Bio Invaders Final (shortened)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PCB2441 - UF Fall 2023 [socred a 94% on exam]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
impact levels
GYPSY (GIP-CE)
genetic
individual
population
community
ecosystem
Genetic Level Impact
gene pool - hybridization, introgression
genetic level example
non-native Spartina and native Spartina interbreeding

individual level impact
behavior, morphology, demographic rates
individual level example
invasive ants changing behavior of mice

population level impact
population growth, composition
population level example
Burmese pythons reducing populations
community level impact
diversity, composition
community level example
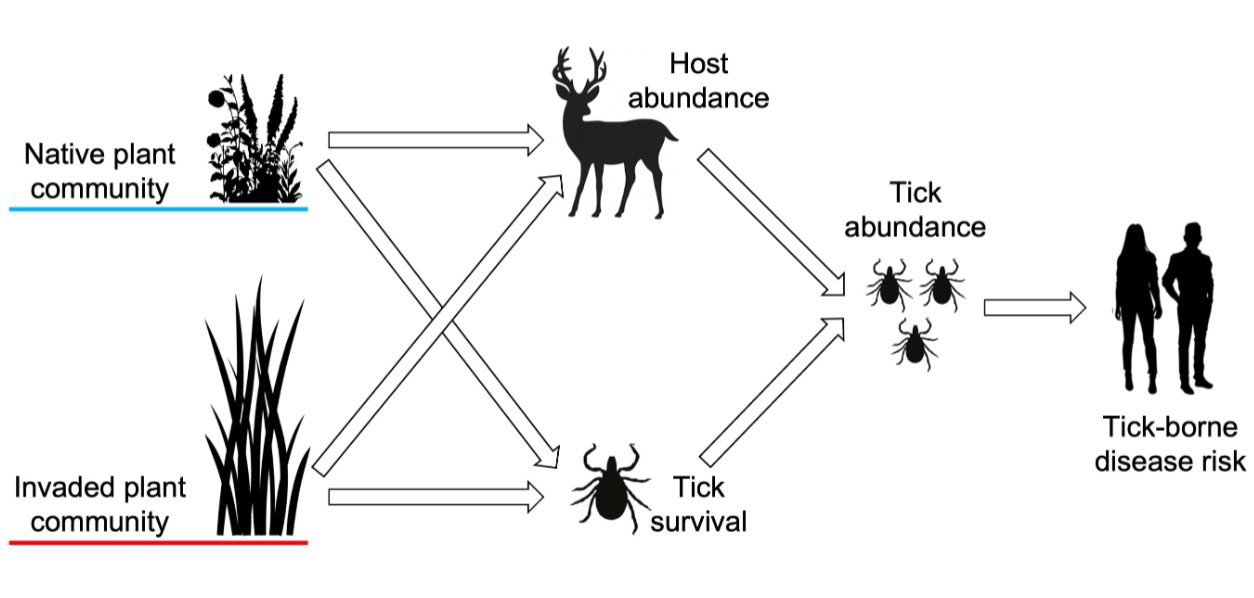
invasive plants affecting tick survival and host abundance
Hemlock Woolly Adelgid reducing forest diversity
ecosystem level impact
material flow and operations
ecosystem level example
Reed Canary Grass - hydrology
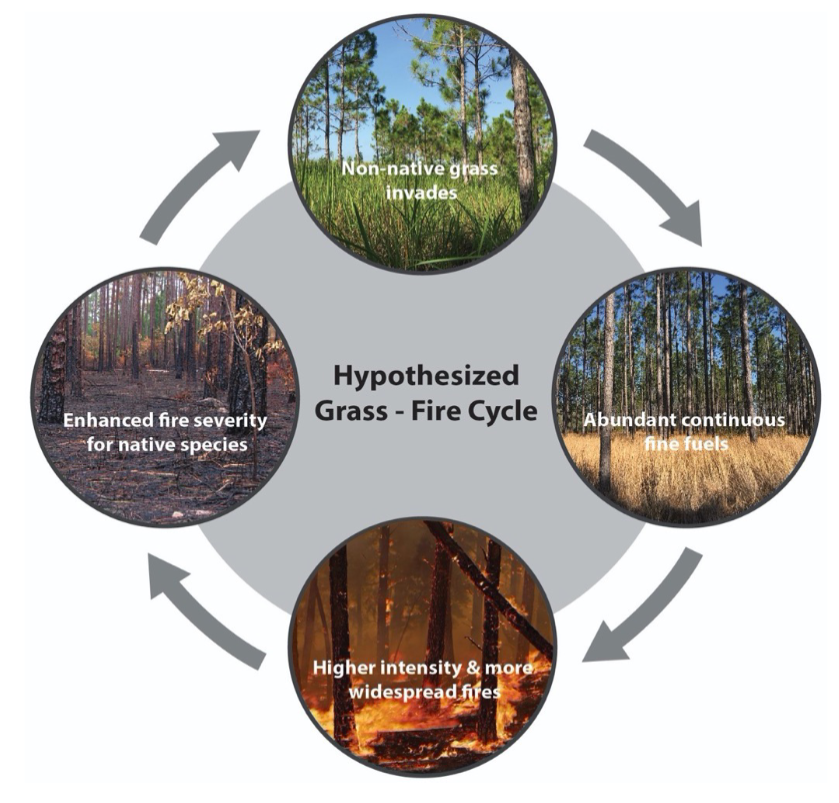
Cogongrass - fire regime
Morella Faya - nitrogen fixation
Hemlock Woolly Adelgid - carbon storage, fish populations, nutrient flow, stream warming
methods to evaluate
Observation
Removal
Introduction
observation method
invader v. invader-free areas
shows broad patterns
quick and easy
hard to disentangle cause/effect
removal experiment method
method determines result
effects may not be removed
experimental introduction method
under controlled conditions
not realistic
ethical concerns
possible interactions
additive (+)
synergistic (x)
offsetting (-)
inspection policy
large cargo volume
relies on exporting country
ineffective laws
focus on agriculture
uses dirty lists
tight/competitive budgets
often too late
inspection policy example
Microstegium - worst invader, not regulated
ineffective laws example
FIRFA 1947 - regulation of pesticides
biocontrol steps
Fast, Fried, Quick, P.R.E. (FF-Q-PRE)
Feasibility
Foreign Host Range
Quarantine
Permit for Release
Release and Establishment
Evaluations
biocontrol pros v. cons
PROS
widespread invasions
CONS
expensive
many years
cannot be contained
chemical/mechanical pro v. cons
PROS
affordable for short-term
quick
targeted
CONS
expensive for long-term
controversial
can be used improperly
can fail
chemical method examples
backpack sprayer
airboat
injections
baits
mechanical method for plants examples
cut stump
dig + burn
mowing
mechanical method for animals examples
trapping
fencing
shooting
Blackburn Model
TIES-I
Transport
Introduction
Establishment
Spread
Impact
speciation
allopatric - gographic
sympatric - behavior
global drivers of biodiversity
ORID
old habitats
reinforcing
isolation
divided landscapes
continent v. island
resistance: against disease/extinction
persistence: somewhere else
ballast
soil, sand, rocks brings weeds and insects
traits of invasive animals
fast growth rate
high fecundity
quick maturity
toleration of conditions
broad diet
highly competitive
few predators/disease
barriers of invasion
Billy Goes Camping, Spreading Red Dust Everywhere
BARRIERS
Geography
Captivity/Cultivation
Survival
Reproduction
Dispersal
Environment
traits of invasive plants
fast growth rate
high fecundity
thrive under disturbed conditions
habitat generalists
extended phenology
allelopathy
alter soil conditions
inavsive mechanisms
propagule pressure
abiotic factors
biotic factors
propagule pressure
size x frequency
null hypothesis
abiotic factors
disturbance causes favorable conditions
biotic factors
enemy release hypothesis
biotic resistance