PMI Exam 3
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Feeding and Swallowing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the general anatomical differences between infants and adults/older kids?
Infants have:
Smaller jaw
Relatively larger tongue
Smaller hard & soft palate
Larger Buccal and fat pads
Uvula/epiglottis closer together
What pressure changes are involved with bottle feeding?
Compression (+ pressure) and Suction (- pressure)
How is compression created?
Upward movement of the tongue and jaw toward the palate during suckling.
What happens if there is only positive or negative pressure, instead of both?
Less efficient, take more time, and more energy.
What is the purpose of surfactant?
Provide greater gas exchange and respiratory performance, doesn’t let lungs collapse during exhale.
What are the protective reflexes?
Tongue protrusion
Baby sticking out tongue
Tongue lateralization
Moves food in mouth
Phasic bite
Pressure on gums causes open and closing of jaw
Gag
Prevents choking
Coughing
Airway protection
What are the adaptive reflexes?
Rooting
Locate source of food
Suckling
Reflexive oral pattern, self-soothe and feed from breast or bottle
What are the types of foods, their examples, and ages they are used?
Breastfeed/Bottlefeed
0-24 mnths
Pureed foods: rice cereal, yogurt, pureed fruit/veggie/meat
4-6 mnths
Mashed foods: mashed potato, squash, pumpkin, banana, avocado
7-9 mnths
Soft pieces: pieces of banana/avocado, cooked pieces of potato/squash
9-12 mnths
Soft mechanicals: cheese, roast chicken, meatballs, boiled veggies, pasta
12-18 mnths
Hard mechanicals: beef steak, pork, raw apple, raw carrot
18-24 mnths
Mixed textures: pieces of cooked chicken and pasta in mashed veggies
12-18 mnths
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 0-4 months?
Sidelying, cradle hold, upright supported
Breastfed/bottle fed
Can’t chew/bite
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 4-6 months?
Supported sitting position posture for a period of time
Hands to mouth
Breastfed/bottle fed, pureed foods
Can’t chew/bite
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 7-9 months?
Sit upright, needs support
Hands to mouth.messy self-feeding
Breastfed/bottle fed, open cup/weighted straw
Mashed solids, early chewing/no bite
Starting to get teeth
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 9-12 months?
Sit upright with minimal support
Self-feed + some help
Breastfed/bottle fed, open cup/straw cup
Chewing
Soft pieces
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 12-18 months?
Sit upright without support
Mainly self-feeding
Some breastfed/bottle fed, cup/straw drinking
Chewing, bites through soft foods
Soft mechanicals
What are the developmental feeding milestones for 18-24 months?
Sit upright without support
Mainly self-feeding
Cup/straw drinking, may still breastfeed/bottle feed
Hard mechanicals
When is it recommended to start solid foods?
After 4 months, but should be closer to 6 months
What are some examples of feeding difficulties in infants/children?
limited range of food
restricted volume of oral intake
poor weight gain
choking on bottles
long meal times
family stress related to child’s feeding
What are some disorders that commonly affect feeding?
Prematurity
Less than 37 weeks
Respiratory and cardiac disorders
Apnea, Pulmonary hypoplasia, respiratory distress, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, aspiration pneumonia
Cyanotic and Acyanotic heart defects
Gastrointestinal disorders
NEC (dying bowel), TEF (fistula between esophagus & trachea), CDH (hole in diaphragm allows abdomen to herniate into chest), GERD (abnormal reflux)
Neurological disorders
Microcephaly, Hydrocephalus, Cerebral Palsy, Acquired brain injury, Seizures
Congenital abnormalities
Cleft lip/palate, VPI, Down Syndrome
Maternal and Perinatal conditions
Diabetes, Jaundice, Drug/substance abuse
Iatrogenic complications
Tube feeding
Misc complications
Tonsillitis, Tongue-tie, sensory processing disorder
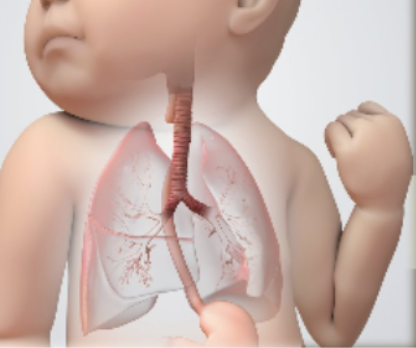
What GI disorder is this?
Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF)
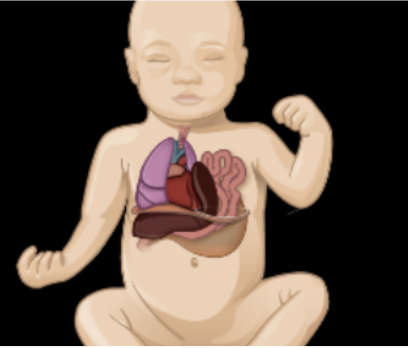
What GI disorder is this?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH)
Who is tube feeding for?
For preterm infants/children who cannot feed by mouth or do not have sufficient skill or endurance to support full, independent oral feeding
What are the types of tube feeding for babies?
NG tube: nasogastric; through nose into stomach
G tube: gastronomy; surgically inserted into abdomen
What is hypersensitivity regarding feeding?
“sensory defensiveness”
Picky eater
Hands off
May have food avoidances
Gags on certain foods
Unusual feeding like may not pick up certain foods but accept by spoon
What is hyposensitivity regarding feeding?
“sensory under registration”
Sloppy or messy eater
Messy hands/face
Overstuffs mouth, drools, choking (poor oral processing)
Oral stimulation through chewing, licking, eating non-food
Prefers rich flavors and textures
What are the alert states?
Deep sleep: Relaxed, sleeping soundly with no movement
Light sleep: Sleeping but moving, startles at noises, in REM
Drowsy: May doze, eyes may open and close with a gazed look
Quiet alert: Eyes open, body relaxed, may be focused on surroundings
Active alert: Eyes open, move around a lot, may be fussy
What is the best alert state for feeding?
Quiet alert
What’s the difference between FEES vs VFSS/MBSS regarding assessment?
FEES
Scope camera through nose and down throat
Difficult in infants
VFSS/MBSS
Video through x-ray of swallowing food in barium
More frequently used since less discomfort
What types of questions should be asked on case history?
Medical history
Growth
Diet
Early feeding history
General development
Cognitive skills
Onset of feeding difficulties
Current eating/drinking ability
Behavior during mealtimes
Parent stress with mealtimes
Details of any specific concerns with child’s eating/drinking
What is a good latch vs a bad latch to breast?
Good latch
Lips widely spread around nipple
Poor latch
Lips are closely sucking nipple
What structures are you looking at/assessing during an OM exam for feeding?
Assessed
Lips
Palate
Tongue
Jaw
Teeth (if present)
Cheeks
Observed
Structure
Symmetry
Appropriate size
Tone
Range of motion
What is aspiration?
Material passing through vocal folds and going below into trachea. Can occur on refluxed or regurgitated stomach contents.
What is penetration?
Material entering larynx but staying above vocal folds
Wet voice, cry, ratty chest, coughing, cyanosis, stress cues like tearing & finger splaying are signs of?
Aspiration or penetration
What is the purpose of thickened liquids?
Children with swallowing problems
Slows rate of fluid flow, allowing more time to close airway before swallow
Hold together better than thin fluids so easier to control in mouth
Infants who display regurgitation
Are less likely to be regurgitated from stomach back into esophagus
What is Operant conditioning?
Improves feeding difficulties and increases oral intake through specific prompted food goals and a reinforcement system.
What is Systematic desensitization?
Improves feeding difficulties and increases oral intake by exposing children to a range of foods in play-based activities, which become gradually more challenging; used now.
What are the pros and cons to Oral-Sensory Motor Therapy?
Pros
Modifies child’s current oral motor skills and sensory processing in relation to eating and drinking
Cons
Lack of specificity
Insufficient evidence to its effectiveness
What is important to consider about positioning for feeding?
Fluids flow faster vertically
More upright position/side-lying position to slow feeds
Older children can do chin-tuck and avoiding neck extension to slow feeds
What is important to consider about pacing for feeding?
Taking breaks to interrupt flow of liquid -> allowing baby time to swallow safely
Infants: feeder actively imposes breaks to allow swallow/catch breath -> SSB
Older children: done based on cues or a set schedule
What is important to consider for using swallowing maneuvers for feeding infants?
Many strategies for adults don’t work on children due to cognitive skills
Require modeling
Generalization limited
What is important to consider about modified foods?
2-3 years, most children eat most solids
Children with developmental delay may require modified food textures beyond
Consider if child can chew a hard solid or cognitively understand what to do with food
What is important to know about feeding equipment?
Slow flow of fluids
Infants: slow-flow nipples, nondrip/compression based nipples
Older children: weighted straw cups, cut-out cups, infatrainer cup
Downward movement of the tongue and jaw creates ____ pressure.
negative
Upward movement of the tongue and jaw creates _____ pressure.
positive