Exam #2 A&P
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Histology & The Integumentary System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Integumentary System
Consists of the skin and its accessory structures, including hair, nails, and glands.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of skin, composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Dermis
The layer of skin beneath the epidermis, containing loose connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue.
Hypodermis
Also known as the superficial fascia or subcutaneous fat; it anchors the skin to deeper structures. not a layer of skin! very vascular and composed of adipose and loose connective tissue.
Sebaceous gland
Glands that produce oily sebum to waterproof and lubricate the skin.
cellulite
A dimpled appearance of the skin caused by fat deposits pushing through the connective tissue beneath the skin, usually occurring in areas such as thighs and buttocks.(not a disorder)
Sweat gland
Glands that produce sweat for thermoregulation and excretion of waste.
Sensory receptors
Detect heat, cold, pain, and pressure in the skin.
Arrector pili muscle
Small muscles associated with hair follicles; cause hair to stand up (goosebumps).
Thermoregulation
The process of maintaining a stable internal body temperature.
Vitamin D synthesis
The process that occurs in the skin, where UV light converts dehydrocholesterol to vitamin D3.
Keratinocytes
The primary cell type in the epidermis that produces the protein keratin.
Melanocytes
Cells in the epidermis that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
Dendritic cells
Immune cells located in the skin that protect against pathogens.
Tactile cells
Sensory receptors in the skin that detect light touch.
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer of the epidermis, consisting of dead, flattened keratinized cells.
Stratum lucidum
A clear layer of dead skin found only in thick skin areas.
Stratum granulosum
A layer of the epidermis where keratinization begins.
Stratum spinosum
Layer of the epidermis where keratinocytes are interconnected by desmosomes.
Stratum basale
The deepest layer of the epidermis, where cell division occurs.
Papillary layer
The upper layer of the dermis, which contains loose connective tissue and dermal papillae.
Reticular layer
The denser, deeper layer of the dermis; contains collagen and elastin fibers.
Melanin
The pigment produced by melanocytes that provides skin color and protects against UV damage.
Erythema
Redness of the skin often caused by increased blood flow.
Pallor
Paleness of the skin due to decreased blood flow.
Cyanosis
A bluish coloration of the skin due to low oxygen levels in the blood.
Jaundice
A yellowish coloration of the skin, often due to liver conditions.
Freckle
A small area of increased pigmentation due to melanin production.
Mole (nevus)
An area of increased pigmentation due to proliferation of melanocytes.
Albinism
A genetic condition characterized by the absence of melanin production.
Acne vulgaris
A skin condition that arises from an accumulation of sebum and dead cells in sebaceous glands.
First-degree burn
A burn affecting only the epidermis, causing redness and minor pain.
Second-degree burn
A burn affecting the epidermis and part of the dermis, causing blisters.
Third-degree burn
A burn that extends through the epidermis and dermis, affecting deeper tissues.
Basal cell carcinoma
The most common type of skin cancer, arising from keratinocytes in the stratum basale.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Skin cancer arising from keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum.
Malignant melanoma
A serious type of skin cancer that originates from melanocytes and can metastasize.
ABCDE rule
A guideline for identifying suspicious moles (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving).
Hair bulb
The base of the hair follicle where hair growth occurs through mitosis.
Hair follicle
The structure from which hair grows; includes epithelial and dermal root sheaths.
Cuticle (hair)
The outermost layer of the hair shaft, made of overlapping keratinized cells.
Cortex
The middle layer of hair, providing strength and color.
Medulla
The innermost layer of hair, composed of soft keratin.
Hair shaft
The visible part of the hair that extends above the skin surface.
Nail plate
The hard protective covering of the fingertip.
Lunula
The visible part of the nail matrix at the base of the nail.
Eponychium
The cuticle that overlaps the proximal end of the nail.
Hyponychium
The skin underneath the free edge of the nail.
Eccrine sweat glands
Sweat glands that are widely distributed across the body, mainly for temperature regulation.
Apocrine sweat glands
Sweat glands found in specific areas (such as armpits), functional at puberty.
Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands in the ear canal that produce earwax.
Mammary glands
Modified sweat glands that produce milk.
Acne
A skin condition caused by the blockage and inflammation of sebaceous glands.
Skin markings
Patterns formed by epidermal ridges; enhance grip and contribute to fingerprints.
Wrinkles
Aged skin appearance due to loss of collagen, elastic fibers, and hydration.
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment.
Histology
The study of normal structures of tissues.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Ground Substance & Protein Fibers. The material surrounding cells in a tissue composed of substances in liquid, gel, or solid forms. provide strength to resist stretching and compression and holds cells in place.
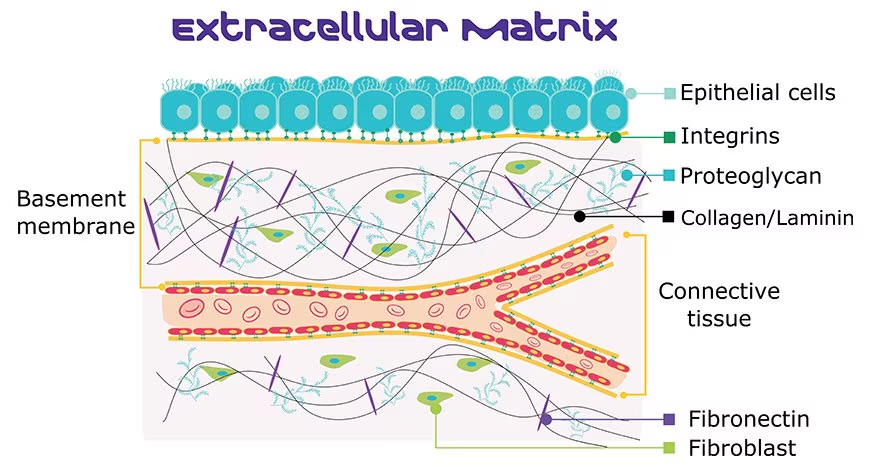
Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue that consists of tightly packed cells that cover and line body surfaces and cavities. provides protection immune defenses, secretion of hormones and oils , transport and sensation. Avascular Tissue and fairly impermeable.
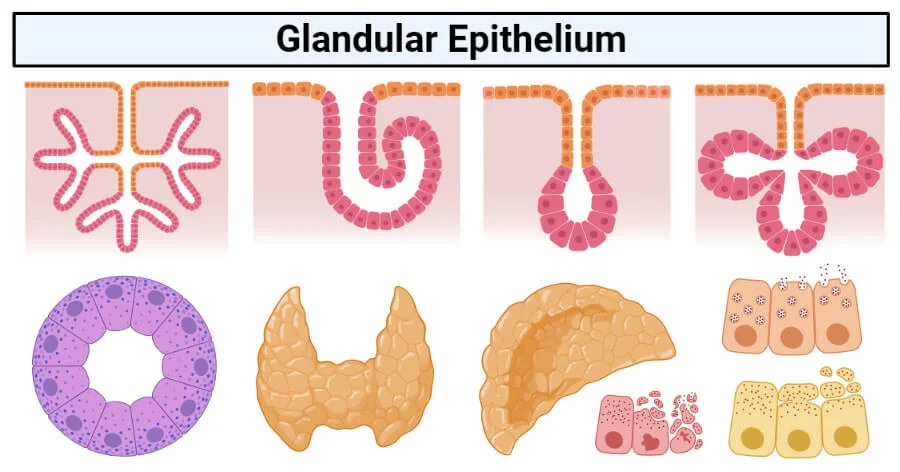
Glandular Epithelia
Epithelia specialized for secretion, including endocrine and exocrine glands.
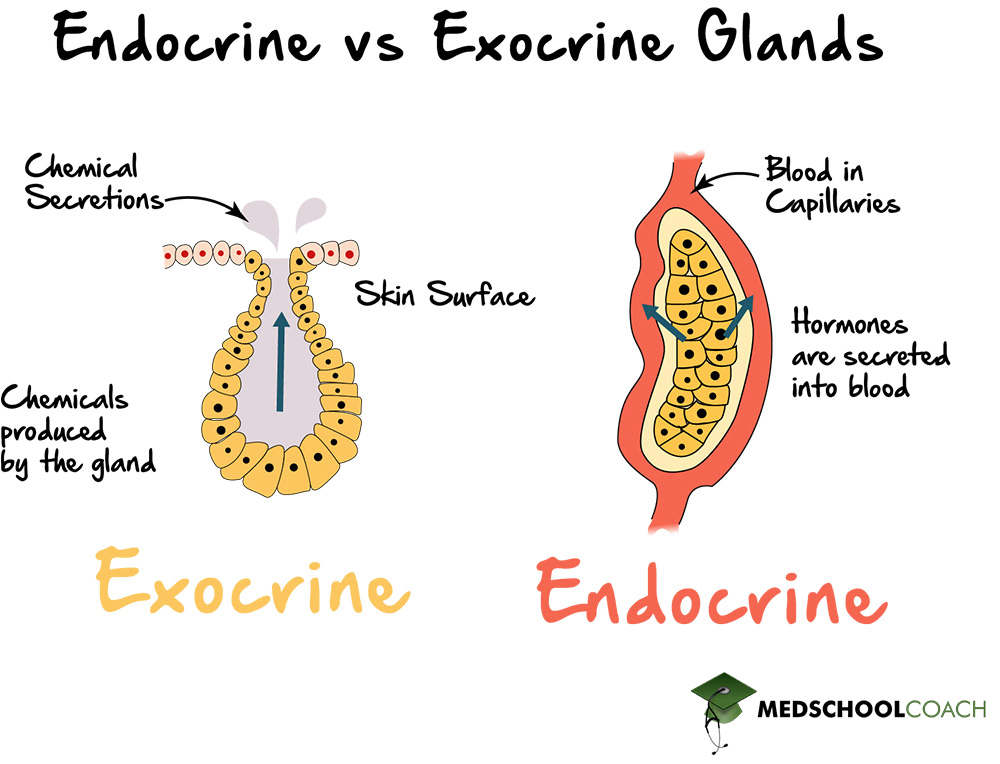
Endocrine Glands
Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream without ducts. ex: thyroid, pituitary, ovary
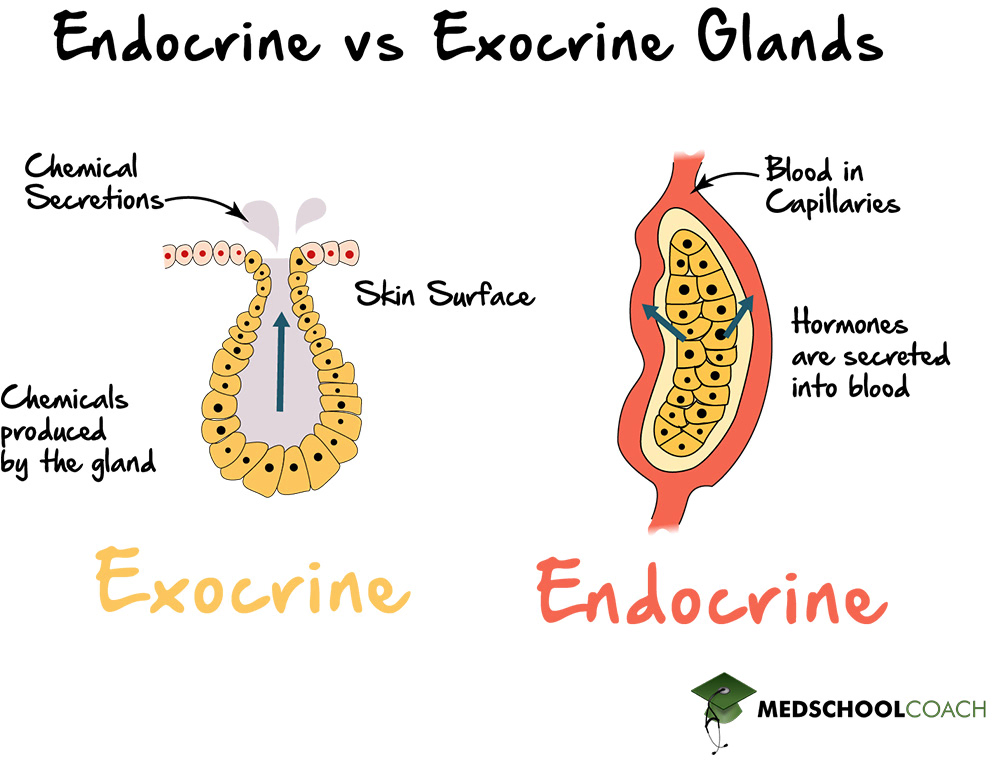
Exocrine Glands
Glands that have ducts and secrete substances with local effects. ex: sweat and salivary glands
Goblet Cells
unicellular and secrete mucus for digestive and respiratory tracts. protects underlying epithelia
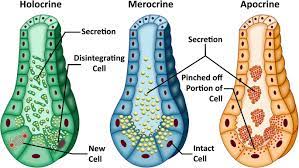
Merocrine Secretion
A type of exocrine secretion where products are released via exocytosis without loss of cell integrity, such as in sweat and salivary glands.
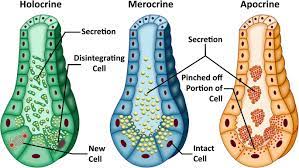
holocrine secretion
A type of exocrine secretion where entire cells disintegrate to release their substance, such as in sebaceous glands.
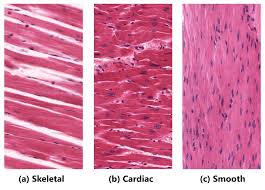
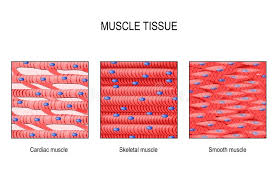
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and under voluntary control.
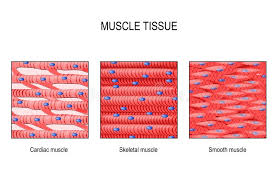
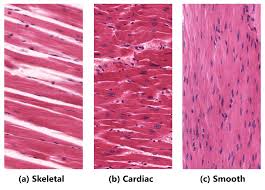
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and involuntary, found in the heart.
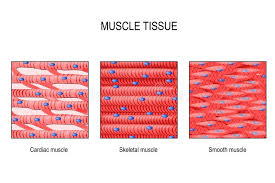
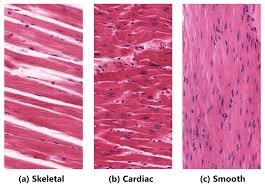
Smooth Muscle Tissue
A non-striated, involuntary muscle tissue found in the walls of hollow organs.
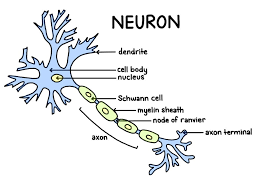
Neurons
Cells in nervous tissue capable of transmitting nerve impulses. They consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. They send and receive messages.
Neuroglial Cells
Support cells in nervous tissue that do not conduct impulses.
Regeneration
The process of replacing damaged or dead cells with the same type of cells.
Fibrosis
The process of scar tissue formation, where fibroblasts produce collagen to repair tissue. results in scar tissue
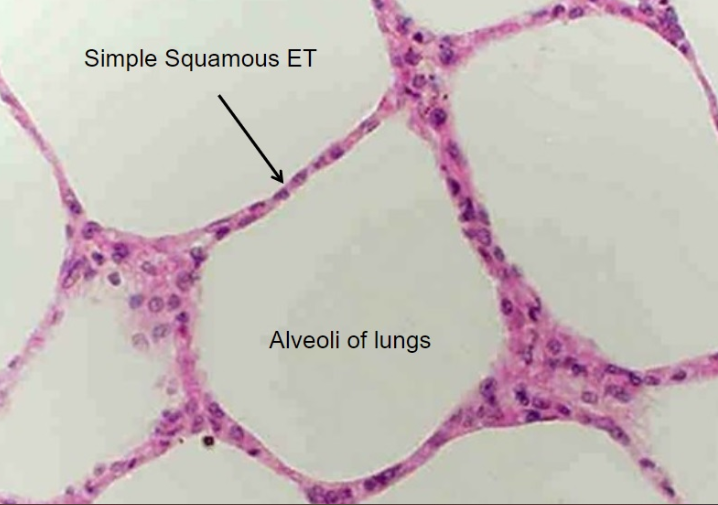
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A single layer of flat cells that facilitates diffusion, found in air sacs of lungs and line blood vessels. good for rapid diffusion
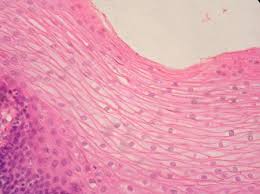
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Multiple layers of cells that protect underlying tissues from abrasion, found in skin, mouth, and throat.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
A single layer of cube-shaped cells that functions in secretion and absorption, commonly found in glands and kidney tubules.
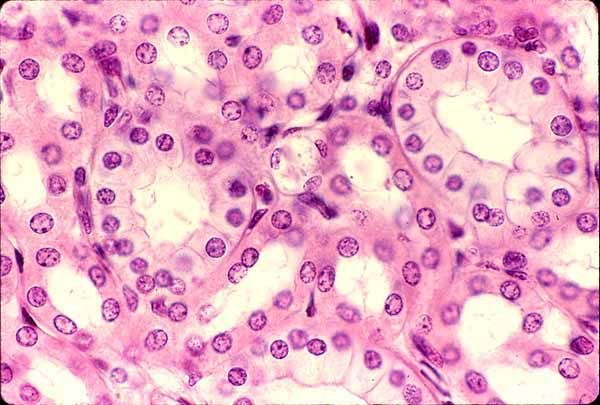
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
rare in humans. lines ducts of sweat glandsand mammary glands, providing protection and some secretion.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
A single layer of column-shaped cells that aids in absorption and secretion, typically found in the digestive tract and uterus. often has microvili to increase surface area for absorption.
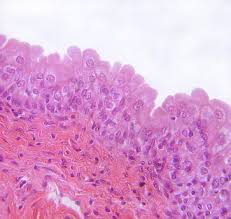
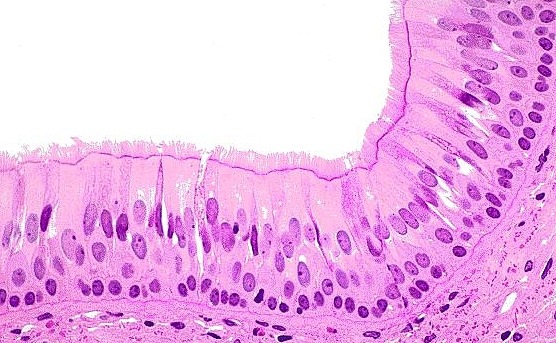
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
multiple layers of column-shaped cells that are rare in humans found in male urethra, cornea, and ducts of salivary glands
Transitional Epithelium (stratified weird)
A type of epithelium consisting of multiple layers of cells that can stretch, found primarily in the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra, allowing for flexibility and expansion. basal cell layers are cuboidal and the upper layers are flattened or dome-shaped.
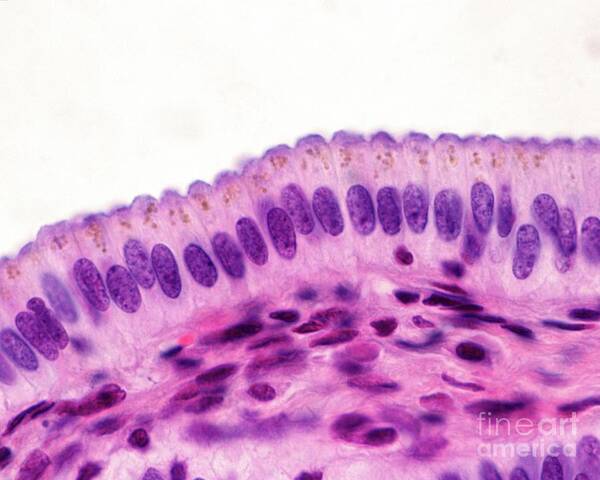
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue that appears to have multiple layers due to varying cell heights but is actually a single layer of cells, often found lining the respiratory tract and containing cilia to help move mucus. Found in Trachea and respriratory passages, it helps trap and move particles out of the airways.
Ground Substance
makes up most of extracellular matrix ECM . Made up of extracellular fluid aka interstital fluid, proteoglycans, GAGs, CAMs, and protien fibers.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
polysaccharides in ECM. ex: chondroitin sulfate (cartilage) and hyaluronic acid
Proteogycans
macromolecules in the extracellular matrix, consisting of a protein core with glycosaminoglycan side chains. They play a crucial role in regulating the movement of water and nutrients within tissues.
Cell-Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
Made up of different glycoproteins that bind surface protein and maintain architecture of tissues
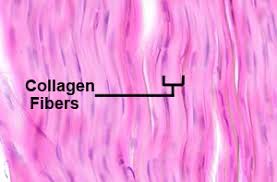
Collagen Fibers
Protein fiber that is resistant to tension and pressure. 20-25% of all proteins in the body. (white, fibrous)
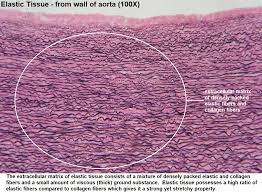
Elastic Fibers
protein fibers that provide elasticity and resilience to tissues, allowing them to withstand stretching. (yellow)
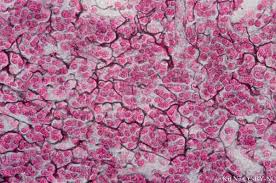
Reticular Fibers
thin, web-like protein fibers that provide a supportive framework for soft tissues and organs. meshwork
carcinogens
substances that are known to cause cancer by altering cellular metabolism or damaging DNA.
carcinoma
a type of cancer that originates in epithelial tissues, such as skin or lining of organs.
basal cell carcinoma
a common type of skin cancer that arises from basal cells in the epidermis. It typically manifests as a growth on sun-exposed areas. basement membrane slows the spread of cancerous cells, making it less aggressive than other skin cancers.
Connective Tissue (CT)
A type of tissue that connects tissues to one another, consists of scattered cells in an ECM, and provides support, protect and transport substances. very vascular
loose connective tissue areolar
a type of connective tissue characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and cells in the extracellular matrix, providing flexibility and support.
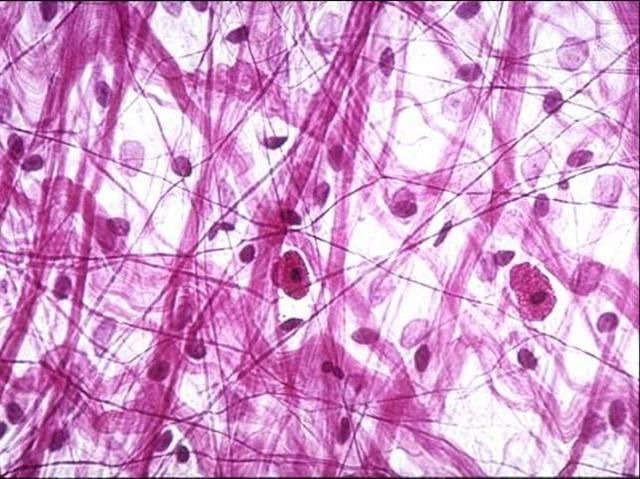
dense regular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that has tightly packed collagen fibers arranged in parallel, providing strength and resistance to tension in one direction.
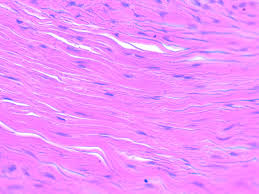
dense irregular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue with collagen fibers arranged irregularly, providing strength and support in multiple directions.
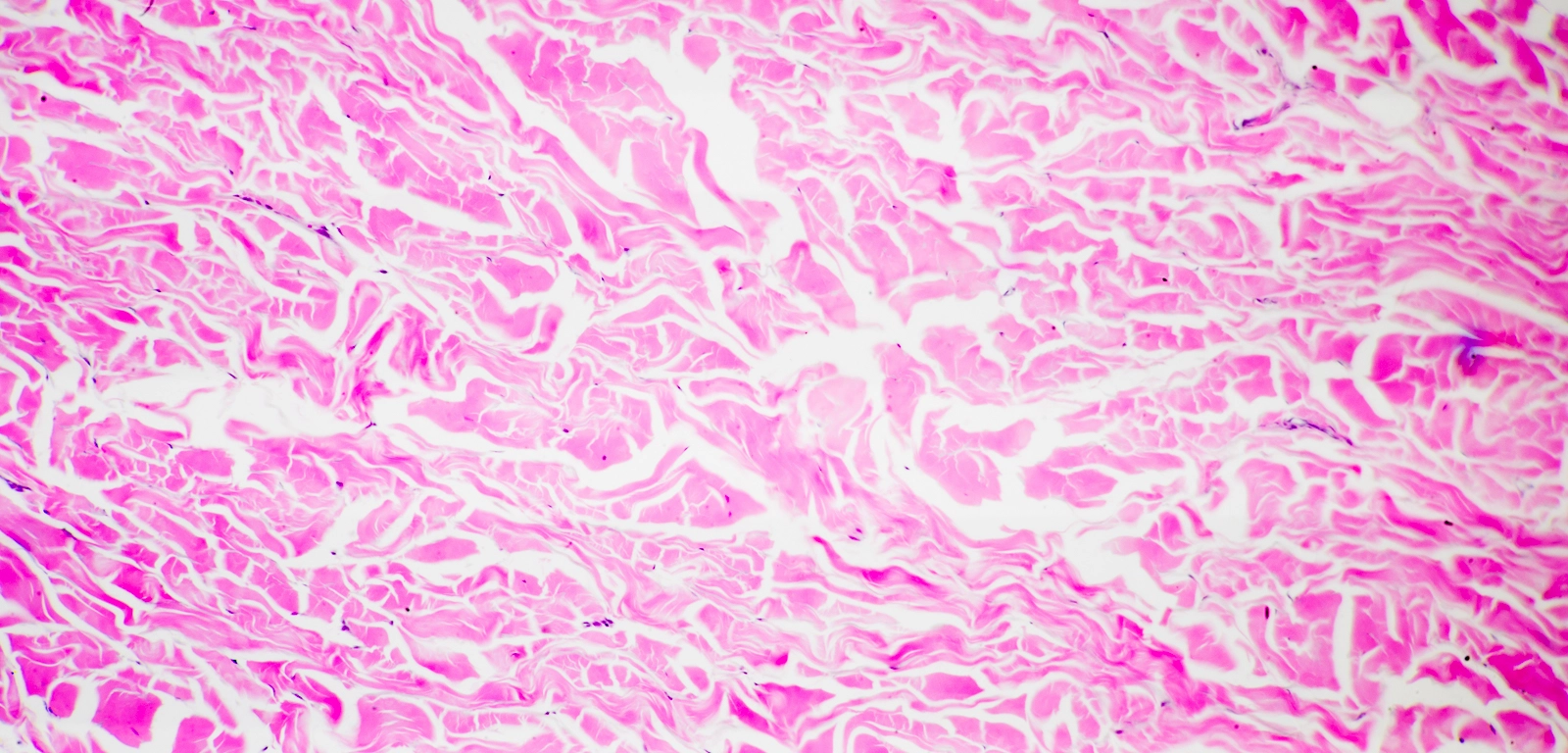
reticular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue composed of a network of reticular fibers and cells, providing structural support and a framework for organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
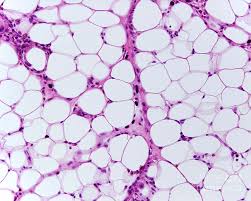
adipose connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores fat, providing insulation and cushioning to the body, as well as serving as an energy reserve.
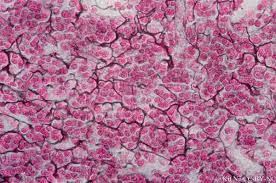
cartilage connective tissue (specialized)
A type of connective tissue that is more flexible than bone, providing support and cushioning to joints, and is found in structures like the nose, ears, and between vertebrae.
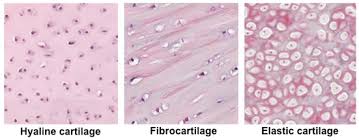
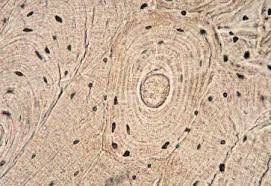
bone specialized c.t.
A type of specialized connective tissue that provides structural support and protection to the body, consisting of a hard matrix mineralized with calcium phosphate and collagen fibers.
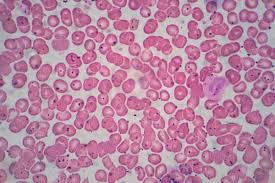
blood specialized c.t.
A type of specialized connective tissue that circulates throughout the body, consisting of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma, and is crucial for transportation of nutrients, gases, and waste.
hypertrophic obesity
A type of obesity characterized by the enlargement of adipocytes, resulting in an increased fat mass and storage within the body.