2. Anatomical Terminology
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Anatomy
Study of form and structure
Gross (macroscopic) anatomy
Study of form and function of an organism which can be done without the aid of a microscope
Microscopic (histology)
Study of tissues
Systemic
Throughout the entire system of the organism
Regional
only specific to a localized area
Pathological
the study of diseased cells/tissues/etc
Topographical
surface references to locate deeper lying structures
Physiological
the study of function of an organism
What are the four biologically important organic molecules found in the human body?
The four biologically important organic molecules in the human body are proteins, complex carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids.
What is the definition of a molecule, and how is it formed?
A molecule is formed when two or more atoms are joined together through chemical bonds.
What are the three subatomic particles that make up atoms?
The three subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What are cells?
Smallest structural and functional units of the human body
What are tissues?
Group of cells and the materials surrounding them that work together to perform a particular function
What are organs?
Composed of two or more tissues work together to provide specific functions and they usually have specific shapes
What defines an organ system? Give four examples of organ systems
An organ system consists of one or more organs that work together to provide a common function. Examples include the integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, and nervous system.
What are four types of tissues?
Connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue
What are the main functions of connective tissue?
Connective tissue provides protection and support.
What is a key characteristic of connective tissue compared to other tissues?
Connective tissue has few cells and a lot of extracellular matrix.
Give five examples of connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone and blood
What are the types of dense connective tissue, and how are the fibres arranged?
The types of dense connective tissue are irregular, regular, and elastic, all of which have tightly packed fibres in the ground substance.
What distinguishes loose connective tissues and what are the types of loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is distinguished by spaced fibres in the ground substance. The types of loose connective tissue include adipose, areolar, and reticular
What types of connective tissue are found in cartilage, and what fibres are present?
Types of cartilage include hyaline (glassy appearance), elastic, and fibrocartilage, containing collagen and elastic fibres in the ground substance.
What are the two types of bone tissue, and what fibres do they contain?
The two types of bone tissue are compact and spongy, both containing collagen fibres in the ground substance.
What are the main functions of epithelial tissue?
The main functions of epithelial tissue are protection and secretion.
Where can epithelial tissue be found in the body?
Epithelial tissue covers surfaces, lines cavities and ducts, and forms glands.
What are the three types of muscle tissue in the human body?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal (striated) muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
What are the two main components of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue consists of neurons and supportive cells.
What are the 11 systems of the human body?
The 11 systems are the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphoid, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
What are the main functions of the integumentary system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are protection from environmental hazards and temperature control. The integumentary system includes the skin, hair and nails
What are the main functions of the skeletal system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are support, soft tissue protection, mineral storage and blood formation. The skeletal system includes the bones and joints
What are the main functions of the muscular system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are locomotion, support and heat production. The muscular system includes the skeletal muscles
What is the main function of the nervous system and which organs are part of it?
The main function is directing immediate response to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems. The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves
What is the main function of the endocrine system and which organs are part of it?
The main function is directing long-term in the activities of other organ systems. The endocrine system includes pituitary (hypofys), thyroid, pancreas, adrenals, ovaries and testes
What is the main function of the cardiovascular system and which organs are part of it?
The main function is the internal transport of cells and dissolved material, including nutrients, wastes and gases. The cardiovascular system includes heart, blood vessels and blood
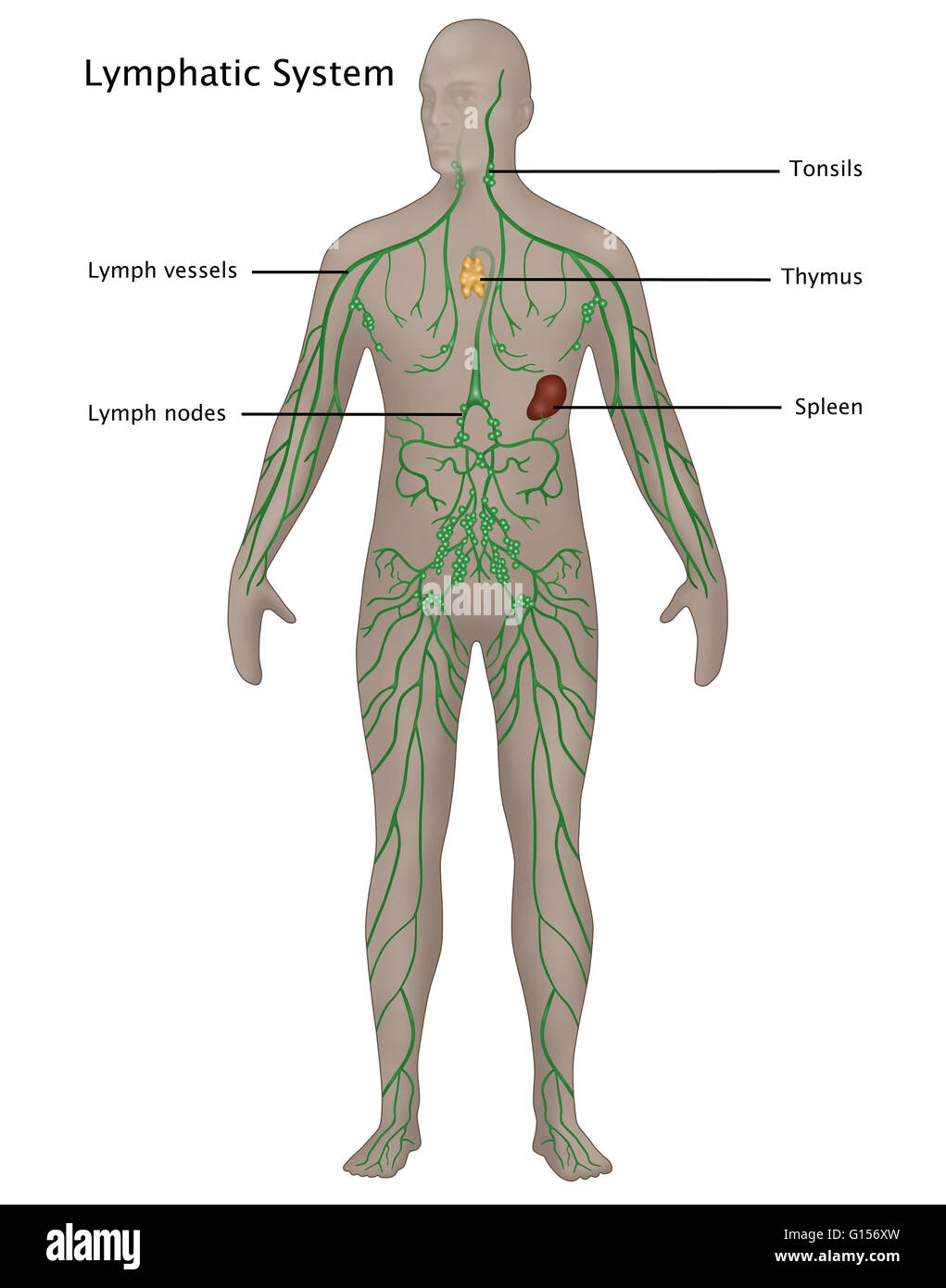
What is the main function of the lymphoid system and which organs are part of it?
The main function is defence against infections and diseases. The lymphoid system includes lymphocytes, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, tonsils, spleen (mjälte) and thymus
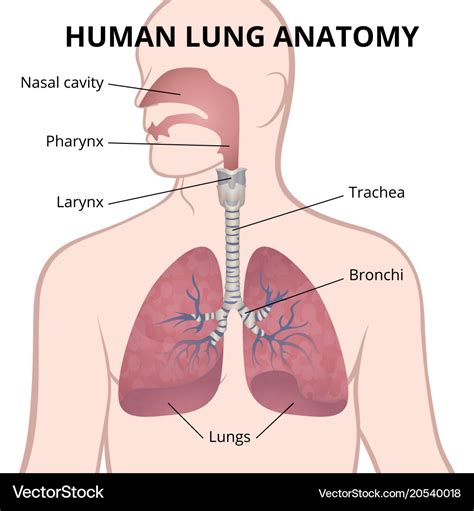
What is the main function of the respiratory system and which organs are part of it?
The main function is the delivery of fresh air where gas exchange can occur between the air and circulating blood. The respiratory system includes nasal cavity, pharynx (svalg), larynx (struphuvud), trachea, bronchi and lungs
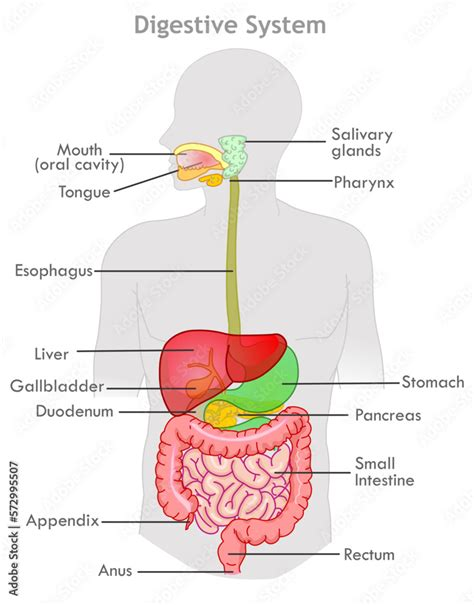
What are the main functions of the digestive system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are the processing of food and adsorption of organic nutrients, minerals, vitamins and water. The digestive system includes mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, intestines, liver and gallbladder
What are the main functions of the urinary system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are the elimination of excess water, salts and waste products and control of pH. The urinary system includes kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra
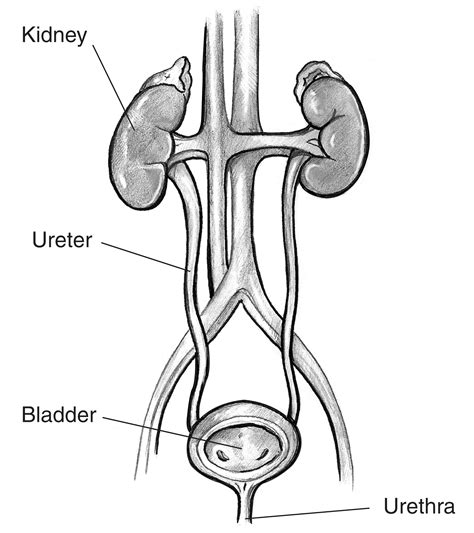
What are the main functions of the reproduction system and which organs are part of it?
The main functions are the production of sex cells and hormones. The reproductive system includes ovaries, uterus, vagina, mammary, glands, testes, penis and prostate
What is the anatomical position, and why is it important?
The anatomical position is a standardized method of observing or imaging the body, where the subject stands upright, faces the observer with the head level, eyes forward, feet flat, arms at the sides, and palms turned forward (ventral). It allows for precise and consistent anatomical references.
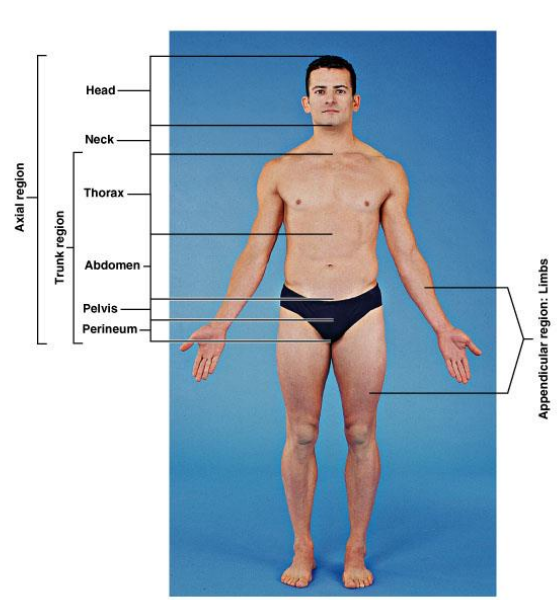
What are regional terms?
Names of specific body areas
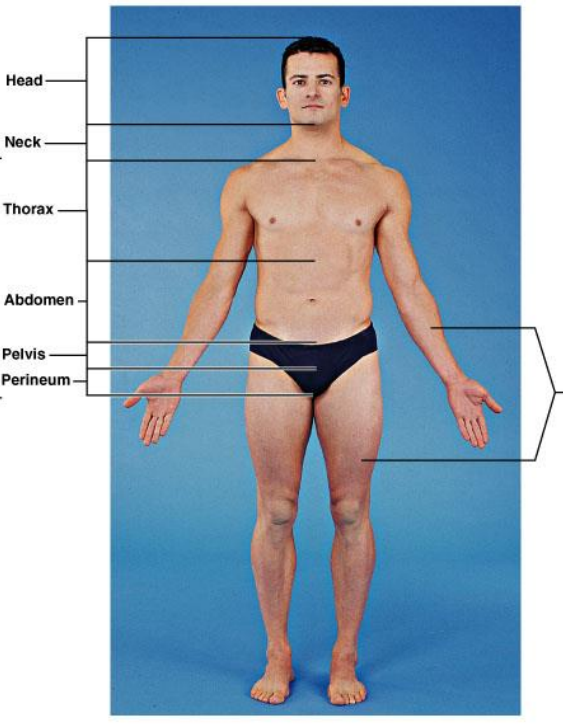
What are included in the axial region?
The main axis of the body. Head, neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis and perineum (region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone))
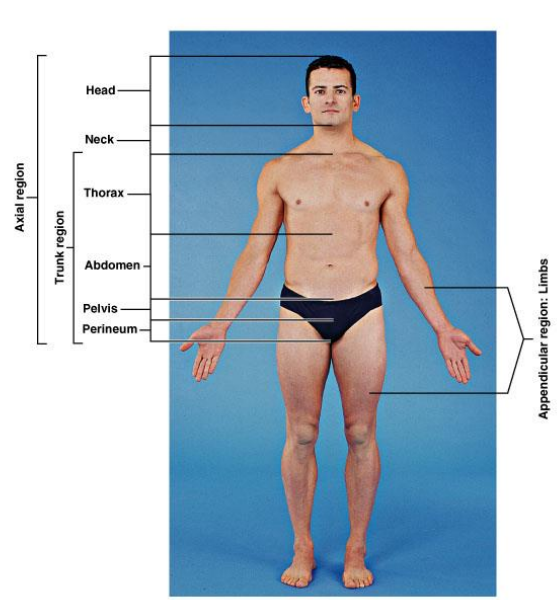
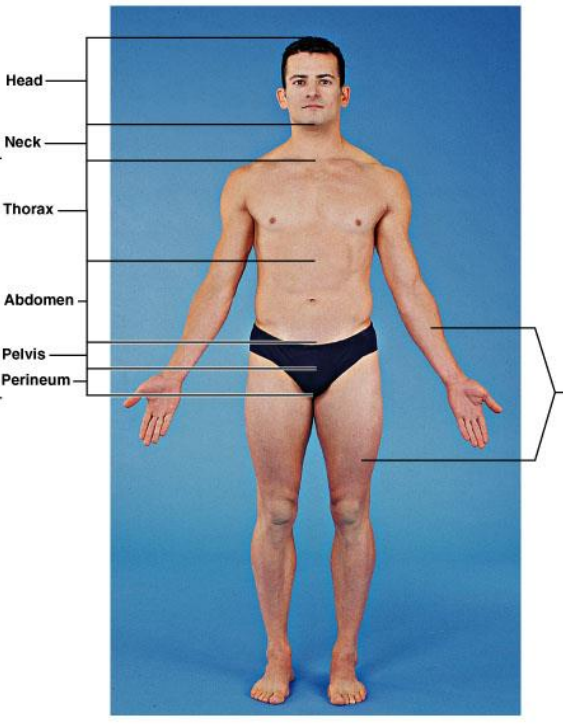
What are included in the trunk region?
Neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis and perineum
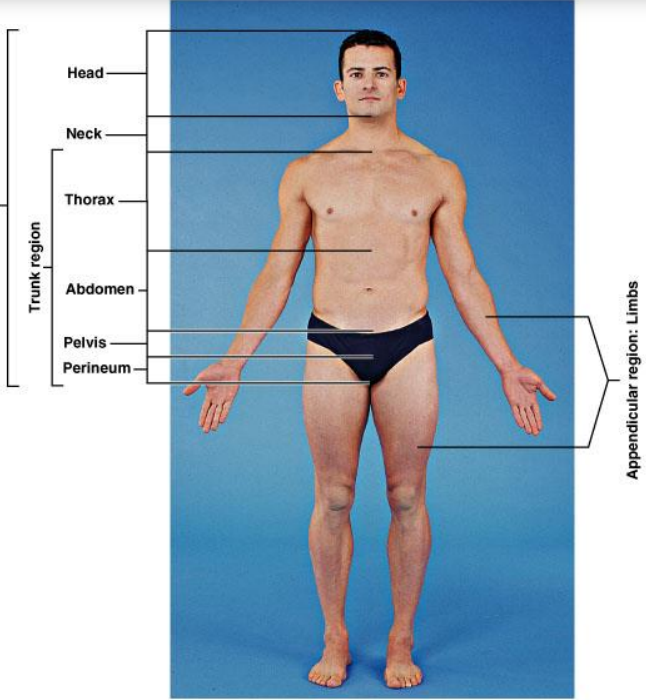
What are included in the appendicular region?
Limbs
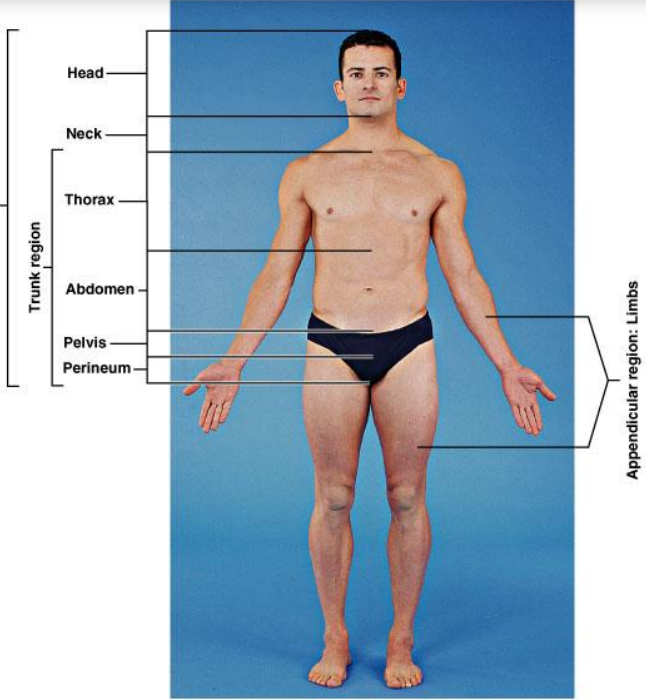
What does directional terminology refer to in anatomy?
Directional terminology refers only to the body in the anatomical position and involves standardized terms that describe locations and directions on the body.
What is the term for the body position when lying face down?
The body is in the prone position when lying face down.
What is the term for the body position when lying face up?
The body is in the supine position when lying face up.
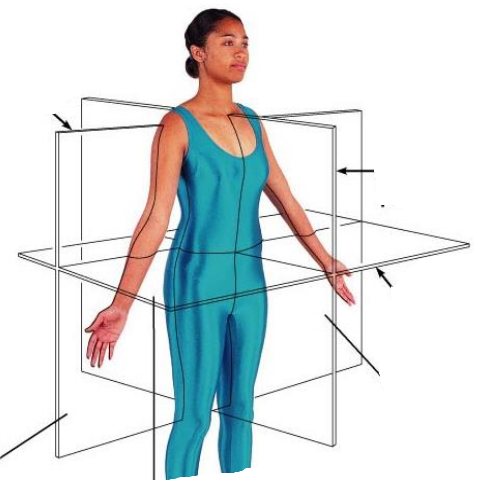
What are the frontal plane, median plane and transverse plane?
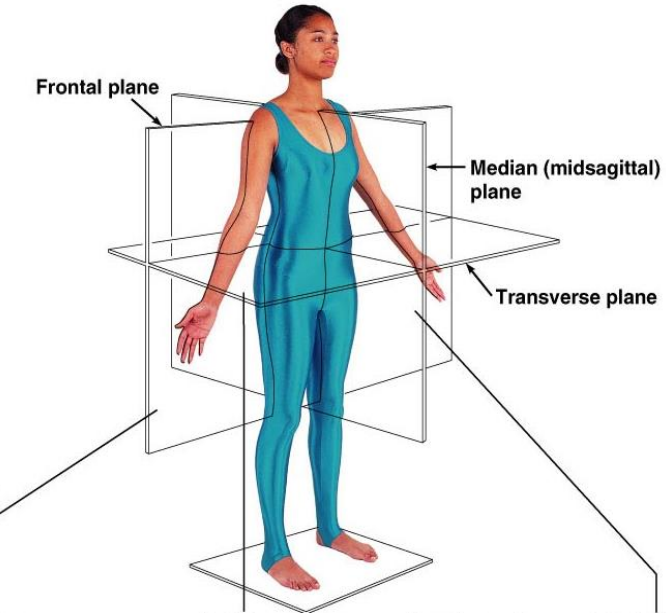
What is transverse or horisontal section?
It separates superior (closer to head) and inferior (further away from head) portions of the body. Sections usually pass through head and trunk regions. Perpendicular to long axis
Which sections are parallell to long axis?
Sagittal, midsagittal, parasagittal and coronal or frontal
What is sagittal section?
It separates right and left positions
What is midsagittal section?
The plane passes through the midline, dividing the body in half and separating right and left
What is parasagittal section?
It misses the midline, separating right and left portions of unequal size
What is fronal or coronal section?
It separates anterior (front of the body) and posterior (back of the body) portions of the body. Coronal often refers to sections passing through the skull
What are main body cavities?
Cranial, vertbral, thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
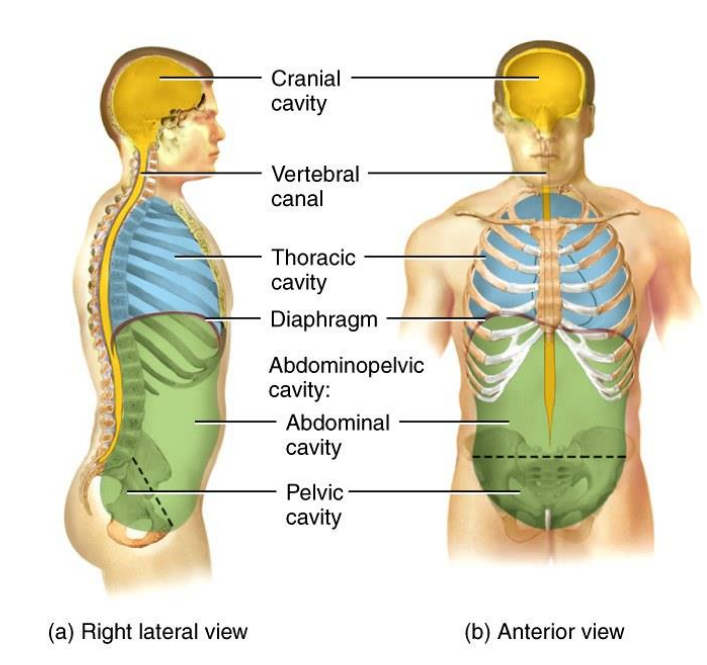
What forms cranial cavity and what does it contain?
Formed by cranical bones and contains brain
What forms vertebral canal and what does it contain?
Formed by vertebral column and contains spinal cord and the beginnings of spinal nerves
Which cavities does thoracic cavity contain?
Chest cavity contains pleural and precardial cavities and mediastinum
Which cavities does abdominalpelvic cavity contain?
Abdomial cavity and pelvic cavity
What does abdomial cavity contain?
Stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small intestine and most of large intestine
What does pelvic cavity contain?
Urinary bladder, portions of large intestine and internal organs for reproduction
What cavity surrounds each lung in the human body?
Pleural cavity
What cavity surrounds the heart in the human body?
Percardial cavity
What is mediastinum and what does it contain?
Central portion of thoracic cavity between the lungs. It contains heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea and several large blood vessels
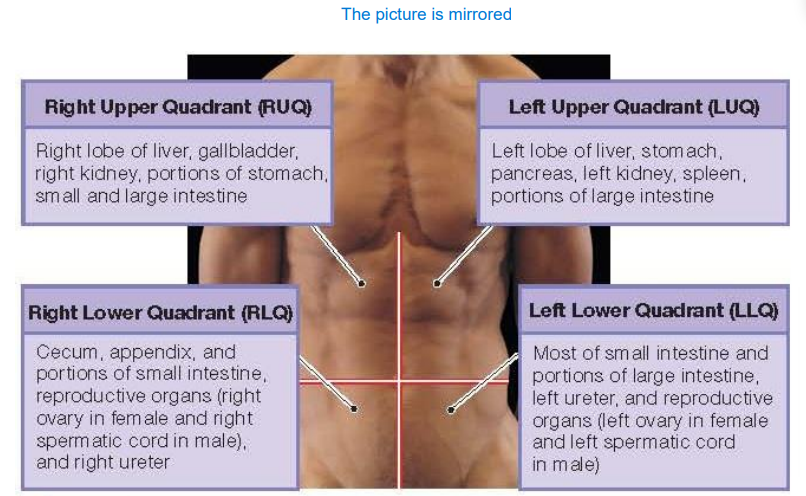
What is abbreviation for Right Upper Quadrant and what does it contain?
RUQ. It contains right lob of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portions of stomach, small and large intestine
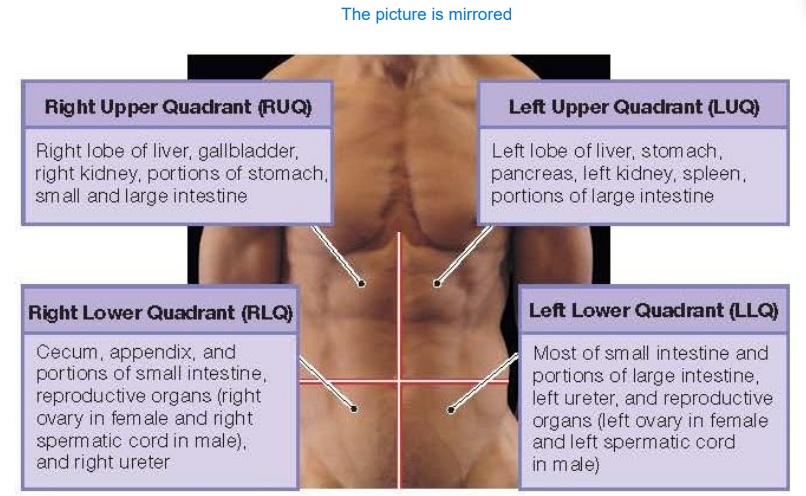
What is abbreviation for Left Upper Quadrant and what does it contain?
LUQ. It contains left lob of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen and portions of large intestine
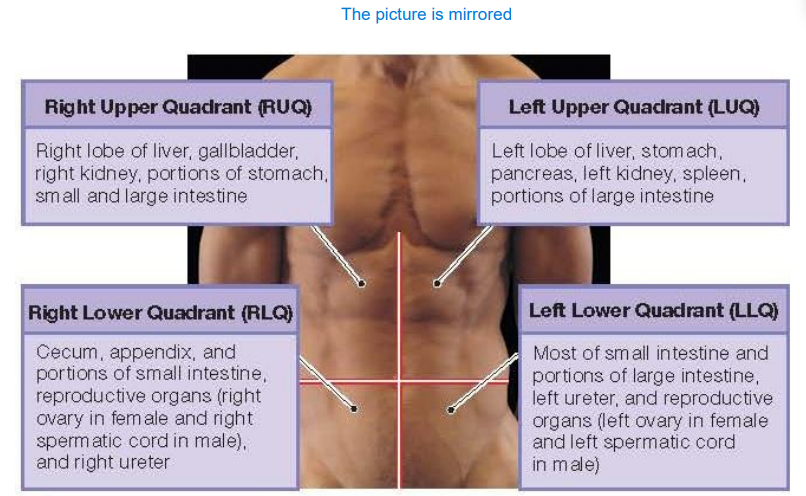
What is abbreviation for Left Lower Quadrant and what does it contain?
LLQ. It contains most of small intestine and portions of large intestine, left ureter and reproductive organs (left ovary and left spermatic cord
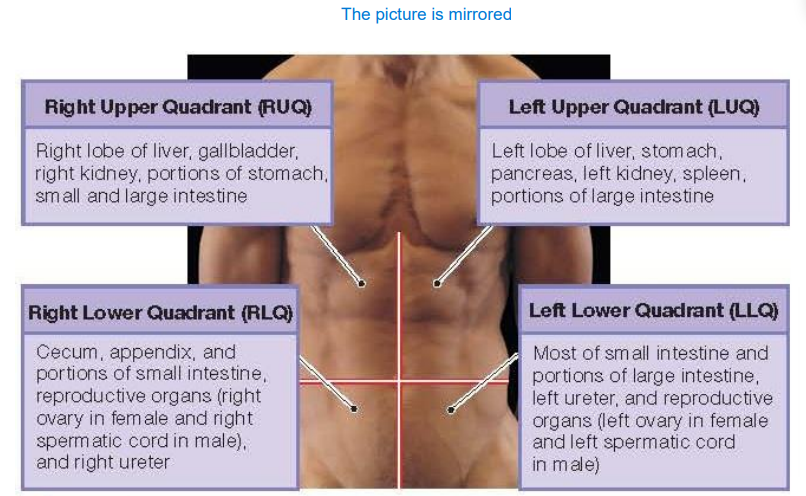
What is abbreviation for Right Lower Quadrant and what does it contain?
RLQ. It contains cecum (beginning of the large intestine), appendix, portions of small intestine, right ureter and reproductive organs (right ovary and right spermatic cord
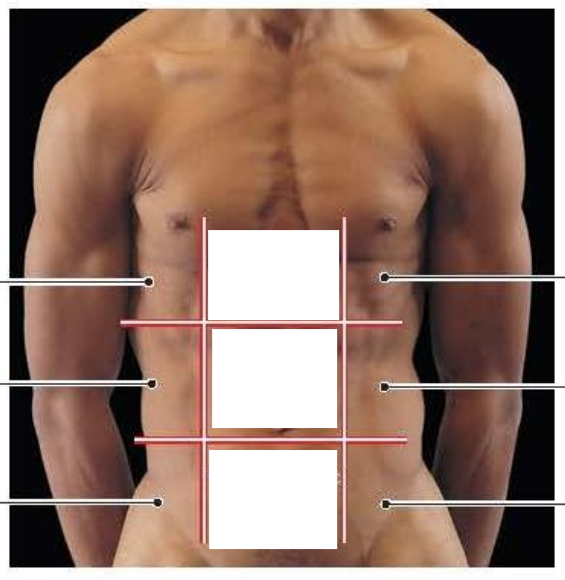
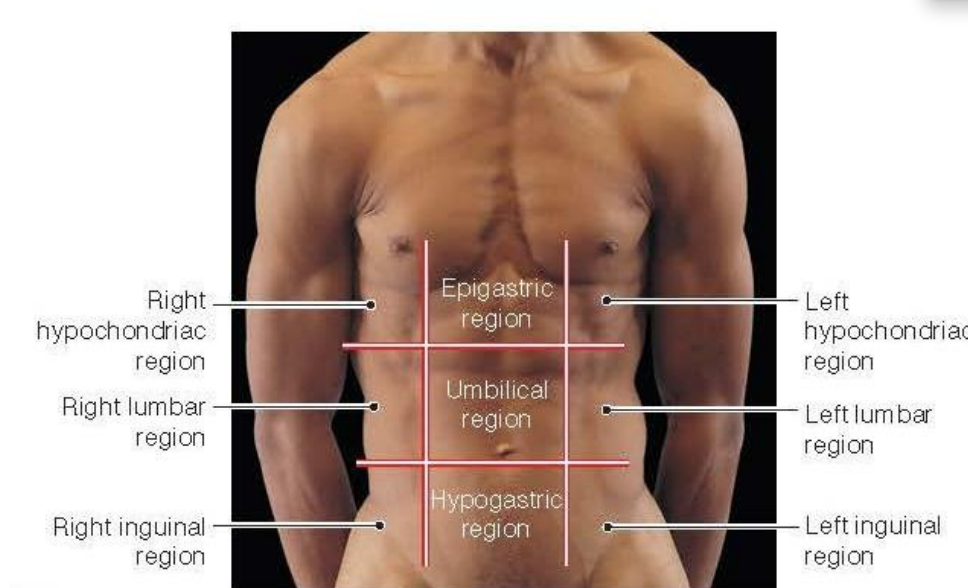
Place the different regions in the abdominopelvic region
Hypochondriac=Below heart
Epigastric=Above stomach
Hypogastric=Below stomach
Lumbar
Inguinal= groin area
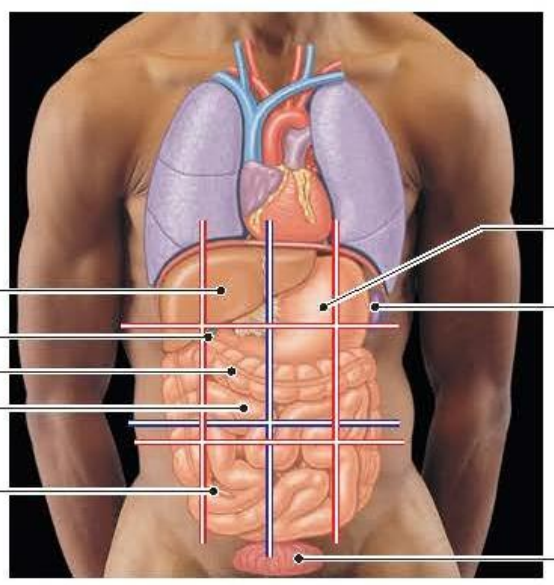
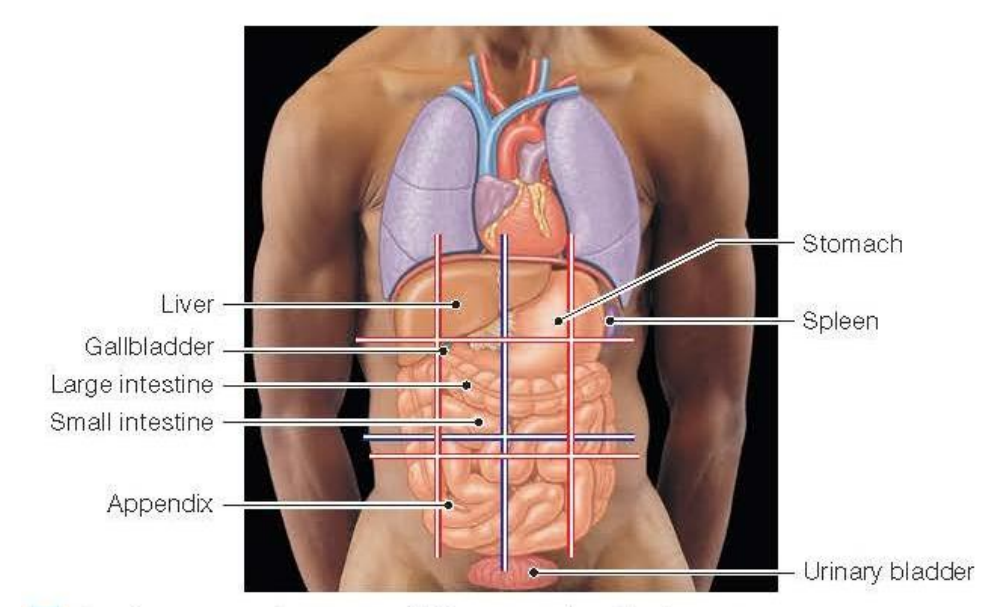
Name different organs
Gallblader
What does superior (cranial) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position toward the head end or the upper part of a structure in the body, meaning above.
For example, the head is superior to the abdomen.
What does inferior (caudal) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position away from the head end or lower part of a structure in body meaning below
For example, the navel is inferior to the chin
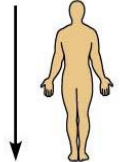
What does anterior (ventral) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position towards or at the front of the body, meaning front of
For example, the breastbone is anterior to the spine
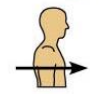
What does posterior (dorsal) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position towards or at the back of the body, meaning back of
For example, the heart is posterior to breastbone
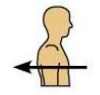
What does medial mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position towards or at the midline of the body, on the inner side of
For example, the heart is medial to the chest
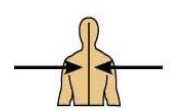
What does lateral mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position away from the midline of the body, on the outer side of
For example, the arms are lateral to chest
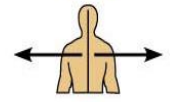
What does proximal mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Usually a joint
For example, the elbow is proximal to the wrist
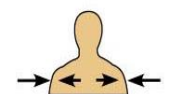
What does distal mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Distance=further away
For example, the knee is distal to the thigh
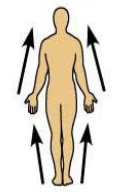
What does superficial (external) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position toward or at the body surface
For example, the skin is superficial to to the skeletal muscles
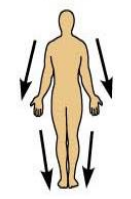
What does deep (internal) mean and can you give an example?
Refers to a position away from the body surface, more internal
For example, the lungs are deep to the skin
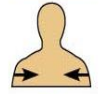
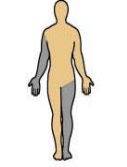
What does ipsilateral mean and can you give an example?
Refers to two positions on the same side of the body
For example, the right hand and right foot are ipsilateral
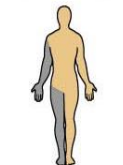
What does contralateral mean and can you give an example?
Refers to two positions on the opposite side of body
For example, the right hand and left foot are contralateral
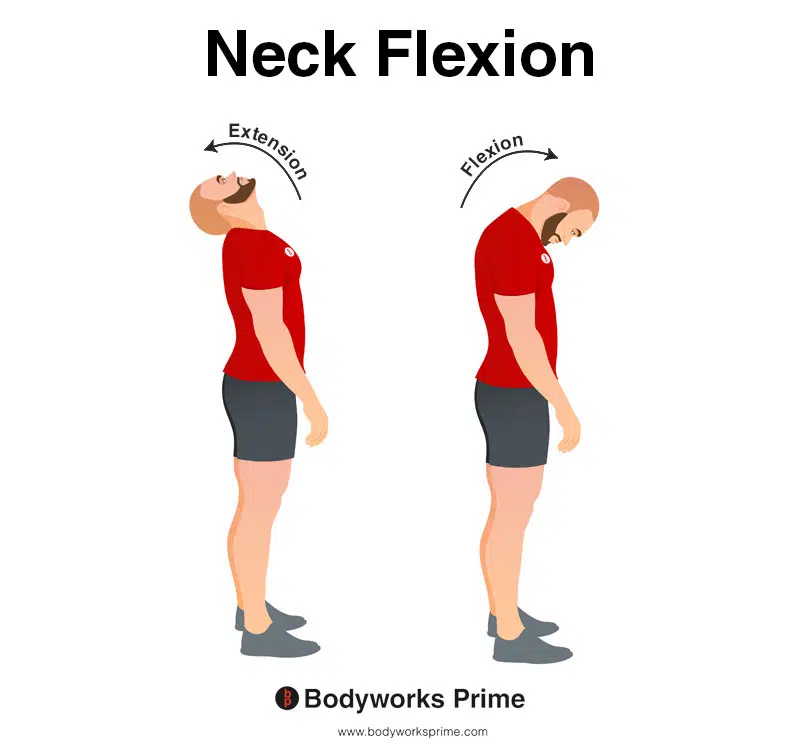
What is flexion, and how does it apply to different parts of the body?
Flexion is a movement that decreases the angle between two bones. Examples include:
Neck: Tilting the head anteriorly.
Trunk: Bending forward.
Shoulder/Hip: Moving the arm or leg anteriorly.
Elbow/Knee: Closing the angle at the elbow or knee.
Fingers: Forming a fist.
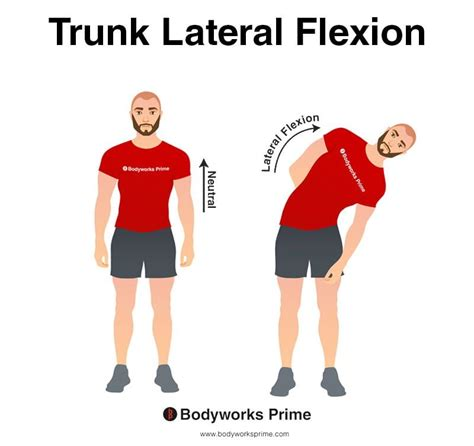
What is lateral flexion?
Lateral flexion is a special type of flexion where the vertebral column bends to the side (laterally).
What is extension, and how does it apply to different parts of the body?
Extensionis a movement that increases the angle between two bones. Examples include: Opposite of flexion
Neck: Tilting the head posteriorly (looking up).
Trunk: Leaning backward (arching the back).
Shoulder/Hip: Moving the arm or leg posteriorly (moving the arm back down or leg straight back).
Elbow/Knee: Straightening the angle at the elbow or knee (increasing the angle).
Fingers: Straightening the fingers (opening a fist).
What is hyperextension?
Hyperextension is a special type of extension beyond the normal range of movement
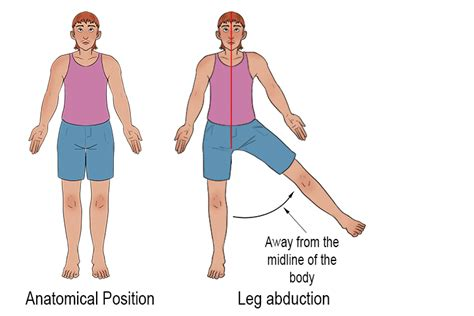
What is abduction, and how does it apply to different parts of the body?
Abduction is a movement away from the median plane/midline. Examples include:
Shoulder/Hip: Arm/leg moved laterally, away from the body
Wrist: In the anatomical position, the hand moves away from the body
Fingers/Toes: Spreading the digits away from the middle one
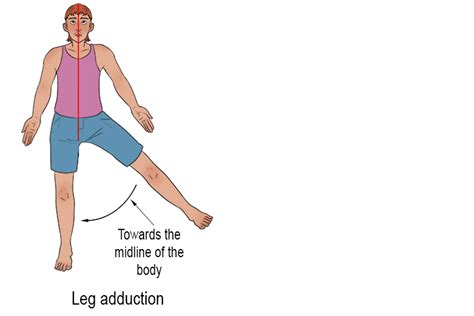
What is adduction, and how does it apply to different parts of the body?
Adduction is a movement towards from the median plane/midline. Examples include: Opposite to abduction
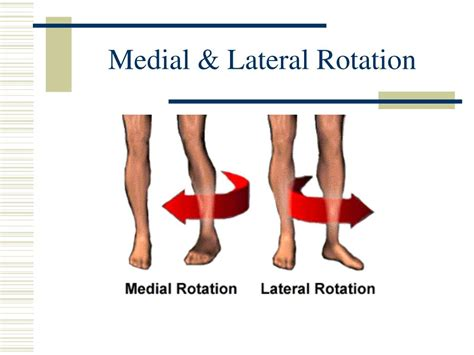
What is medial rotation, and which parts of the body can perform this movement?
Medial rotation is the turning of a bone along its longitudinal axis toward the median plane of the body. It occurs in areas such as the first two vertebrae, trunk, shoulder, and hip.
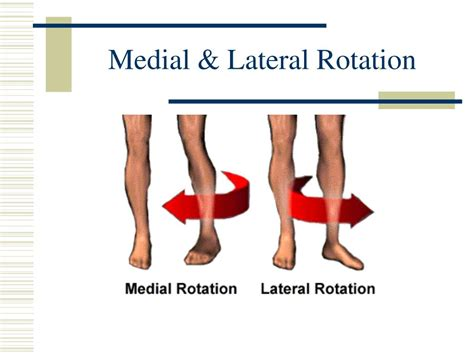
What is lateral rotation, and how does it differ from medial rotation?
Lateral rotation is the turning of a bone along its longitudinal axis away from the median plane. It is the opposite movement of medial rotation, which turns the bone toward the median plane.
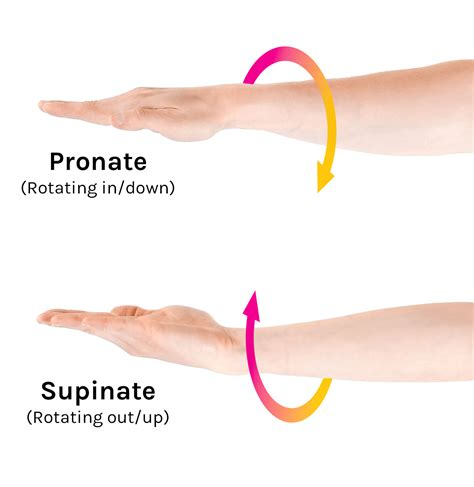
What is supination, and which parts of the body can perform this movement?
Supination is the lateral rotation of the forearm causing the palm of the hand to face anteriorly. It occurs in the forearm
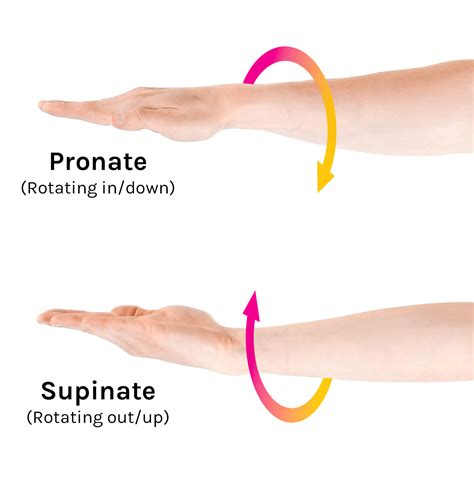
What is pronation, and how does it differ from supination?
Pronation is the medial rotation of the forearm causing the palm of the hand to face posteriorly. It is the opposite movement of supination
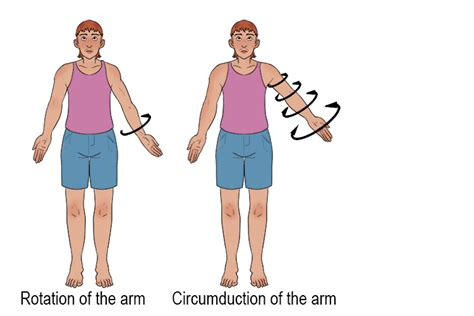
What is circumduction, and which body parts can perform this movement?
Circumduction is the rotation of a limb or finger around its medial axis, creating a circular motion. This movement involves a combination of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction in succession. It can be performed by the fingers, wrist, shoulder, and hip.
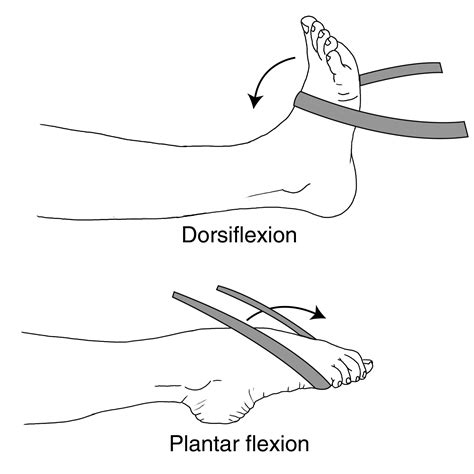
What is plantar flexion, and when does it occur?
Plantar flexion is the downward movement of the foot at the ankle joint, such as when you stand on your toes.
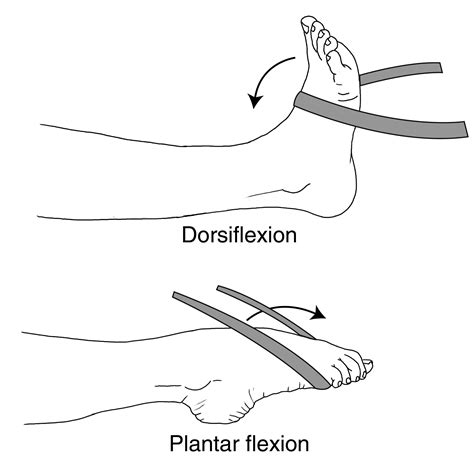
What is dorsiflexion, and how does it occur?
Dorsiflexion is the upward movement of the foot at the ankle joint, such as when you bring the top of your foot close to your shin.
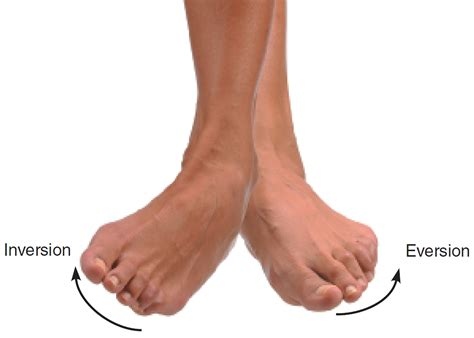
What is inversion, and how does it affect the foot?
Inversion is the movement that turns the sole of the foot inward.
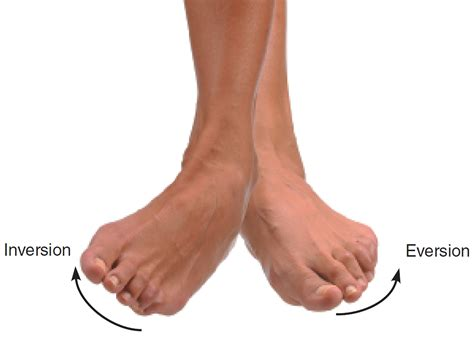
What is eversion, and how does it affect the foot?
Eversion is the movement that turns the sole of the foot outward.
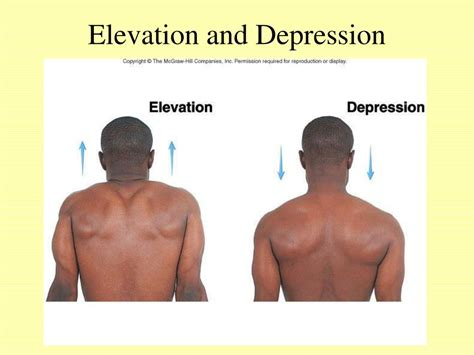
What is elevation, and which body parts can perform this movement?
Elevation is the movement that involves lifting a body part superiorly. This action can be performed by the shoulder girdle and the jaw.
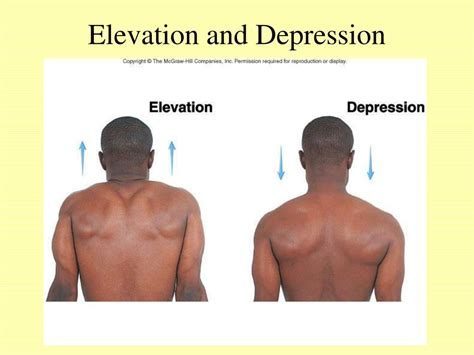
What is depression, and how does it relate to elevation?
Depression is the movement that involves moving an elevated body part inferiorly. It is the opposite movement of elevation.
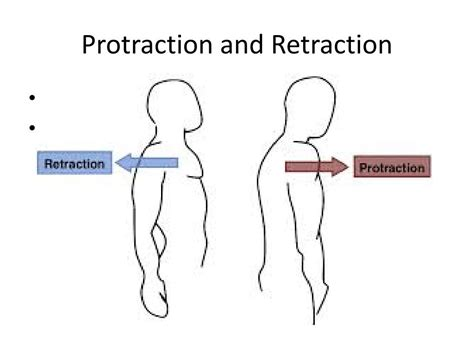
What is protraction, and which body parts can perform this movement?
Protraction is the movement of a body part anteriorly in the transverse plane. This action can be performed by the clavicles and the jaw.