2.1.1 Macroeconomics objectives
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Economic growth
Economic growth is the increase in real and/or potential GDP (output) in an economy in a given period of time
GDP
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is a measure of economic growth.
GDP is the value of production of goods and services in an economy in a given period of time (normally a year).
Nominal and Real GDP
Real – takes into account inflation
Nominal –Not adjusted to take into account inflation
Limitations of using GDP to measure economic growth
GDP overestimates well-being – e.g. it does not take into account the environmental damage of production
GDP underestimates well-being - e.g. natural resources are not included
GDP lacks information – e.g. numbers do not indicate the type of production
GDP does not take into account the quality of production (in particular technological goods)
GDP does not include unofficial or unpaid work.
The economic cycle
The Economic cycle shows how the economy tends to exhibit recurring trends in economic growth rates.
Draw a graph of the economic cycle
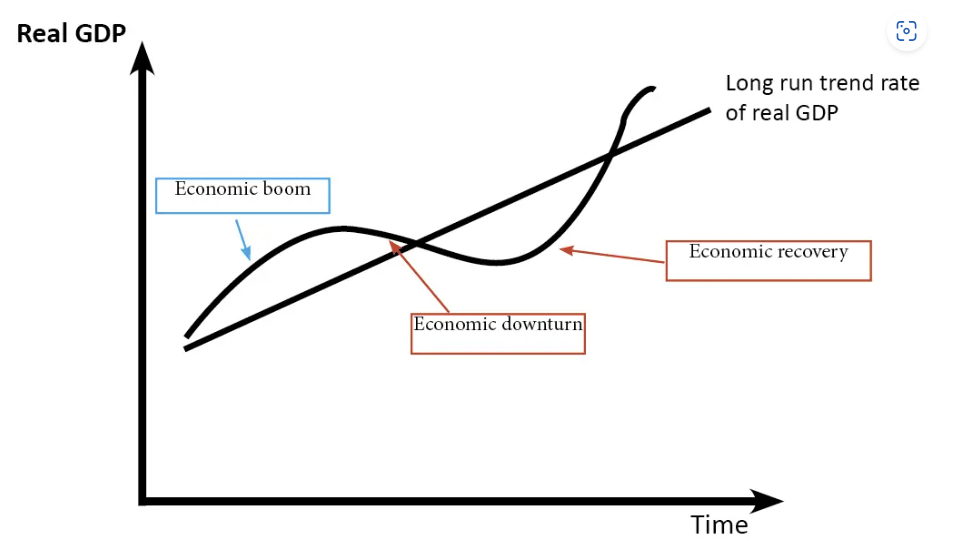
What two main things occur ina n economic boom period
High rates of growth, low rates of unemployment
What is a recession
a period of two or more consecutive quarters of negative economic growth
Characteristics of a recession
Negative rates of economic growth, high rates of unemployment
Benefits of economic growth (6)
Increased revenues and profits for firms.
Increased employment opportunities.
A decrease in absolute poverty rates
Improvement in the environment as more efficient, cleaner technology is developed
Education standards increase
Health improves
Potential costs of economic growth (4)
A negative impact on the environment as non-renewable resources are used up
Increased inflationary pressure
An increase in relative poverty/income inequality
The social effects of increased production – more stress, less leisure time.
Inflation
A general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. This is usually measured using the consumer price index (CPI)
Deflation
A fall in the average price level in an economy in a given period of time.
Disinflation
A fall in the rate of inflation (prices increasing but at a slower rate)
Consumer price index (CPI)
measures the change in prices over a year.
Types of inflation (2)
Demand-pull inflation
Cost-push inflation
Demand pull inflation
An increase in demand with no increase in supply will increase the price level. This is because there is less spare capacity in the economy.
Cost-push inflation
An increase in costs of production can increase the price level in an economy. E.g. an increase in wages, import prices or taxes. Firms will pass increased costs onto consumers.
Costs of high inflation (7)
Lack of purchasing power
Growth and unemployment
International Competitiveness
Wages increase
Redistribution costs
Psychological costs
Uncertainty
Benefits of low inflation (3)
The real value of borrowing is decreased over time
An inflation target can help policy makers make decisions
Stable and low inflation boosts business and consumer confidence
Employment and unemployment
Employment – those in paid word
Unemployment – when individuals are without a job but actively seeking work
Unemployment rate
Number unemployed divided by the population of working age.
Types of unemployment (5)
Frictional unemployment
Seasonal unemployment
Structural unemployment
Cyclical or demand-deficient unemployment
Voluntary unemployment
Frictional unemployment
Short-term unemployment. People who are in-between jobs or those who have just finished studying.
Seasonal unemployment
Occurs when people are unemployed at certain times of the year, because they work in industries where they are not needed all year round. E.g. tourism.
Structural unemployment
Unemployment resulting from industrial re-organization, typically due to technological change, rather than fluctuations in supply or demand. This often happens because there is occupational and geographical immobility of labour. Structural unemployment is likely to have a more long-term detrimental effect than others such as frictional and seasonal.
Cyclical or demand-deficient unemployment
Unemployment resulting from there being insufficient demand in an economy. This tends to vary with an economic cycle.
Voluntary unemployment
when a person chooses not to work
Consequences of unemployment
Loss of income
Use of scarce resources
Poverty
Government spending on benefits
Loss of national output
Loss of tax revenue
Social costs
Consumer confidence
Business confidence
Social costs
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation
A countries current account equation
value of exports – value of imports
Current account deficit
the value of imports is greater than the value of exports. This means money is flowing out of the country. The current balance will be negative.
Current account surplus
the value of exports is greater than the value of imports. This means money is flowing into the country. The current balance is positive.
Impact of a current account deficit (3)
Leakage from the economy
Can be inflationary if prices rise abroad: Low demand for our exports
Problems finding foreign reserves to fund the deficit
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation
Business activity that damages the environment (4)
Mining
Power generation
Agriculture
Construction
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation
Ways businesses damage the environment
Visual pollution (including litter)
Noise pollution
Air pollution
Water pollution
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation
Government intervention to protect the environment (5)
Taxation
Subsidy
Regulation
Fines
Pollution permits
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation
Income inequality
differences in income that exist between the different groups of earners in society, that is, the gap between the rich and the poor
Absolute poverty
Where people do not have enough resources to meet all of their basic human needs.
Relative poverty
poverty that is defined relative to existing living standards for the average individual. There is no precise measurement of relative poverty
Reasons to reduce poverty and inequality
Meet basic needs
Raise standards of living
Ethical reasons – some people feel the need to act morally correct and give to charity to help end poverty.
Government intervention to reduce inequality and poverty (3)
Progressive taxation
Redistribution through benefit payments
Investment in education and healthcare
Refer to notes for more in-depth explanation