Ch. 5 Test #2
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
epithelial
protection, secretion, absorption, excretion ➡ sweat, waste
where is epithelial located
it covers body surfaces, cover and line internal organs (on body cavity), compose glands
distinguishing characteristics of epithelial tissue
lack blood vessels, readily divide; cells are tightly packed
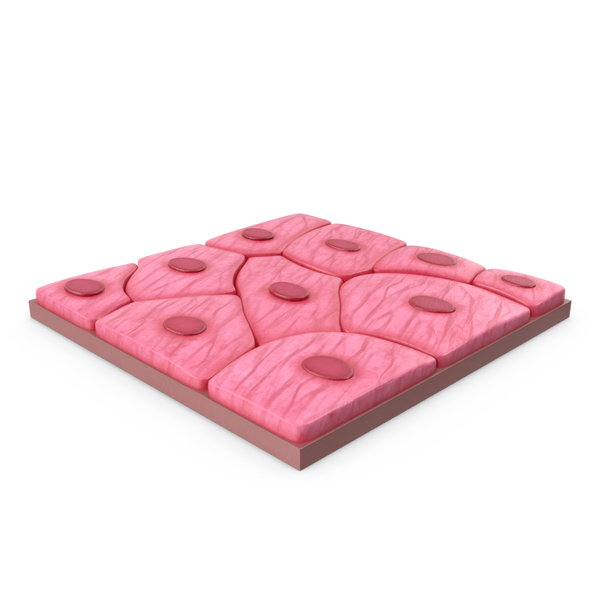
simple squamous
1 layer, flat
diffuse quickly
found in: lungs, capillaries, blood vessels, lymph vessels

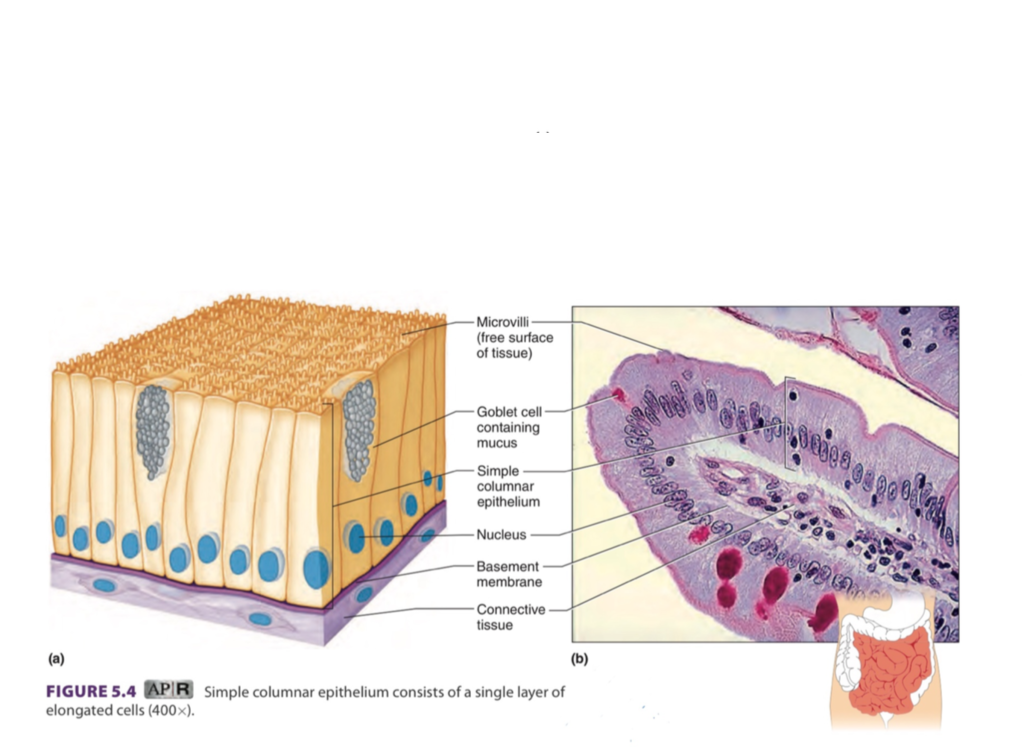
simple columnar
1 layer, rectangular
some have cilia ➡ provides movement, protection
microvilli: small hair-like structures
some have goblet cells ➡ produces mucus
found in: female reproductive tract, digestive tract
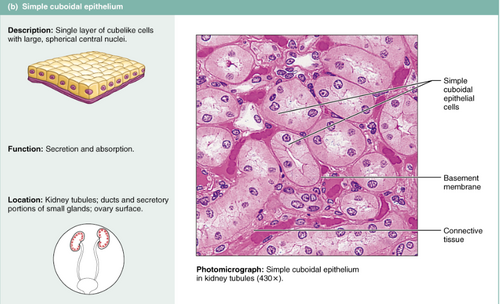
simple cuboidal
1 layer, tightly packed, cube-shape
it stores things, secretion, absorption
lumen is found
found in: ovaries, kidneys, ducts of glands
has nucleus
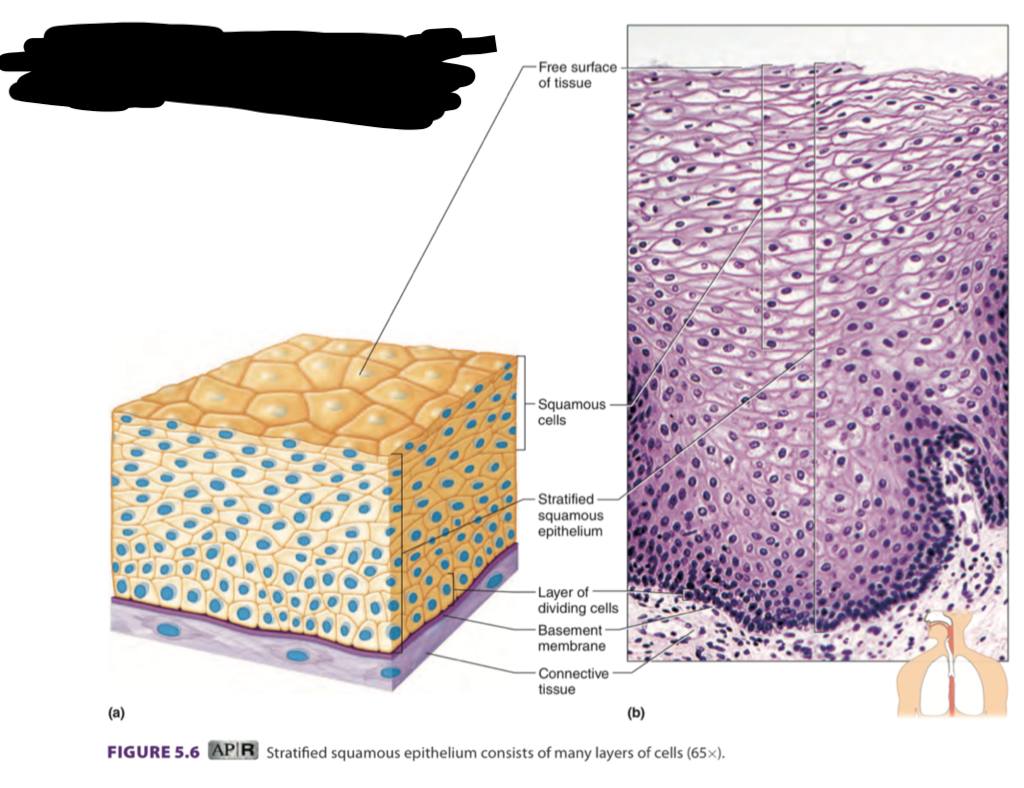
stratified squamous
many layers of flat cells
keratin - harden cells
keratinized = hardened
non-keratinized = not hardened
it works their way up
found in: epidermis, mouth, esophagus, anal canal, vagina
⬆ they are non-keratinized so they need protection from this tissue
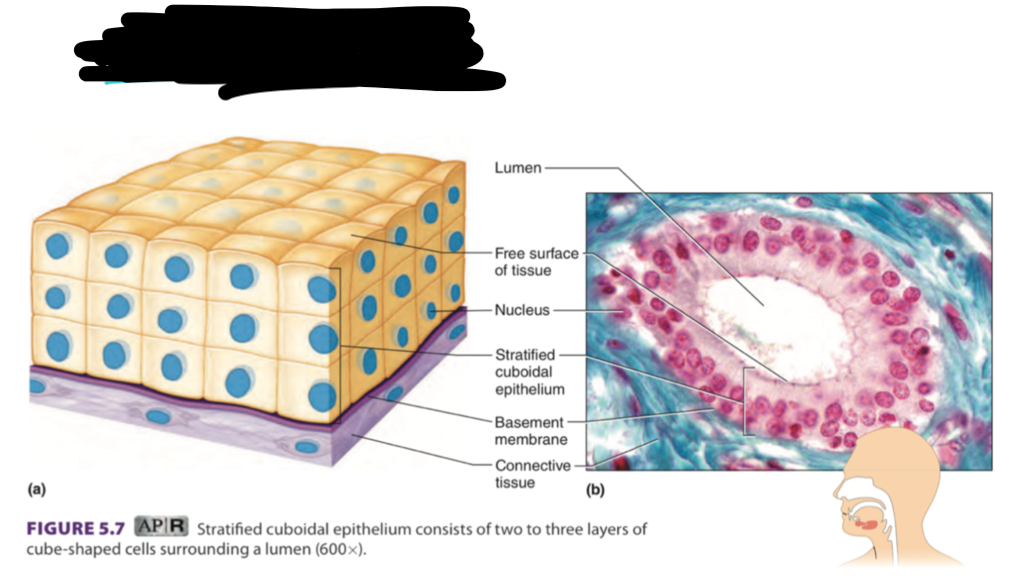
stratified cuboidal
2 or 3 layers
provides protection
found in mammary, glands (sweat, salivary), pancreas, reproductive
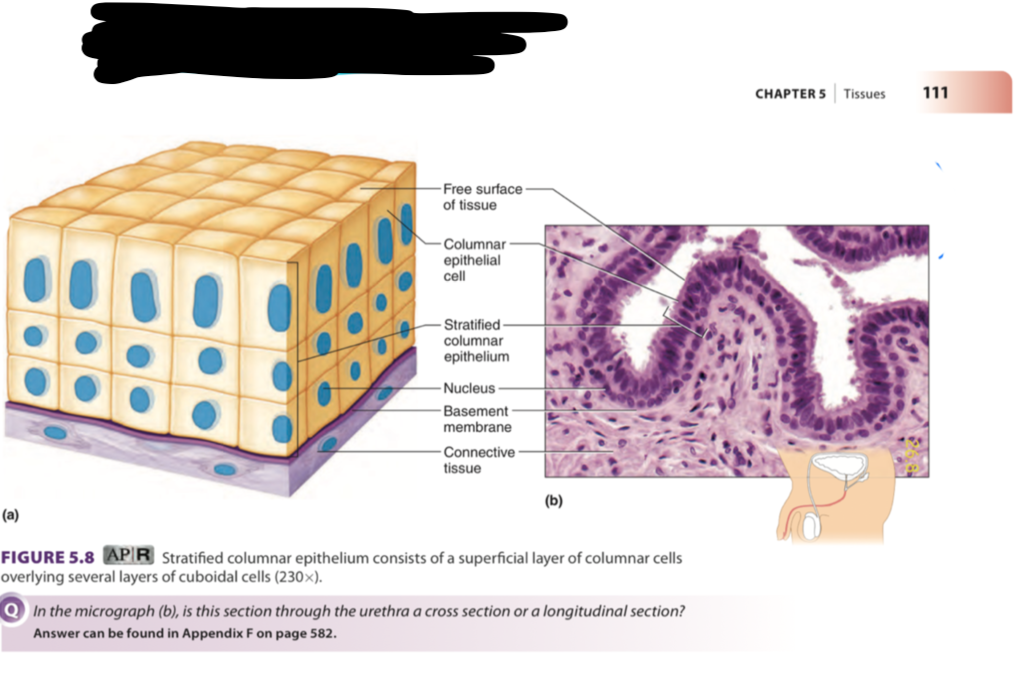
stratified columnar
many layers, rectangular and cube-shape
found in: male urethra
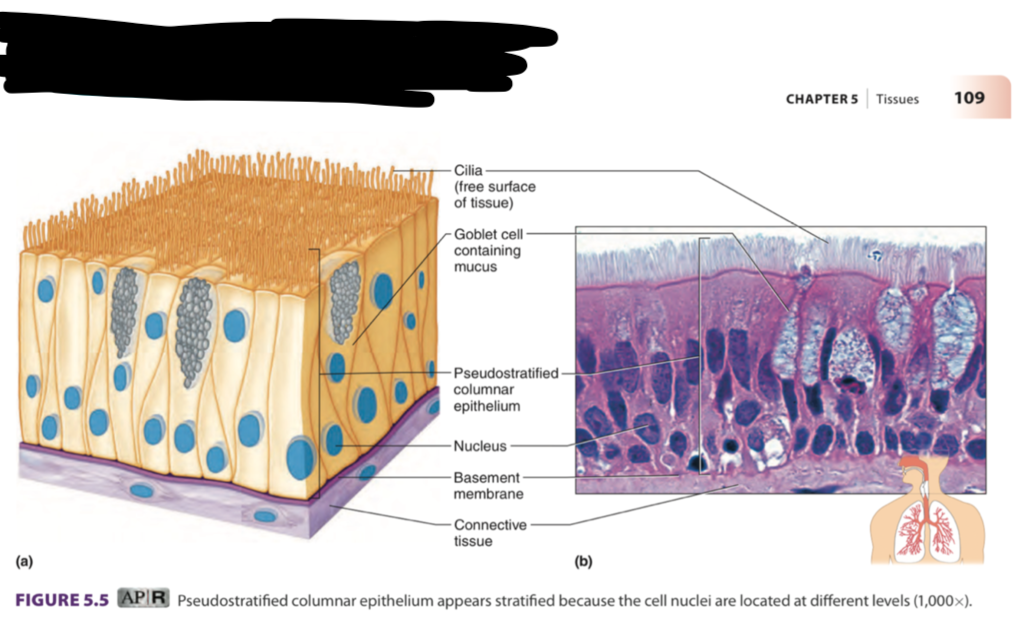
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
fake layers - appear stratified but not
has cilia
found in: respiratory system
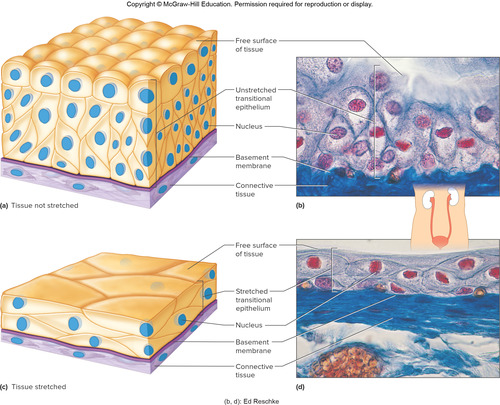
transitional
it changes shape ➡ when it responds to tension
found in: urinary tract bladder
Ex: changes shape when urine fills up the bladder
dense regular
closely packed
they have poor blood supply
makes up our: ligaments, tendons
has fibroblasts, thick collagen fibers
binds body parts together
supports, protects, and holds bones, muscles, and other tissues and organs in place
adipose
loose CT
acts as a cushion
good insulator, stores fat
found in: under skin, around certain joints, around kidneys, behind eyeballs, surface of the heart
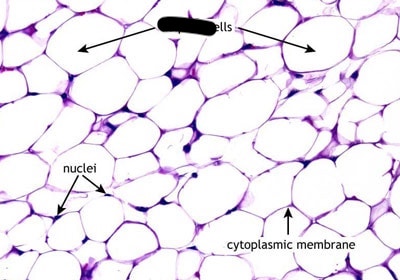
areolar
loose CT
delicate & thin
made mainly fibroblasts w/ collagen & elastic fibers
binds skin to organs
found in: in between muscles, blood vessels
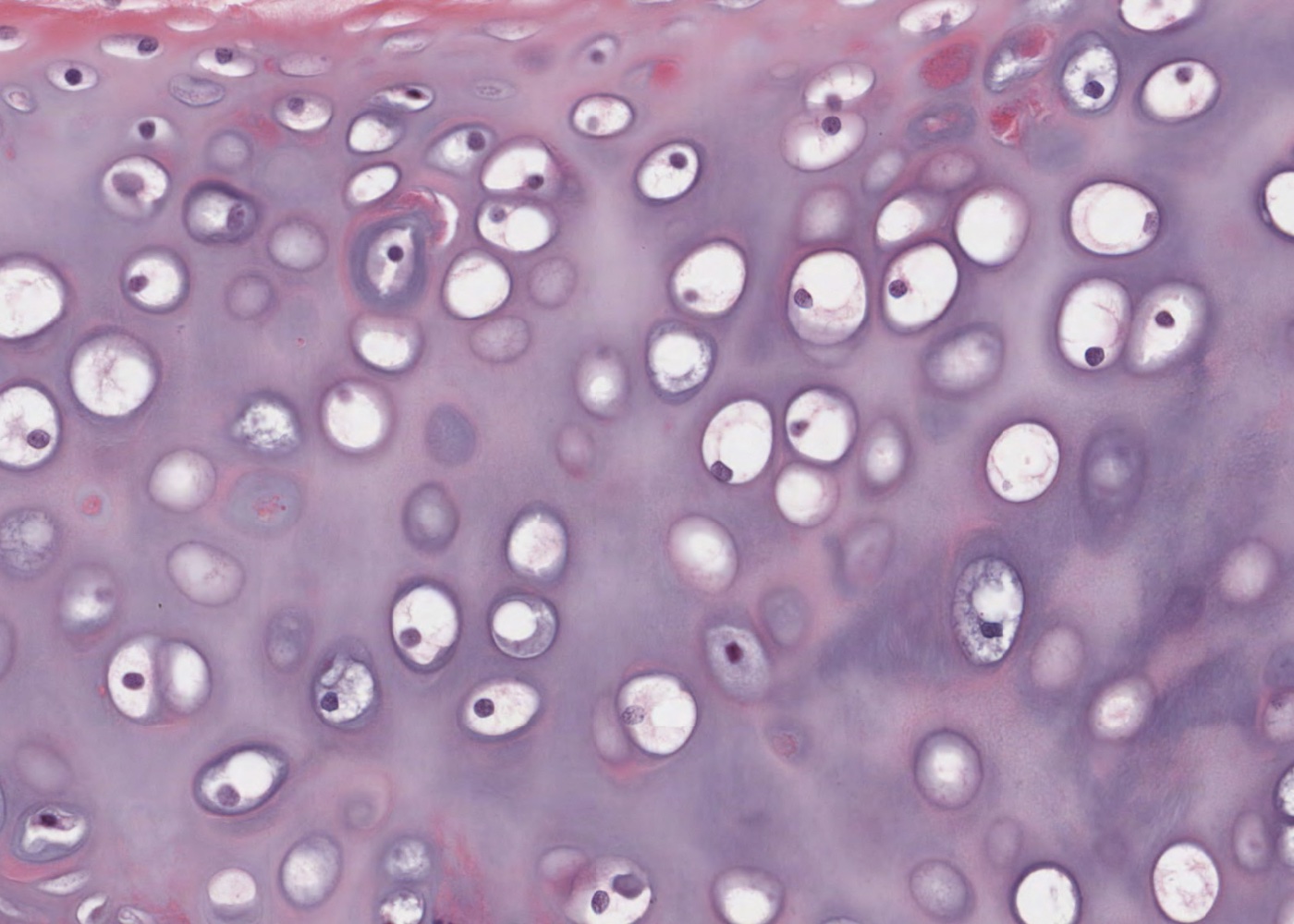
hyaline cartilage
most common, flexible
found in: ends of bones, nose
lines your joints and caps the ends of your bones
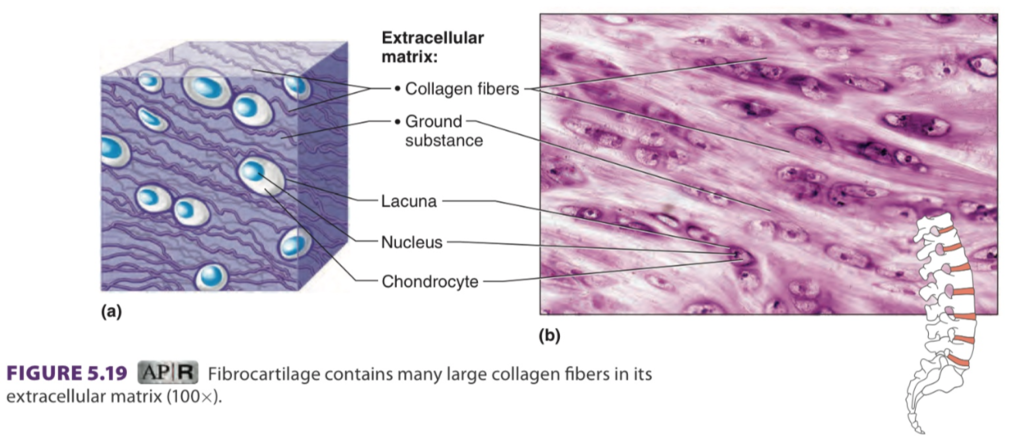
fibrocartilage
shock absorber
very tough, many collagen fibers
found in: discs in vertebral column
cushions bones in knee and pelvic girdle
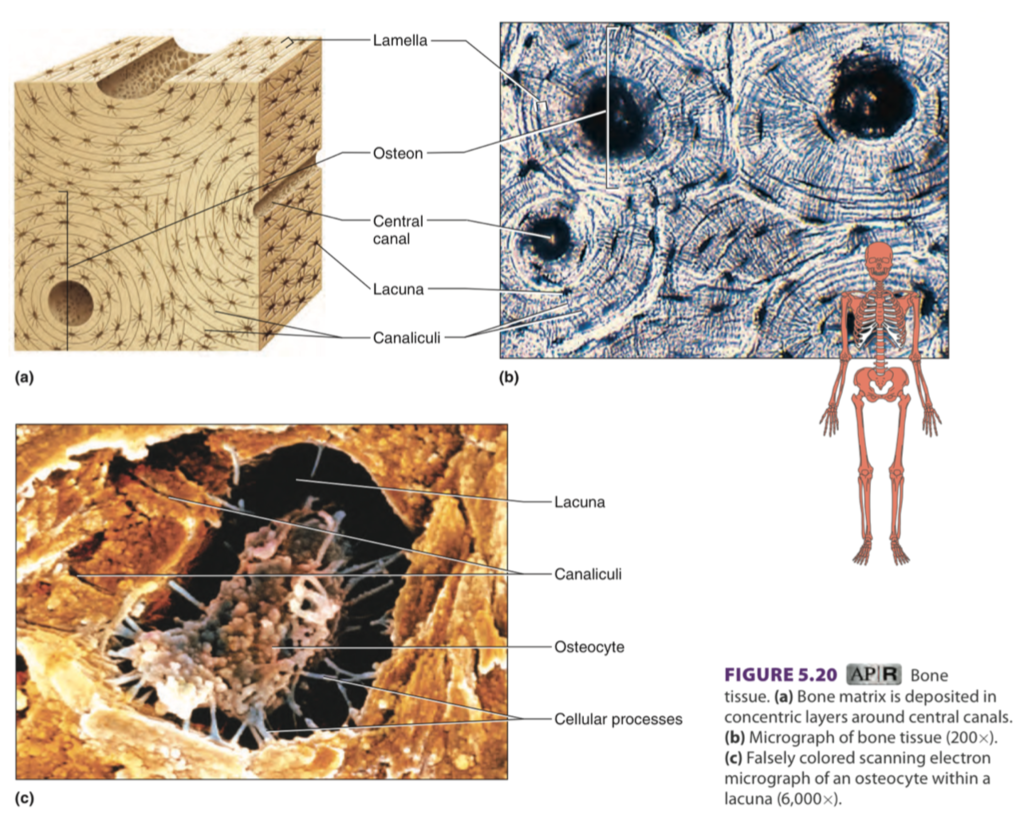
bone
Supports, protects, provides framework
located: Bones of skeleton
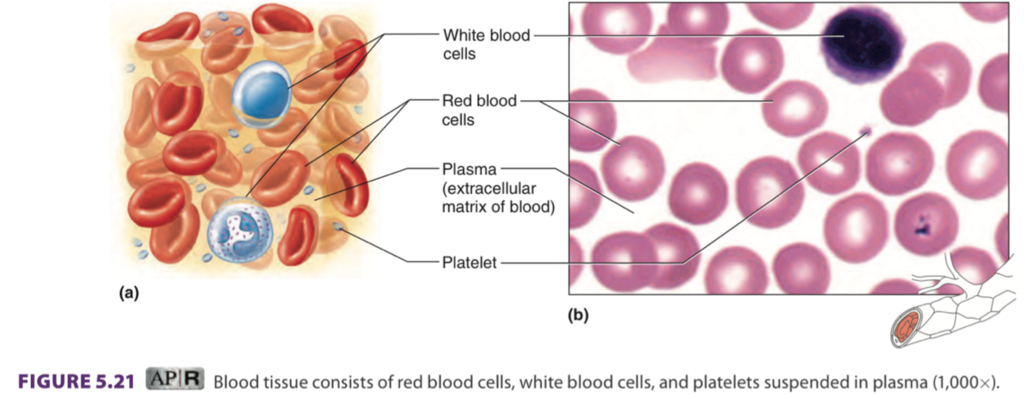
blood
Transports substances, helps maintain stable internal environment
located: Throughout body within a closed system of blood vessels and heart chambers
White blood cells, Red blood cells
Platelet
Plasma (extracellular matrix of blood
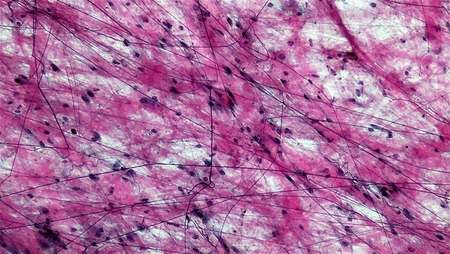
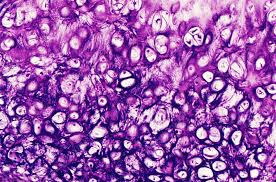
elastic cartilage
flexible
continues to grow
provide tensile strength and resistance to stretching
compare collagen and elastin
collagen is thick, found in bundles, ligaments & tendons, good for pulling forces
elastin is more elastic and weaker
Why is there lots of collagen in tendons and not much elastin?
Tendons need to be stronger and require less stretching
why is there lots of elastin in arterial walls?
arterial walls need to stretch more, but do not need to be as strong