Monopoly
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Characteristics of Monopoly
A monopoly is a market structure in which there is a single seller
There are no substitute products
The firm has complete market power and is able to set prices and control output
This allows the firm to maximise supernormal profit in the short-run
There is no long-run erosion of supernormal profit as competitors are unable to enter the industry
High barriers to entry exist
One of the main barriers is the ability of the monopoly to prevent any competition from entering the market
E.g. by purchasing companies who are a potential threat
The UK Competition and Markets Authority defines a legal monopoly as any firm having more than 25% market share
It acts to prevent this from happening in most industries
Profit Maximising Equilibrium
As a single seller of goods/services, the firm in a monopoly market is also the entire market. Its concentration ratio is CR1=100%
There is no differentiation between the firm and the industry
It is a price maker or price setter
This means that its demand and revenue curves are downward sloping
In order to maximise profits, it produces at the point where marginal cost (MC) = marginal revenue (MR)
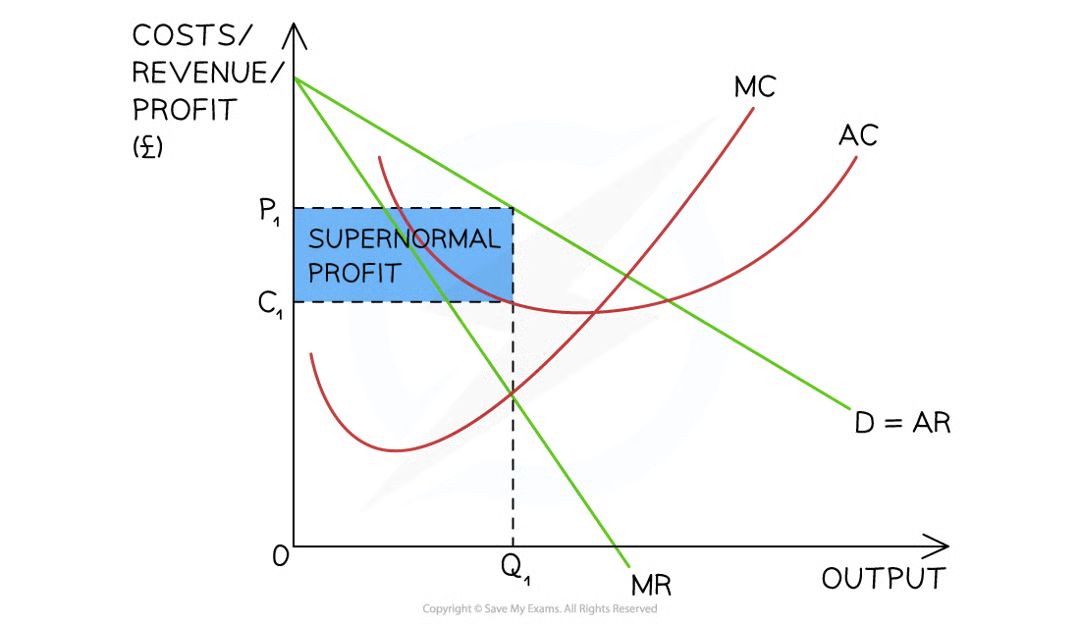
A diagram illustrating a monopoly making supernormal profit in the short-run and long-run as the AR > AC at the profit maximisation level of output (Q1)
Diagram analysis
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output, where MC = MR (Q1)
At this level, the AR (P1) > AC (C1)
The firm is making supernormal profit
(P1-C1)XQ1
When does price degree price discrimination occur?
Price discrimination occurs when a firm charges a different price for the same good/service in order to maximise its revenue
Three degree price discrimination
Third degree price discrimination occurs when a firm charges different prices to different consumers for the same good/service e.g. rail fares are priced differently depending on the time of travel
Markets are often sub-divided based on time, age, income and geographic location
Some airline ticket portals charge higher prices to customers using an Apple computer as they are likely to have higher income
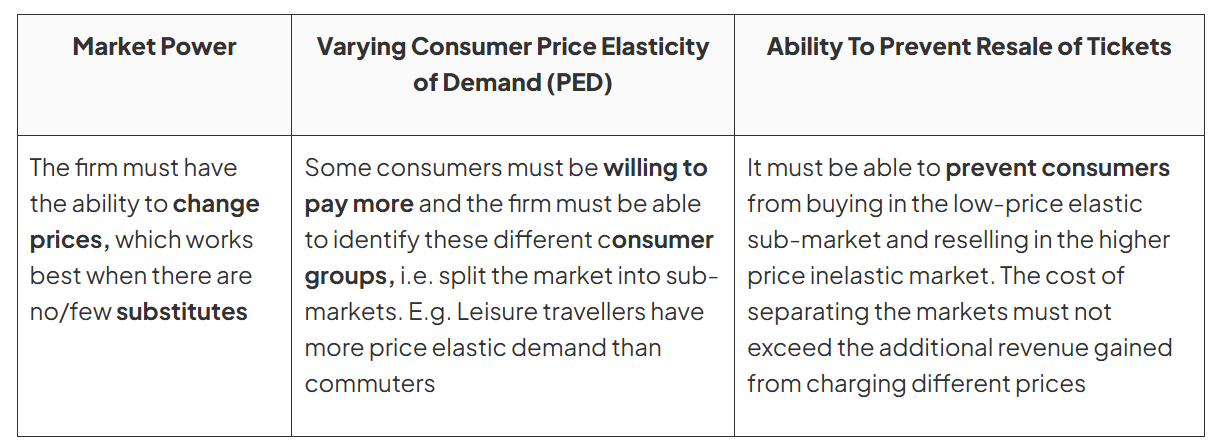
The Following Conditions Must Be Met for Third Degree Price Discrimination to Occur
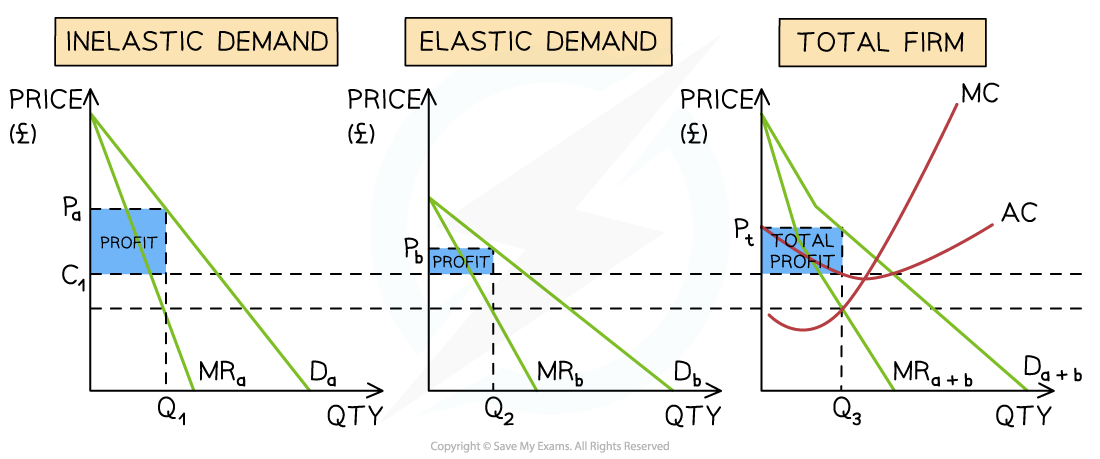
A third-degree price discrimination diagram demonstrates a market that has been divided based on price inelastic (peak travel) and price elastic demand (off-peak travel). Following the revenue rule, prices are raised for peak demand and lowered for off-peak demand
Diagram analysis
Each train route has an effective monopoly provider
The overall firm is producing at the profit maximising level of output where MC=MR
This point is extrapolated to both sub-markets on the left by using the lower dotted line
The average cost is extrapolated across both sub-markets using the upper dotted line (C1)
A higher price for peak travel has been set at Pa and a lower price for off-peak travel has been set at Pb
Following the revenue rule, total revenue increases in both markets
The profit for sub-market A = (Pa-C1) * Q1
The profit for sub-market B = (Pb-C1) * Q2
The firm's total profit is the average selling price - the average costs
Total profit = (Pt-C1) * Q3
The firms' total profits are higher than if they had charged a single price to all customers
Costs and benefits of third-degree price discrimination
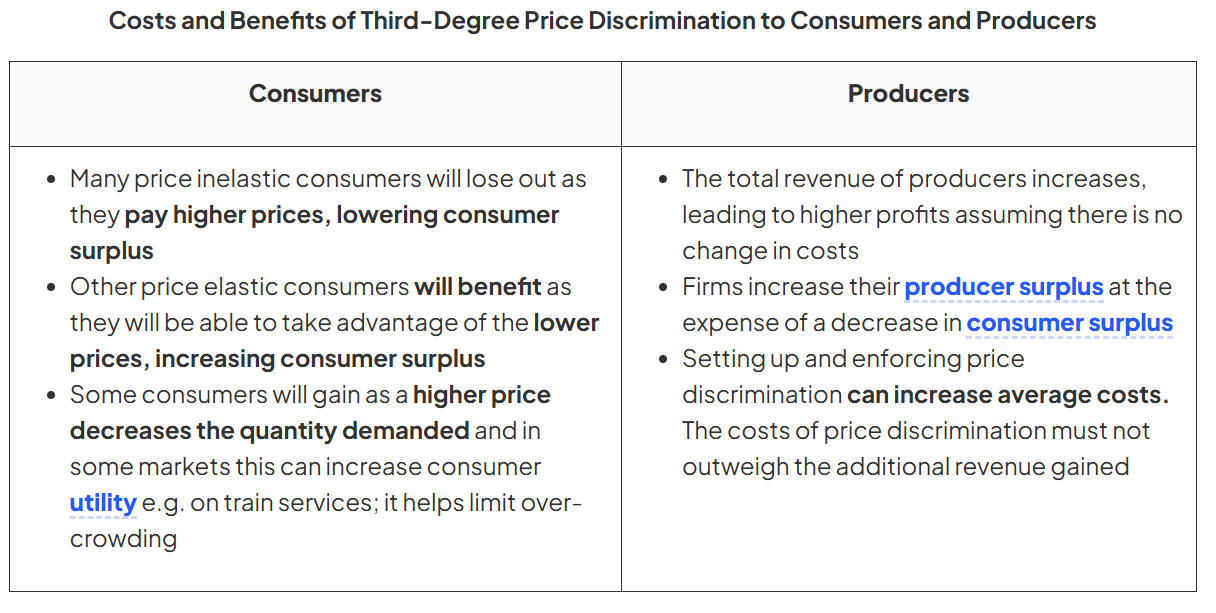
Costs & Benefits of Monopoly
In several instances where the Competition and Markets Authority has acted to decrease/limit monopoly power, firms have taken the Regulator to court to attempt to convince them that the firms market power will benefit consumers
Theoretically this is possible, however, in many cases, the desire to maximise profits would prevent this from happening
The Advantages and Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power
The firm: The Advantages and Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power
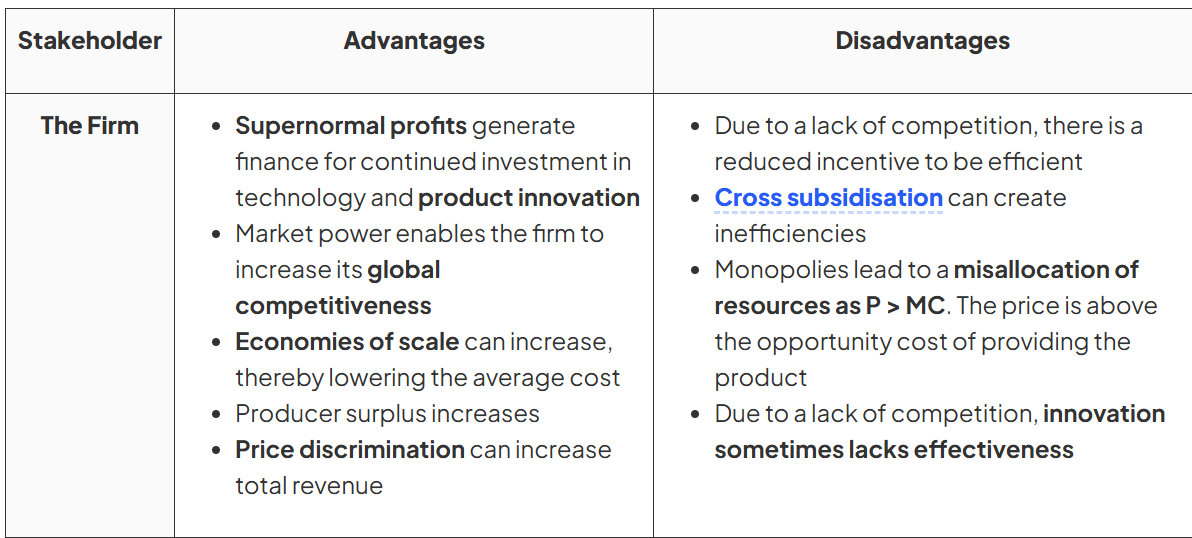
The Advantages and Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power: employees

The Advantages and Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power - consumer
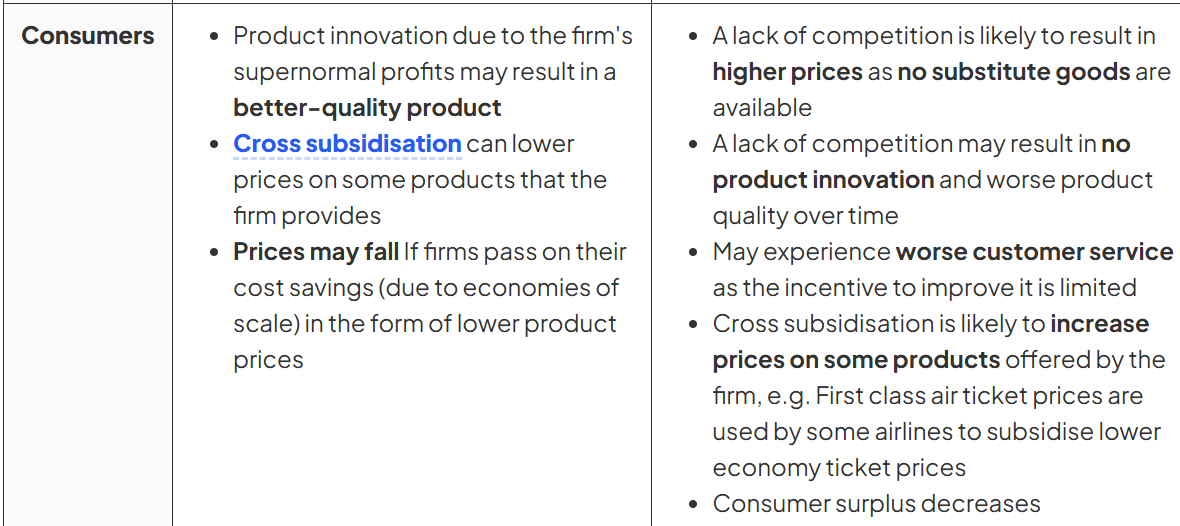
The Advantages and Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power - suppliers

Natural monopoly
A natural monopoly occurs when the optimum number of firms in the industry is one
This is often due to associated infrastructure issues e.g. delivery of utility services like water, where it does not make sense to have multiple pipelines
It can also be due to the significant cost that is generated when entering or exiting the industry, e.g. the sunk costs
It can also be due to the ability of economies of scale to lower prices for consumers, e.g. it makes sense to have one firm building five nuclear power stations as opposed to five firms, as average costs will be lower with one firm constructing
Even one firm in the industry cannot achieve an output at the lowest average cost where AC=MC, productive efficiency. More competition would simply increase average costs, further increasing prices for consumers
When do natural monopolies occur:
Natural monopolies usually occur in utility industries and are regulated by the Government to ensure that consumers are not charged higher monopoly prices
This regulation is often in the form of a maximum price or a price cap
The monopoly model
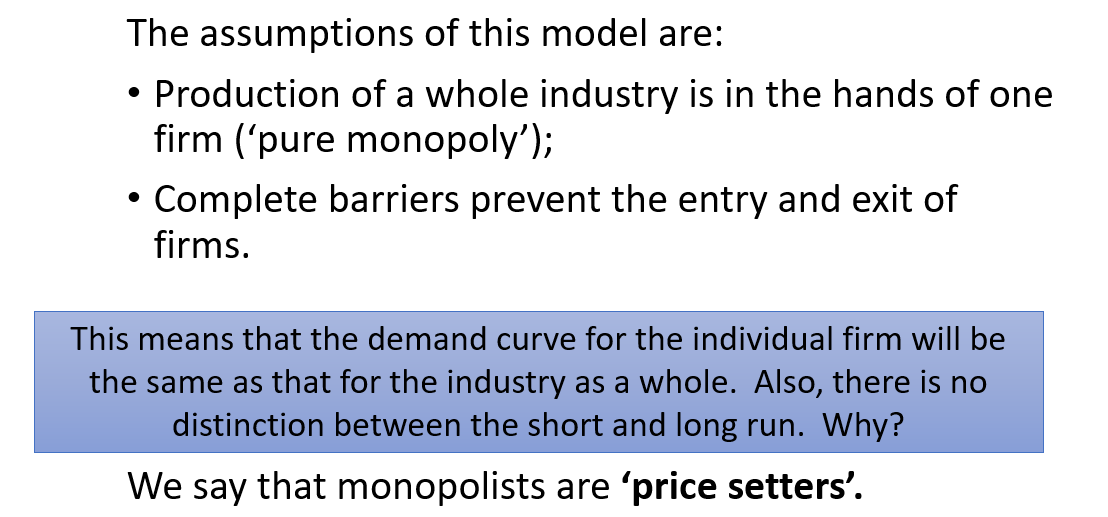
Assumptions – perfect competition vs. monopoly

If markets exist which conform to the monopoly model:


Economic efficiency

X-inefficiency

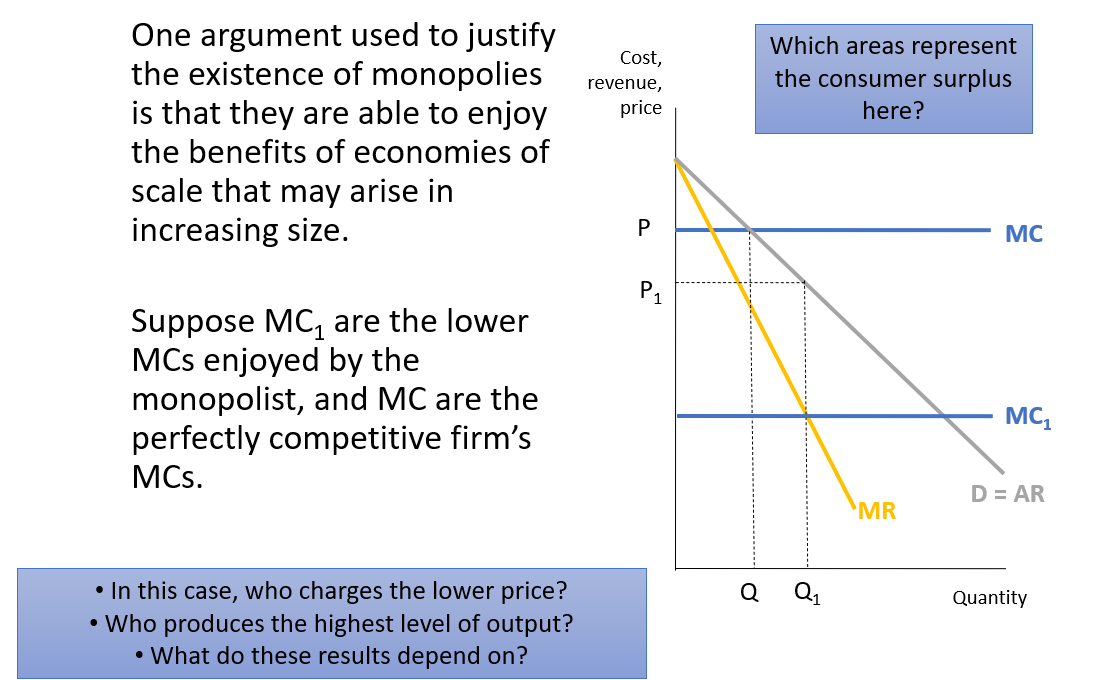
Monopolies and economies of scale
Barriers to entry




How do monopolies arise?
Barriers to entry 1


Barriers to entry 2

Barriers to entry
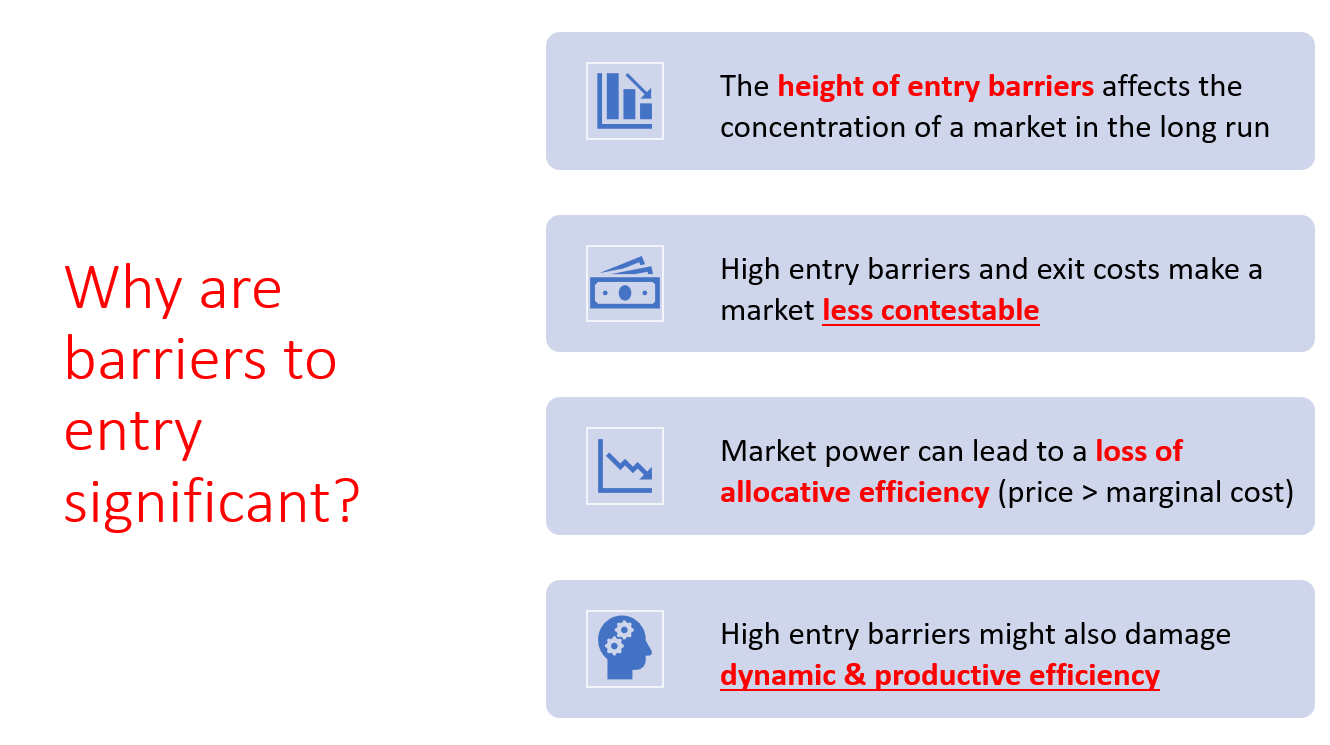
Why are barriers to entry significant?
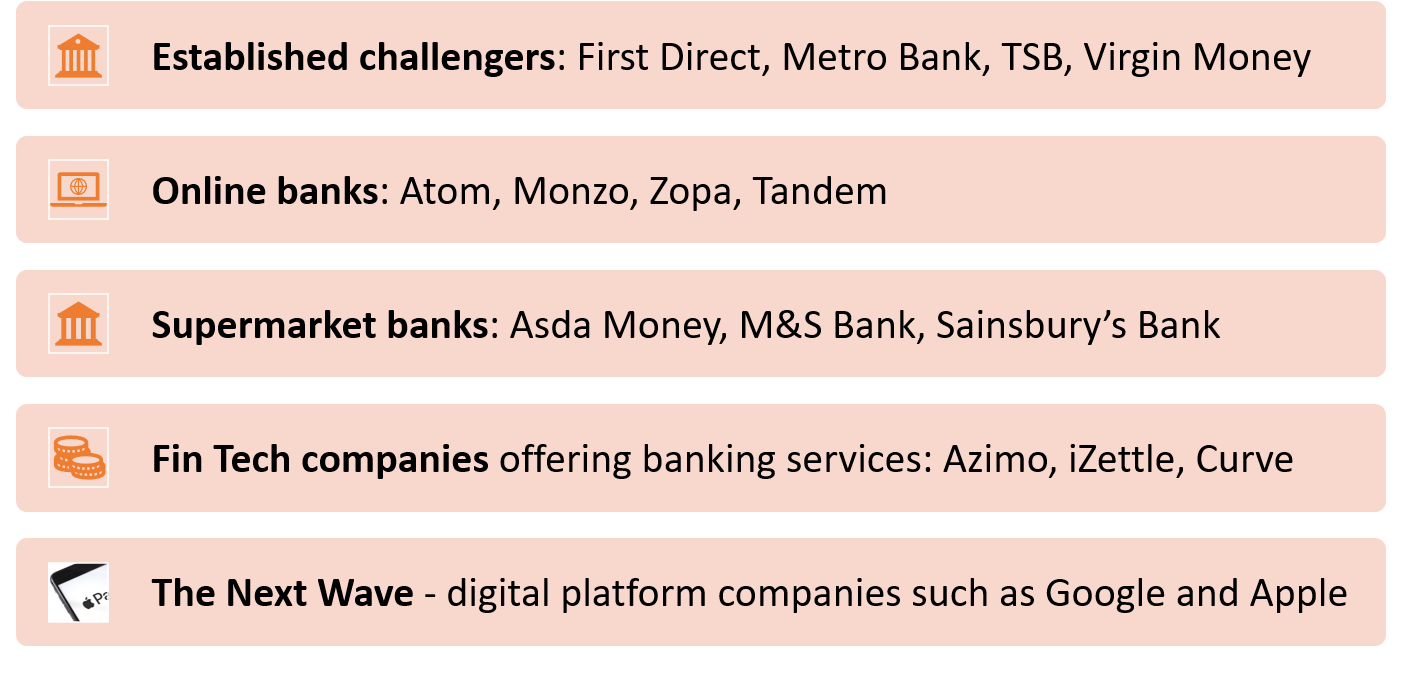
Barriers to entry in commercial banking

First mover advantage

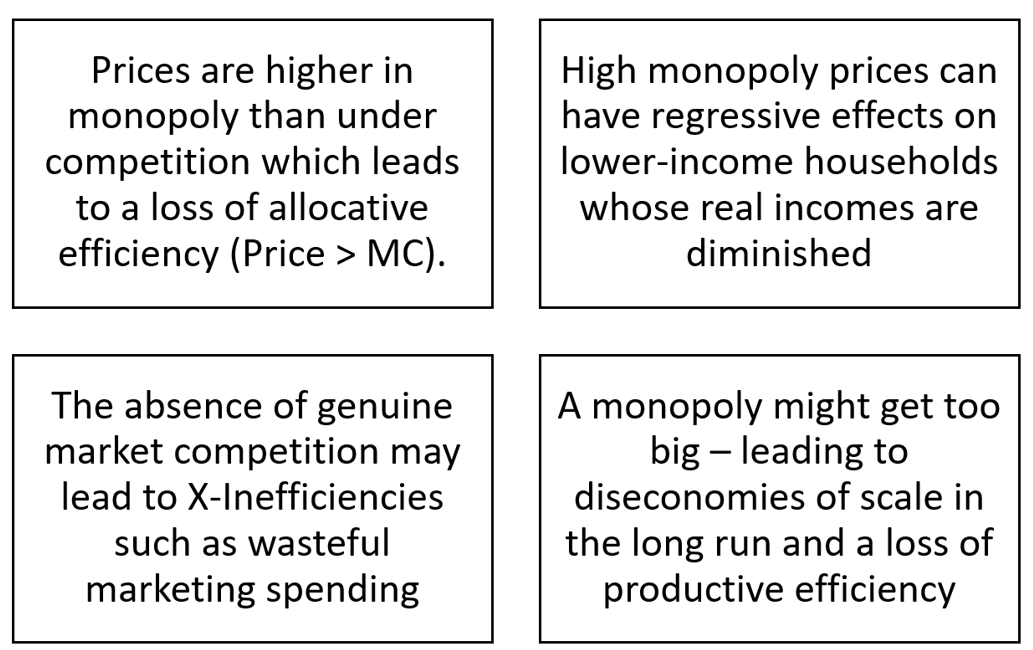
Disadvantages of monopoly power
Potential advantages of monopoly power

price discrimination
Price discrimination happens when a firm charges a different price to different groups of consumers for an identical good or service, for reasons not associated with costs of supply.
Main aims of price discrimination