Phonological Approaches and Theories in Speech Sound Disorders
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are the three main areas focused on in Phonological Approaches?
1. Targeting groups of sounds with similar patterns of errors. 2. Establishing previously neutralized phonemic contrasts. 3. Emphasizing a naturalistic communicative context.
What is the goal of Contrast Approaches in phonological treatment?
To increase effectiveness by addressing lost phonemic contrasts in the child's speech.
What are the three major methods used in Contrast Approaches?
Minimal contrasts, maximal contrast, and multiple contrasts.
What defines Minimal Contrasts in phonological therapy?
Phoneme contrasts limited to one or just a few features, such as voicing or place.
Give an example of a Minimal Pair.
bat-pat, which vary only in voicing in the initial phoneme.
What is the purpose of using Minimal Pairs in therapy?
To help children differentiate between similar sounds and improve their phonological awareness.
What is the recommended number of word pairs for Minimal Pair therapy?
5 to 10 word pairs.
What is the first phase of treatment in Multiple Contrasts therapy?
Familiarization and production of contrasts.
What is the focus of Maximal Contrast therapy?
Using word pairs that contrast multiple features between phonemes.
Provide an example of a Maximal Contrast.
chop-mop, which vary in features such as sonorant, nasal, voice, and more.
What is the Empty Set approach in phonological therapy?
Pairing two phonemes not in the child's speech to create contrasts.
What should be considered when writing goals for phonological disorders?
Goals should increase intelligibility, consider normal sound development, and prioritize atypical processes.
What does SMART stand for in goal writing?
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.
What is an example of a goal for a child with a phonological disorder?
Sally will correctly produce velar sounds (k, g) in all positions of words with 80% accuracy given minimal visual/verbal cues.
What is the significance of auditory discrimination in Minimal Pair therapy?
It helps ensure the child can differentiate between the target sounds before production training.
What is the role of carryover training in phonological therapy?
To progress the child's sound production in more complex speech situations, such as phrases and sentences.
What is the difference between Minimal Pairs and Multiple Contrasts?
Minimal Pairs focus on one contrast at a time, while Multiple Contrasts address several errors simultaneously.
What is the goal of production training in Minimal Pair therapy?
To create an 'aha' moment of communicative breakdown when the child incorrectly produces a word.
What is the importance of familiarization in the Minimal Pair method?
It helps the child understand the target sounds through meaningful context before practicing.
What should be the focus of goals when treating phonological disorders?
The underlying phonological system rather than just training individual sounds.
What is the significance of using near minimal pairs or nonwords?
They can be used when exact minimal pairs are not available or suitable for the child.
What is a theory in the context of phonology?
A coherent group of tested general propositions used as principles of explanation and prediction for a class of phenomena.
Why is it important to discuss theories of phonology?
Understanding underlying concepts is crucial for assessment and treatment principles, and for educating parents and stakeholders.
What is phonology?
The systems and patterns of phonemes that occur in a language, literally meaning 'Sounds and Knowledge'.
What is a phoneme?
The central unit of phonology; a speech sound used contrastively to create words and convey meaning.
What are the two parts of speech when communicating?
The actual sounds produced and the meaning conveyed by those sounds.
What is generative phonology?
A theory presented by Noam Chomsky that assumes an abstract underlying form called phonological representation and phonetic representation.
What are the three steps of natural phonology?
1. Limitation: restricting differences to specific sounds. 2. Ordering: revising substitutions to more ordered patterns. 3. Suppression: stopping the use of phonological processes.
What are the three categories of phonological patterns?
1. Syllable structure processes/patterns. 2. Substitution processes/patterns. 3. Assimilation processes/patterns.
What is cluster reduction in syllable structure patterns?
The deletion of one or all members of a cluster to make it easier to produce, which may be total or partial.
What is the role of distinctive features in analyzing speech?
They help identify patterns in a child's speech by examining the characteristics of phonemes.
What is the significance of the Complexity approach in phonology?
It is guided by the principle that treating marked features should generalize to unmarked features without direct treatment.
What is a consonant cluster?
A group of two or more consonants that appear together in a syllable.
What is final consonant deletion?
The omission of a final singleton consonant or consonant cluster, resulting in an open syllable.
What is epenthesis?
The insertion of an unstressed vowel, usually the schwa /ə/, between two consonants.
What is coalescence in phonology?
The combination of features from two adjacent consonants into a new consonant.
Define metathesis.
The reversal or swapping of two consonants in a word, often referred to as a 'slip of the tongue.'
What is migration in phonological processes?
Movement of a sound from one position in a word to another.
What is diminutization?
The addition of a vowel /i/ to the end of a word, often seen in 'baby talk.'
What does stopping of fricatives entail?
The substitution of stops for fricatives, typically in the initial position of a word.
What is stopping of affricates?
The replacement of an affricate by a stop, affecting /tʃ/ and /dʒ/.
Define deaffrication.
The replacement of an affricate by a fricative, specifically affecting /tʃ/ and /dʒ/.
What is velar fronting?
The replacement of velar sounds /k/, /g/, /ŋ/ with sounds made in a more anterior position.
What is palatal fronting?
The substitution of postalveolar consonants with alveolar consonants.
What does gliding of liquids refer to?
The substitution of /l/ and /r/ with glides /w/ and /j/, often in pre-vocalic positions.
What is context-sensitive voicing?
Loss of voice or voiceless contrasts within syllable initial and syllable final contexts.
What is consonant cluster simplification?
The substitution of one or more consonants within a cluster without deletion.
What is fricative simplification?
The substitution of an interdental consonant with a labial consonant.
Define vocalization in phonological processes.
The substitution of a vowel for a syllabic liquid or nasal, replacing /ɚ/ or /ɝ/ with /ə/ or another vowel.
What is alveolarization?
The substitution of labiodental or interdental consonants with alveolar consonants.
What does labialization involve?
The substitution of non-labial consonants with labial consonants.
What is stopping of liquids?
The substitution of a liquid consonant with a stop consonant.
What is assimilation in phonology?
A process where one sound changes to become more like a neighboring sound.
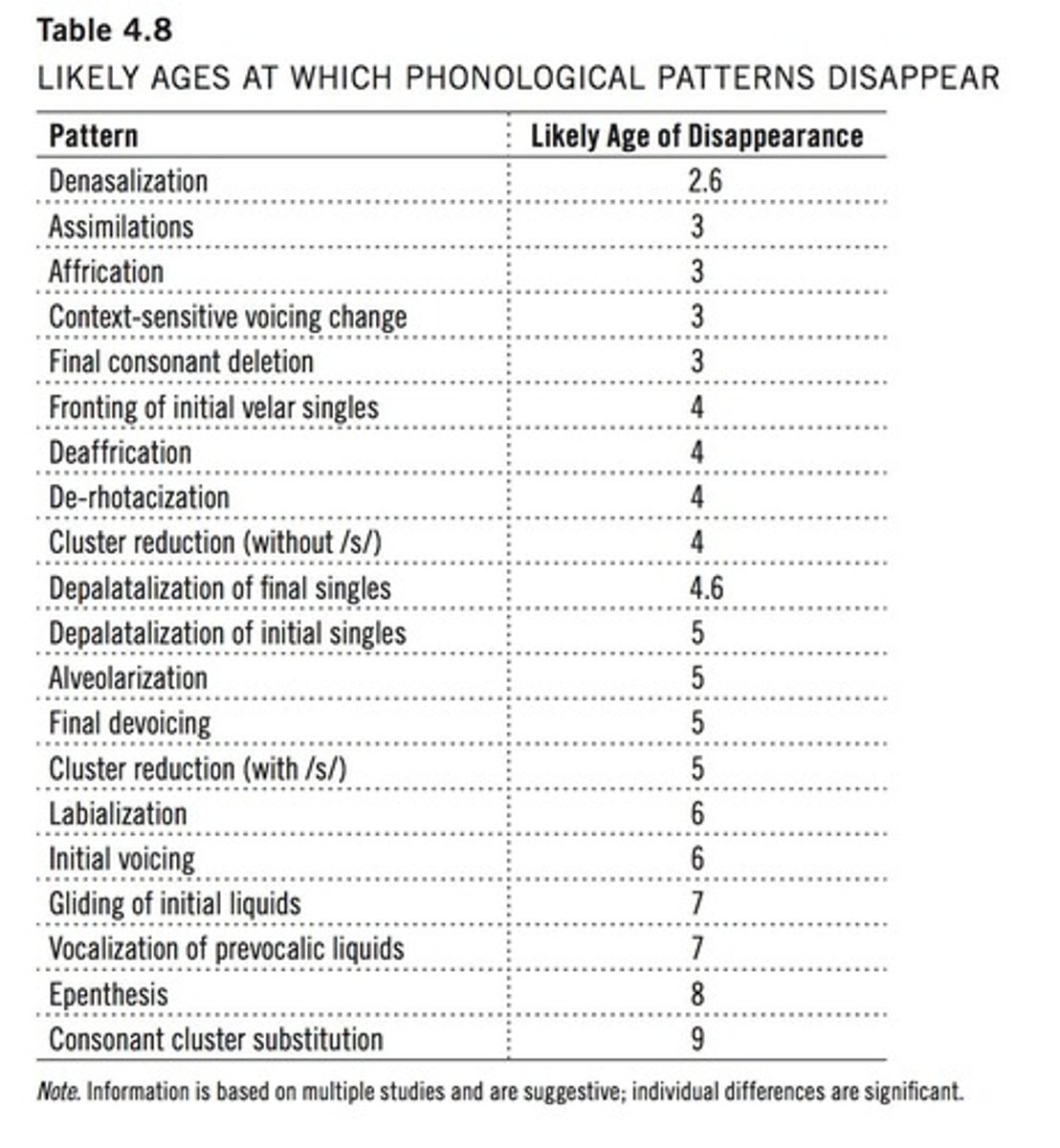
What is labial assimilation?
A non-labial consonant becomes a labial due to the influence of another labial sound.
What is velar assimilation?
A non-velar consonant becomes velar due to the influence of another velar sound.
What is backing in phonological processes?
The replacement of anterior sounds with posterior sounds.
What is initial consonant deletion?
The omission of a singleton consonant or consonant cluster in the initial position of a word.
What is gliding of fricatives?
The substitution of fricatives with glides.
What is denasalization?
The process of losing nasal quality in sounds.
What is affrication?
The process of creating an affricate from a stop and a fricative.