Chapter 9
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what is motive?
internal force that moves us to act in a certain way and not others
what is an instinct?
its a tendency to behave in a particular way
wiliam james believes that humans are… (instinct)
impelled by biologically based motives that are triggered by features of the environment

spiders have the ____ to spin webs and birds to build nest
the instinct

what is homeostasis
the bodys tendency to maintain internal equilibrium through various forms of self regulation
homeostasis can create an internal state of….
biological and psychological tension called a DRIVE

what is drive?
humans have the drive to eat sleep and so on to help them return the body to equilibrium
pain matrix
a network of brain regions (the amygdala)
what does the amygdala do when responding to types of pain
it activates the pain matrix
what is an example of a response
that dread feeling we get whiling waiting for something awful to happen (like getting a shot)
how does pain impact our behavior
it gives us the desire to avoid pain while motivates our behavior
why doe people self harm?
because adding physical pain decreases a far greater psychological pain

intrinsically rewarding
being pursued for its own sake like playing soccer because the experience itself is fun

extrinsically rewarding
being pursued because of rewards that are not inherent part of the activity or object like getting paid to mow the lawn
getting paid to mow the lawn is motivated by….
pleasure associated with the rewarding activity or outcome
rat bar pressing for pleasure is an example of?
extrinsically rewarding
feeling of wanting =
amygdala
feeling of like =
circuit between the nucleus accubens and ventral pallidum
dual center theory
holds 2 center of the hypothalamas, which regulates our feeling of hunger and fullness
hypothalamus acts as…. and ventromedial hypoth. acts as…
hypo- go ventro- stop
humas with more testosterone tend to…
experience higher levels of sexual desire
Bridge test: what’s the independent and dependent variable
Indep: Scary or Normal Bridge
Depend: Calls back to female or TAT for sexual content
Placebo effect
“vitamin supplement” study
motivation can guide..
behavior towards satisfying specific goal
what factors motivation
need: biological or social, failure to satisfy a need leads to psychosocial or physical impairment
incentives
external objects or goals that motivates us (money, fame, respect) Operant Cond.

Sigmund Freud take on pleasure:
pleasure principle: seek pleasure the “Id” biological urges and desires and wanting immediate gratification
what environment influences causes sexual behavior
media: porn
fixed mindset
believing intelligence is fixed so they respond negatively to challenging feedback.
growth mindset
believing intelligence can grow and respond positively about challenging feedback
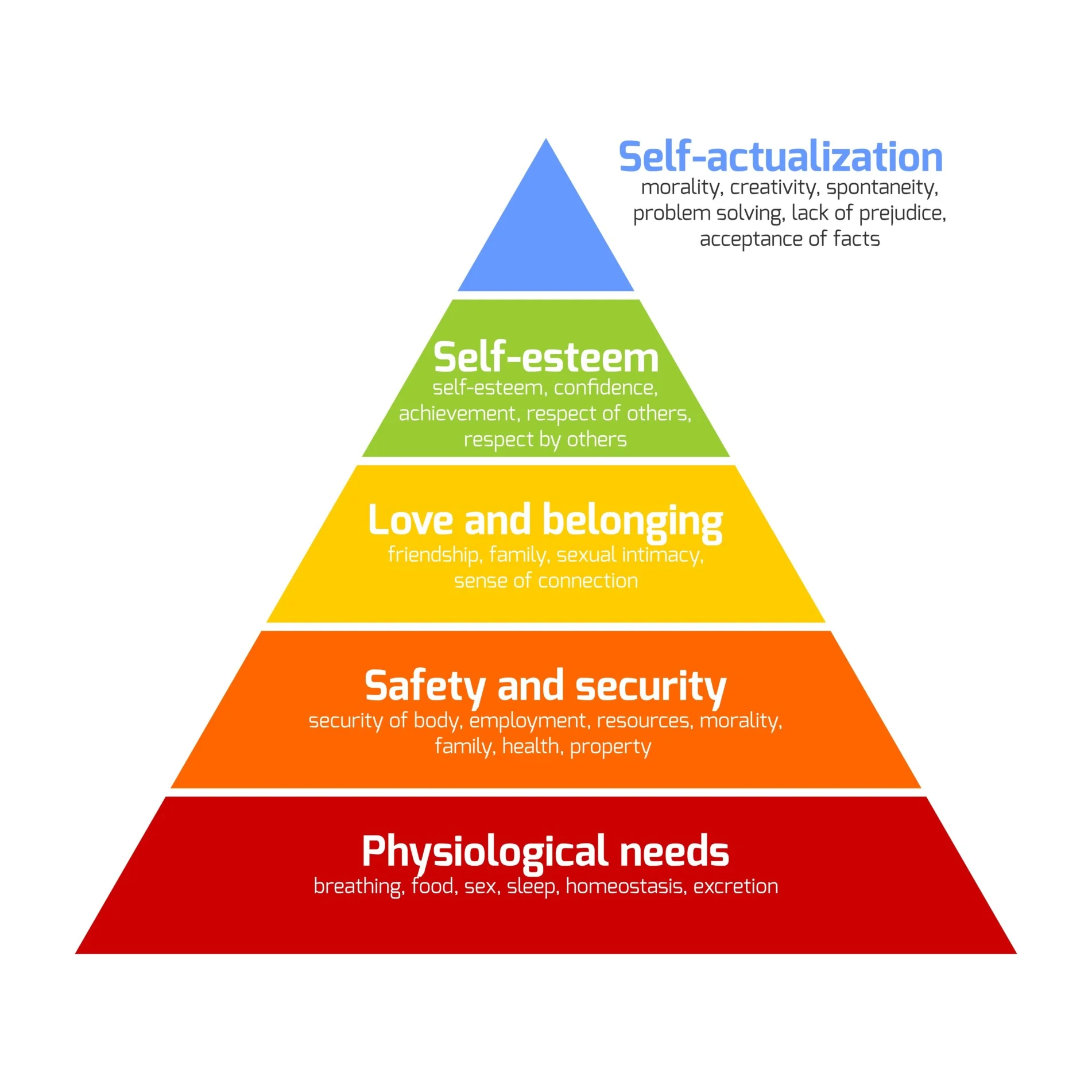
maslows hierarchy of needs
James Lange Theory
Stimulus - Physiological Response - Emotional Experience
Cannon Bard Theory
Stimulus = both physical response and emotional experience
Schachter Singer Theory
Stimulus - Physical Response - Judgement - Emotional response
which theory of emotions suggest that is it not easy to distinguish the bodily changes that accompany different emotions?
the cannon bard theory
affect as information perspective
the idea that affective state plays an important role in shaping problem solving and decision making
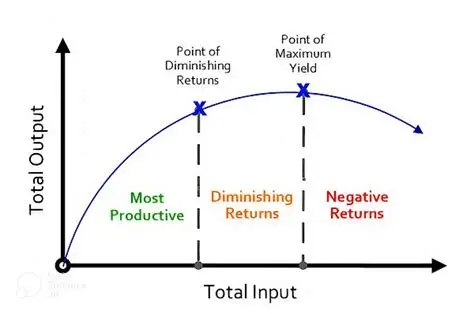
Yerks Dondson law
some arousal is good performance, too much of it leads to bad performance
emotions are
adaptive and change
charles darwin takes in emotions are
emotions are our central player for survival
Cannon Bard theory created the
fight or flight
james lange theory input on facial feedback hypothesis
feedback that face muscles evoke or magnifies emotions
cannon bard theory believed that the mind and body worked…
independently, physical sensation and cognitive perception happen simultaneously
thalamus relays on….
information to the brain and body
thalamus play a role in
how we interpret emotion
limbic system
hypothalamus releases hormones to body for increased arousal, amygdala sends messages to cortex for interpreting experience