AP Music Theory Terms
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
253 Terms
Accelerando
a tempo of increasing speed
Accidental
a note that is not part of the scale indicated by the key signature, typically sharp, flat, or natural
Accompaniment
A musical part that supports a main melody, often played by instruments or voices
Adagio
Slow and stately tempo, generally around 55-65 BPM
Agogic Accent
A subtle emphasis on a note that is achieved by slightly prolonging its duration; not written—>a performance technique
Alberti Bass
An arpeggiated accompaniment where the notes of the chord follow the order of lowest, highest, middle, highest

Allegretto
A moderately fast tempo that falls between andante and allegro
Allegro
A fast and lively tempo
Anacrusis
Also known as an upbeat or pickup (can be a note or a group of notes); precedes the first measure

Andante
A moderate tempo, often interpreted as a walking pace
Andantino
A tempo slightly faster than andante, typically considered to be a moderately fast walking pace
Antecedent
The first phrase in a musical period; often characterized by an “opening” feel
Anticipation
A non-chord tone that is played before the chord to which it resolves, creating a moment of suspense; a rhythmic embellishment

Appoggiatura
A non-chord tone that is approached by a leap and resolved by a step in the opposite direction

Arpeggiated 6/4
A second inversion chord where the bass is arpeggiated, creating a sense of movement while the upper voices sustain the chord; also used to prolong a harmony
Arpeggio
A musical technique that involves playing the notes of a chord in rapid succession rather than simultaneously, creating a flowing sound
Articulation
The manner in which notes are performed, affecting their duration and emphasis
Asymmetrical meter
A type of musical meter that does not divide evenly into regular beats, often creating a sense of irregularity and uniqueness in rhythm; examples include 5/4 and 11/8
Augmentation
When a motif is repeated and the rhythmic values are lengthened; durations are typically doubled
Augmented interval
An interval that is a half step larger than a major interval
Augmented triad
A triad made up of two M3 intervals
Authentic
A cadence that ends on the tonic
Bar line
Vertical line that separates the measures of a piece
Basso continuo
A continuous bass line with improvised harmonies in Baroque period music
Beat
The basic unit of time in music
Beat division
How a beat is further subdivided into smaller, quicker pulses; in 4/4, the beat division can be an 8th note or 16th note
Beat unit
The note value that represents the duration of one beat in a given meter; in 4/4, the beat unit is 1 quarter note
Brass
A family of musical instruments made of brass or other metals that produce sound by means of vibrating lips; they include trumpets, trombones, tubas, and French horns
Bridge
A contrasting section in a song that provides a departure from the verses and chorus, often offering a different perspective or emotion
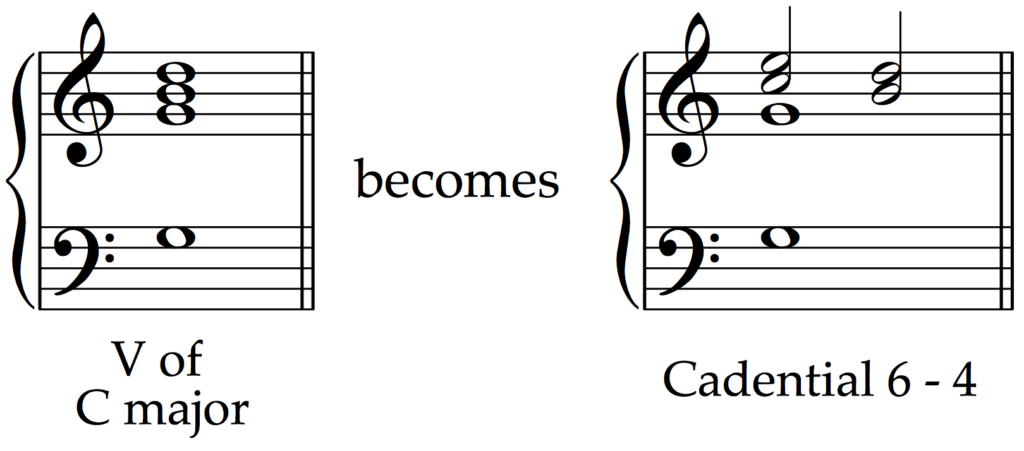
Cadential 6/4
A 6/4 chord that embellishes the V chord by displacing it with simultaneous 6-5 and 4-3 suspensions above the bass note (5); occurs on a strong beat and appears before the V chord
Call and response
A musical form where one performer or group plays or sings a phrase (the "call"), and another performer or group responds with a complementary phrase (the "response")
Canon
A round
Canonic
Describes the structure of a canon
Chain of suspensions
A series of suspensions where the resolution of one is used as the preparation for the next
Changing meter
A technique in music where the time signature changes frequently, creating varying rhythmic feels within a piece
Chord inversion
A technique where the notes of a chord are rearranged so that a different note serves as the bass note
Chordal accompaniment
A style of accompaniment that uses chords played in harmony, typically providing support to a melodic line
Chordal homophony
A texture in music where one main melody is supported by chordal accompaniment, creating a harmonious effect
Chorus
A repeated section of music that usually includes the main theme or message, often contrasting with verses
Chromatic
The use of notes outside the standard diatonic scale of a given key (all 12 notes in an octave)
Circle of fifths
A visual representation of the relationships between the twelve tones of the chromatic scale, showing how key signatures relate through perfect fifths
Close position
Chord arrangement where the notes are spaced as tightly together as possible (usually within an octave)
Coda
A concluding passage added to a piece of music, often used to summarize and bring closure to the composition
Codetta
A brief or diminished coda that solidifies a section of the music, rather than the entire piece itself
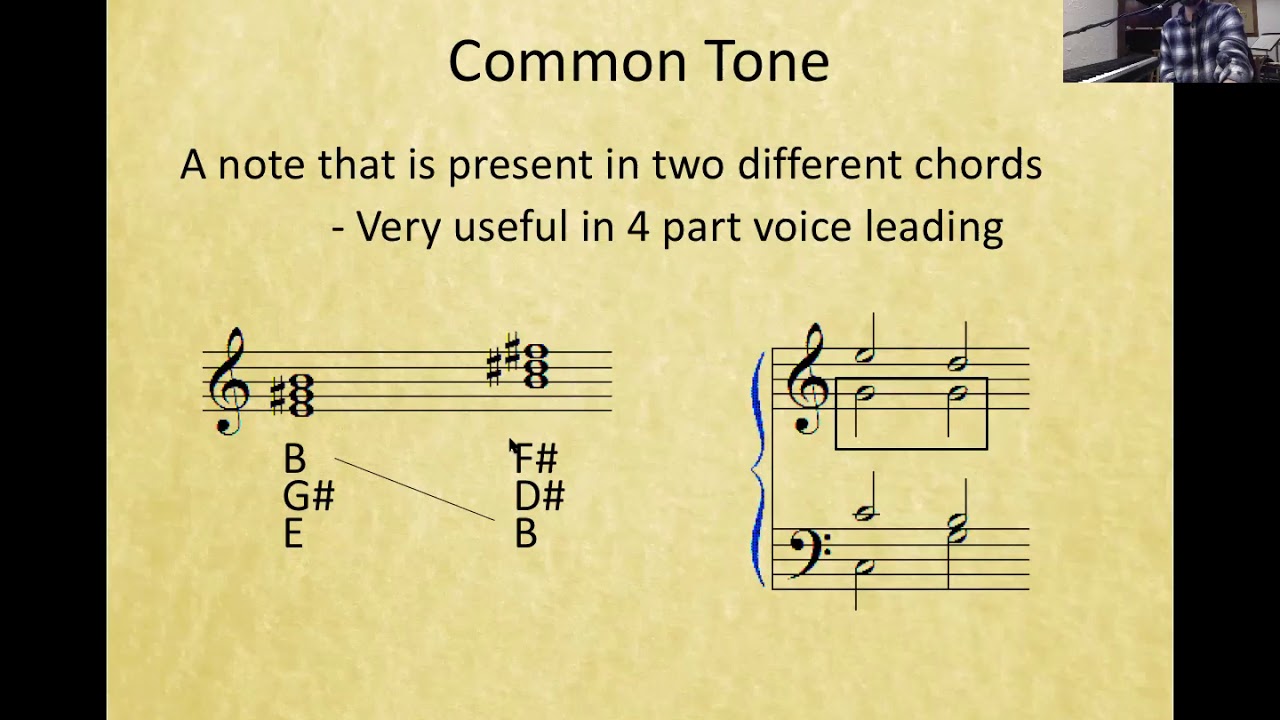
Common tone
A shared note between two chords or sets of notes
Compound interval
An interval that is larger than an octave
Compound meter
Meters where the beat divides into three and then further subdivides into six (6/8)
Conclusive cadence
A cadence that ends on the tonic, providing a feeling of closure
Conjunct
Melodic movement by stepwise motion
Consequent
The second phrase of a musical period that follows the antecedent, typically completing a musical thought
Consonance
A harmonic or melodic interval that sounds stable and pleasant to the ear; PU, P8, P5, P4, M3, m3, M6, m6
Contrapuntal
Also known as counterpoint; two or more melodic lines that intertwine and create a rich, complex texture
Contrary motion
A type of melodic movement where two or more lines move in opposite directions
Contrasting period
A type of period where the antecedent and consequent phrases begin with different melodic material
Countermelody
A secondary melody that complements the main melody, often adding harmonic richness and depth
Counterpoint
The relationship between two or more melodic lines that are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and contour
Crescendo
A gradual increase in loudness or intensity in music
Cross relation
A dissonance that occurs when a note in one voice is followed by a chromatic alteration of that same note in a different voice
Cross rhythm
A rhythmic pattern where two or more distinct rhythms are played at the same time
Deceptive cadence
A musical phrase that creates the expectation of a resolved cadence but instead moves to an unexpected chord, typically VI
Deceptive progression
A chord progression that resolves to an unexpected chord, creating a sense of surprise (usually VI)
Diatonic
Relating to the seven notes of a standard scale without chromatic alterations
Diminished interval
An interval that is one half step smaller than a minor interval, often creating a tense sound
Diminished triad
A triad made up of two m3
Diminuendo
A gradual decrease in volume or loudness in musical performance
Diminution
Shortening the note values of a melody, making the sound faster, while maintaining the overall pulse
Direct fifths (hidden fifths)
A voice leading error that occurs when two voices approach a P5 by similar motion, implying parallel fifths; bass moves by step and soprano moves by leap
Direct octave (hidden octave)
A voice leading error that occurs when two voices approach a P8 by similar motion, implying parallel octaves: bass moves by step and soprano moves by leap
Disjunct
Referring to a melody that moves in leaps
Dissonance
A sound that creates tension and instability, typically requiring resolution to a consonance; M2, m2, tritone, M7, m7
Dominant
The fifth scale degree of a diatonic scale, often creating a tension that resolves to the tonic
Dominant function
The role of the dominant chord in a musical piece, typically leading to the tonic chord and creating a sense of resolution
Dominant seventh chord
A seventh chord built on the 5th scale degree of a diatonic scale (major triad, minor 7th)
Dorian
A musical mode composed of a natural minor scale with a raised 6th
Dot, double dot
Notational symbols used to extend the duration of a note by half its value (dot) or by three-quarters of its value (double dot)
Dotted rhythm
A rhythm characterized by the alternation of long and short notes, typically involving dotted notes that extend the value of a note
Doubling
Root position (double root), first inversion (double root or 5th), second inversion (double bass)
Downbeat
The first beat of a measure, typically emphasized or accented in music
Duple meter
A musical meter characterized by two beats per measure, often providing a strong, regular pulse (2/4 in simple meters, 6/8 in compound meter)
Duplex
A musical texture featuring two independent melodies occurring simultaneously, often creating a rich harmonic interaction
Dynamic accent
Emphasizing a note or chord by playing it stronger that surrounding pitches
Embellishing tone
A non-harmonic tone that decorates or embellishes a melody, often resolved to a chord tone
Embellishment
A musical ornament that decorates or adds nuance to a melody by altering or supplementing the main pitch
Enharmonic equivalent
Notes that sound the same but are written differently, such as C# and Db
Fermata
A symbol indicating that a note or rest should be prolonged beyond its usual duration
Figured bass
A musical shorthand notation indicating chords and intervals, where numbers are written below the bass line to inform the performer of harmonic structure
Forte
A dynamic marking indicating to play loudly or with strength
Fortissimo
A dynamic marking indicating to play very loudly
Fragmentation
A compositional technique where a motif or musical idea is broken down into smaller units and reused in various forms throughout a piece
Fully diminished seventh
A seventh chord made up of a diminished triad and a diminished 7th
Chord
A combination of three or more different pitches played simultaneously, forming harmony
Genre
A category of music characterized by specific styles, forms, and conventions, influencing the way music is composed and performed
Grave
A musical term indicating a very slow tempo, often suggesting a serious or solemn character
Half cadence
A cadence that ends on the V chord
Half step (semitone)
The smallest interval in Western music, equal to one semitone, typically between two adjacent keys on a piano
Half-diminished seventh chord
A seventh chord made up of a diminished triad and a minor 7th
Harmonic minor
Minor scale where the 7th scale degree is raised by a half step, pulling toward the tonic note
Harmonic rhythm
The speed at which chords change in a piece of music
Hemiola
A rhythmic device where two groups of three beats are grouped together to create the feel of three groups of two beats

Heterophony
A texture consisting of a single melody played with variations by different performers, resulting in a rich, complex sound