Unit 1.3 Review - DNA and Protein Synthesis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
RNA polymerase
enzyme that unzips DNA and links together a chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription, using a DNA strand as a template
double helix
term that describes the shape of the DNA molecule
nucleotide
monomer of DNA, made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base
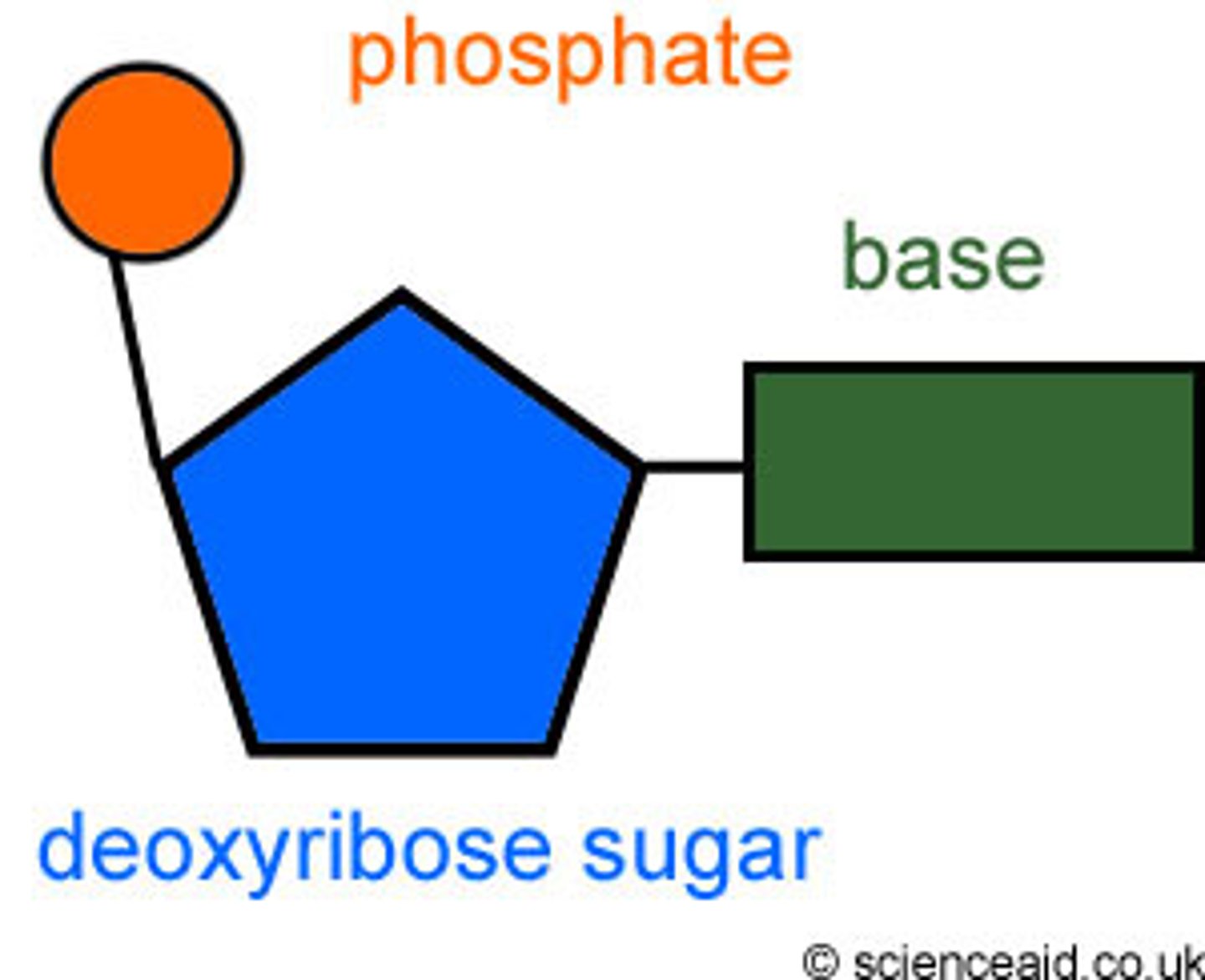
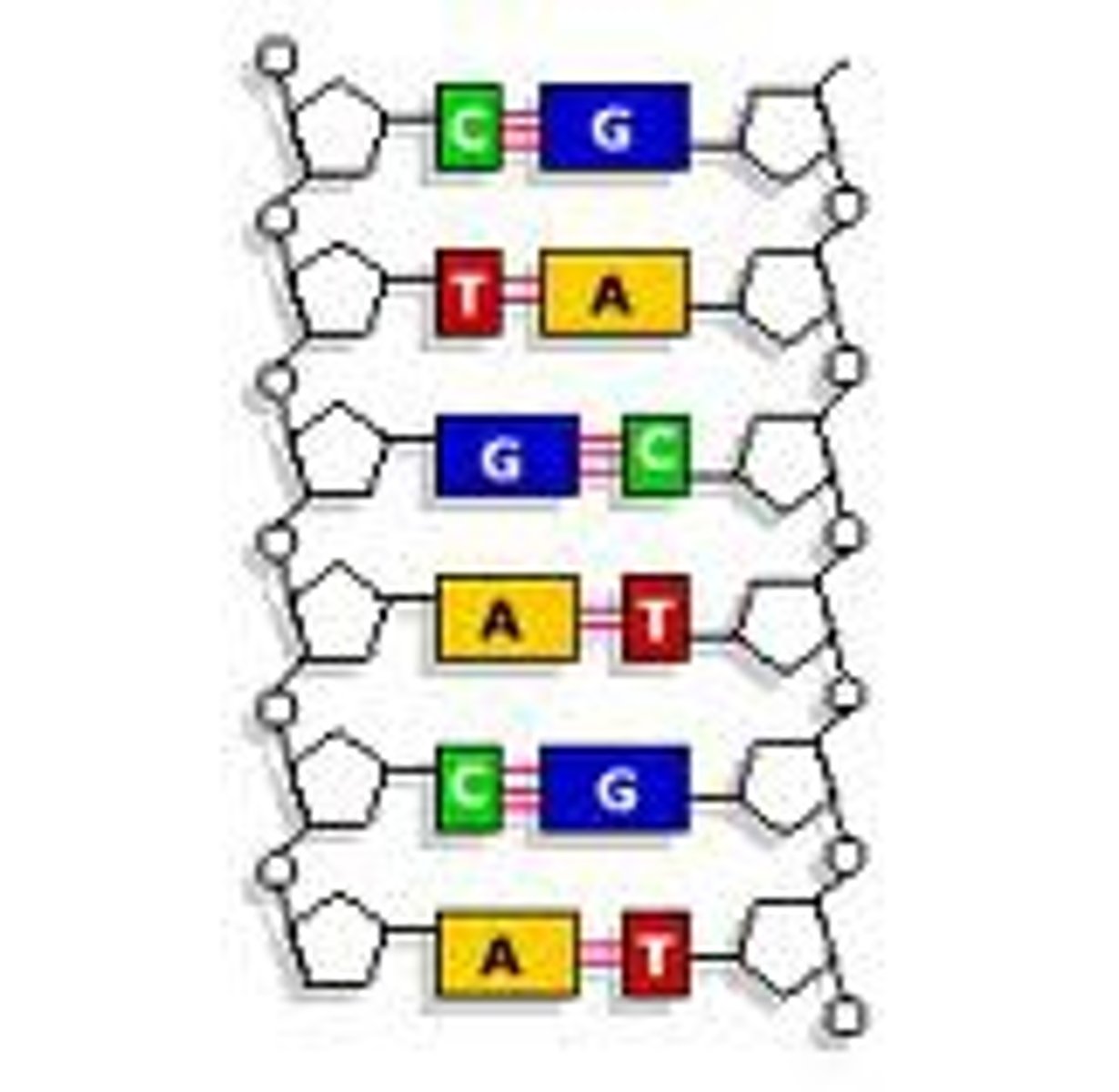
hydrogen bonds
type of bond holding the nitrogen base pairs together in DNA
covalent bonds
the type of bond that holds the backbone of DNA together (holds phosphate and sugar together)
A-T and C-G
Base pairing rules for DNA
Central Dogma of Biology
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
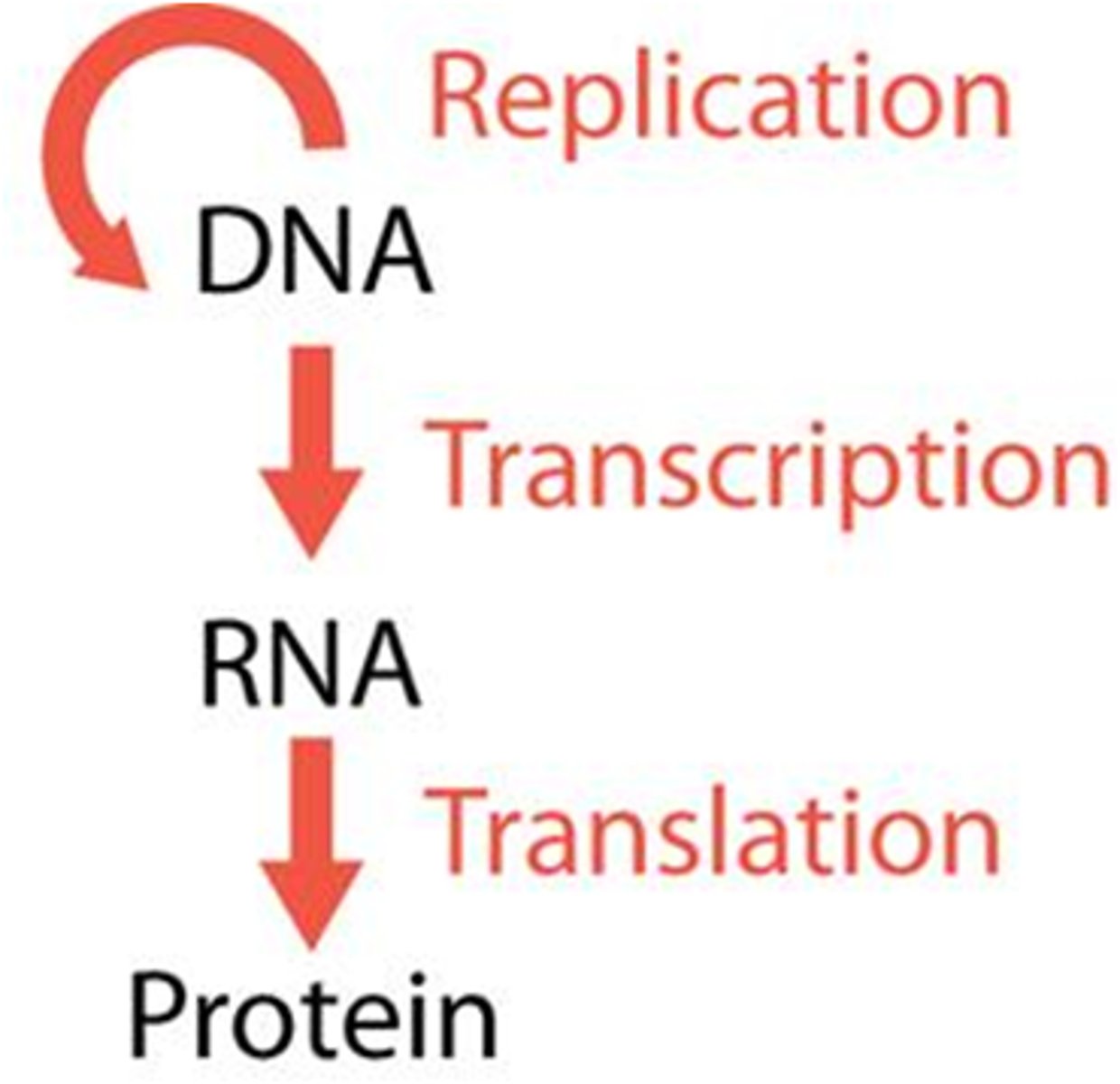
Transcription
the first step of protein synthesis; a messenger RNA molecule is made from a DNA template
Translation
second step of protein synthesis; process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein (chain of amino acids) is produced
primary structure of a protein
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain; important because it determines the final shape/function of the protein
amino acids
monomer of a protein
peptide bond
Bonds that connect amino acids.
codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Transcription must always take place in the ___.
nucleus
Use an mRNA codon chart to determine what the codon AAA stands for.
Lysine
What organelle provides the proper environment to processes and fold a protein into shape?
endoplasmic reticulum
What organelle folds and packages proteins into vesicles for shipment around the cell?
golgi apparatus
ribosome
organelle that translates the mRNA message and links amino acids together to form proteins
transfer RNA
RNA type that brings amino acids to the ribosome; in order to build a protein
What would be the anticodon to the following codon: AUC?
UAG
A sequence of DNA is as follows:
A A C T G G T A C
What mRNA strand would be made from this sequence?
U U G A C C A U G
What does a stop codon do?
Signals the end of translation and the ribosome releases the protein
What does a start codon do?
tells the ribosome where to start;
codes for methionine, the first amino acid
polypeptide
-A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
-many polypeptide can be joined together to make a protein
What ultimately determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
The sequence of bases in a gene
mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information and possible protein production
polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
quaternary protein structure
2+ polypeptide chains forming functional protein