Marine Science Final
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
emphasis on section three - key themes and topics from sections 1-2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
What are Nekton?
Free swimmers in the animal kingdom
Large size means ______ abundance.
low
What are the major groups of Nekton?
large invertebrates
fishes
ocean-living reptiles
marine birds
marine mammals
What are three issues all nekton have adapted to solve?
They are large and have to swim through the ocean without sinking
They must deal with stressors in the ocean such as cold temps, high salinity, high pressure, and an abundance of life at depth
they must be able to find food, avoid predators, and reproduce
How have nekton adapted to swimming without sinking?
Streamlining to reduce drag
Fins for locomotion, balance, and lift
Buoyancy mechanisms
Describe four buoyancy mechanisms
swim bladders which hold gases
storing blubber → reduce density to increase flotation (whales and seals)
oil storage in livers and muscles (sharks and fish)
sea birds have light bones, air sacs, and oil on feathers to seal air against skin
What are five adaptations nekton may have to deal with stressors in the ocean?
countercurrent heat exchange to maintain temps
cold and warm blood vessels run next to each other minimizing heat loss
regulating salt content
dealing with high pressure at depth (wax or fat lined bladders and bio-compounds)
obtaining oxygen and removing CO2 with gills
What are four adaptations nekton may have to find food, avoid predators, and reproduce?
schooling provides protections, foraging success, saves energy, and increases reproductive success.
migrations (both diel vertical and horizontal)
dispersal of offspring through a planktonic stage
camouflage
What are Anadromous fish
born and lay eggs in freshwater but spend juvenile period in ocean
what are catadromous fish
born and lay eggs in ocean but spend most of life in freshwater
what is countershading?
a form of camo, looking dark when viewed from above and light when viewed from below
what is bioluminescence?
a form of camo or startling predators, making your own light
most fish are found in areas of high/low primary productivity
high
what are adaptations deep sea fish have
large mouths
hinged jaws
needle like teeth
extendable stomachs
bioluminescence
stay small and float to conserve energy/able to go long periods without a meal
Nekton are autotrophs/heterotrophs in __________trophic levels
heterotrophs, middle to upper
how are nekton supported
mainly by planktonic production consumed by zooplankton
nekton are often top ______
predators
which group of marine organisms are able to swim against the currents?
Nekton
Regions with greater fish abundance and catches are generally associated with lower/greater GPP?
Greater
Benthos
bottom dwellers
Why is there tremendous diversity among benthos?
numerous habitats and niches to fill
What are infauna?
animals that live in the sediments
what are Epifauna?
animals that live on or attached to the seafloor
What are sessile’s?
animals not able to move
What are suspension feeders?
animals that feed on particles in the water
what are filter feeders?
animals that actively filter particles from the water
What are deposit feeders?
Animals that ingest sediment and extract organic matter
what are detritivores?
animals that ingest detritus
What are scavengers?
Animals that search for carcasses and other organic matter
What do most benthos rely on for food?
rain of organic matter or food falls
Where is the highest biomass of benthos?
below areas of highest pelagic productivity and in productive coastal regions
Many benthic organisms have a ___________ stage allowing dispersal
planktonic
What are meroplankton?
spend only part of their lives in the plankton
what are some adaptations of seaweeds and marine plants?
holdfast and stape to stay anchored
pigments in green, brown, and red algae help maximize use of light over depth
what is the role of seaweeds and marine plants in the benthos habitat?
they provide food and shelter for animals, most food enters as detritus
What is the rocky intertidal habitat of benthos
highly energetic and rapidly changing conditions over tidal cycles
What do organisms have to face in the upper zone of the rocky intertidal?
Exposure to stressors such as drying/wetting, temp, salinity, moisture, pH, DO, and food supply, AND predation
What do organisms have to face in the lower zone of the rocky intertidal?
organisms must compete for space and deal with predation
An organisms ability to cope with stresses results in __________ zonation in the intertidal
vertical
Why are coral reefs so productive?
Symbiosis of photosynthetic dinoflagellates living inside the heterotrophic coral animal
Why are hydrothermal vents so productive?
Chemosynthetic communities - symbiosis between tube worms and bacteria
“Benthic” refers to which region of the ocean?
The seafloor
Benthic animals include:
Herbivores
Carnivores
Omnivores
Detritivores
All of the above
all of the above
Organic matter that fuels benthic organisms originates from:
sinking phytoplankton
marine snow
benthic plants and algae
detritus
food falls
all of the above
all of the above
Organisms that feed on particles in the water column are called:
Suspension feeders
Organisms that ingest sediments and digest the associated organic matter are called:
Deposit feeders
What strategy do benthic organisms use to widely disperse their offspring?
Larval stages in the plankton
What are the most common water waves and what are they generated by?
short period waves generated by winds
What is wavelength?
The distance between adjacent crests and troughs
What is wave height?
elevation from trough to crest
energy moves in a ______ direction
linear
water moves in ______
orbits - circular paths
In waves there is _____ net water transport
zero
Wavelength (L) / 2 =
the wave base
Is there motion when depth = L/2?
no
deep water waves
depth > L/2
Shallow water waves
depth < L/20
Transitional waves
L/20 < depth < L/2
In shallow waves orbits become ______ with depth
flatter
at the bottom of shallow water waves water moves ______ & ______
back & forth
Longer waves move slower/faster than shorter waves
faster
Sorting/Dispersion
longer waves move ahead of the shorter waves with distance from the source
Swells
the pattern of crests and troughs formed by longer waves
what is wave height affected by?
wind speed
wind duration
fetch
Fetch
the distance over water that the wind blows in the same direction
Wave energy increases/decreases rapidly with wave height
increases
why does the southern ocean have the largest waves?
less land and lots of storms
what is wave refraction
bending of the waves when they hit at an angle to depth contours
Waves are focused on __________ and refracted towards the edges of _________
headlands, embayments
What is wave reflection
the wave bounces off at the same angle it hit
what is wave diffraction
the spread of wave energy laterally around an obstacle
what is the surf zone
waves slow, steepen, and break at the coast as the shallow-water waves “feel bottom”
Rip currents
waves slowly pile water up along the beach which rushes back out at particular points
Tsunamis are produced by _________ action and can travel across entire _____ _________
seismic , ocean basins
Internal waves
develop along density interfaces within the ocean
Seiches/standing waves
do not progress but reflect back on themselves across an entire body of water
four types of long period waves
tsunamis
standing waves/sieches
tides
internal waves

what feature is marked with the arrow?
wavelength
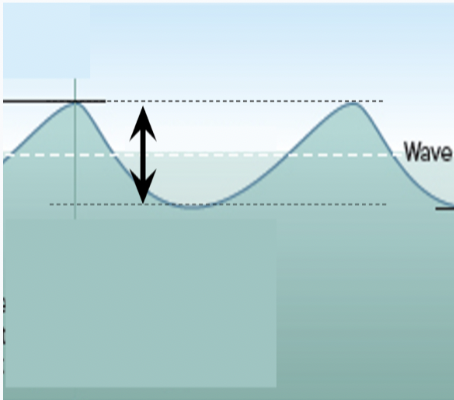
what feature of the wave is marked with the arrow?
height
The time it takes for two successive wave crests to pass a point is called the ___________
period
as depth increases, size of wave orbits
decrease
which statement is true about deep water waves?
wave base is shallower than water depth
wave base is deeper than water depth
wave base and water depth are equal
wave base is shallower than water depth
what happens to shallow water waves as they approach the coast?
orbitals flatten, the bottom of the wave drags along the bottom, friction with the bottom can change wave direction, the wave slows, steepens, and eventually breaks
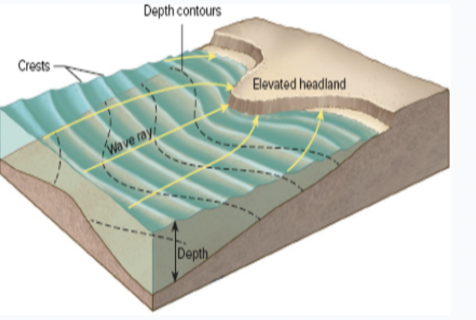
what process is shown in the figure
wave refraction
waves that travel along the pycnocline are called
internal waves
Tides are generated by ________ forces and ______
gravitational, inertia
what is the tide range
the difference in water level from high to low tide
what is the flood tide
period when water level is rising, resulting in flood currents
what is the ebb tide
the period when water level is falling, resulting in ebb currents
what is slack tide
the period of slow or zero tidal currents at high and low tide
Diurnal tides
one high tide and one low tide per day
Semidiurnal tides
two high tides and two low tides per day (of equal height)
Semidiurnal mixed tides
two high and two low tides per day of unequal height
How long is a tidal day
24 hours and 50 min
how long is a tidal period
12 hours and 50 min
spring and neap tides are caused by what
gravitational attraction by the sun
how many spring and neap tides are there per month?
~2
what are spring tides
occur during new and full moons when the sun, earth, and moon are aligned
neap tides
tides with the smallest difference between high and low water levels
what leads to tidal patterns
declination of the moon and sun