Chapter 1- components and types of a computer system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:33 AM on 1/30/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
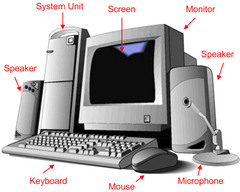
Hardware
the physical parts of a computer
2
New cards
Software
the programs and other operating information used by a computer.

3
New cards
Motherboard
A circuit board that contains all of the computer system's main components.

4
New cards
RAM (Random Access Memory)
is a memory chip in a computer which holds all programs and data when they are in use.

5
New cards
ROM (Read Only Memory)
Chips that contain programming code and cannot be erased.

6
New cards
Internal hard disk drive
Stores data that is not instantly needed for an indefinite time. It also stores programmes and is used commonly to back up data.

7
New cards
CPU (central processing unit)
The central processing unit that is generally made from a single integrated circuit that performs all the processing and calculations.

8
New cards
Fetch-Execute cycle
• Fetch (retrieve) next instruction from memory
• Decode (translate) instruction to work out what it is
• Execute (carry out) the instruction
• Decode (translate) instruction to work out what it is
• Execute (carry out) the instruction
9
New cards
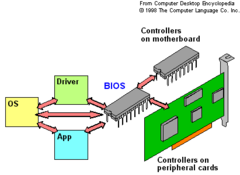
BIOS (basic input/output system)
Firmware that can control much of a computer's input/output functions, such as communication with the keyboard and the monitor.
10
New cards
CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)
A type of non-volatile RAM that holds information about the most basic parts of your PC

11
New cards
OS (Operating System)
An operating system is a system software that manages the general operation of a computer system.

12
New cards
Roles of the OS
● Provides security and prevents unauthorised access to a system
● Allows users to load, run and store applications. Also resolve errors occurring applications
● Decided what should be loaded and deleted from memory
● Helping save, organise, find and delete files
● Manages input, output and backing devices
● Helps the user interact with the computer through a user interface.
● Allows users to load, run and store applications. Also resolve errors occurring applications
● Decided what should be loaded and deleted from memory
● Helping save, organise, find and delete files
● Manages input, output and backing devices
● Helps the user interact with the computer through a user interface.
13
New cards
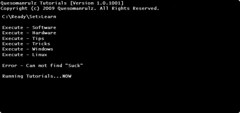
CLI (Command Line Interface)
is a user interface to a computer's operating system or an application in which the user responds to a visual prompt by typing in a command on a specified line, receives a response back from the system, and then enters another command, and so forth.
14
New cards
GUI (Graphical User Interface)
A type of interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation, as opposed to text-based interfaces, typed command labels or text navigation.

15
New cards
phablet
A device that combines the features of a smartphone with a tablet.

16
New cards
mainframe computer
A large, multi-user computer commonly used in large businesses and government agencies; more powerful than a minicomputer.

17
New cards
CAT (computer assisted translation)
a type of language translator that uses software in the translation process
18
New cards
Holography
technique used to make a 3-D image

19
New cards
Input device examples
Keyboard, mouse, speaker, touchscreen, storage device, scanner, microphone

20
New cards
Output device examples
Monitor, printer, storage device, speakers, projector

21
New cards
Keyboard Examples
QWERTY, concept, numeric

22
New cards
Trackerball
A pointing device where a ball on top of the device moves the cursor. Ideal for environments with little space. Users are less likely to suffer injuries such as RSI.

23
New cards
DDE
Direct Data Entry
24
New cards
Magnetic Stripe Reader
Reads data from a special magnetic stripe on a card when it is swiped

25
New cards
Contactless card reader
debit or credit cards that allow customers to pay for items without entering a PIN; a small chip emits radio waves
26
New cards
Chip and PIN readers
Reads the chip inserted in a card which contains information. The user then is asked to input a PIN to access the information.
27
New cards
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)
Input devices that reads simple multiple-choice style answers by looking for marks on the paper.

28
New cards
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
scanning text printed on paper and translating the images into words
29
New cards
barcode reader
An input device that reads barcodes.
30
New cards
Quick Response (QR)
a type of barcode made up of a matrix of filled in dark squares on a lighter background
31
New cards
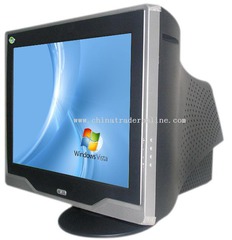
CRT Monitor (Cathode Ray Tube)
desktop monitor that contains a cathode-ray tube
32
New cards
Thin Film Transistor (TFT)
A technology for LCD displays in which transistors are positioned at each pixel.

33
New cards
LCD monitor
A computer monitor that takes advantage of the polarizing properties of liquid crystals to produce images on a screen

34
New cards
LED monitor
Type of monitor which uses LED backlighting to illuminate the colours on the screen.
35
New cards
OLED (Organic Light-emitting Diode) monitor
A type of monitor that uses a thin LED layer or film between two grids of electrodes and does not use backlighting.
36
New cards
laser printer
A printer that produces images using the same technology as copier machines.

37
New cards
inkjet printer
A type of printer that uses a nonimpact process. Ink is squirted from nozzles as they pass over the media.

38
New cards
dot-matrix printer
A type of impact printer that uses small pins to strike an inked ribbon to produce tiny dots on the paper.

39
New cards
3-D printers
A printer that creates objects by adding layers of material onto one another. Also known as additive manufacturing.
