Comp Sci Unit 1 (1.2.1 - 1.2.16)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:54 PM on 9/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
Terminology
Hardware, software, peripherals, network, human resources
2
New cards
Hardware
Any physical parts to a computer
EG:
CPU
Keyboard
Mouse
EG:
CPU
Keyboard
Mouse
3
New cards
Software
Programs/instructions that control the computer
Non-physical
EG:
Databases
Web Browsers
Communication platforms
Non-physical
EG:
Databases
Web Browsers
Communication platforms
4
New cards
Peripherals
An outside device that allow the computer to interact with the environment or exchange info
Connected EXTERNALLY
Used to expand the host’s capabilities
EG: Input Peripherals
Scanner
Microphone
EG: Output Peripherals
Screen
Speakers
Connected EXTERNALLY
Used to expand the host’s capabilities
EG: Input Peripherals
Scanner
Microphone
EG: Output Peripherals
Screen
Speakers
5
New cards
Network
Group of computers connected together to share resources
Can interconnect with other networks to form larger networks
Can interconnect with other networks to form larger networks
6
New cards
Human resources
The people operating the computers
EG:
The people who are responsible at maintaining employee data, promotions or hiring
EG:
The people who are responsible at maintaining employee data, promotions or hiring
7
New cards
Roles of a Computer
Client, Server, DNS Server, Firewall, Router
8
New cards
Client
Computer accessing resources that are hosted from another computer
Resources may include:
Documents
Printers
Scanners
Resources may include:
Documents
Printers
Scanners
9
New cards
Types of Clients
Fat, thin, hybrid
10
New cards
Fat clients
Performs the bulk of the processing
Doesn’t necessarily rely on the server
Doesn’t necessarily rely on the server
11
New cards
Thin clients
Relies on the resources from the server
12
New cards
Hybrid clients
A mix of both fat and thin clients
13
New cards
Server
A computer hosting resources to be shared in the network for clients to access
Combination of both hardware and software
The computer provides services for other users to access
EG:
Google
Wikipedia
Combination of both hardware and software
The computer provides services for other users to access
EG:
Wikipedia
14
New cards
DNS Server
Special type of server
Maps web addresses to IP addresses
IP Address: Internet Protocol, identifies a device/network on the internet
Allows for the user to access any website without having to look for the IP address
Maps web addresses to IP addresses
IP Address: Internet Protocol, identifies a device/network on the internet
Allows for the user to access any website without having to look for the IP address
15
New cards
Firewall
Computer/software package
Any message passed through the internet passes through a firewall
Monitors/protects network traffic of a computer
Decides which computers get access to the network based on a set of rules
Basically like a security service
Any message passed through the internet passes through a firewall
Monitors/protects network traffic of a computer
Decides which computers get access to the network based on a set of rules
Basically like a security service
16
New cards
Router
A routing network that passes information between two or more networks
Uses a different medium for information transfer
Also forwards data to the intended IP address
EG:
Phone Cables
Uses a different medium for information transfer
Also forwards data to the intended IP address
EG:
Phone Cables
17
New cards
Relevant Stakeholders in developing a new system
Systems analyst, end users, software manufacturer, client company
18
New cards
Systems analyst
Collects information on present systems in order to examine the problems of it
Uses that information to develop a more efficient system
Designs the new system
Tests the system for any arising issues
Evaluates the system to see if it matches expectations
Uses that information to develop a more efficient system
Designs the new system
Tests the system for any arising issues
Evaluates the system to see if it matches expectations
19
New cards
End users
The clients of the service
The actual users of the system
The actual users of the system
20
New cards
Software manufacturer
Builds/develops the systems in order to be sold
21
New cards
Client Company
Employer organization
22
New cards
Methods for researching
Questionnaires, observations, interviews, documentation
23
New cards
Pros of Questionnaires
Answered quickly/honestly
Cheap
Analysed automatically
Cheap
Analysed automatically
24
New cards
Cons of Questionnaires
People don’t often complete/return it
Unclear questions cannot be explained
Difficult to ask specific questions
Unclear questions cannot be explained
Difficult to ask specific questions
25
New cards
Pros of Observation
Systems analyst can easily see advantages/disadvantages of current system
Not expensive
Not expensive
26
New cards
Cons of observation
Person being watched may feel uncomfortable and work differently than usual
27
New cards
Pros of interviews
Questions can be explained
Questions can be changed
A full set of data can be recorded
Questions can be changed
A full set of data can be recorded
28
New cards
Cons of interviews
Takes more time/money
Answers aren’t always honest
Answers aren’t always honest
29
New cards
Pros of Documentation
Saves time
Can see existing inputs/outputs
Allows for prediction of the size for the new system
Can see existing inputs/outputs
Allows for prediction of the size for the new system
30
New cards
Cons of Documentation
Very time consuming/expensive
Time could be wasted if info isn’t relevant to existing system
Time could be wasted if info isn’t relevant to existing system
31
New cards
Appropriate techniques for gathering information to arrive at a workable solution
Search, review current systems, analyze products, consult other people
32
New cards
Search
Identify, collect, and organize various sources to find information
E.g. search engines, databases, libraries, news articles
E.g. search engines, databases, libraries, news articles
33
New cards
Review current systems
Analyze current systems for effective features, functions, and other elements
E.g. system documentation
E.g. system documentation
34
New cards
Analyze Products
Analyze system/products that have been developed for the same purpose and end-users
E.g. look for vulnerabilities, limitations, successful characteristics, breakthroughs, benefits, and design features
E.g. look for vulnerabilities, limitations, successful characteristics, breakthroughs, benefits, and design features
35
New cards
Consult other people
Identify all critical organizational capabilities that are essential to support effective planning and development
E.g. interviews
E.g. interviews
36
New cards
Representations to illustrate system requirements
System flow chart, data flow diagram, and structure chart
37
New cards
System flow chart
Diagrams representing how different parts of the system are linked together and how the system should work in general
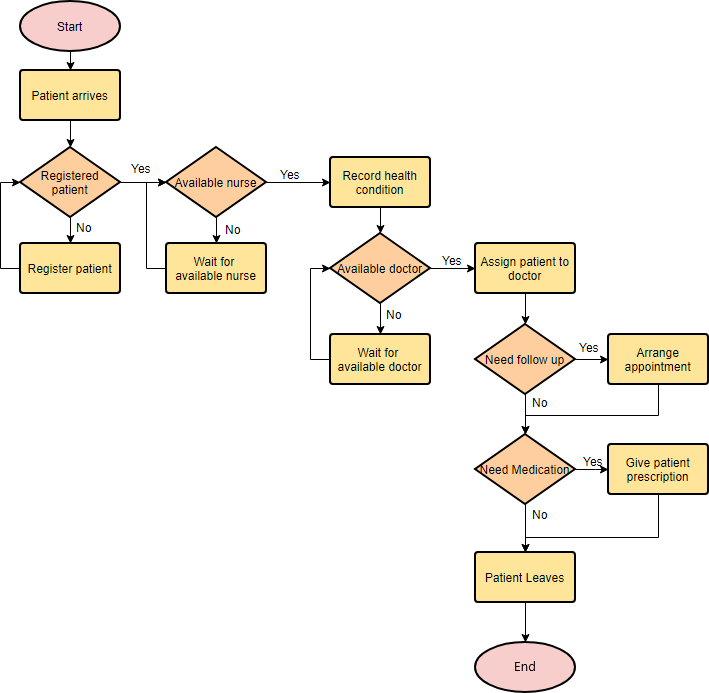
38
New cards
Data flow diagram
Diagrams representing how information is moving through the system together with identifying all relevant inputs and outputs to the system
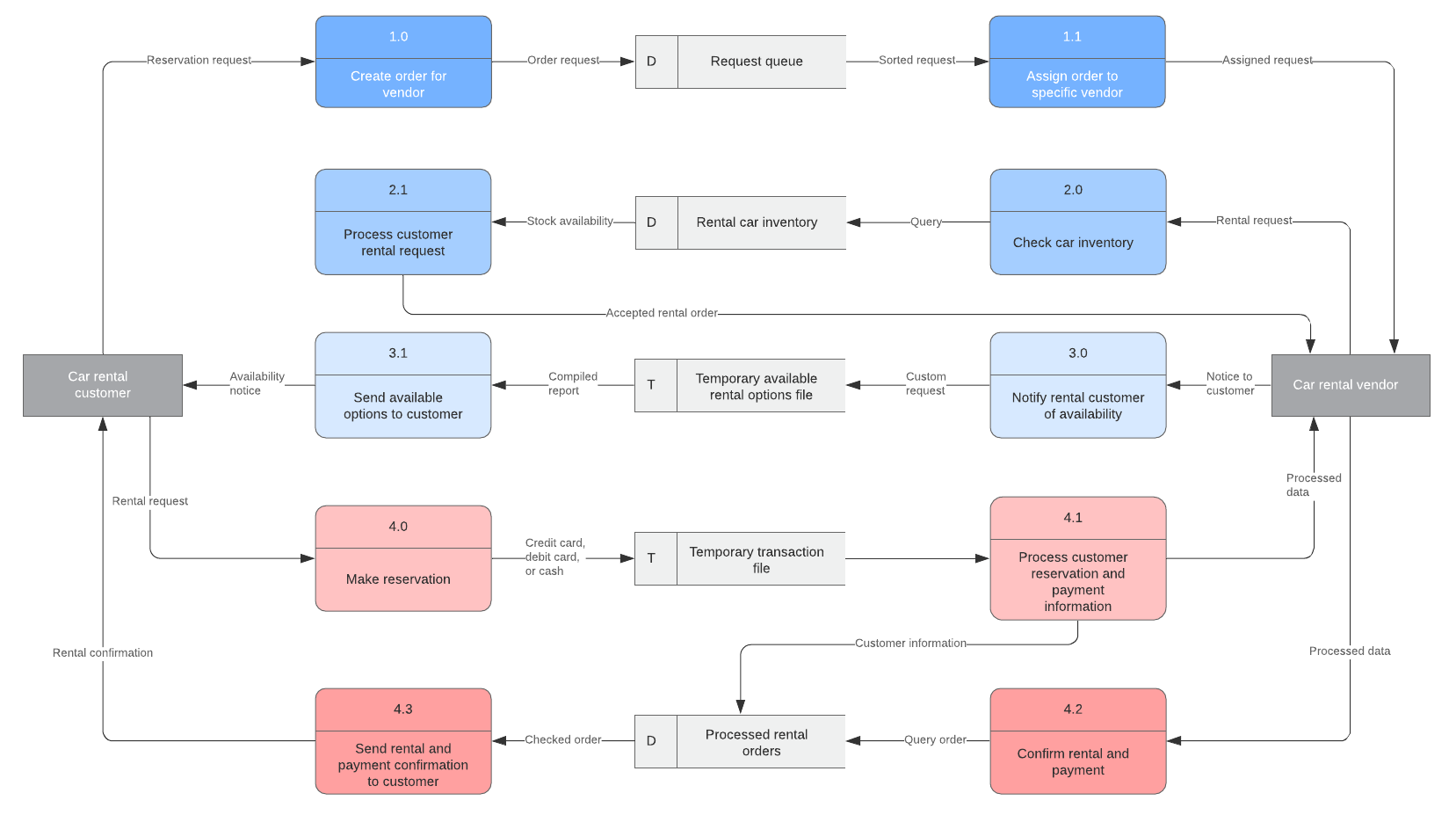
39
New cards
Structure charts
Diagram representing the organization of a system, usually with showing the different parts in hierarchical order
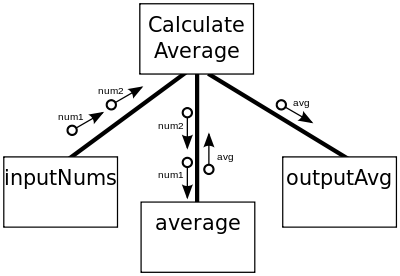
40
New cards
Prototype
the process of building a model of a system, used to help system designers build an information system that is intuitive and easy to manipulate for end-users. A process that is involved with analysis phase of the systems development life cycle
41
New cards
Purpose of Prototypes
Reduced development time, reduces development costs, requires user involvement, developers receive user feedback, facilitates system implementation since users understand what to expect, results in higher user satisfaction
42
New cards
Steps of software life cycle
Inquiry and analysis
Developing ideas
Creating the solution
Evaluation
Developing ideas
Creating the solution
Evaluation
43
New cards
Iterations
the repetition of a set of instructions for a specific number of times or until the operations yield a desired results
44
New cards
Importance of iterations
plenty of opportunity for user feedback, more likely to detect issues, improved usability, efficient and cost effective adaptability to project/client/team
45
New cards
Consequences of failing to involve the end-user in the design process
solve a different issue(s), address issues outside of the project’s scope, not addressing criteria issued by stakeholders, waste resources (time and money), be incompatible with end-user systems (app made for windows, but the computers are mac), end user may not be able to interpret UI elements
46
New cards
Social and ethical issues associated with the introduction of new IT systems
Firing workers because computer systems can do the same job but cheaper
Because of mobile phones, workers can be reached even out of work
Less social interaction due to home offices
Because of mobile phones, workers can be reached even out of work
Less social interaction due to home offices
47
New cards
Terms for usability
Learnability
Efficiency
Memorability
Errors
Satisfaction
Complexity/Simplicity
Effectiveness
readability/comprehensibility
Efficiency
Memorability
Errors
Satisfaction
Complexity/Simplicity
Effectiveness
readability/comprehensibility
48
New cards
Usability problems (examples)
GPS systems, tablets
49
New cards
Problems of usability in GPS systems
Low quality speakers
Outdated street data
Inefficient routing software
Poor antenna
Outdated street data
Inefficient routing software
Poor antenna
50
New cards
Problems of usability in tablets
Accidental touches
Poor scaling
Small button size
Difficult to learn features of different brands
Poor scaling
Small button size
Difficult to learn features of different brands
51
New cards
Methods to improve the accessibility of systems
Visual impairment (Braille input devices), speakers (text to speech),
Hearing and speech impairment (Subtitles), Cognitive problems & learning disabilities (Special software to provide sensory stimulation they need), Mobility impairment (Specialty keyboards/mice), Special replacements for common input items
Hearing and speech impairment (Subtitles), Cognitive problems & learning disabilities (Special software to provide sensory stimulation they need), Mobility impairment (Specialty keyboards/mice), Special replacements for common input items
52
New cards
Problems that come with Learnability
Very complicated and poor instructions
53
New cards
Problems that come with Efficiency
Very inefficient in processes and input
54
New cards
Problems that come with Memorability
Hard to remember
55
New cards
Problems that come with Errors
Having many errors that interfere with what the system is meant to do
56
New cards
Problems that come with satisfaction
Poor quality
57
New cards
Problems that come with Complexity/simplicity
So simple its useless, so complex it is hard to use
58
New cards
Problems that come with effectiveness
Doesn’t do its job
59
New cards
Problems that come with readability/comprehensibility
Not understandable
60
New cards
Moral/Ethical implications of interaction with humans and machines
AI and rights
61
New cards
Social implications of interaction with humans and machines
AI tricking humans with false info
62
New cards
Economic implications of interaction with humans and machines
Losing jobs for more efficiency
63
New cards
Environmental implications of interaction with humans and machines
Damaging environment, ways to make up with machines