Anatomy Semester 1 Review
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
Study of structure
anatomy
study of function
physiology
List the Characteristics of life
Responsiveness
Conductivity
Contractility
Growth
Development
Reproduction
Respiration
Digestion
Excretion
Secretion
Circulation
all the chemical and physical reactions in the body
metabolism
to build up molecules
anabolic
to break down molecules
catabolic
What is the organization of humans?
chemical → Organelle → Cells → Tissue → Organs → System → Organism
What are the four types of tissues?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
What are the 11 systems of the human body?
Integument
skeletal
Muscular
Nervous
Endocrine
Cardiovascular
Lymphatic
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive
When the body is standing with arms at side, palms facing forward, legs slightly spread
anatomical postion
What does the axial skeleton include
head, neck, and trunk
What does the appendicular skeleton include
upper and lower limbs
Cavity at the front of body
ventral cavity
cavity at the back of the body
dorsal cavity
cavity including the rib cage and diaphragm
thoracic cavity
cavity around the lungs
pleural cavity
cavity that separates the lungs and includes the trachea, esophagus, and heart
mediastinum cavity
cavity from bottom of hip bones to diaphragm
adominopelvic cavity
cavity from top of the hip bones to diaphragm
adominal portion
cavity formed by the hip bones
pelvic portion
cavity that houses the brain
cranial cavity
cavity that houses the spinal cord
spinal/vertebral cavity
membranes attached to the wall of a cavity
parietal membranes
membranes attached to the organs/interior
visceral membranes
adominal pelvic membrane
peritoneum
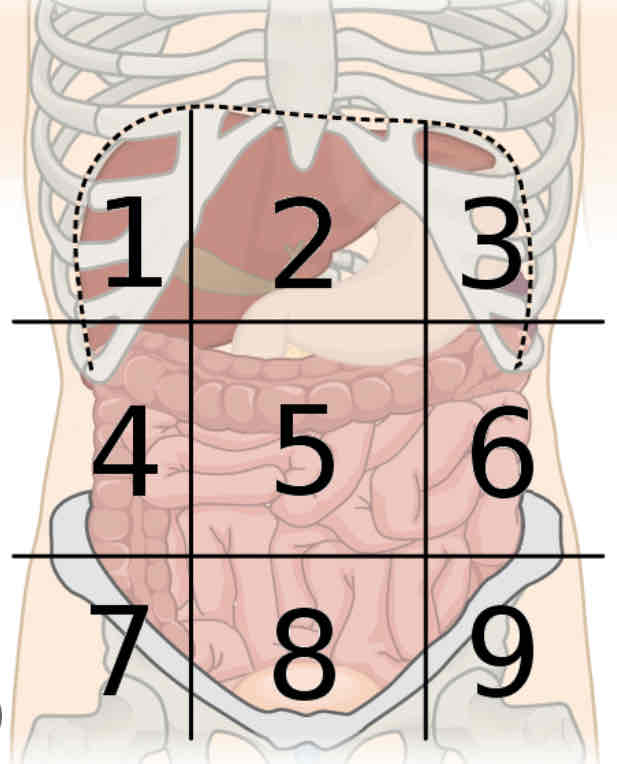
What is region 1
Right hypochondriac
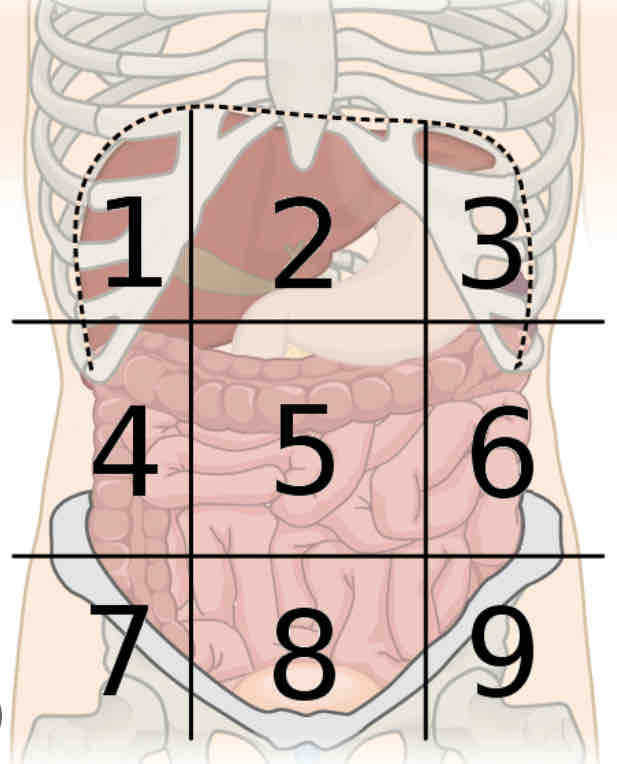
What is region 2
Epigastric
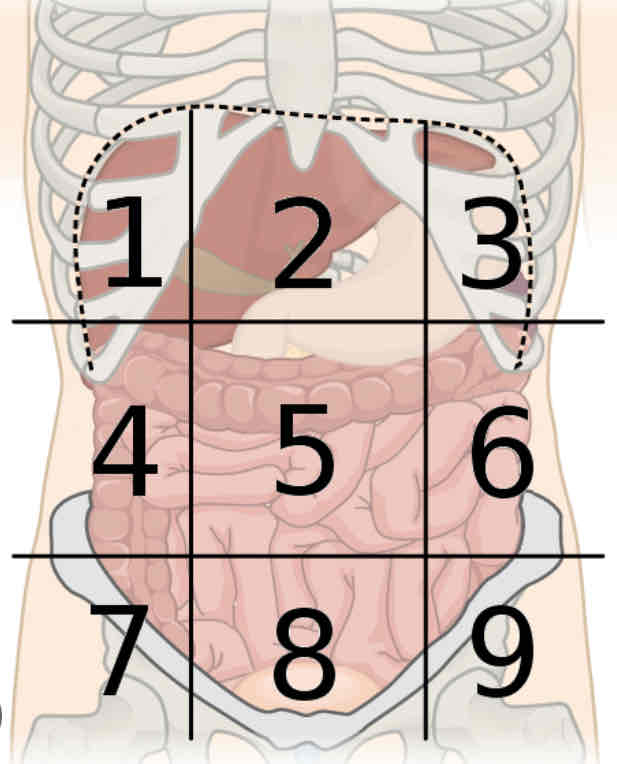
What is region 3
Left hypochondriac
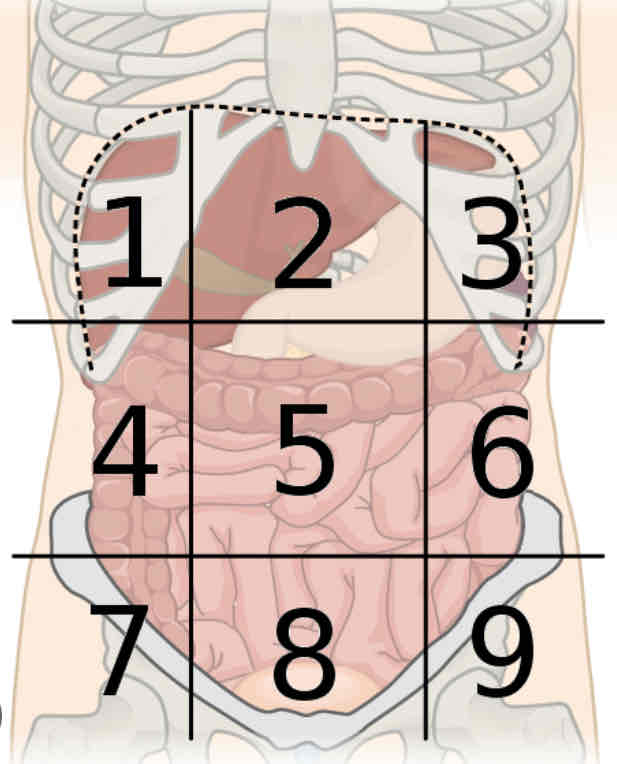
What is region 4
Right lumbar
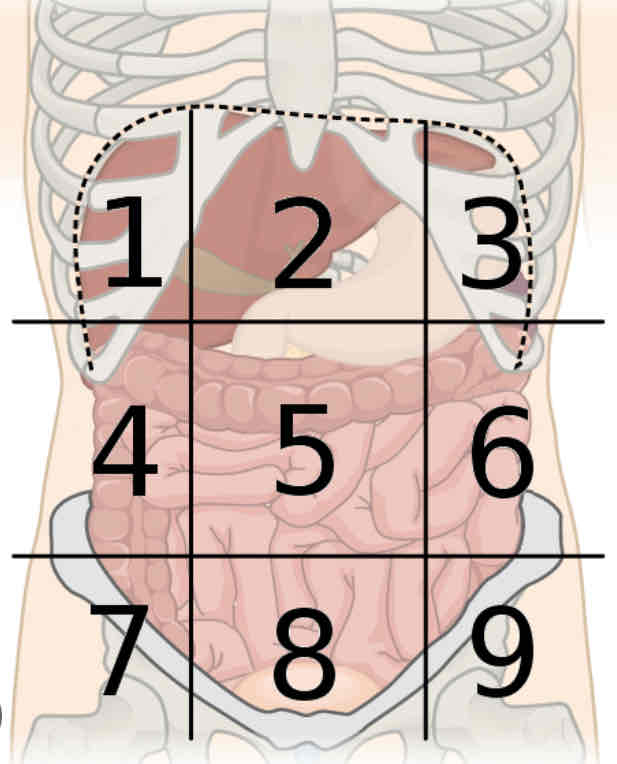
What is region 5
Umbilical
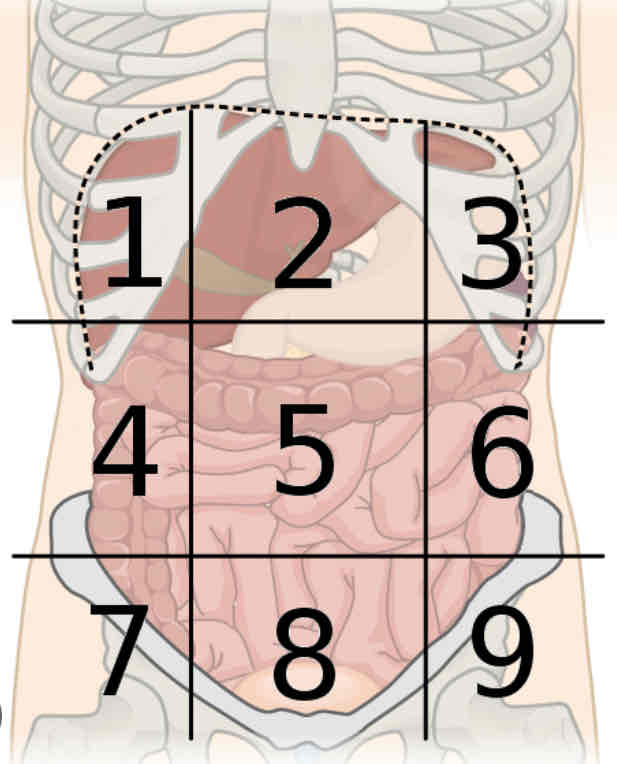
What is region 6
Left lumbar
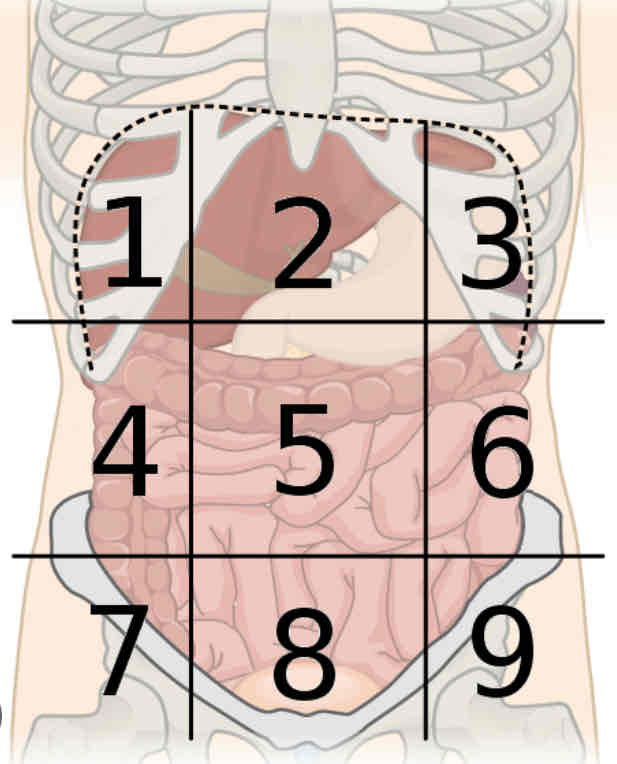
What is region 7
Right iliac
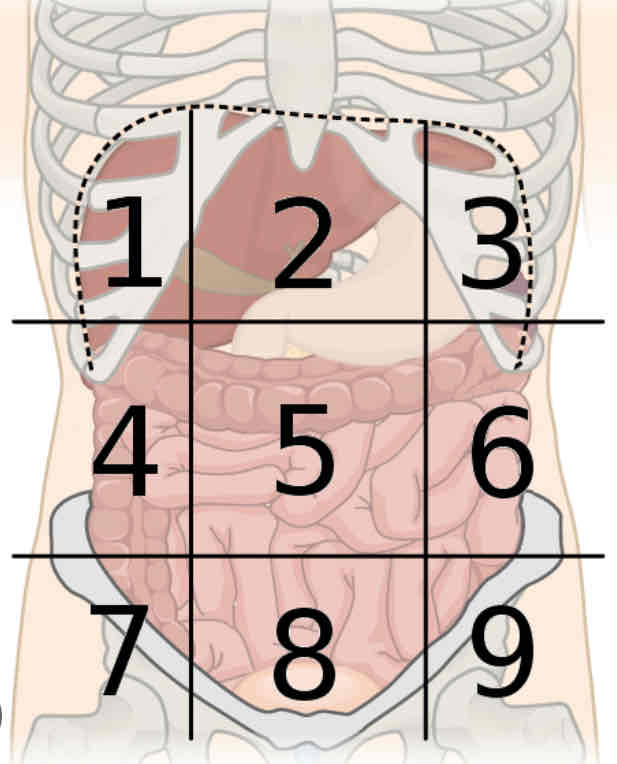
What is region 8
Hypogastric
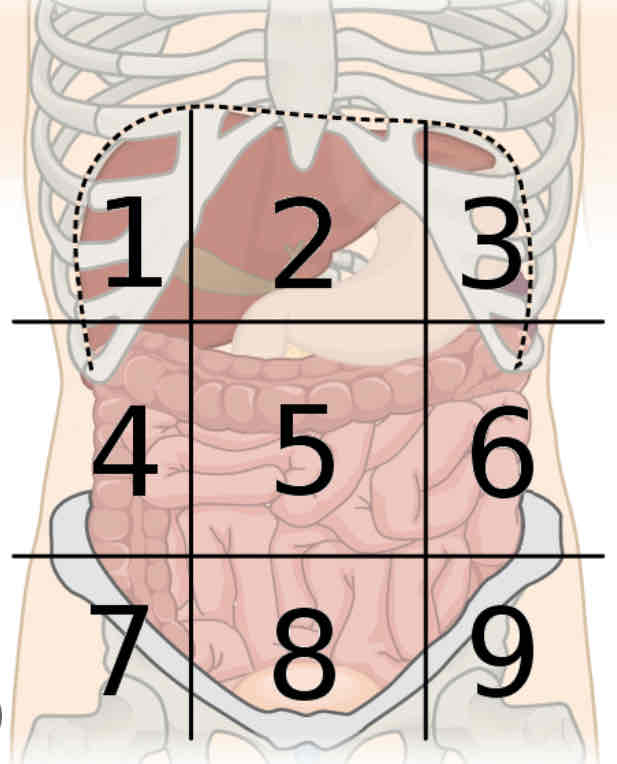
What is region 9
Left iliac
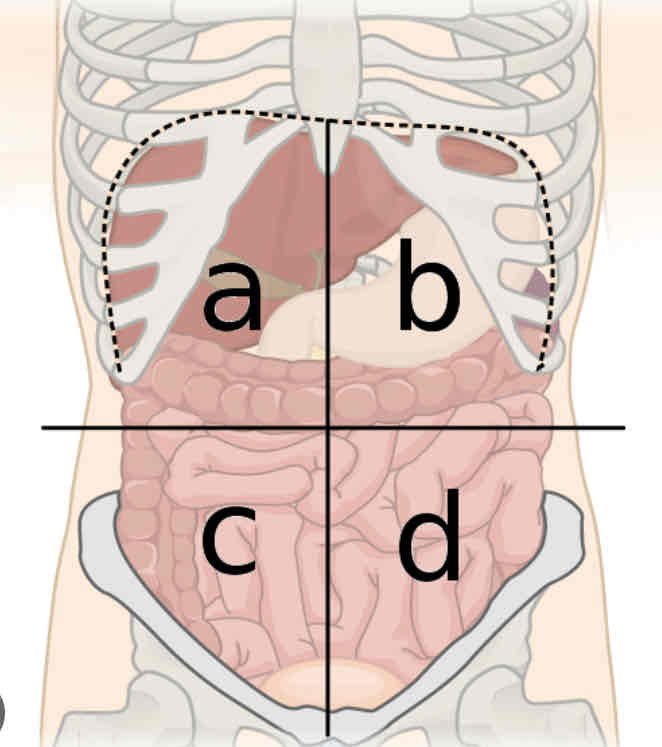
What is a
Right upper quadrant
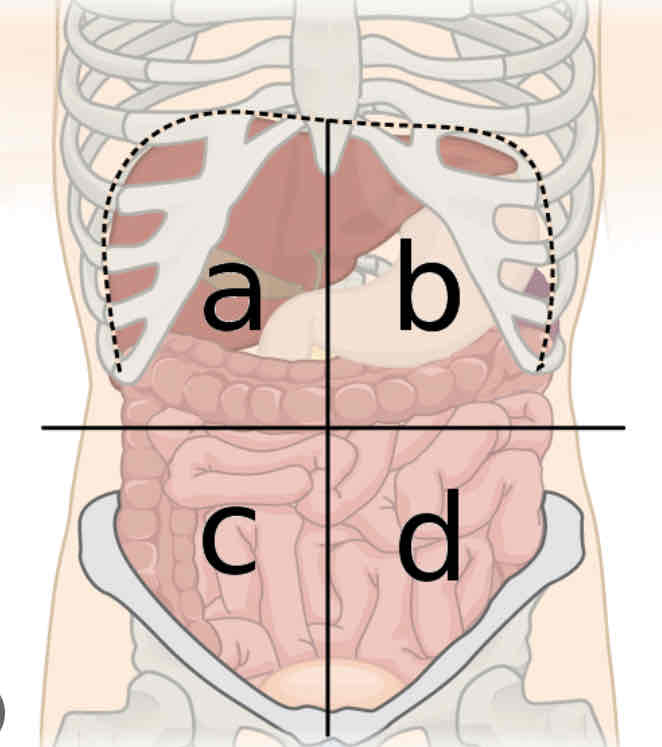
What is b
Left upper quadrant
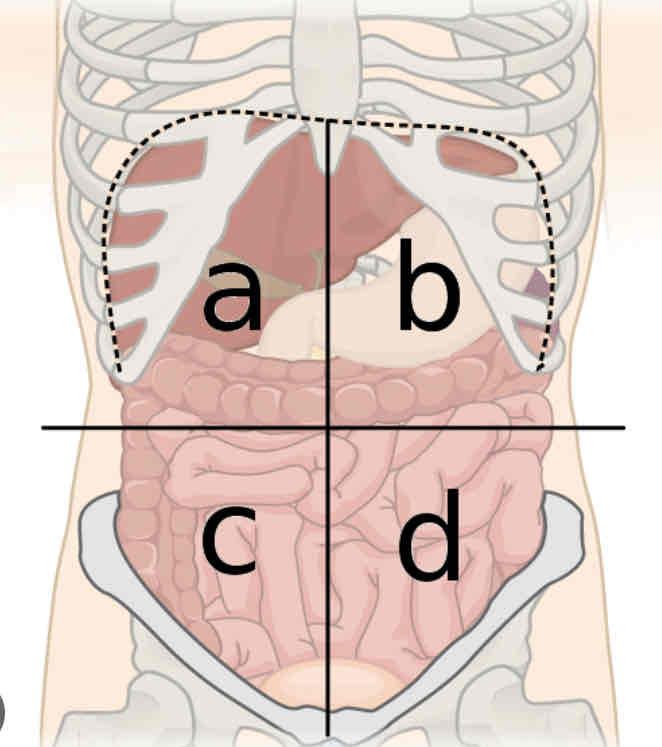
What is c
Right lower quadrant
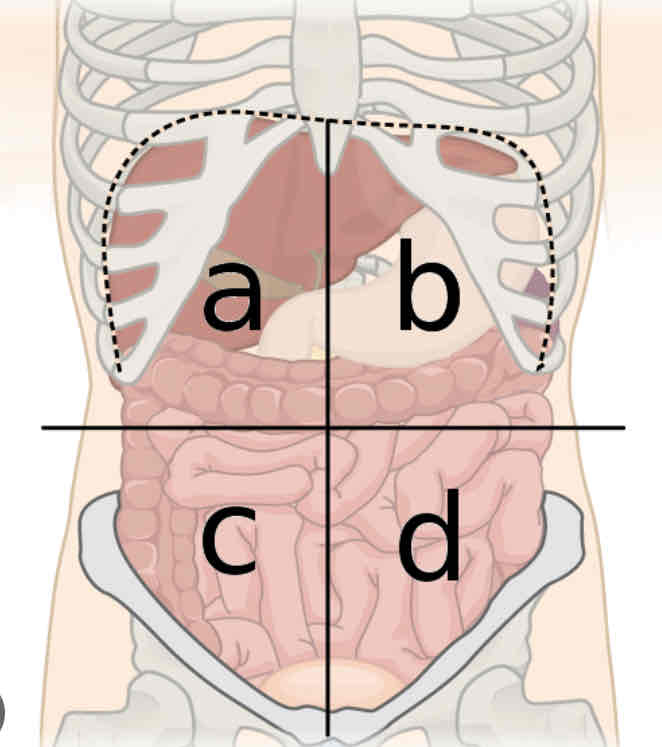
What is d
Left lower quadrant
What directional term means above
superior/cranial
What directional term means below
inferior/caudal
What directional term means front
anterior/ventral
What directional term means towards back
posterior/dorsal
What directional term means middle
medial
What directional term means left or right of mid line
lateral
What directional term means structures on opposite sides
contra lateral
What directional term means structure on same side
ipsilateral
What directional term means closer to point of attachment of limbs
proximal
What directional term means farther away from point of attachment for limbs
distal
What directional term means close to the body surface
superficial
What directional term means farther from body surface
deep
What directional term means sole of feet
plantar
What directional term means hands
palmer
cavity inside the organ or tubular vessel
lumen
toward center
central
away from center
peripheral
inner most part
medullary
outer most part
corticol/cortex
forms base, closest to attachment
basal
peak, furthest from attachment
apical/apex
What body plan divides into left and right
sagittal
What body plan divides anterior and posterior
coronal/frontal
What body plan divides superior and inferior
transverse/horizontal
sagittal plane at the midline
midsagittal
sagittal plane that’s between lateral to midline
parasagittal
maintenance of relatively stable internal environment
homeostasis
a regulatory mechanism in which a change in a controlled variable triggers a response to oppose change
negative feedback loop
regulatory mechanism in which changes in controlled variable triggers response that drives changes further from set point
positive feedback loop
fluid inside cells
intracellular fluid
fluid outside cells
exracellular fluid
fluid directly around cell
interstitial fluid
used to dissect and study the human body
cadavers
short wavelength, high energy radiation passes through solid object
X-rays/radiography
radar technology that uses sound waves to visualize structures
ultrasonography
Uses x-ray scanner goes 360 degrees around patient uses contrast agent
CT scan
a unique high-speed volume imaging x-ray scanner based on computed tomographic principles
DSR
Uses strong magnets to image body
MRI
uses short lived radio pharmaceuticals to evaluate area scanned
PET scan
group of similar cells carrying out a particular function
tissue
study of tissues
histology
What are the epithelial shapes?
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
What are the epithelial layers?
simple
stratified
Type of epithelial cells found in protected areas with function of absorption and secretion
simple squamous
Type of epithelial cells found in esophagus, anus, line oral cavity, and surface of skin with the function of withstanding mechanical stress
stratified sqamous
Type of epithelial cells found in ovaries, kidney tubules, and glands, with the function of secretion and absorption
simple cuboidal
Type of epithelial cells found in mammary glands, pancreas, glands of reproductive tract with the function of secretions
stratified cuboidal
Type of epithelial cells found in small intestine, rectum and uterus with the function of absorption
simple columnar
Type of epithelial cells found in male urethra and ductus deferens and pharynx/nasal epithelium
stratified columnar
Type of epithelial cells found in respiratory and reproductive tract with the function of high absorption and movement. Includes goblet cells and cilia
pseudostratified columnar
Is epithelial tissue vascular(bv) or avascular(no bv) ?
avascular
What are the defining characteristics of CT?
extracellular matrix; protein fibers, fluid, nonfibrous protein, surround, support, communication, point of attachment
CT cells that synthesize and secrete fibers for matrix
fibroblasts
CT immune cell
macrophage
CT fat cell
adipose cell
CT cells that secretes melanin
melanocyte
CT cells that is not fully differentiated
stem cell
Thick fibers that are strong to resist pulling found in ligaments and tendons
collagen
spring like fiber that can be stretched and return to original found in vocal cords
elastic fibers
thin fibers the provide delicate support that is still collagen
reticular fibers
CT that is 99% collagen fibers and found in tendons and ligaments
dense regular CT
CT that is 60% collagen fibers and is found in the dermis of the skin
dense irregular CT