Light and Matter Lecture Notes
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of flashcards covering key concepts and definitions from the lecture on light, mirrors, refraction, and lenses.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the speed of light in relation to different materials?
Light travels fastest through no particles and slower through solids.
What is transparent matter?
Matter that allows almost all light to pass through, making the object on the other side clear.
What is translucent matter?
Matter that allows some light to pass through it, making the object on the other side blurry.
What is opaque matter?
Matter that does not allow light to pass, so you cannot see the object on the other side.
What is the law of reflection?
When a wave is reflected from a surface, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence.
What is a virtual image?
An image that forms when light rays change direction, as seen in a flat mirror.
What is a concave mirror?
A mirror that is curved inward.
What does it mean for rays to converge?
Rays come together at a point along the optical axis.
What is the focal point of a mirror?
The point along the optical axis where reflected rays converge.
What is the relationship between focal length and curvature?
More curved mirrors have shorter focal lengths; flatter mirrors have longer focal lengths.
What is a real image?
An image that appears upside down and is formed when an object is behind the focal point.
What is a convex mirror?
A mirror that is curved outward.
What is regular reflection?
Reflection from a smooth, shiny surface.
What is diffuse reflection?
Reflection from a rough surface.
What is refraction?
The change in direction of a wave as it changes speed while moving from one medium to another.
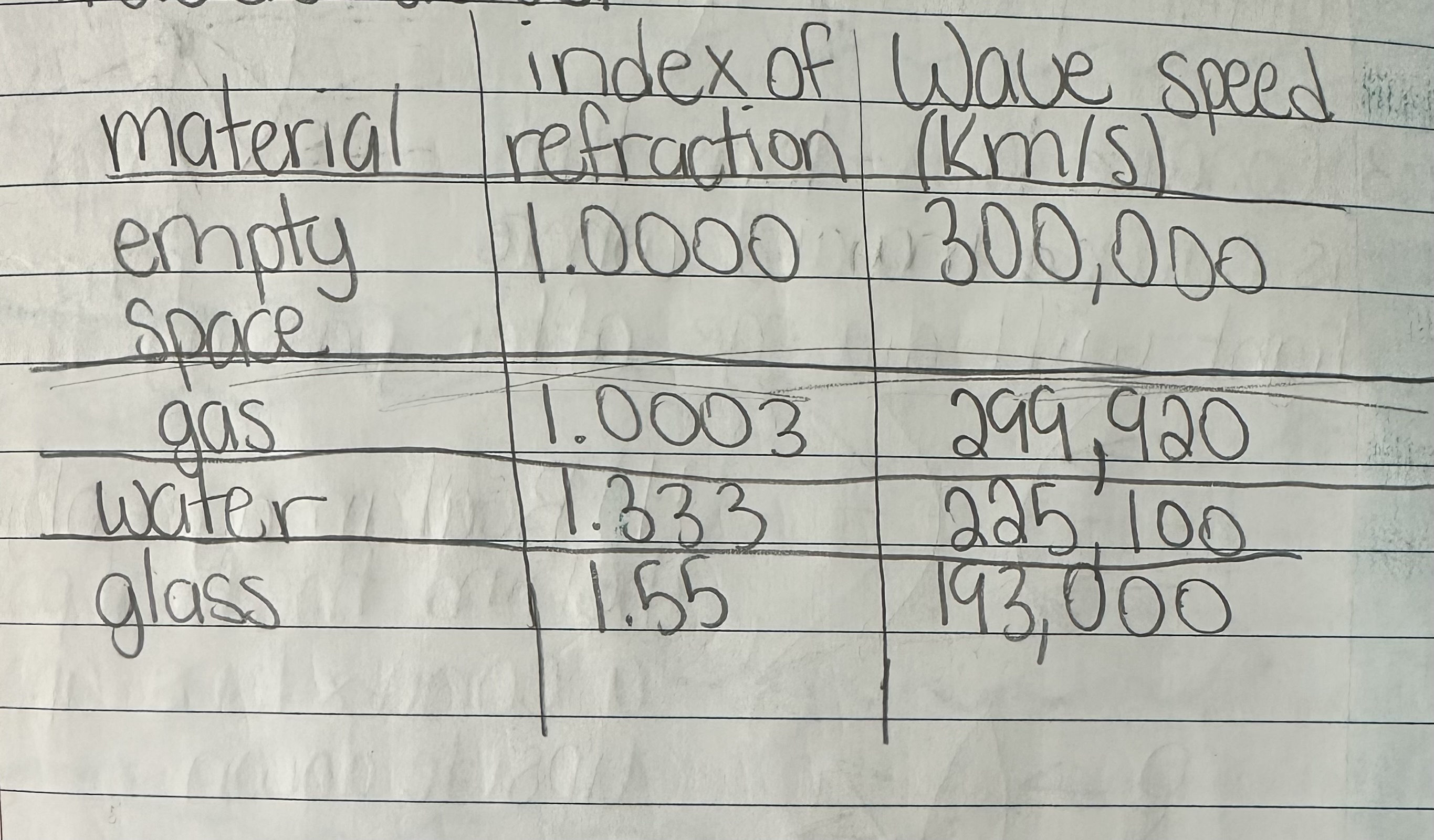
What does the index of refraction indicate?
A low index means light travels faster, while a high index means light travels slower.
What is a lens?
A transparent object with at least one curved side that causes light to refract.
What is a convex lens?
A lens that is curved outward where light will converge after passing through.
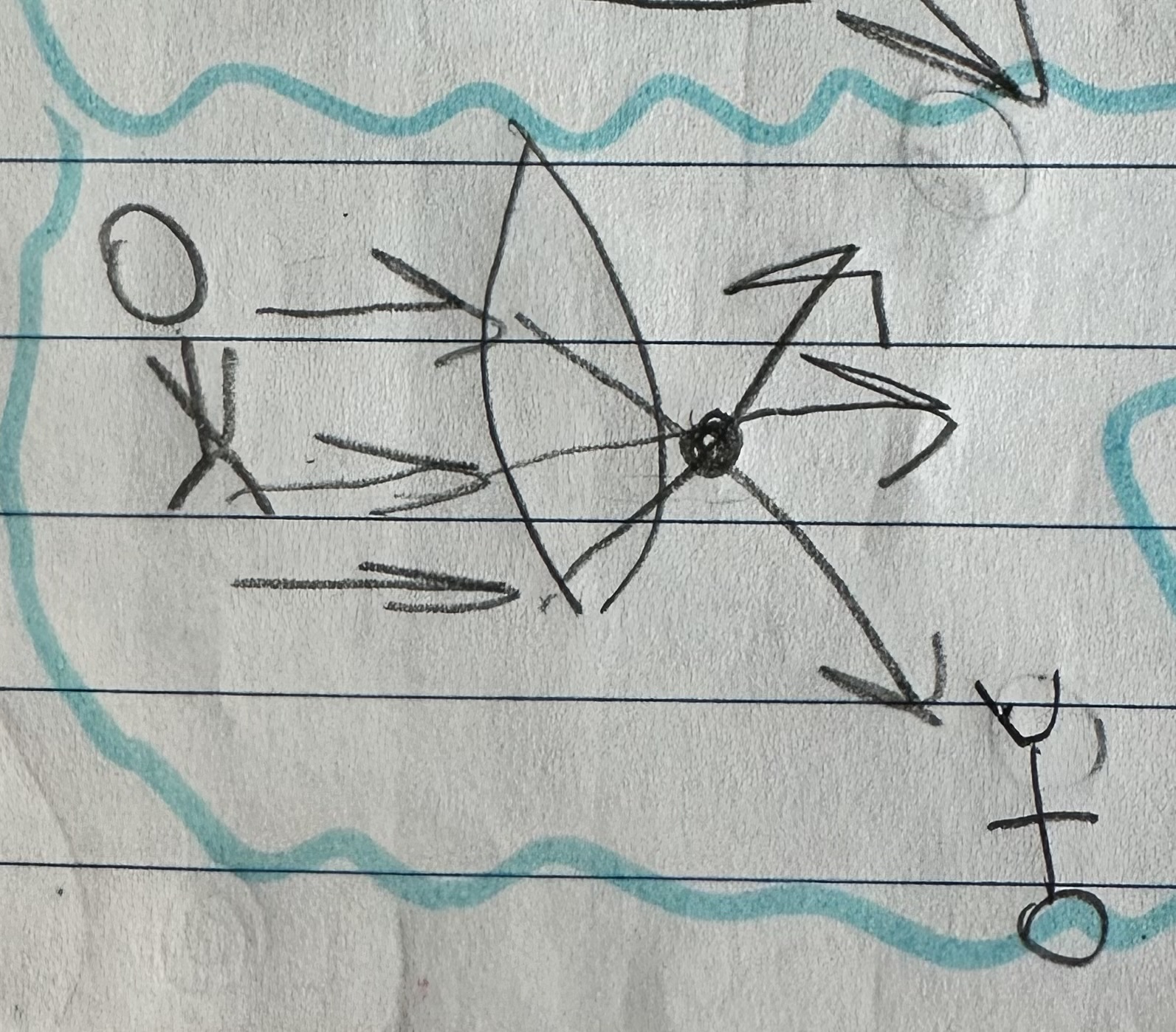
What is a concave lens?
A lens that is curved inward where light will diverge after passing through.
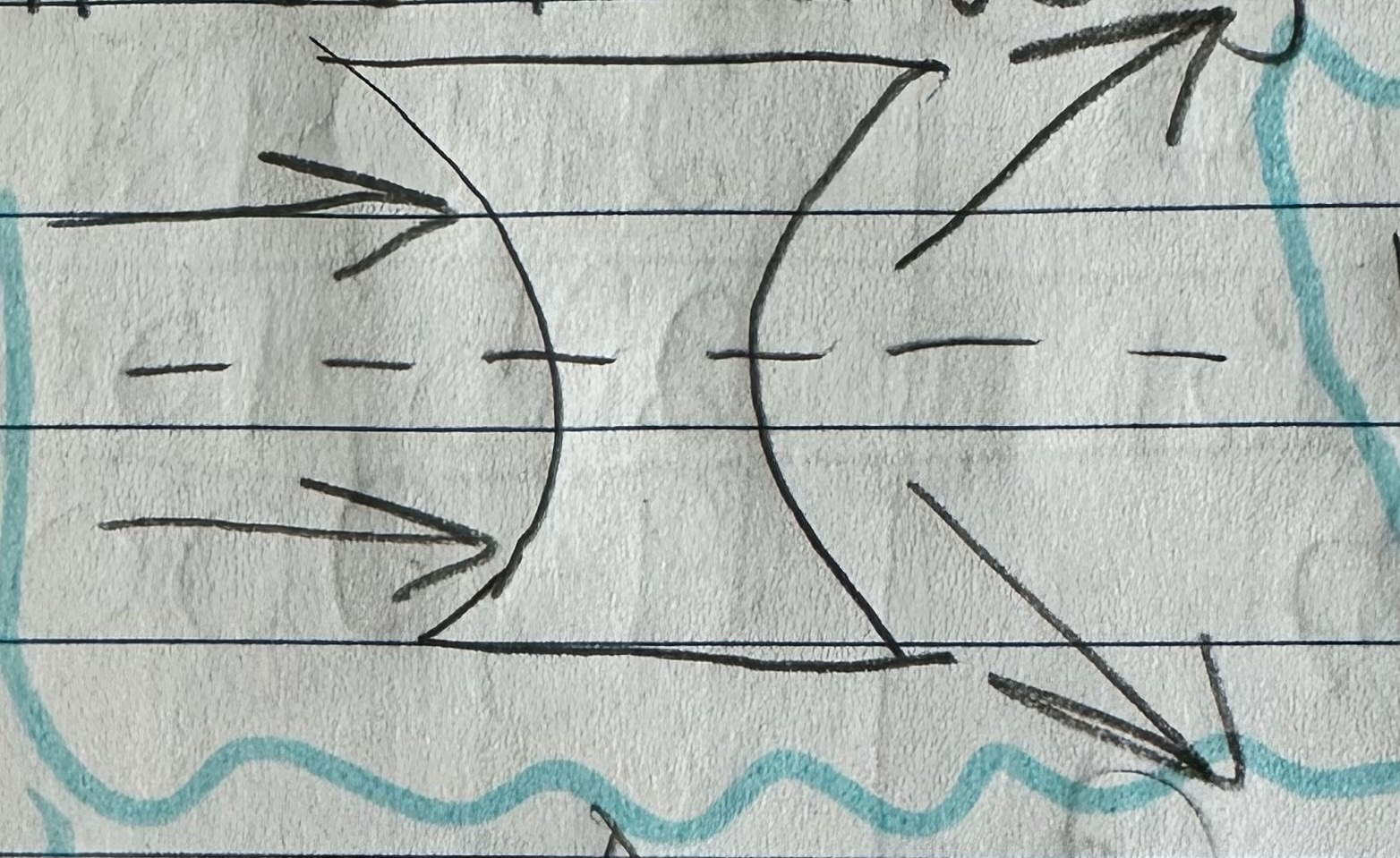

What characterizes a real image formed by a convex lens?
An object behind the focal point appears upside down.
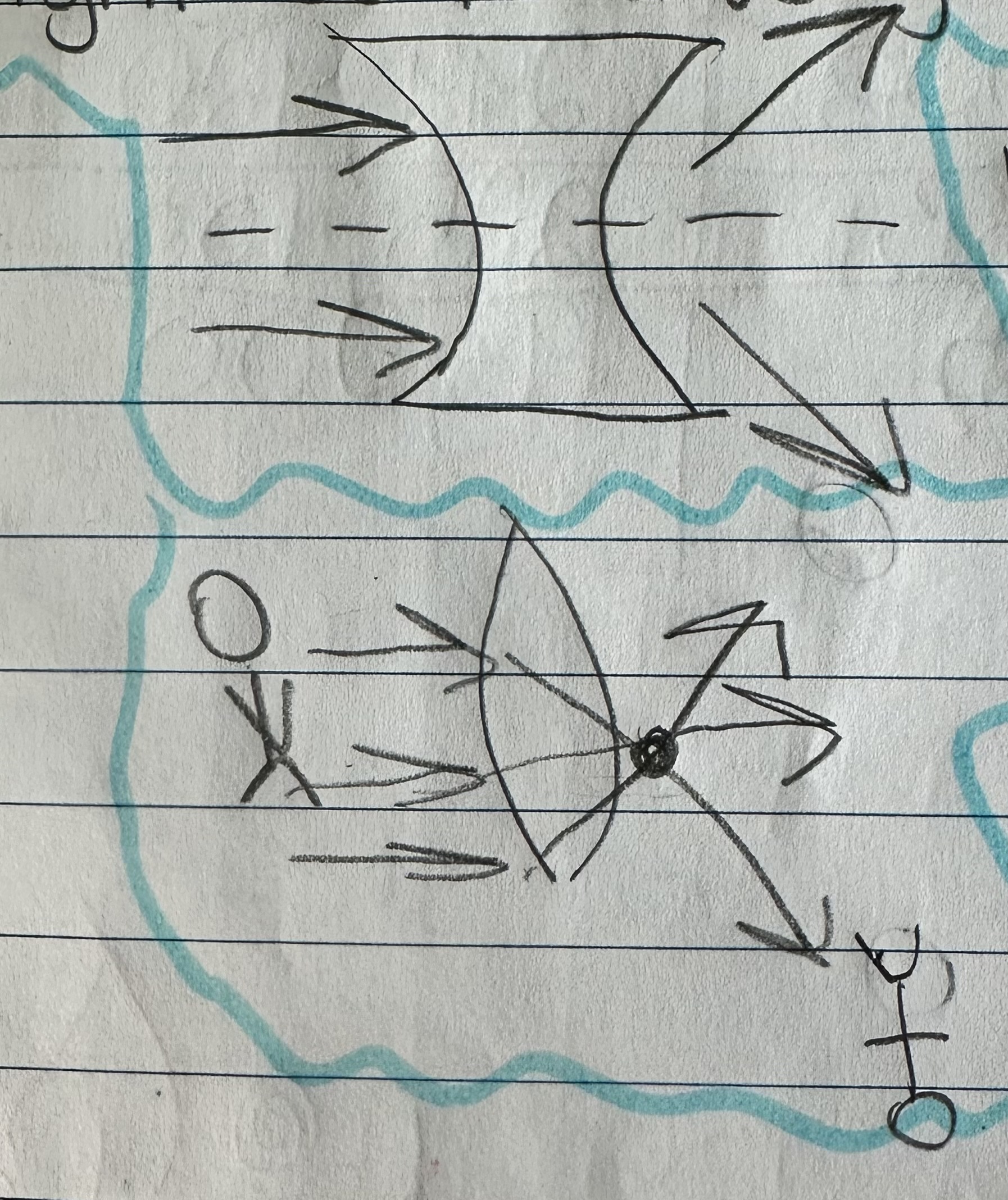
What does diverged mean?
Spread apart
Diffuse Image Example

When separating light, what does a higher frequency cause?
More refraction when passing through the matter.
What are rod cells?
Rod cells allow you to see objects in a dimmer light.
What are cone cells?
Cone cells allow you to see color.
What is the color order and what color has the longest and shortest wave length?
ROY G. BIV
Red has the longest wave length and violet has the shortest wave length.