Cariology
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ergonomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
shortening of this muscle may contribute to radicular symptoms
pectoralis muscle, scalene muscles (neck),
inspiratory muscles
scalene muscles
most prevalent muscular disorder among dentists
Neck pain (70-80%)
Right handed clinicians
between 7 and 1
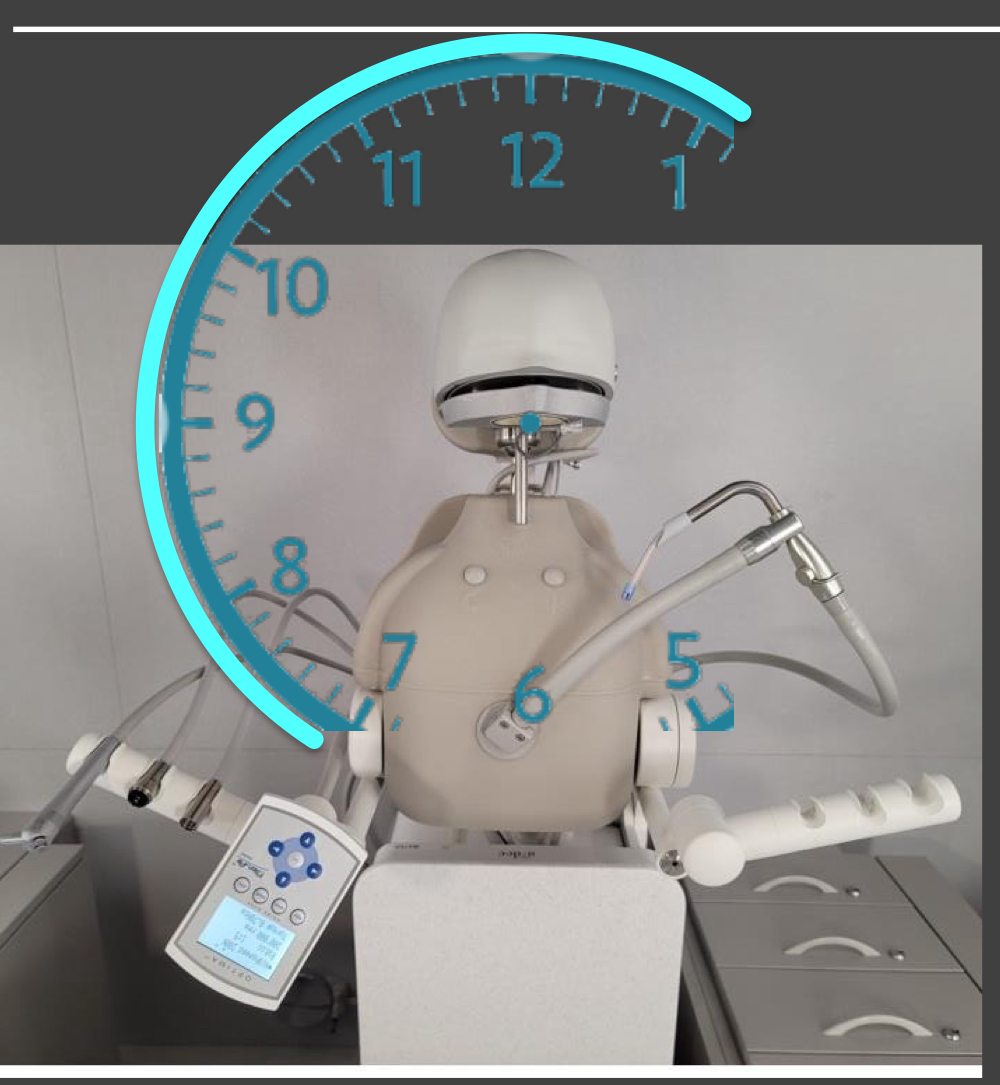
left handed clinicians
between 5 and 11
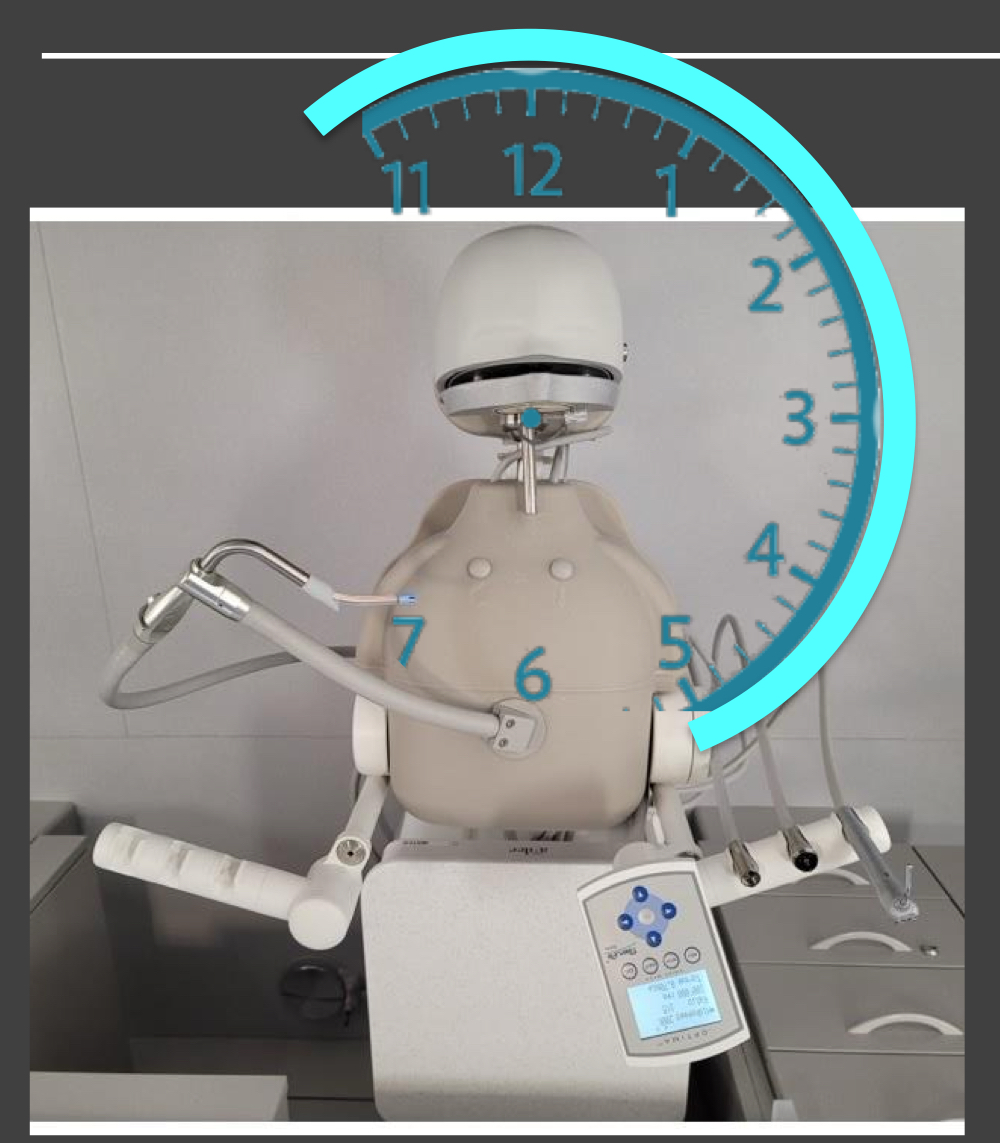

RHD: 8-9
maxillay and mandibular anterior toward
RHD: 9
mandibular posterior toward
maxillary posterior toward
RHD 12
anterior away (maxillary and mandibular)
RHD 10-11
mandibular posterior away
maxillary posterior away
LHD 3-4
maxillary anterior toward
mandibular anterior toward
LHD 12
mandibular anterior away
maxillary anterior awayL
LHD 3
mandibular posterior toward
maxillary posterior toward
LHD 1-2
posterior away (max and man)
low back MSD
60-70%
Shoulder MSD
65-75 %
neck
70-80% (most prevalent)
hand / wrist MSD
60-70%
shoulder complex
muscles:
trapezius
levator scapulae
rhomboids
serrates anterior
sources of radiating pain
cervical radiculopathy
thoracic outlet syndrome
carpal tunnel cysdrome
thoracic outlet syndrome
compression of neuromuscular structures in the cervicothoracic region
may cause global arm pain, paresthesias, weakness
main entrapment points of TOS
scalenes (neck muscles)
costoclavicular space
pectorals minor
nerves that supply the arm travel through the shoulder region
exit neck
under clivicle/ collar bone
under chest muscles
the arm
peripheral nerves: median, radial, ulnar
shoulder, upper arm, forearm, wrist
how many mmHg compression can damage nerve
30
fingertip pinch - 5 newtons
stretch
8-10 % tension can cause severe pain
11% reduce blood flow in 50% animal models
shortening of which muscle contributes to radicular symptoms
pectoralis minor
scalene
neuromuscular bundle of brachial plexus pass under
pectoralis minos
scalene muscles
inspiratory
26,000 breaths/ day
narrowing of space may contribute to radicular symptoms
costoclavicular space
2nd most prevalent MSD
lower back pain
critical pH of enamel
5.5
below this level (more acidic) : minerals dissolve
critical pH for dentin
5.5 - 7
more alkaline (more basic )
dentin is less calcified, progression of caries is faster
How long to progress from enamel to dentin.
4-5 years
vinegar/ acid causes
EROSION
NOT CARIES
diminishes enamel from the outside
is pain felt in enamel caries ?
no
vertical transmission
from parent to child / during birth
horizontal transmission
between peers/ significant other
pellicle
glycoproteins is saliva
cover tooth immediately (good bacteria)
attachment of early colonizers
0-24 hours (immediately)
co-adhesion and growth of attached bacteria/ formation of micro- colonies
4-24 hours
microbial succession
increased diversity
continued co-adhesion
growth of micro colonies (1-7 days)
climax community
1 week or older
resident oral fluora
hydrogen peroxide
bacteriocins
STREPTOCOCCUS
Major hypothesis
ecological plaque hypothesis
ecological plaque hypothesis
disease is the result of a shift in the balance of the resident microfluora driven by a change in local environmental conditions
white spot lesions
S. mutans
actinomyces
veillonella
dentinal caries and tubule infection
S. mutans
lactobacillus, actinomyces
bifidobacterium
prevotella
Root Caries
S. Mutans
actinomhyces
bifidobacterium
what kinds of dentin are salvageable
demineralized dentin
sclerotic dentin
tertiary dentin
(caries affected (transparent zone))
what kind of dentin is not salvageable
zone of destruction (caries infected, discolored )
mono saccharides
glucose (brain and muscle)
fructose (liver)
galactose
dissacharides
lactose
sucrose
maltose
polysaccharides
starch
amylose
amylopectin
sugar alcohols
non-cariogenic:
xylitol
mannitol
sorbitol
maltitol
lactitol
isomalt
tubule composition closer to DEJ
20,000 tubules/ mm2
closer to pulp
40,000 tubules / mm 2
what must happen before any adhesive procedure
teeth must be cleaned with OIL FREE PUMICE SLURRY
remove biofilm which has accumulated biofilm by day 3
what will decalcify enamel
phosphoric acid
smear layer
amorphous layer
on top of the tooth
created after drilling : bits of the fur, residual organic / inorganic debris
1-5 micrometers thick
which bur creates thinner smear layer
carbide bur: less friction / heat
smear layer is 2 micrometers
diamond bur : 5 micrometers
smear is more of a problem on
DENTIN
smear must be removed / made permeable by
PHOSPHORIC ACID
most important part of restoration
Bonding
contact angel
angle adhesive makes with the tooth :
hydrophilic - lower contact angle : better because enamel and dentin contain water
micromechanical bond
penetration
permeation
polymerization - mechanical interlocking
chemical bond
not strongest part
chemical bonding to hydroxyapatite via ionic bonding/ salt formation
chemical bonding to collagen via covalent bonding
classifications of adhesive systems
etch and rinse
self etch
universal
self - adhesive
bifunctional monomers :
HEMA
BIS GMA
G DMA
10 MDP
TEG DMA
U DMA
bifunctional monomers are both
hydrophobic (resin bonding) and
hydrophilic ( enamel and dentin )
solvents
water, ethanol , acetone
displaces water
reduces viscosity of co-monomer blend
allows permeation into collagen matrix
adhesive/ bonding resin
bifunctional monomers + photoinitiators + fillers
most common filler in resin
silica / silicon dioxide SiO2
2 step etch and rinse
primer and bond combined in single bottle
must be applied twice (essentially 3 steps)
high immediate bond strength
decreases over time
requires etch.
higher concentration of solvent (50%)
self etch
two step (self-etching primer)
one step (all in one)
two step self etch
etch and primer combined in one bottle
primer is more acidic : pH : 1.25-1.9
attempts to etch enamel and dentin simultaneously
smear layer is not removed but more permeable
bonding resin is hydrophobic and solvent free
must etch enamel again (acidic primer doesn’t work on enamel )
nano - layering
10 MDP forms monomer-calcium salt with hydroxyapetic (chemical bond)
one step self etch
highest hydrophilic monomer content : acts as a semi-permeable membrane on dentin surface - causes water sorption (bad )
universal / multi mode adhesive
single component light cured
can be applied as etch and rinse/ self etch, selective etch.
wet or dry
10 MDP makes interface resistant to degredation
pH : 2-3
universal adhesive composition
bi functional monomer s: bisgma, tegdma, 10dmp , 1- mdp phosphate, hema
solvent + photoinitiators (CQ, silane) fillers
common fillers
SiO2
BaO
Al2O3
NaSiF5
2SiO2
which mode do we use universal bond at USC
etch and rinse
type 1 etching pattern
dissolution of core of enamel rods
STRONGEST PATTERN
OCCLUSAL POSTERIOR
FACIAL ANTERIOR
type 2 etching pattern
dissolves periphery of enamel
INTERPROXIMAL
Aprismatic enamel
Aprismatic enamel = enamel without rods, highly mineralized, outermost layer, more acid-resistant.
TYPE III
aprismatic enamel
mix of type 2 and 1
what shape does dentin take after etching
funnel
acid etch
35% phosphoric acid
removes 3-5 micrometers of dentinal tissue
rinsing time
30 sec same as etching time
teeth should be shiny (not over dried )
MMP inhibitor
step 2.
matrix metallo proteinase
2% chlorhexidine
MMP
controls growth of DENTIN , eats collagen
awakened by etch
application of Chlorhexidine
only on DENTIN (where MMP’s are)
gentle scrubbing motion, 30 sec
gentle air dry (glossy)
universal adhesive
step 3
4 layers - active application
air dry 5-15 sec
MUST APPEAR GLOSSY
light cure
final step:
20 sec
nano filler
SiO2
2-5 micrometers
incorporated within hybrid layer
essential in formation of bond to tooth structure
HYBRID LAYER
normal salivary flow
1-2 ml / min
hyposalivary flow
< 0.5 ml/ minl=
caries risk assessment and documentation, LOW risk
D0601
caries risk assessment and documentation, MODERATE risk
D0602
caries risk assessment and documentation, HIGH / EXTREME HIGH risk
D0603