh an electrically charged object brought near a neutral object creates a charge in the object
Is the coulomb force stronger compared to gravitational force?
yes
Which can cancel… gravitational or coulomb?
COULOMB
grvaitational force is just
attractive
coulomb force is
attractive or repulsive
How is the electric field defined?
it represents only the source charge and it is unique at every point in space
electric field
E= F/q
electric field depends on whate?
Q (charge) and r (distance)
electric field is independent of…?
test charge q
magnitude of electric field
E=k Q!/ r2