DIG Exam 2 Sos and Lopez
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Frequency of liver metastasis
Colorectal 70%
Pancreatic 50-60%
Breast 30-50%
Lung cancer 20-30%
Liver border vertically
5th intercostal to costal margin
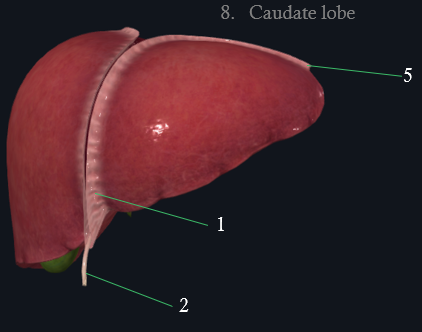
1: falciform ligament
2: round ligament of liver
5 Left triangular ligament
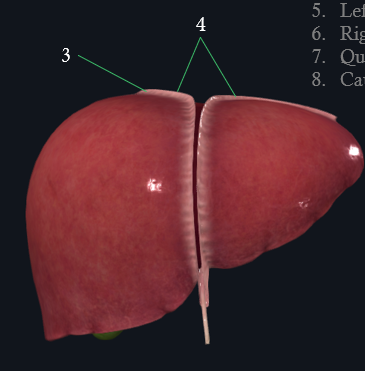
4: coronary ligament
3: Right triangular ligament
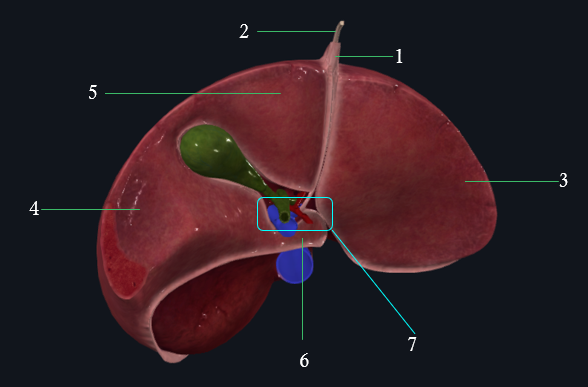
1: Falciform ligament
2: Round ligament
3: Left anatomical lobe
4: Right anatomical lobe
5: Quadrate lobe
6: Caudate lobe
7: Porta Hepatis
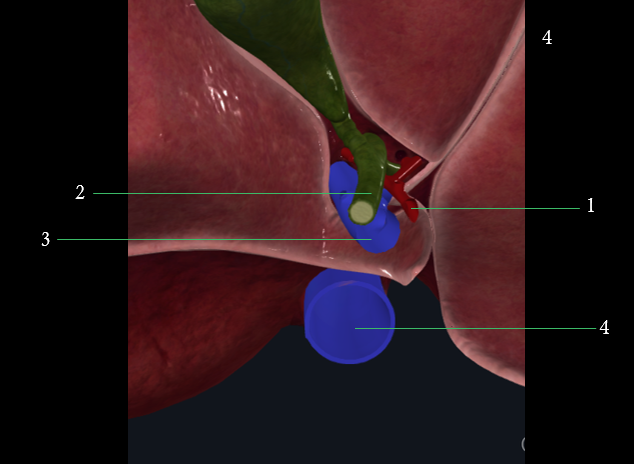
1: Hepatic artery proper
2: Bile duct
3: Portal vein
4: IVC
The hepatic portal system is a vital component of the circulatory system that directs blood from part of the ______ and _____ to the liver
GI tract
Spleen
Blood from the hepatic portal system delivers _____, ______. and other substances to the liver for _____, _______, ______, and other processing before it enters systemic circulation
nutrients, toxins
metabolism, detoxification, storage
IMV, SMV, Splenic vein, gastric veins
Main tributaries of hepatic portal system
Important portal-caval shunts
periumbilical, distal esophagus, hemorrhoids?
Each segment of the liver has its own vascular _____, _____, and ______ drainage
inflow, outflow, and biliary
Each segment has its own portal vein branch, hepatic artery branch, bile duct branch, and hepatic vein drainage
of the liver
____ vein: Divides the liver into upper and lower segments
Portal
____ ______ vein: Divides the liver into right and left lobes functionally (not the same as anatomic lobes).
Middle Hepatic
_____ and ___ _____veins: Further divide the lobes into sectors.
Right and left hepatic
_____ _______vein → separates segments V&VIII (anterior) from VI&VII (posterior).
Right hepatic
_____ ______ vein → separates right from left functional lobes
Middle hepatic
_____ ______ vein → separates segments II–III (lateral) from IV (medial).
Left Hepatic
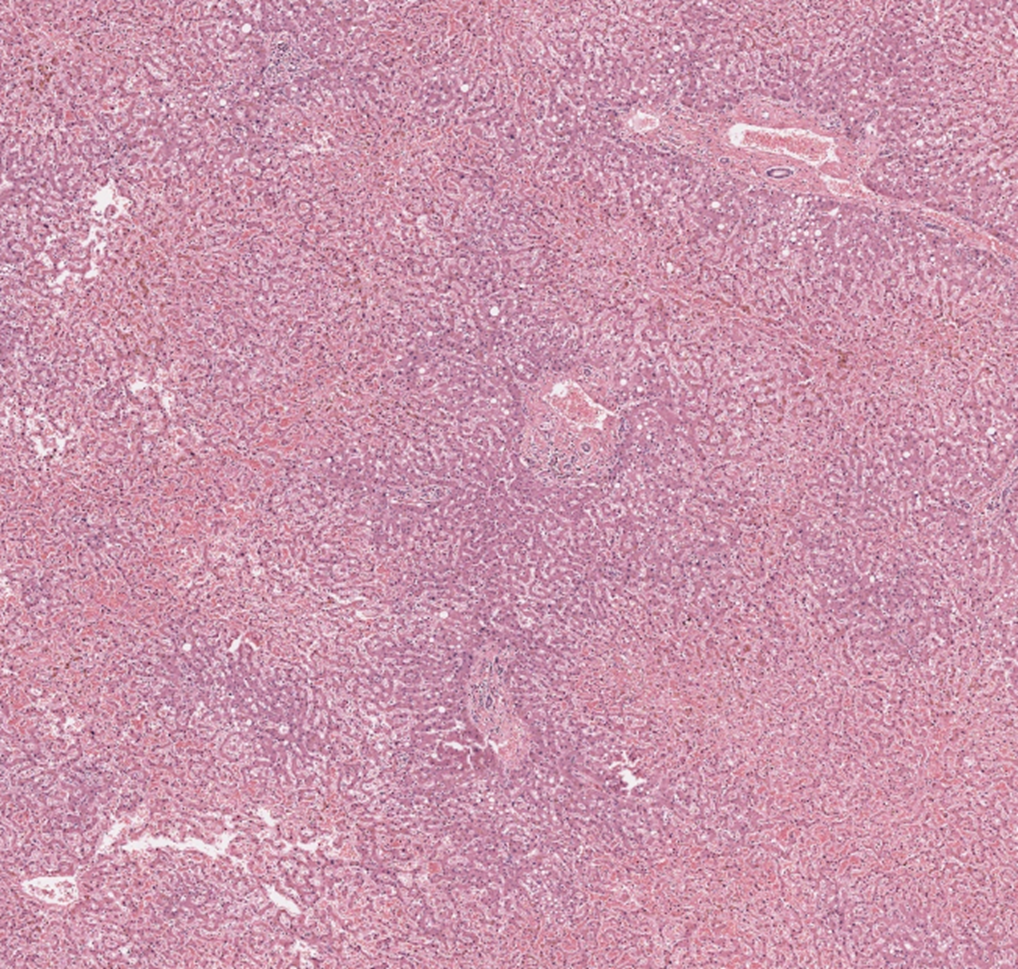
Normal liver
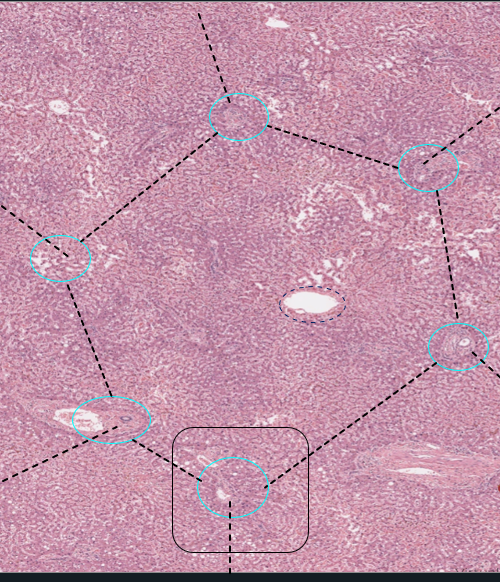
Hepatic Lobule
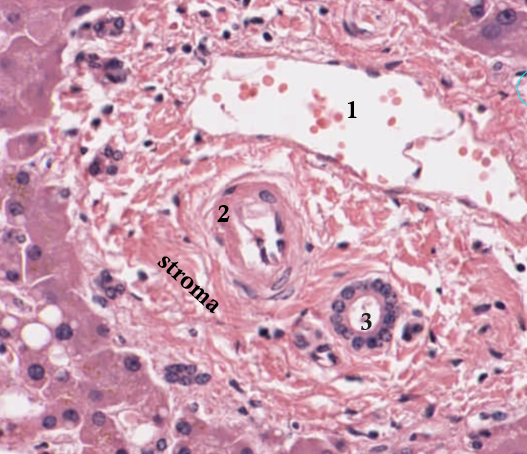
1: Portal Vein
2: hepatic artery
3: bile duct
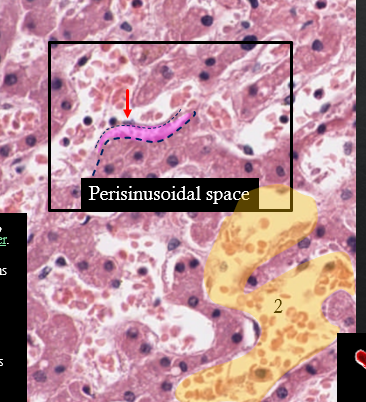
2: Sinusoid
Hepatocyte stains _____ and has a ______ places _____ nuclei
eosinophilic; centrally; round
Hepatocytes make up __% of the liver’s mass
80%
Is it normally for some hepatocytes to by binucleate?
Yes
Some functions of hepatocytes include
Protein synthesis
Protein storage
Transformation of carbohydrates
Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids
Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances
Initiation of formation and secretion of bile
Contains the blood plasma and microvilli of hepatocytes
Contains hepatic stellate cells (also known as Ito cells) [store fat or fat soluble vitamins]
Space of Disse
Specialized macrophages located in the sinusoids of the liver, derived from monocytes.
Kupffer cells
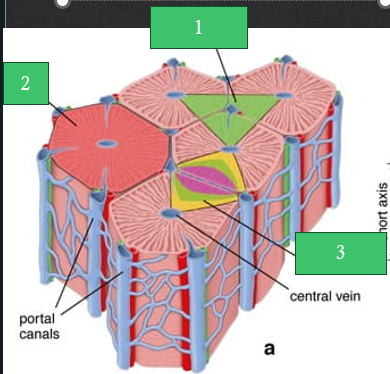
1: Portal lobule
2: Classic lobule
3: Liver acinus
Zone 1: Closest to the portal triads, this zone receives the most __________ blood and is most active in _________ metabolism
Zone 2: intermediate levels of oxygenation and metabolic activity
Zone 3: Farthest from the blood supply, this zone receives the least _______ blood. More susceptible to _______ injury and toxins
oxygenated; oxidative
oxygenated; ischemic
Comprises all hepatocytes that drain into a SINGLE bile duct bound peripherally by the ventral veins
Portal lobule
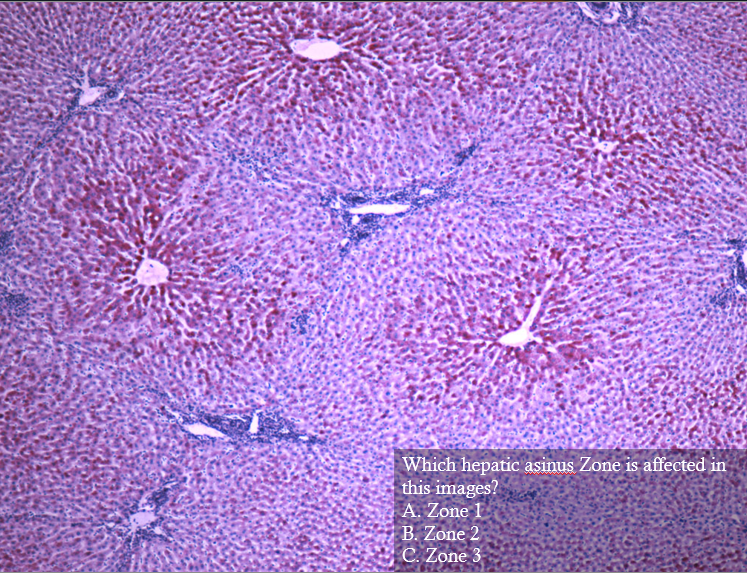
C. zone 3
Central vein - _____ veins - _______ - IVC
interlobar veins; hepatic veins
A 50-year-old man presents with a dull, aching pain in the epigastric region that radiates to the back. The pain has been persistent for the past several weeks and is associated with nausea. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the epigastric region, and imaging shows a mass in the right lobe of the liver. The visceral somatic innervation responsible for transmitting the pain from the liver to the spinal cord is most likely mediated by which of the following nerves?
Greater splanchnic nerve (T5-T9)
Difficulty breathing
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
Bowel sounds in the chest
symptoms of
diaphragmatic hernia
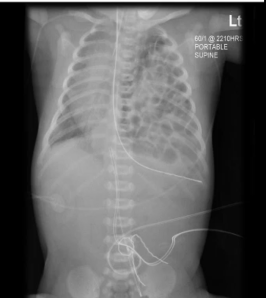
Diaphragmatic hernia: congenital defect
Acceleration/deceleration and crush injuries
Tears along the falciform and round ligament and triangular ligament
Liver trauma
What maneuver do you use to control liver hemorrhage?
Pringle
Liver trauma is the ______ most common abdominal injury
second, spleen is number 1
Space between the right lobe of the liver, right kidney, and right colic flexure?
Hepatorenal recess or Morison’s pouch
Fluid around the spleen
Peri splenic space
Fluid between uterus and rectum
Rectouterine pouch or pouch of Douglas
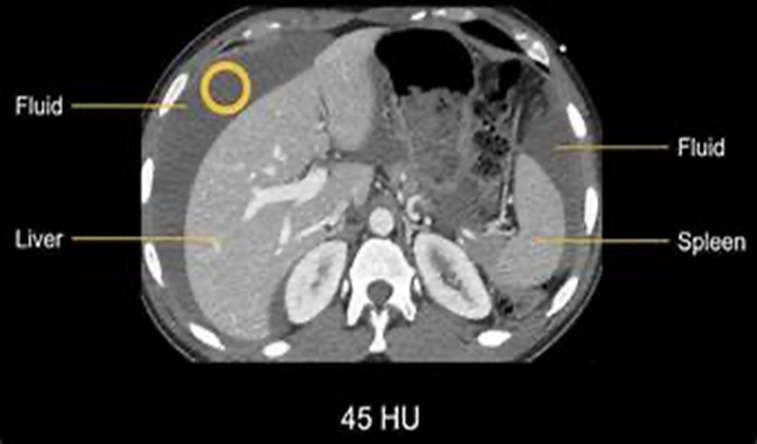
Left -back Morison’s pouch and right peri splenic space
Cuboidal epithelial parenchymal cell of the liver main functions metabolism, storage, digestion, coagulation factors, and bile production
Hepatocytes
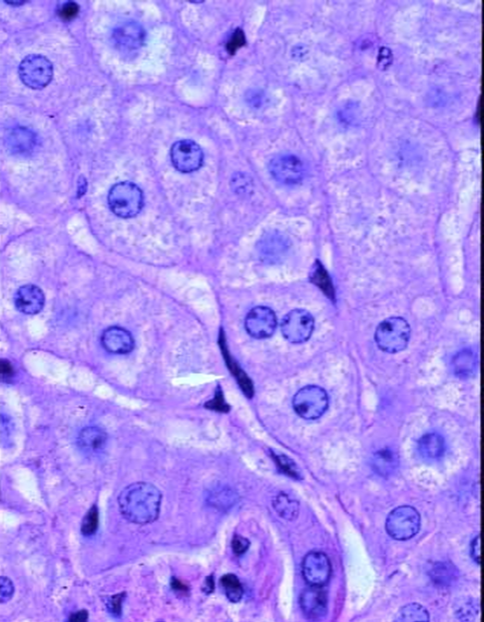
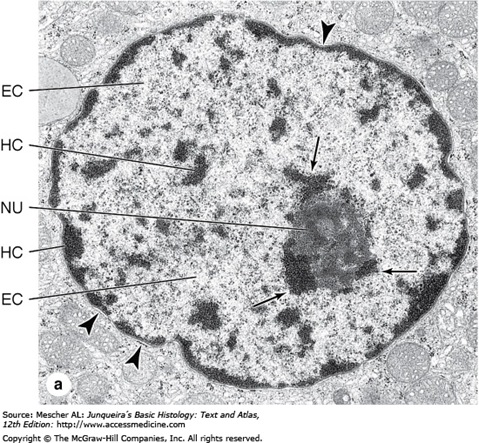
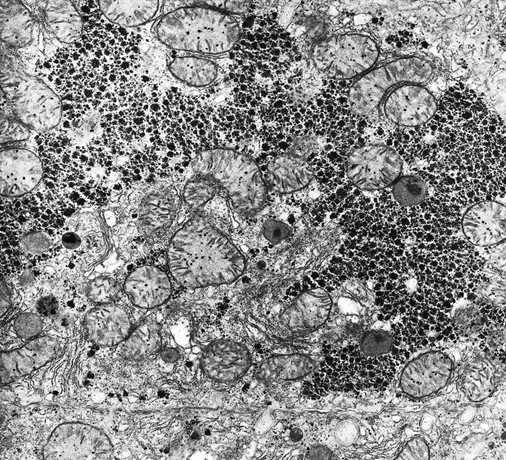
Hepatocytes. Large active nucleolus. Glycogen granules
___% of blood is recieved from the portal vein
75
__% of blood is received from the hepatic artery
25
Hepatocytes are arranged in single rows or ____ with ____ surface facing bile canaliculi and ______ surfaces facing sinusoids.
cords, apical, basolateral
Perisinusoidal space between basal surface of hepatocytes and the endothelial cells of the sinusoids.
Space of Disse
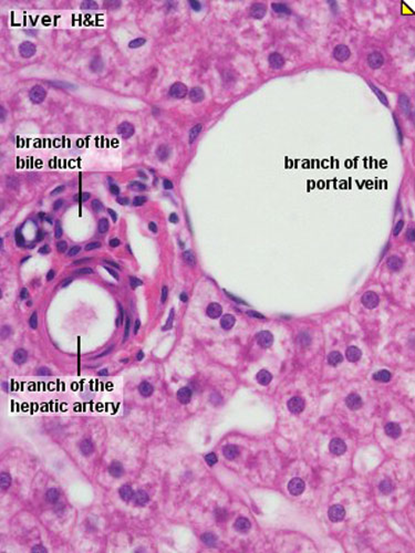
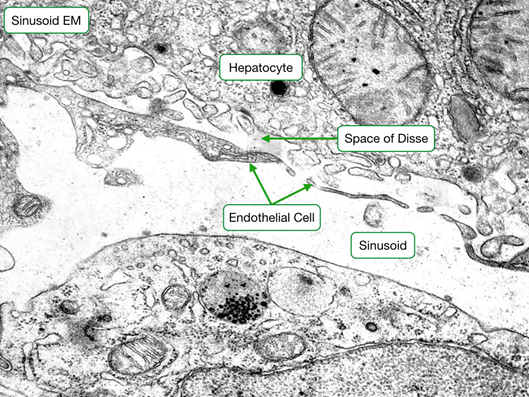
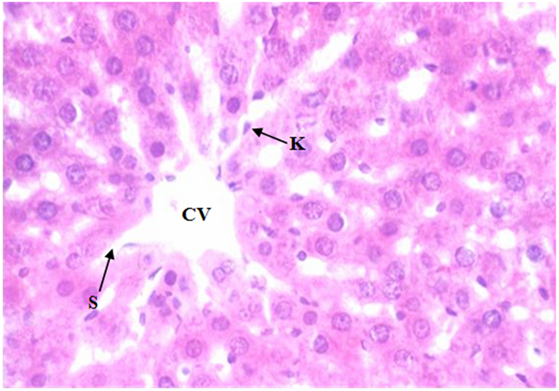
Liver histology
Liver cell injury, inflammation, and fibrosis starts in ___________?
space of Disse
____ is the most common drug-induced liver injury in the US, zone __ necrosis
Acetaminophen; 3
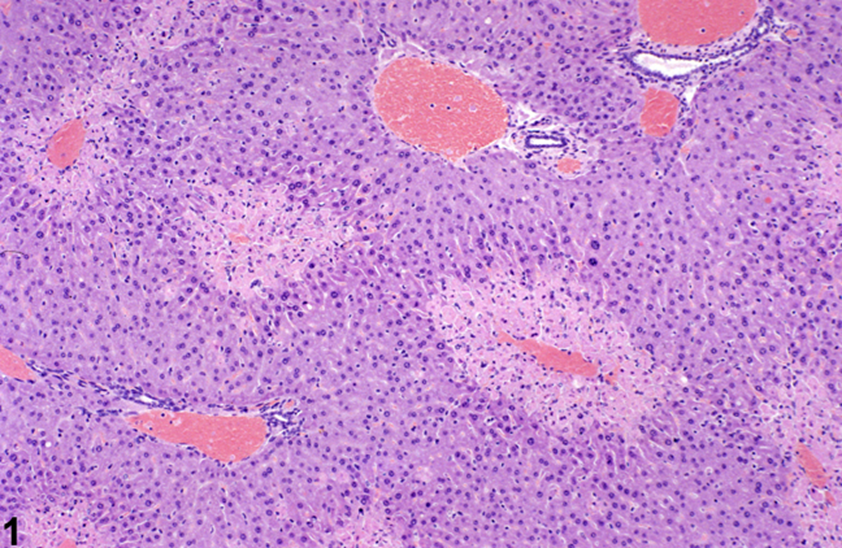
Zone 3 necrosis, could be from acetominophen
Rare but serious acute illness that causes liver and brain damage, a rapidly progressive encephalopathy.
Affects children and teens recovering from a viral infection most commonly the flu or chickenpox
Symptoms: Diarrhea, rapid breathing, confusion, seizures and loss of consciousness
Aspirin used for relief of fever or pain
Reye’s syndrome
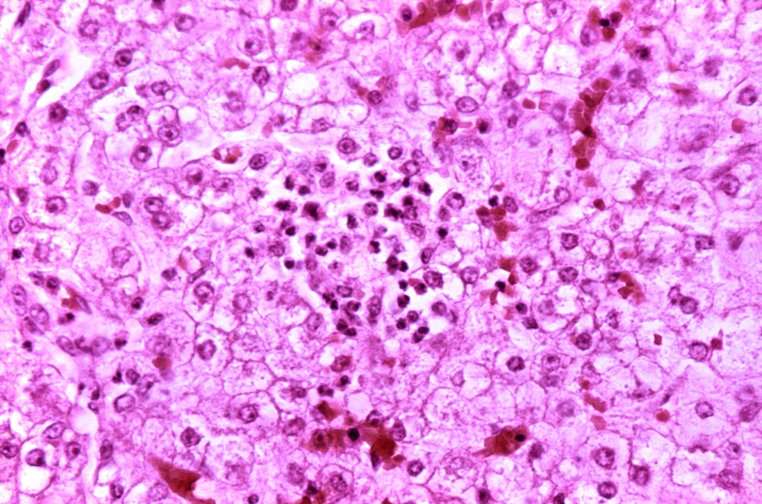
Liver microvesicular steatosis and hepatitis
Reye’s syndrome
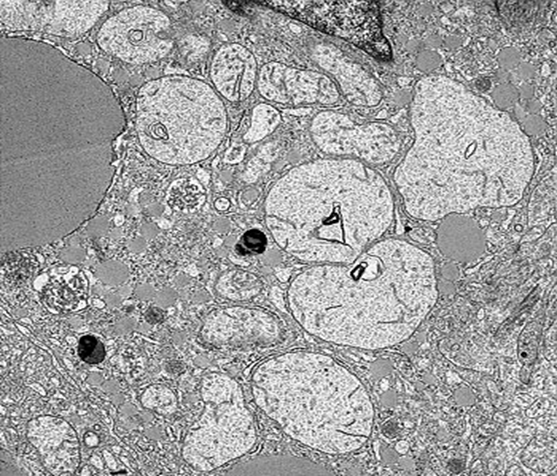
Mitochondrial swelling
Reye’s syndrome
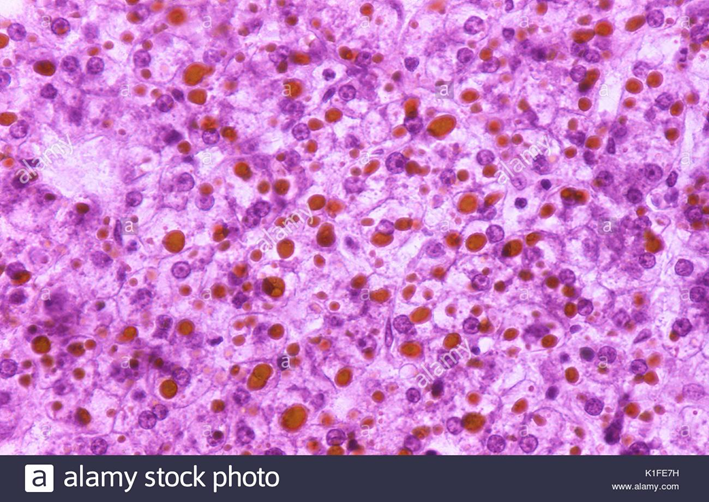
Fat stained with Oil red O or PAS
Reye’s syndrome
The liver stores vitamin ___ , ____ , ___ , ___ and B12
ADEK
Bile secretion and dietary fat breakdown is essential for absorbing ______ vitamins
ADEK
Occurs in animal products and mostly stored in the liver (stellate cells) an important in eye health, skin, intestines, lungs and immune system
Vitamin A (retinal)
Produced by the skin during exposure to the sun and the primary role is calcium absorption and bone health
Vitamin D
Primary role is as an antioxidant
Vitamin E
A group of vitamins required to make prothrombin involved in blood clotting “blood-clotting vitamin”
Vitamin K
Water soluble as all B vitamins. Naturally found in meats and important in brain functions and red blood cell synthesis. B12 deficiency involved in pernicious anemia, Crohn’s disease, gastritis, celiac disease and chronic alcoholism. B12 deficiency can cause permanent nerve and brain damage
Vitamin B12 Cobalamin
Alcohol consumption is the ____ leading risk factor for both death and burden of disease and injury
7th
_____ is a major cause of preventable liver disease worldwide
Alcohol
At least 20 year history of regular consumption of alcohol above threshold
Alcohol-related liver disease
AST > ALT (2:1)
think Alcohol-related liver disease
_____ consumed with food takes a priority to metabolize
Ethanol
The metabolic by-product of alcohol is ______ which is toxic to the body and increases ______
Acetaldehyde; inflammation
Final product of ethanol metabolism is?
Acetyl-CoA which is converted to fats and cholesterol
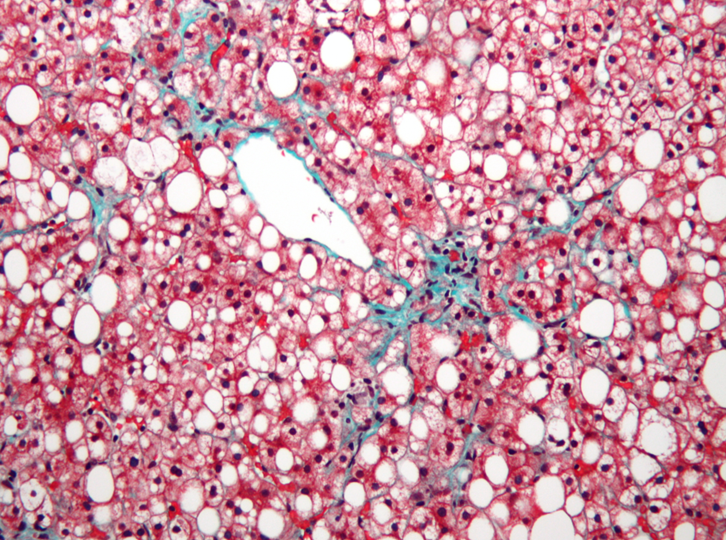
steatosis
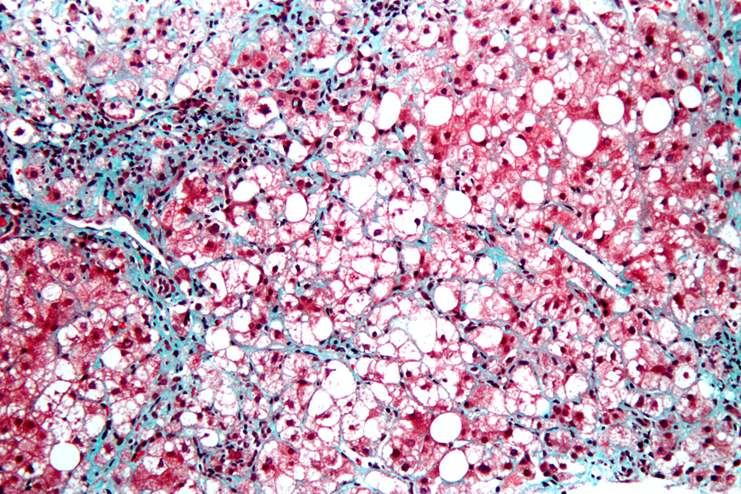
steatohepatitis
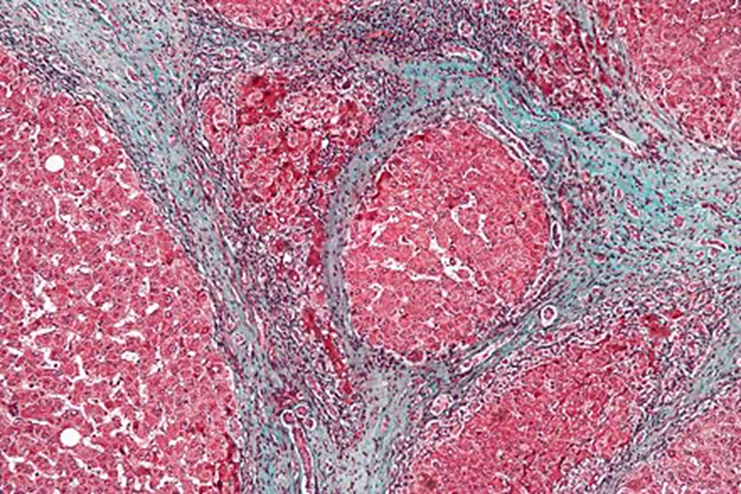
liver fibrosis
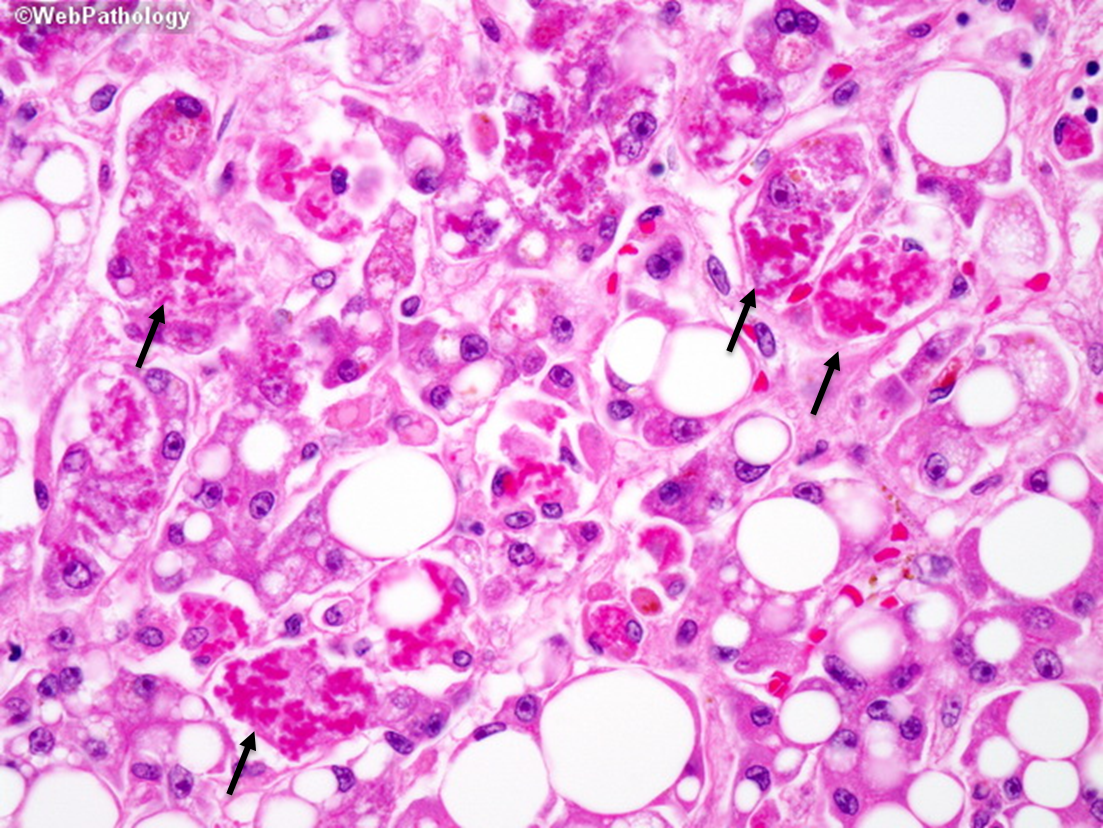
Hepatocyte changes include Mallory bodies, cellular inclusions consisting of damaged cytokeratin filaments
Also has steatosis
Alcohol abuse and other disease
Liver parenchyma is replaced with scar tissue, an end stage organ damage state
Fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss, jaundice and itchy skin, bruises and bleeding, edema, brown to orange urine, pale stool, disorientation
20% of chronic alcoholics
Alcohol-induced cirrhosis
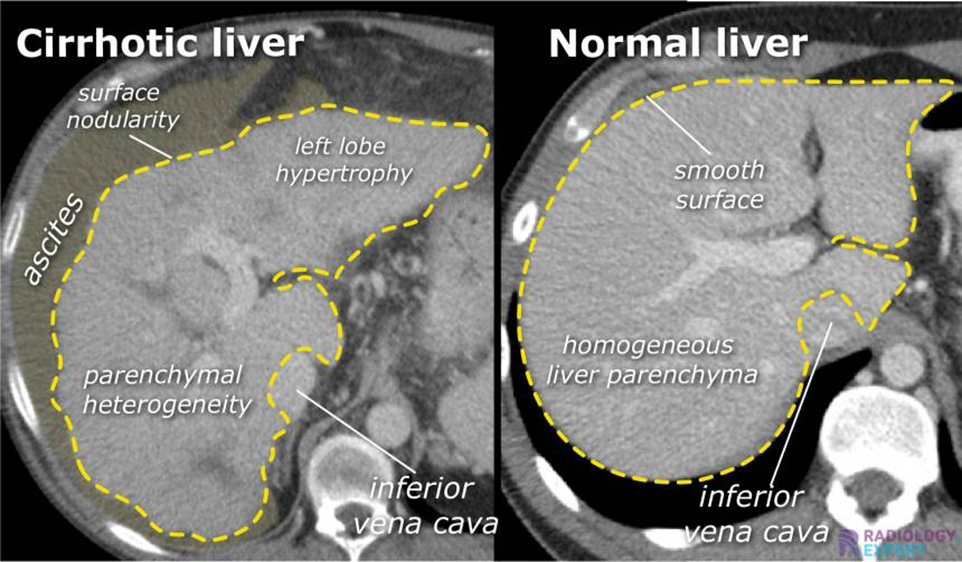
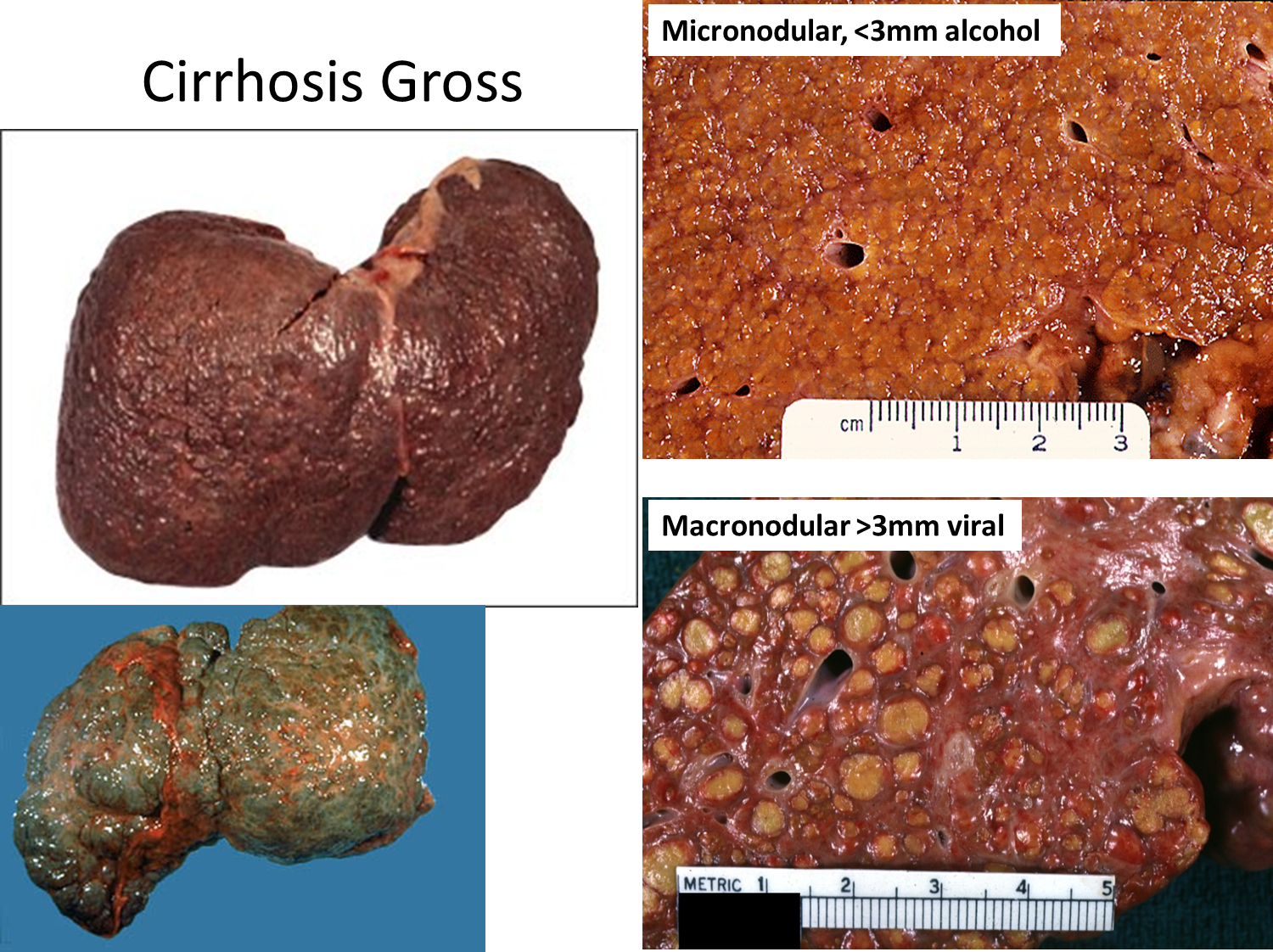
Cirrhotic liver
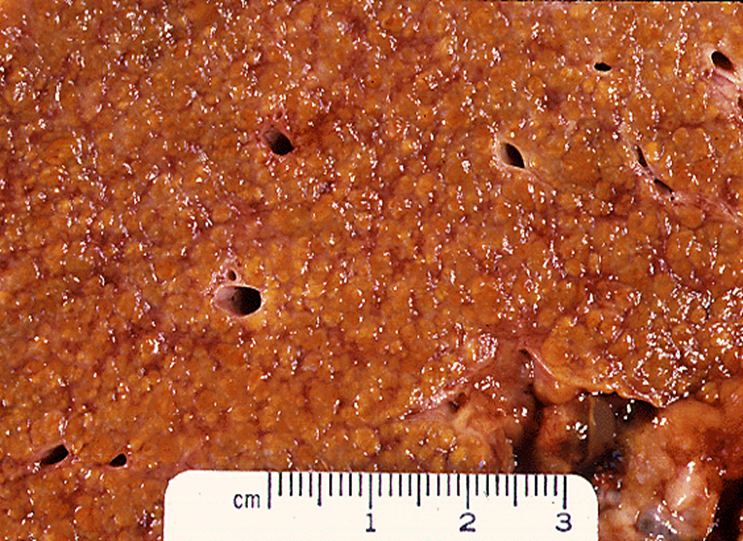
Micronodular cirrhosis
Alcohol
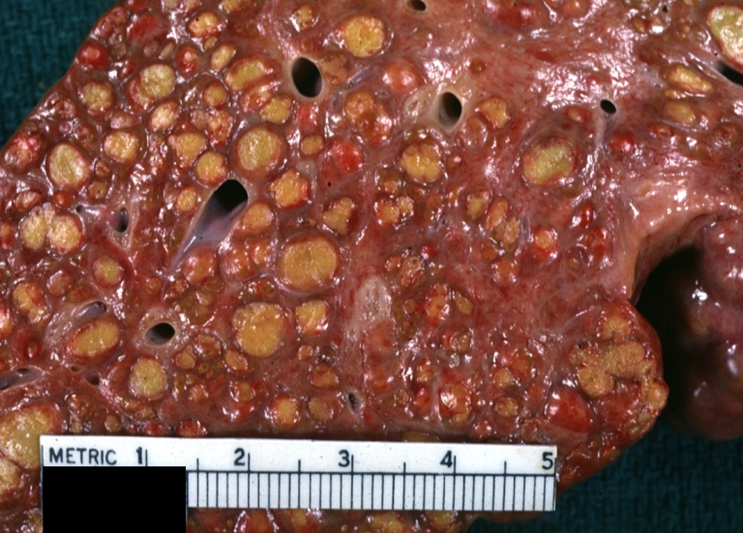
Macronodular cirrhosis
Viral
Portal-systemic (cava) collaterals
Where fluid builds up when liver is backed up
Esophageal, periumbilical, rectal, retroperitoneal (gutters of large intestine)
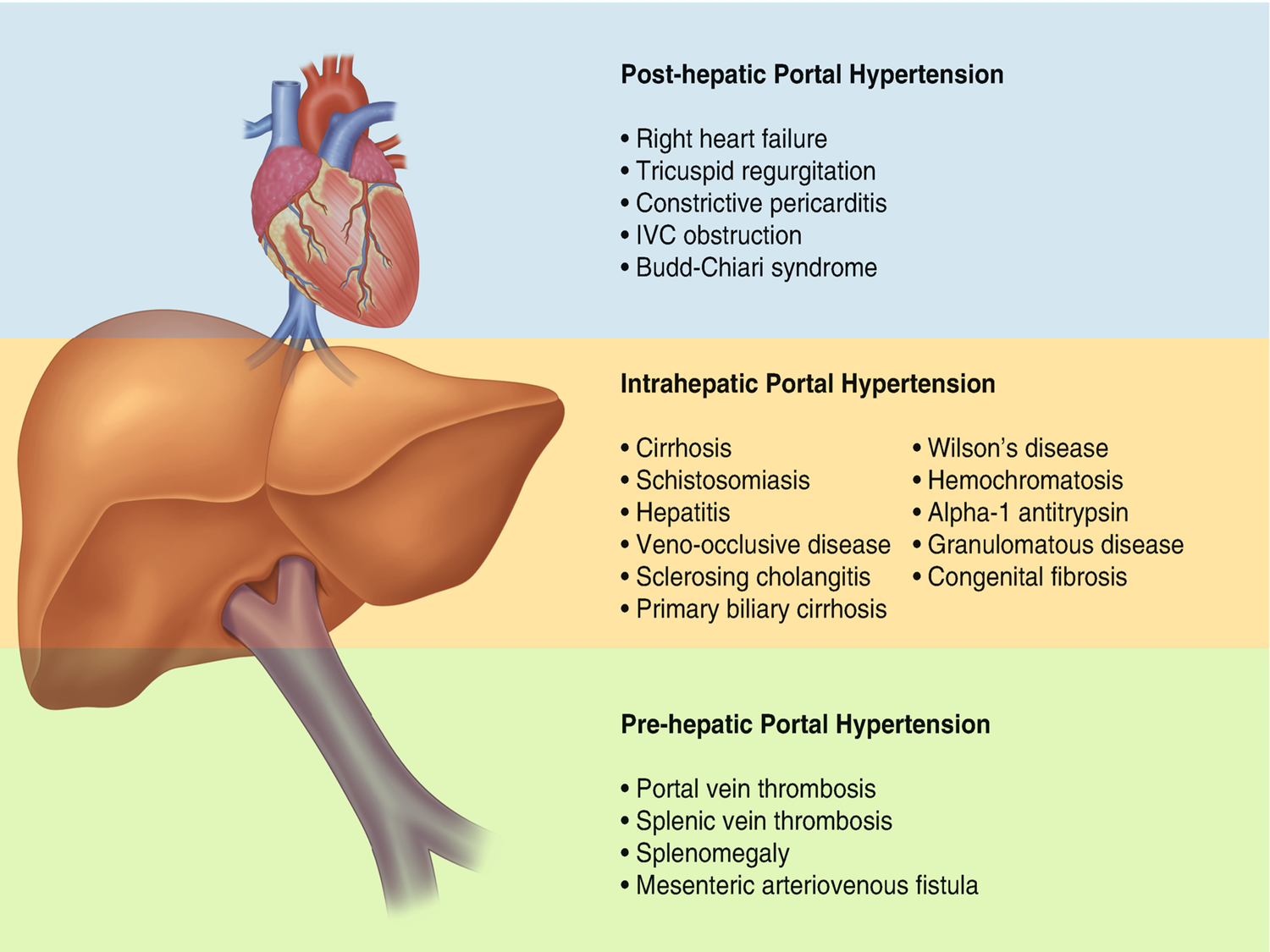
Study
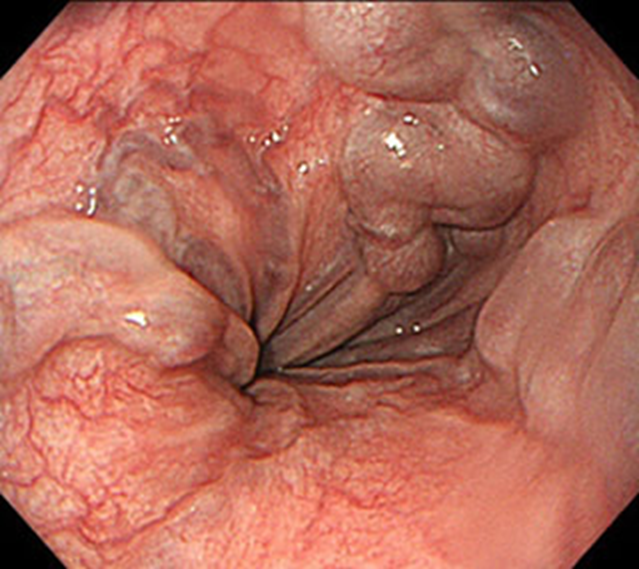
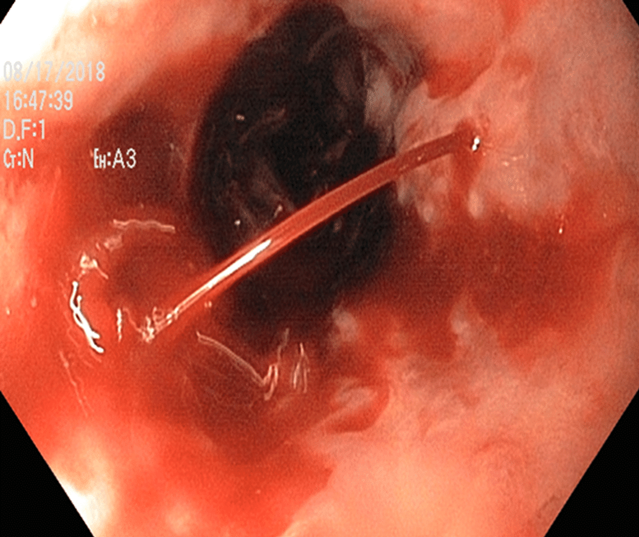
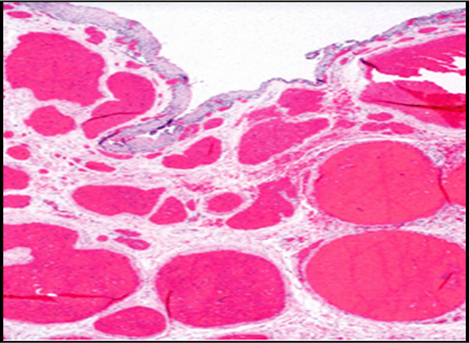
Esophageal varices
Edema secondary to obstruction of vascular flow
Ascites
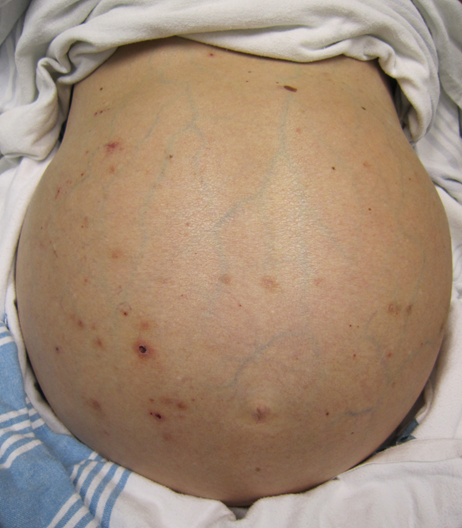
Ascites

Caput medusae
Ascites and cirrhosis
Infection of ascitic fluid without apparent source
Fever and malaise worsen with increased hepatic failure
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
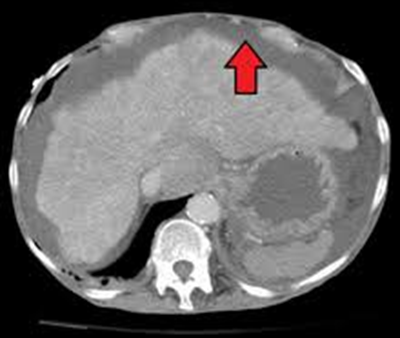
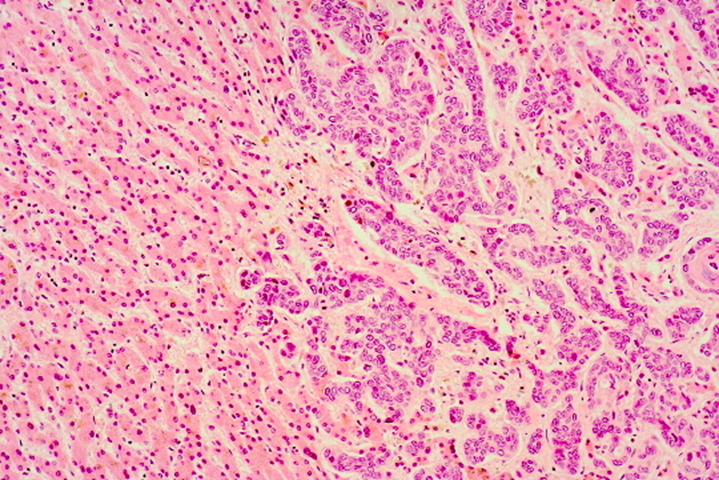
Hepatocellular carcinoma lives in a _____ liver
SICK
Hepatocellular carcinoma
could also be metastatic liver cancer
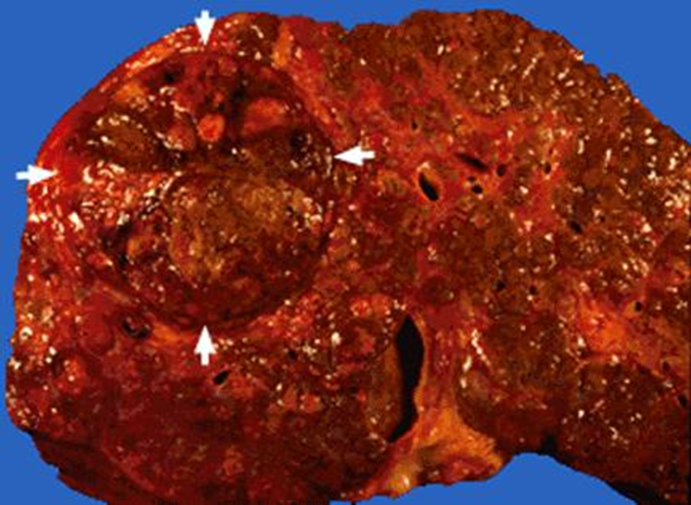
Hepatocellular carcinoma
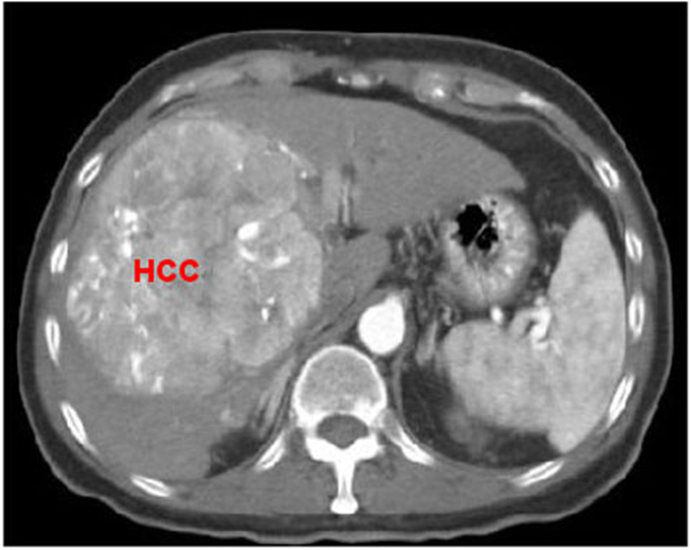
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Normal liver- steatosis - alcoholic steatohepatitis - fibrosis - Cirrhosis - HCC
Alcohol liver disease
____ used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring but not specific for HCC. Used after HCC is removed.
Alpha-fetoprotein
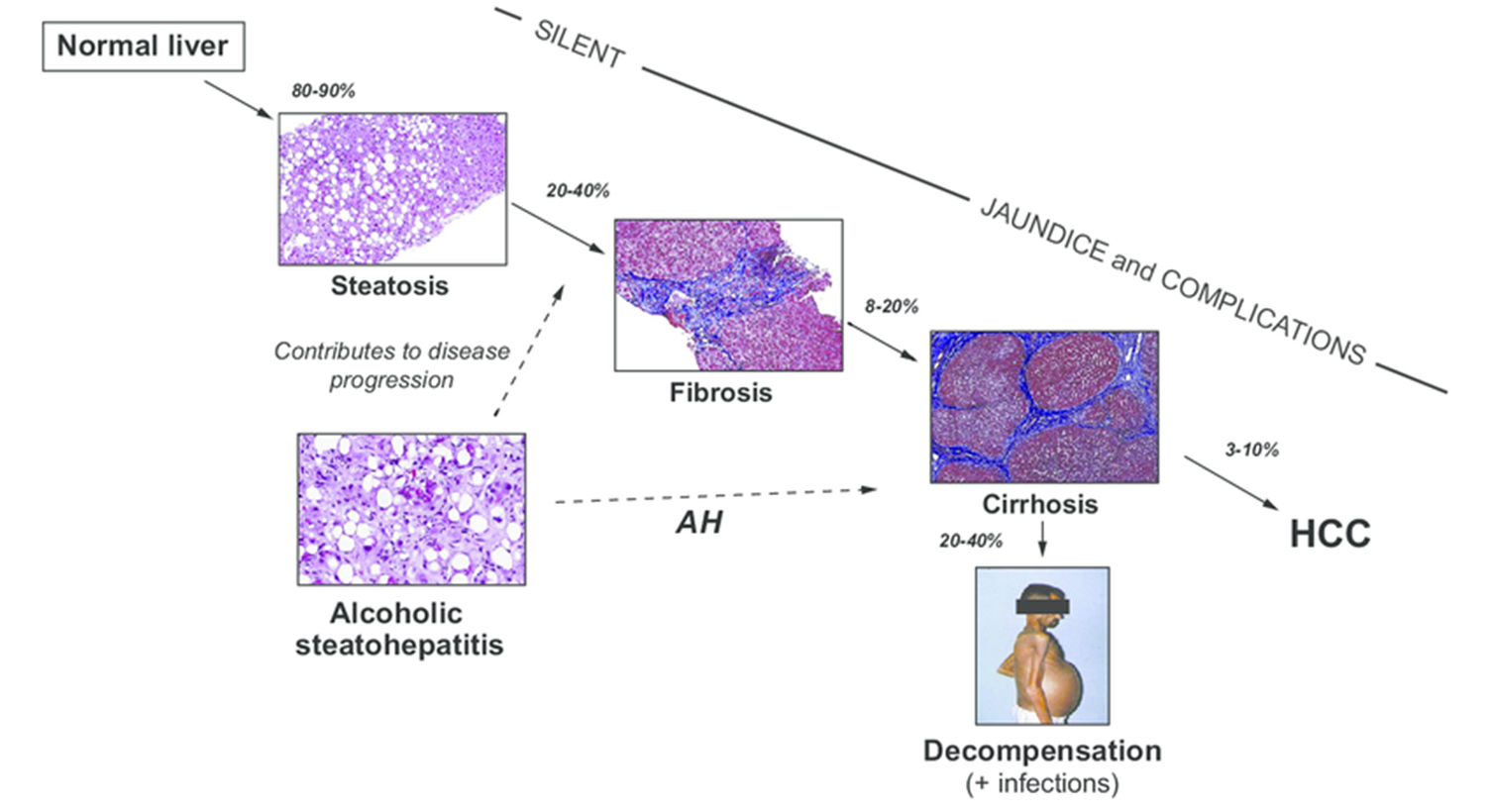
Summary fpr alcohol liver disease
Steatosis is _______
reversible
Chronic inflammation involving portal triads, leading to bridging inflammation to additional triads
Inflammation is replaced with portal triad fibrosis and then bridging fibrosis
Cirrhosis is end result
Viral hepatitis
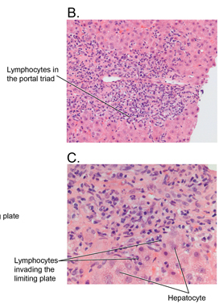
Autoimmune hepatitis
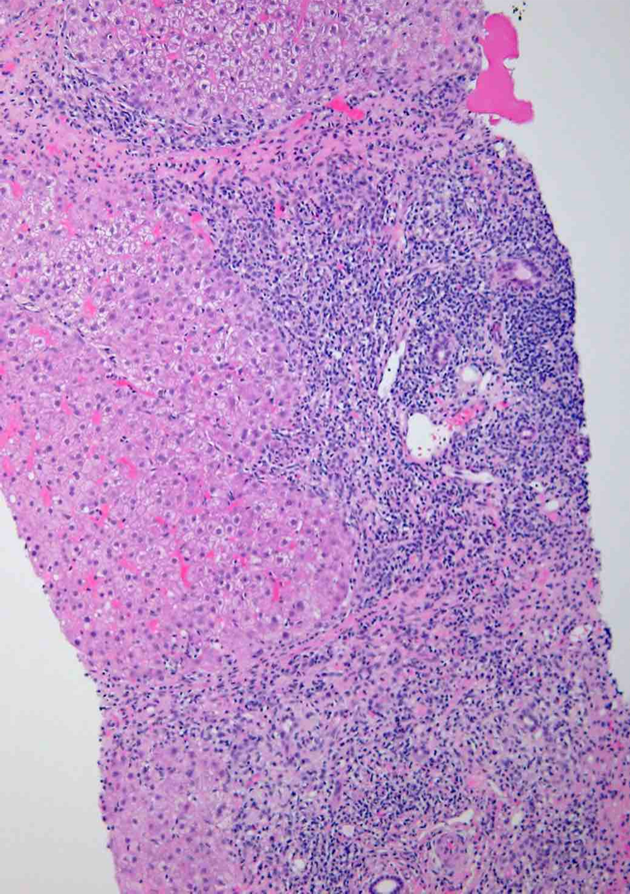
Hepatitis chronic inflammation, portal tracts
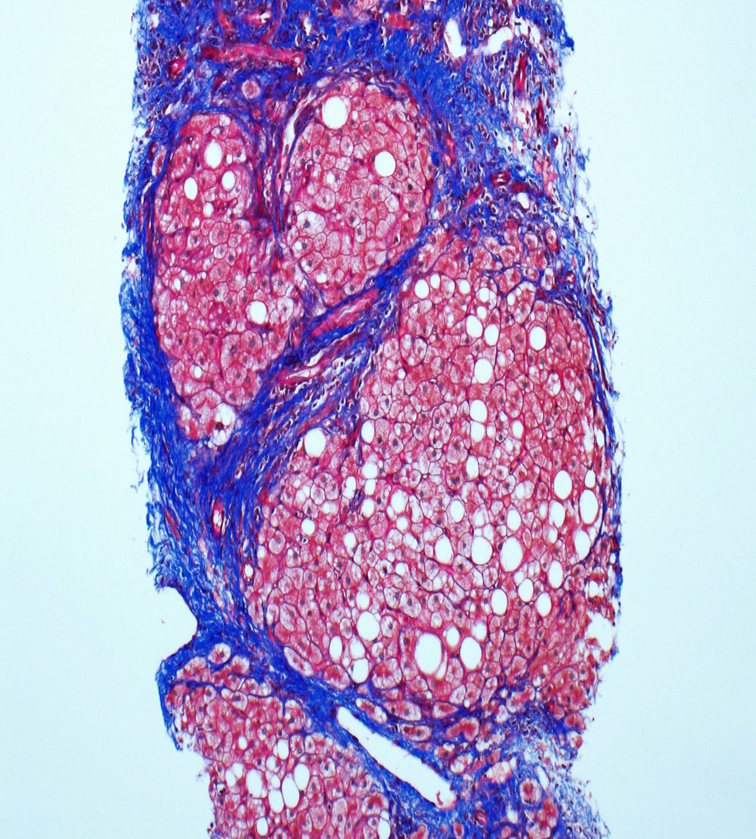
Cirrhosis
most common benign liver tumor
typically, does not need to be resected
Liver hemangioma