The Skin & Body Membrane
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/109
Last updated 4:34 PM on 2/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
sheets of tissue
Function:
covers and lubricate body
line body cavities
form protective sheets around body organs
Types:
epithelial membrane
connective membrane
covers and lubricate body
line body cavities
form protective sheets around body organs
Types:
epithelial membrane
connective membrane
2
New cards
subcutaneous
just under the skin
3
New cards
dermal
on top of the skin
4
New cards
integument
the skin when it is considered as a body organ
5
New cards
integumentary system
the skin when it is considered as a body system
6
New cards
function of the integument
regulation of body temp.
protects body tissues from injury
acts as a physical barrier to prevent germs from entering the body
aids in vitamin D synthesis
elimination of waste products
provides for sensations; touch, pressure, warmth and cold
provides protection from UV light
permits the absorption certain drugs and other chemicals
protects body tissues from injury
acts as a physical barrier to prevent germs from entering the body
aids in vitamin D synthesis
elimination of waste products
provides for sensations; touch, pressure, warmth and cold
provides protection from UV light
permits the absorption certain drugs and other chemicals
7
New cards
cutaneous
What kind of membrane is the skin?
8
New cards
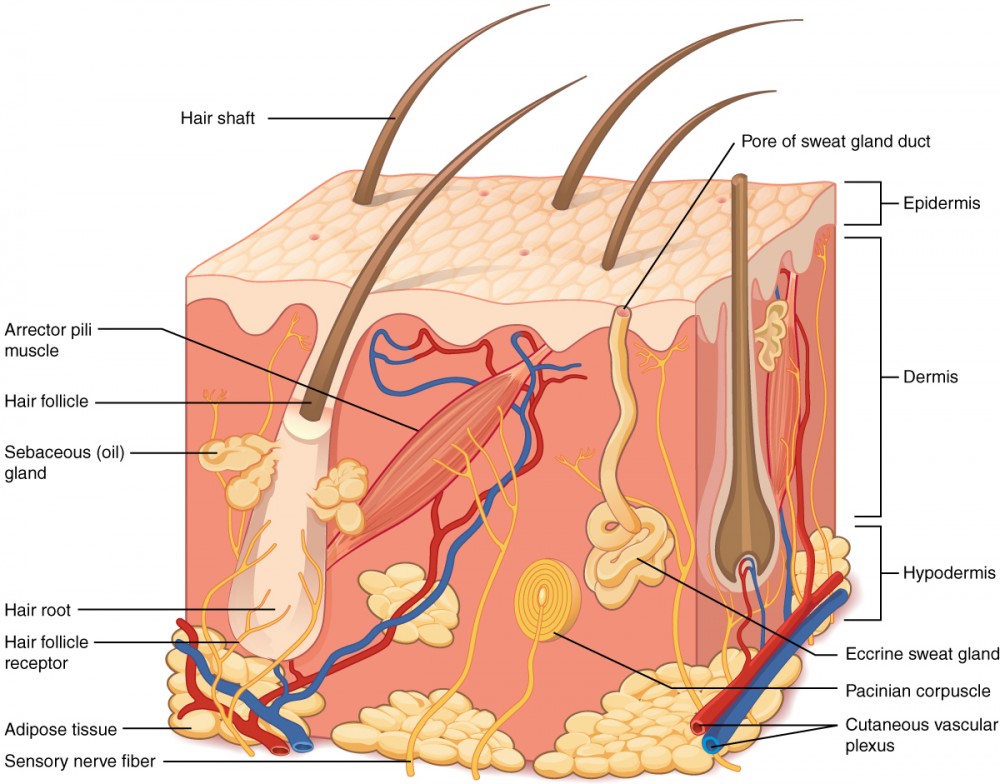
epithelial membrane
consists of:
epithelial & connective tissue
each component represents a main division of the skin
epithelial & connective tissue
each component represents a main division of the skin
9
New cards
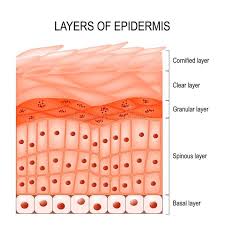
epidermis
consists entirely of stratified squamous epithelium
consists of subdivisions which are represented by layers of cells making up the SSE
consists of subdivisions which are represented by layers of cells making up the SSE
10
New cards
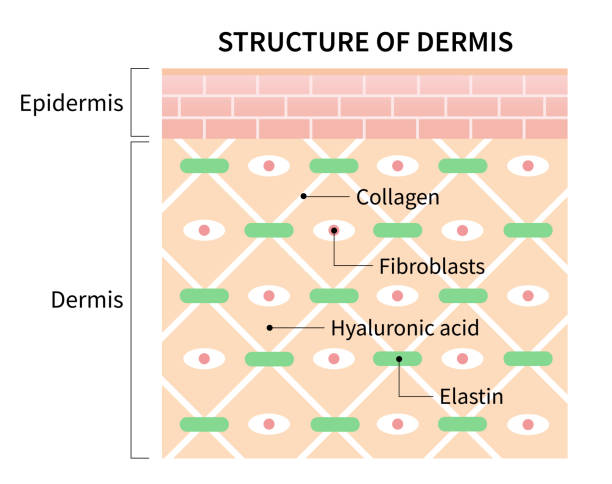
dermis
composed of connective tissue containing collagen and elastic protein fibers; also contains blood vessels, nerves, glands and hair follicles
11
New cards
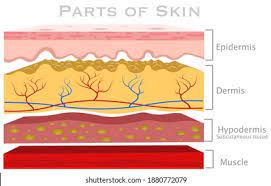
hyodermis
AKA. subcutaneous layer/ superficial fascia
NOT a division of the skin
connects the dermis to underlying bones and muscles
composed of areolar and adipose connective tissue
hypodermic injection/needle
NOT a division of the skin
connects the dermis to underlying bones and muscles
composed of areolar and adipose connective tissue
hypodermic injection/needle
12
New cards
avascular
Is the division of the epidermis vascular or avascular?
13
New cards
stratum germinative
germinating layer; made up of cells attached to the basal lamina which is very mitotically active & replaces cells lost in the upper layers
14
New cards
stem cells
What are the cells in the stratum basal referred to as?
15
New cards
stratum spinosum
spiny layer; consists of the next several layers of cells; cells begin to shrink; mitotically active of the cells slows
16
New cards
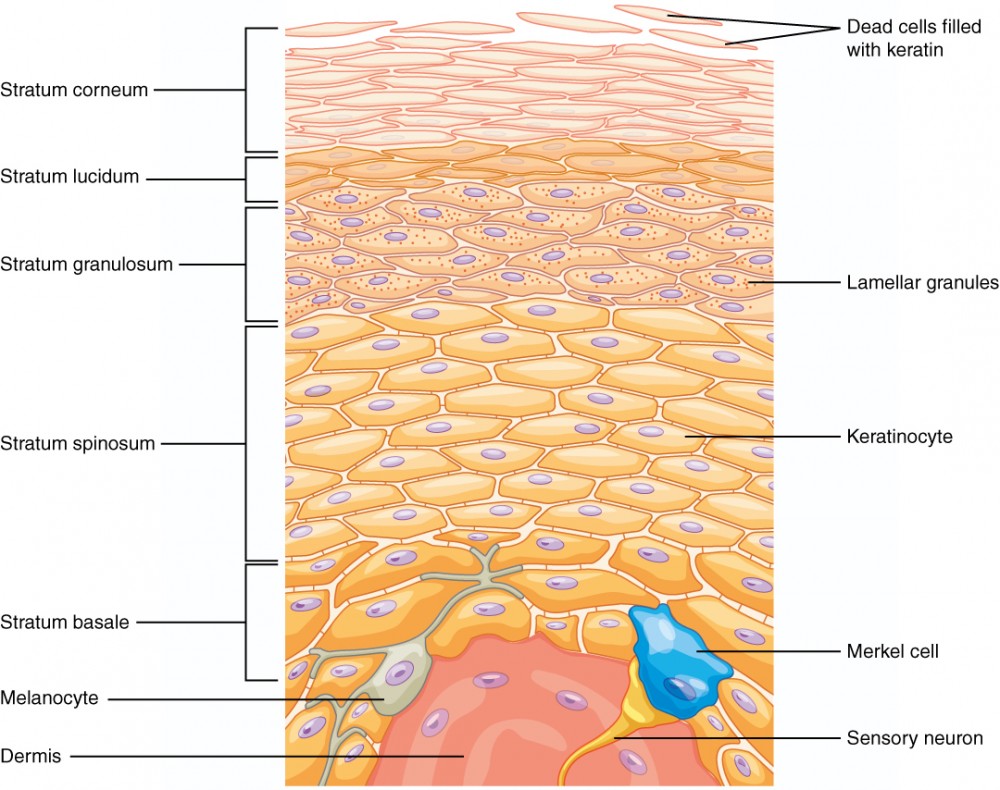
corneum
lucidum (thick skin)
granulosum
spinosum
stratum basal
lucidum (thick skin)
granulosum
spinosum
stratum basal
What are the layers of the epidermis?
17
New cards
stratum basal
What is the most nourished epidermal layer b/c of the nutrients diffusing it from the dermis?
18
New cards
stratum granulosum
granular layer; 1-3 cell layers; mitotic activity stops; cells begin to manufacture the protein keratohyalin
19
New cards
stratum lucidum
clear layer; present only in thick skin; keratohyalin leads to production of the protein eleidin; cells are densely packed and flattened and do not contain nuclei
20
New cards
eleidin
product of the amino acid complex; not alive; deposited in form of the minute granulars
21
New cards
stratum corneum
horny layer
outermost division
20-30 cells layers
comprises 75% of the epidermal thickness
plasma membrane thickens- reduces permeability and water loss
eleidin is converted to keratin- a very strong waterproof protein
outermost division
20-30 cells layers
comprises 75% of the epidermal thickness
plasma membrane thickens- reduces permeability and water loss
eleidin is converted to keratin- a very strong waterproof protein
22
New cards
25-45 days
How long does it take for a totally new epidermis?
23
New cards
bacteria & viruses from blood
What does the corneum prevent?
24
New cards
stratum corneum
Where is keratin abundant in?
25
New cards
stratum corneum
What layer is replaced by a deeper layer?
26
New cards
epidermal ridges
deep layers of the epidermis which extend into dermis below
contain nerve receptors that provide sensitivity to change
contain nerve receptors that provide sensitivity to change
27
New cards
melanocytes
pigment cells that are squeezed between the cells of the S. germinativum; manufactures the inclusion melanin
28
New cards
melanin
produces skin tone; provides protection from UV light
29
New cards
Merkel’ cells
large, oval cells located in the S. basal
associated with touch (have sensory nerve endings)
associated with a highly malignant skin tumor
associated with touch (have sensory nerve endings)
associated with a highly malignant skin tumor
30
New cards
Langerhans cells
macrophages used in the body’s defense against microorganisms
located primarily in the S. spinosum
located primarily in the S. spinosum
31
New cards
dermis
(deep layer); composed of connective tissue containing collagen and elastin protein fibers; contains blood vessels, nerves, glands, and hair follicles
32
New cards
lamellar corpuscle
deep pressure receptors gets activated when their is deep pressure
33
New cards
papillary region
superficial region characterized by papillae
34
New cards
papillae
fingerlike projections located between the epidermal ridges; uneven peg-like projections
35
New cards
reticular layer
the deep layer of connective tissue that contains both collagen and elastic fibers
36
New cards
hypodermis
not a division of skin
connects dermis to underlying bones and muscles
composed of areolar and adipose connective tissue
connects dermis to underlying bones and muscles
composed of areolar and adipose connective tissue
37
New cards
hair
consists of the fibrous protein keratin; vellus, intermediate, terminal, lanugo
38
New cards
vellus
peach fuss
39
New cards
intermediate
hair of the arms and legs
40
New cards
terminal
heavy, dark hair (head, eyebrows, and eyelashes)
41
New cards
lanugo
the very fine hair that covers a newborn infant- shed shortly after birth
42
New cards
shaft
the visible portion above the skin surface
43
New cards
root
portion below the skin surface
44
New cards
follicle
the socket which surrounds the hair; consists of stratified squamous epithelium
45
New cards
bulb
an onion-shaped swelling located at the base of the hair
46
New cards
papilla
the indentation at the bottom of the follicle; it contains blood vessels and nerves
47
New cards
matrix
a layer of germ cells that produce new hairs
48
New cards
medulla
the soft, flexible center of the hair; contains soft keratin (cross-section)
49
New cards
cortex
a region of hard keratin that surrounds the medulla; gives the hair stiffness (cross-section)
50
New cards
cuticle
a layer of hard keratin that coats the hair (cross-section)
51
New cards
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle in the dermis that is attached to both the hair follicle and skin
its contraction causes “goosebumps” and hair to stand up
connect each side of the hair follicle to the dermal tissue
its contraction causes “goosebumps” and hair to stand up
connect each side of the hair follicle to the dermal tissue
52
New cards
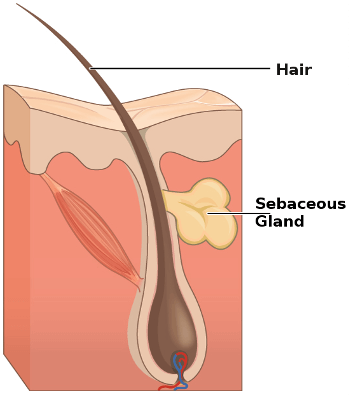
sebaceous glands
produce sebum, oil /holocrine glands, found everywhere except the the palms of hands and soles of feet
ducts usually empty into a hair follicle, but some open directly onto the skin
ducts usually empty into a hair follicle, but some open directly onto the skin
53
New cards
sebum
mixture of oily substances fragmented cells
lubricate that keeps the skin soft and moist and prevents the hair from becoming brittle
contains chemical that kill bacteria present on the skin surface
lubricate that keeps the skin soft and moist and prevents the hair from becoming brittle
contains chemical that kill bacteria present on the skin surface
54
New cards
sebaceous follicles
ducts that lead to pores in the skin
55
New cards
sudoriferous glands
secrete sweat/perspiration; apocrine and eccrine
56
New cards
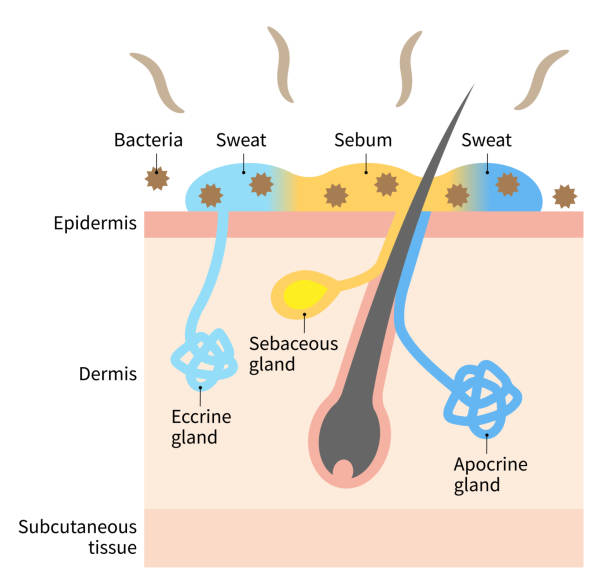
apocrine
ducts empty into hair follicles
are largely confined to the axillary (armpit) and genital areas
plays a minimum role in thermoregulation
secretion contains fatty acids and proteins
activated by nerve fibers during pain and stress
are largely confined to the axillary (armpit) and genital areas
plays a minimum role in thermoregulation
secretion contains fatty acids and proteins
activated by nerve fibers during pain and stress
57
New cards
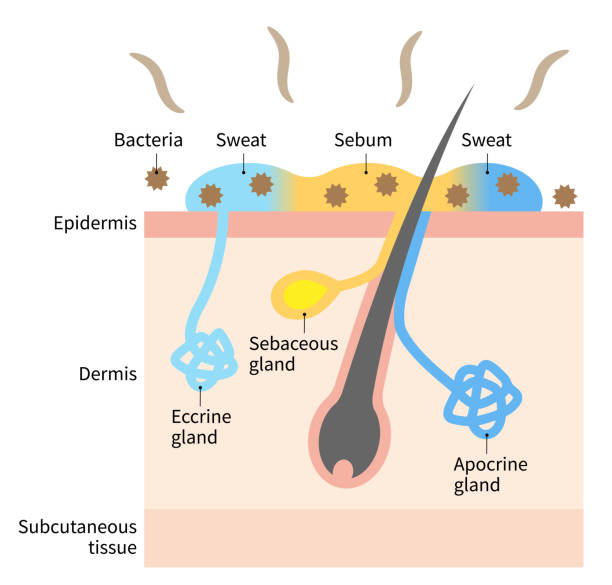
eccrine
produce sweat
highly important and efficient part of the body’s heat-regulating equipment
supplied with nerve endings that cause them to secrete sweat when the external/body temperature is high
open directly to pores
2-5 million
highly important and efficient part of the body’s heat-regulating equipment
supplied with nerve endings that cause them to secrete sweat when the external/body temperature is high
open directly to pores
2-5 million
58
New cards
eccrine glands
What do these functions describe?
cool the surface of the skin to reduce body temperature
excretion of water and electrolytes
cool the surface of the skin to reduce body temperature
excretion of water and electrolytes
59
New cards
apocrine glands
What does this describe?
coiled, tubular glands that secrete a sticky, cloudy and potentially odorous perspiration into hair follicles
coiled, tubular glands that secrete a sticky, cloudy and potentially odorous perspiration into hair follicles
60
New cards
nails
hard plates of tightly packed keratinized cells
clear
cover the dorsal surface of the last phalanges of fingers and toes
protect the ends of fingers and toes
clear
cover the dorsal surface of the last phalanges of fingers and toes
protect the ends of fingers and toes
61
New cards
body
the visible portion of the nail
62
New cards
root
an epidermal fold that is not visible from the surface
63
New cards
nail bed
the area of the epidermis covered by by the nail body
64
New cards
eponychium
cuticle- a region of stratum corneum covering the nail body near the root
65
New cards
lunula
a pale, crescent-shaped area near the root
66
New cards
hyponychium
an area of thickened stratum corneum beneath the free edge of the nail
67
New cards
thermoregulation
refers to the body’s ability to maintain a homeostatic balance between heat production and heat loss
68
New cards
hypothalmus
the body’s thermostat (inter brain; diencephalon)
set to 36.5 degrees C to 37.8 degrees C
maintained via heat loss and heating mechanisms
set to 36.5 degrees C to 37.8 degrees C
maintained via heat loss and heating mechanisms
69
New cards
heat promoting
Is vasoconstriction a heat promoting or loss mechanism?
70
New cards
heat loss
Is vasodilation a heat promoting or loss mechanism?
71
New cards
vasoconstriction
sweat glands close
shivering (muscle contract)
reduces speed of heat loss
goosebumps & hair stand on end
blood vessel size reduces
shivering (muscle contract)
reduces speed of heat loss
goosebumps & hair stand on end
blood vessel size reduces
72
New cards
vasodilation
sweat glands open
allows for water to come to surface of skin and evaporate
opening of blood vessels (expands the lumen)
allows for water to come to surface of skin and evaporate
opening of blood vessels (expands the lumen)
73
New cards
above normal
Does this describe temp. above/below normal:
sweat glands activated, pores open
increased blood flow to skin
allows for evaporation
sweat glands activated, pores open
increased blood flow to skin
allows for evaporation
74
New cards
below normal
Does this describe temp. above/below normal:
sweat glands inactivated
pores closed
decreased blood flow to skin
sweat glands inactivated
pores closed
decreased blood flow to skin
75
New cards
1. heat
2. radiation
3. electric shock
4. chemical agents (acids & bases)
What are the 4 reasons for a burn?
76
New cards
partial thickness
first degree burns
second degree burns
second degree burns
77
New cards
full thickness
third degree burns
78
New cards
head= 4.5%
arms= 4.5%
truck= 18%
legs= 9%
perineum= 1%
arms= 4.5%
truck= 18%
legs= 9%
perineum= 1%
Explain rule of 9s
79
New cards
first degree burns
affect only the epidermis
red, tender, dry, absent of blisters'
mild sunburn
scaring does not occur
2-3 days of discomfort
red, tender, dry, absent of blisters'
mild sunburn
scaring does not occur
2-3 days of discomfort
80
New cards
second degree burns
affect epidermis and parts of the dermis
red, blistered, painful, possible swelling, may be moist
liquid burns, severe sunburn
red, blistered, painful, possible swelling, may be moist
liquid burns, severe sunburn
81
New cards
third degree burns
affect the epidermis and all of the dermis; often also involves hypodermis
appears white or charred
no pain
chemical or electrical burns
appears white or charred
no pain
chemical or electrical burns
82
New cards
nerve endings are destroyed
Why do 3rd degree burns have no pain?
83
New cards
sufficient epithelial cells still present regeneration of epithelium can occur
How is infection prevented for 2nd degree burns?
84
New cards
wounds
injuries that result in an internal or external break in the skin
85
New cards
incision
a clean precise cut
glass, knife, papercut, scapel
glass, knife, papercut, scapel
86
New cards
laceration
similar to incision, but has jagged edges
splitting skin, rock, picked scab, animal bite, knocking body
splitting skin, rock, picked scab, animal bite, knocking body
87
New cards
abrasion
epidermis is rubbed or scrapped away; exposing knee with blood vessels
rug/brush burn, skinned knee
rug/brush burn, skinned knee
88
New cards
puncture
an object pierces the skin with little bleeding
nail, splinter
nail, splinter
89
New cards
avulsion
a portion of the skin is ripped or torn away
blisters
blisters
90
New cards
contusion
a cluster of broken capillaries caused by a blunt blow of the skin
bruise
bruise
91
New cards
tumors
neoplasm- new and abnormal growth of tissues
out of control rapid mitotic division when an unnecessary that have undergone some type of mutation
out of control rapid mitotic division when an unnecessary that have undergone some type of mutation
92
New cards
benign
tumor remain localized as discrete mass, rarely fatal
93
New cards
malignant
tumor that is invasive and metastasizes, fatal
referred to as cancer
referred to as cancer
94
New cards
metastasizes
move to other sites
95
New cards
basal cell carcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant melanoma
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant melanoma
What are the most common types of skin cancer?
96
New cards
basal cell carcinoma
located: basal cells in the stratum germinativum
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight, UV will disrupt/mutate the DNA
areas affected: face, neck, scalp, shoulders, ears
warning signs: open sore, reddish patch, shiny bump, pink growth, scar-like area
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight, UV will disrupt/mutate the DNA
areas affected: face, neck, scalp, shoulders, ears
warning signs: open sore, reddish patch, shiny bump, pink growth, scar-like area
97
New cards
squamous cell carcinoma
located: squamous cells of the epidermis
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight
areas affected: face, neck, bald scalp, shoulders, arms, back, sometimes trunk
warning signs: wart-like growth, persistent scaly red patch open sore that bleeds and crusts for weeks
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight
areas affected: face, neck, bald scalp, shoulders, arms, back, sometimes trunk
warning signs: wart-like growth, persistent scaly red patch open sore that bleeds and crusts for weeks
98
New cards
desquamation
loss of dead squamous cells
99
New cards
malignant melanoma
location: melanocytes
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight
areas affected: legs, trunk, arms, scalp in men
warning signs: small brown/black (or larger) multicolored patches; plaques or nodules with an irregular outline; many arise from pre-existing moles
causes: chronic exposure to sunlight
areas affected: legs, trunk, arms, scalp in men
warning signs: small brown/black (or larger) multicolored patches; plaques or nodules with an irregular outline; many arise from pre-existing moles
100
New cards
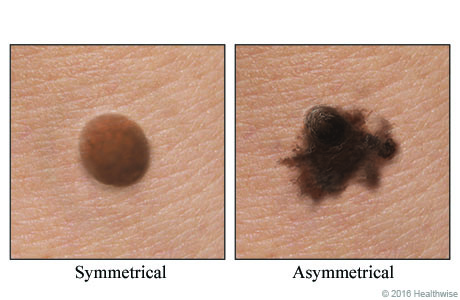
asymmetry
half of the mole does not match the other half