Growth Charts (Kaulfers)
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kaulfers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
You can see that the average height of boys and girls are about ___ inches (__ cm) apart.
5
13
Weigh a baby with only a _____ on
diaper
For children that are standing, measure the height ____ times and take the average
three
Most Important Feature of growth chart is the Growth ______
velocity
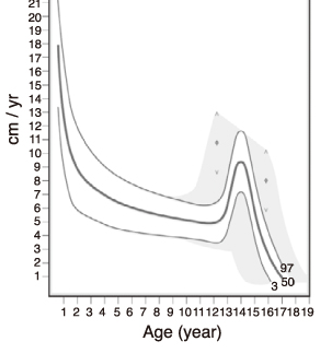
Boy height velocity
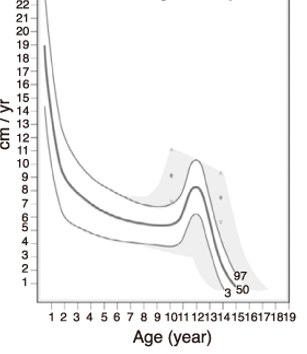
Girls’ height velocity
Ages 5-puberty: __ cm/year is typical
5
Puberty: rapid growth again, ___ cm/year for boys and __ cm/year for girls.
10
8
Infancy and childhood: very rapid growth, so you don’t “calculate” a growth velocity until after age _ years old
3
Boys stop growing around ___; Girls stop growing around ___
16
14
Height velocity: __ cm/year
Normal for most ages: ___-__ cm/year
During pubertal growth spurt: ___-__ cm/year
5
4-8 (about 2 inches)
8-12 (about 4 inches)
Things that warrant a medical evaluation:
Poor height velocity (falling percentile lines)
Height “below the curve” (below -2 SD for age)
Height below the child’s genetic potential
95% of children will come within __ inches of this number for their final adult height
2
Girls height calculation
(Dad’s ht minus 5 inches) + Mom’s ht, divided by 2
Boys height calculation
(Mom’s ht plus 5 inches) + Dad’s ht, divided by 2
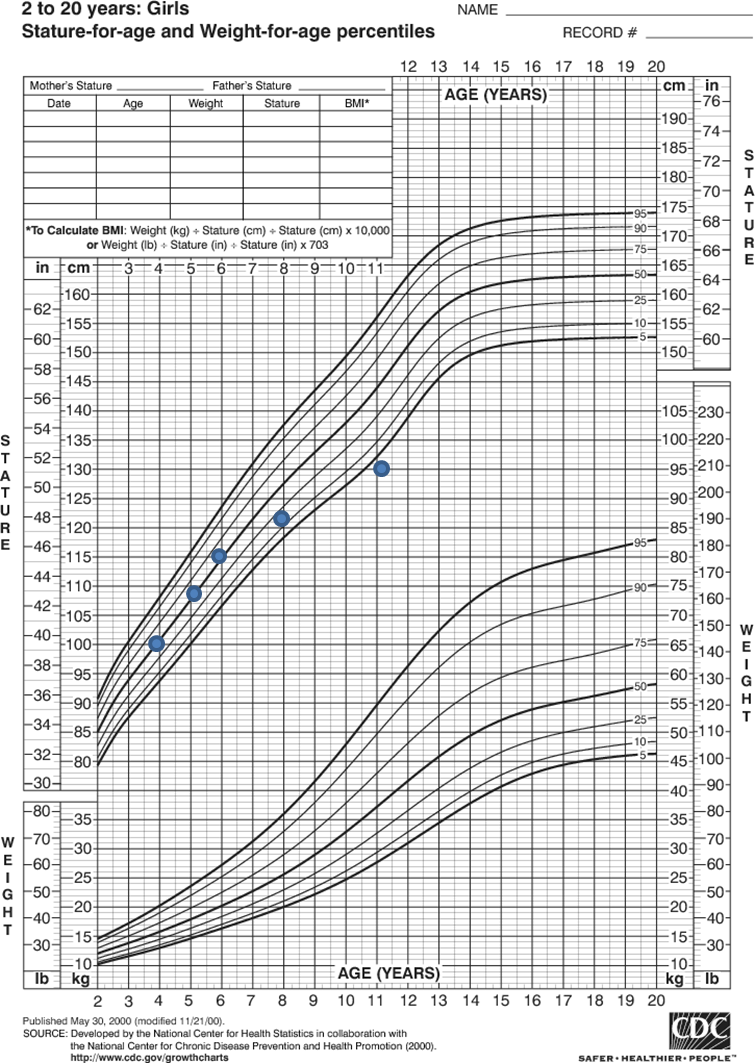
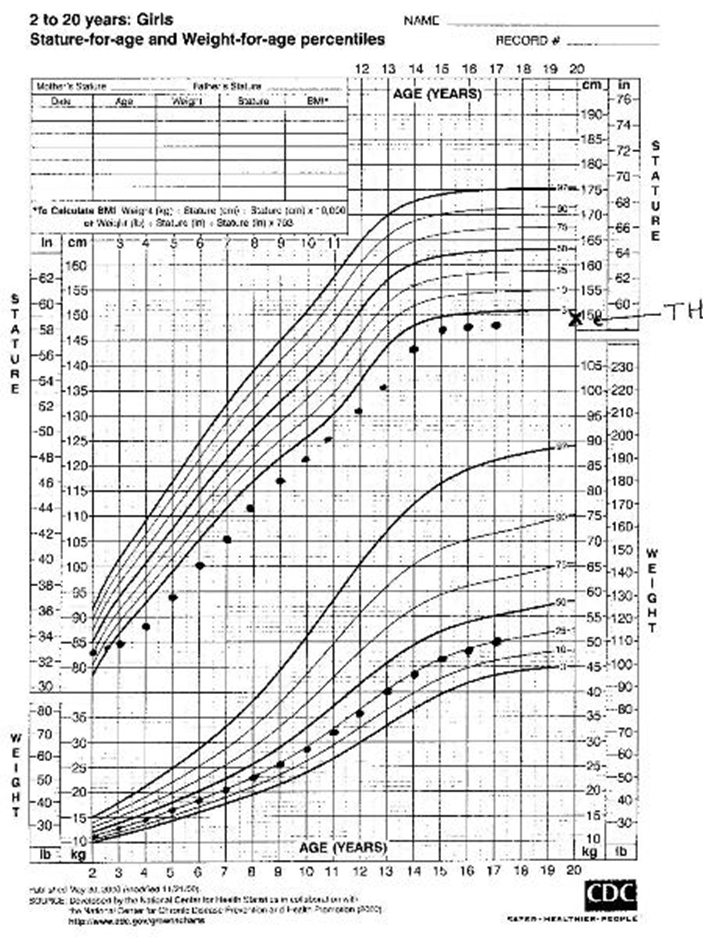
On curve, Falling percentiles, below curve
Falling percentiles: Always worked up, could be brain tumor, growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroid, excess cortisol
Genetic potential aka
Mid-parental height
Target height
True Endocrine disease only accounts for __% of the causes of short stature
5
_________ is a major cause of short stature worldwide
Malnutrition
Most cases of short stature are either ______ short stature or _______ delay of growth (late bloomer)
familial
constitutional
If you are malnourished, the ____ will not work
GH growth hormone
Familial short stature
Normal Bone Age
Normal Labs
Growth curve is at the level of the Target Height
Familial short stature
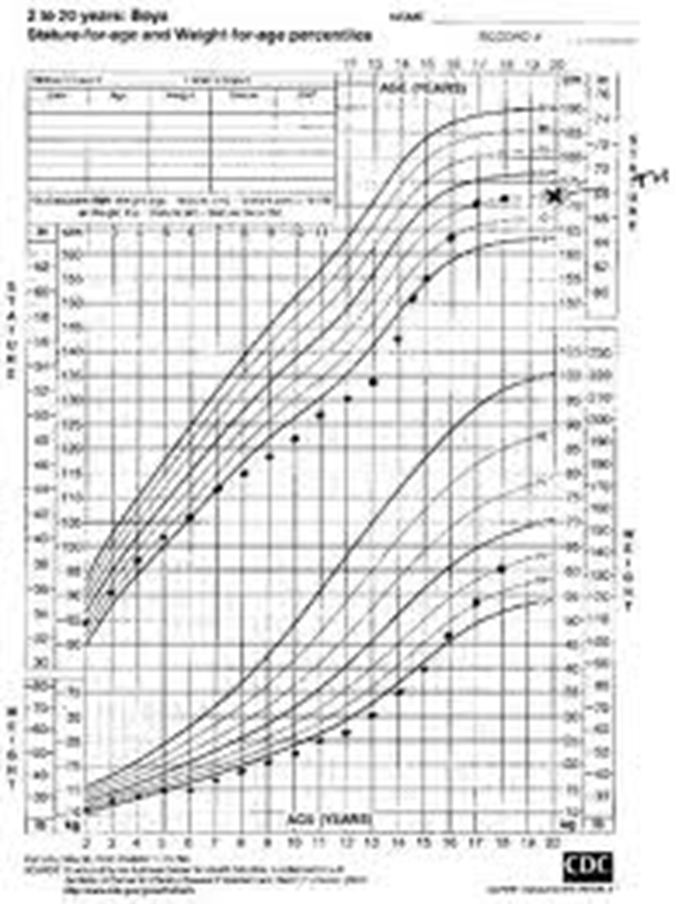
Constitutional Delay of Growth
“Late Bloomer”
Delayed Bone Age
Normal Labs
Poor growth, or growth along the bottom of the curve until the child hits puberty (after age 14 years usually) then has catch-up growth quickly and the adult height is equal to the target height
Constitutional Delay of Growth
“Late Bloomer”
Late bloomer child will have normal size at birth, and then fall to the bottom of the curve by __ years of age.
5
Some late bloomers can benefit from a short course of Testosterone therapy to induce the ______ changes – you can refer them to Endocrinology.
Pubertal
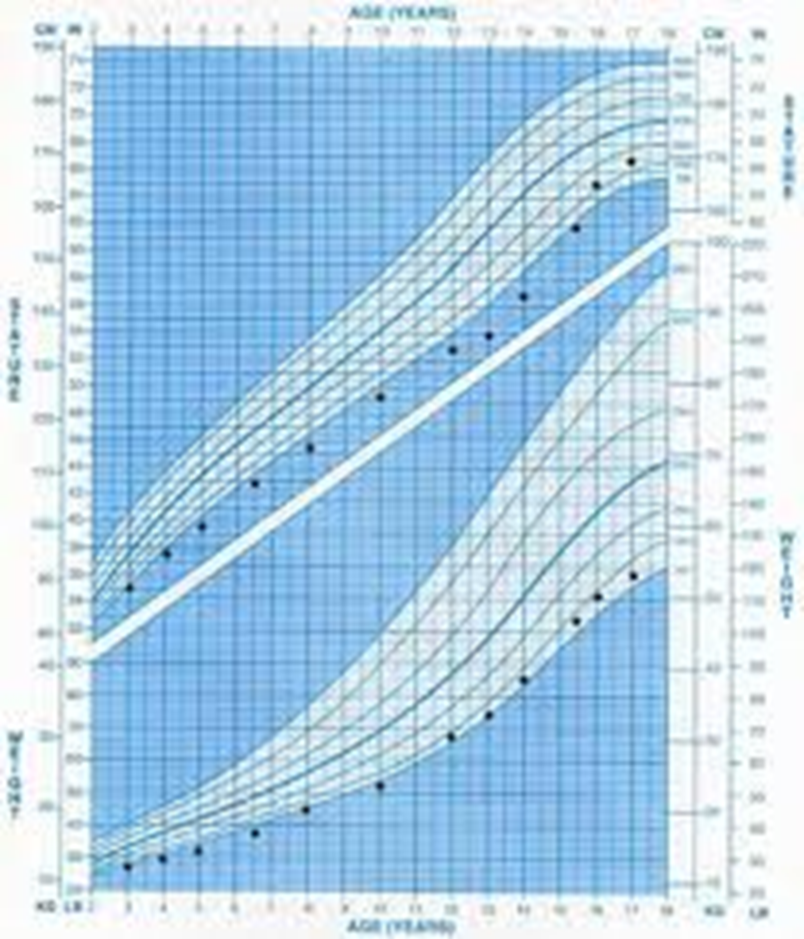
Constitutional delay of growth
Late bloomer
Tallest Turner’s girl on average is
5 foot most well in 4 foot range
Need both Xs to get tall
Can benefit from growth hormone
Falls off around 5 years old
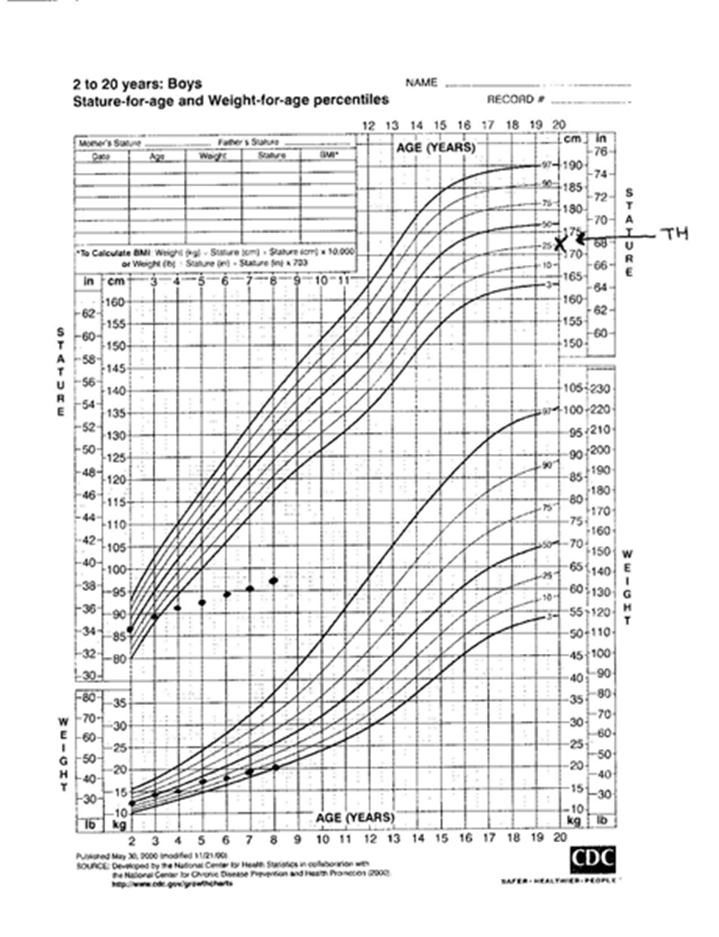
Growth Hormone deficiency
Delayed bone age
Height falling percentiles
Height below target
Weight percentile is more than height percentile for age
Normal labs except low IGF-1 and low IGF-BP3
Growth hormone deficiency
Weight percentile is more than height percentile for age
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency normal labs except low _____ and low _____
IGF-1
IGF-BP3
In 35% of growth hormone deficiency cases is due to brain _____or brain _____.
tumors
radiation
In 20% of the growth hormone deficiency cases are _______.
Congenital
Most cases of growth hormone deficiency are ______
Idiopathic
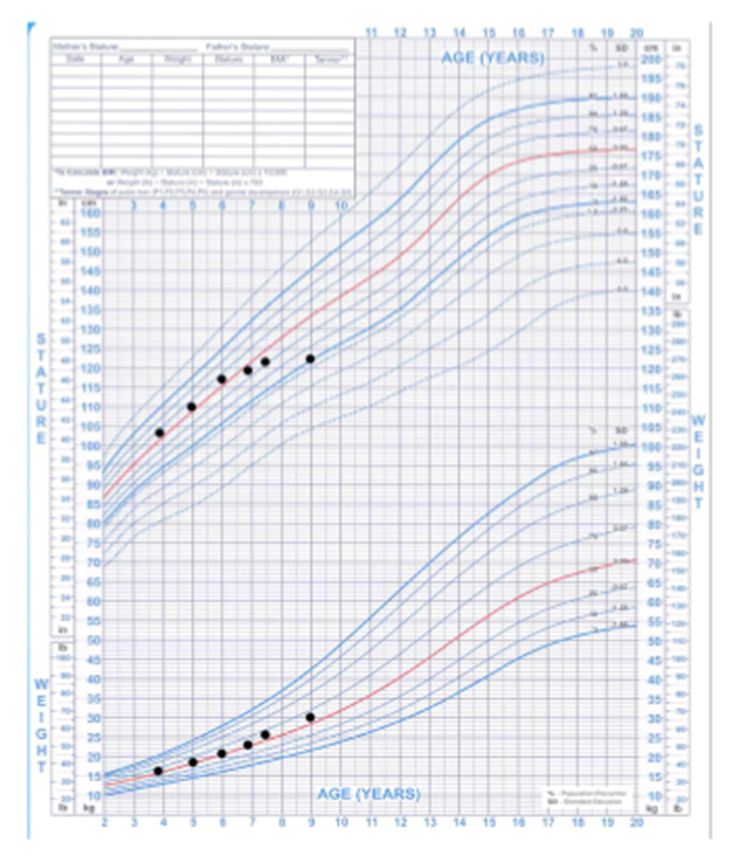
Growth hormone deficiency
Weight did not stop but height did
Growth hormone deficiency
GH tells the _____ to make IGF-1 and IGF-BP3
Liver
IGF-BP3 binds up most of the IGF-1 and gives it to the ______, so the ____ can grow
Bones
Before birth, and up to the first year of life, the body is not dependent on ___
Growth hormone
GH in infancy controls _____ ____
Blood sugar
Usually due to hypopituitarism and can be associated with midline structural defects
Congenital growth hormone deficiency
Congenital growth hormone deficiency can be associated with ______ structural defects
Midline
(single central incisor, abnormal midbrain, nystagmus)
low body temp, poor IQ, prolonged jaundice
No TSH
small penis, no palpable testes
No LH or FSH
low blood sugar, normal birth length
No GH
low blood sugar
No ACTH
usually high due to feedback issues in congenital growth hormone deficiency
Prolactin
If all hormones are normal except GH, growth failure won’t be noticed until age ___-__ years
2-3
Usually due to a brain tumor, traumatic brain injury, or possible ADHD or ADHD meds
Acquired Growth Hormone Deficiency
Common brain tumor that causes acquired growth hormone deficiency
craniopharyngioma
Normal growth until the tumor develops or until the brain injury occurred, or the meds were started, then will have progressive growth failure
“Falling percentile lines”
Acquired growth hormone deficiency
Tumors can cause complete hypopituitarism, but usually it just knocks out ___
GH
Short stature, delayed bone age, low IGF-1, REALLY, REALLY HIGH growth hormone levels on a stimulation test
Laron’s dwarfism
Treated with pure IGF-1, called Increlex
Acquired Hypothyroidism
Other Endocrine Cause of Growth Failure
Most common cause of hypothyroidism is
Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism 1-2% of children, with females being __ times more likely to get this condition
4
Children will usually NOT have the typical symptoms of fatigue and weight gain
Growth Failure may be the only symptom
Acquired hypothyroidism most commonly Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism
High TSH low thyroid levels
Acquired Hypothyroidism
either from taking high dose oral steroids too long or from a tumor, called Cushing’s syndrome
Glucocorticoid Excess
Other Endocrine Cause of Growth Failure
can be from an ACTH-producing brain tumor or a primary adrenal tumor
Cushing’s syndrome
Growth failure, truncal obesity with thin limbs, round facies, “buffalo hump”, delayed puberty, striae, easy bruising, glucose intolerance, osteoporosis, high blood pressure.
Cushing’s syndrome
Diagnose with a 24-hour urine for free cortisol
Cushing’s syndrome
The growth chart will look identical to someone with growth hormone deficiency or acquired hypothyroidism.
Cushing’s syndrome
The receptor on bones that waits for IGF-1 so it can grow is the same shape as an insulin receptor. So the excess insulin pretends to be IGF-1 and tells the bones to grow
Too much insulin too many carbs
Too much insulin will cause too much growth and your bone age will advance so fast that you will go into _____ early and fuse your growth plates early, so you will end up being ____ as an adult
puberty
short
A tall overweight child
needs to go to a dietician
over nutrition
A short overweight child
needs to go to Ped Endo
A short thin child
needs to go to Ped GI
Malnutrition
Things that medication can’t fix:
If you were born early/preterm
Genetic syndromes – Down’s
Short parents (Familial short stature)
Poor social situation – Psychosocial dwarfism
Weird bones – Scoliosis, achondrodysplasia
Late bloomer (Constitutional delay of growth)
Adopted kids that did not get love
Psychosocial dwarfism
poor weight AND poor height
Reasons for not growing that are not hormone related
Celiac disease – gluten allergy
Liver or kidney disease
Heart or lung disease – cystic fibrosis
Stomach problems
Inflammatory bowel, Crohn’s, food allergies, “short gut”, etc
Endocrine causes of growth failure:
poor height but INCREASED weight
Thyroid hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
Syndrome of excess cortisol (Cushings)
Problems that qualify for growth hormone therapy:
Turner’s syndrome, Noonan’s syndrome, Kidney disease, AIDS wasting, Prader-Willi syndrome, SHOX deficiency, SGA, idiopathic short stature
Upper body is longer than lower body until age __, then it should be equal
10
Arms are shorter than body before age 10-11 years, then it is arms are equal to the body from age 10-__ years, then after age __ years, arms are longer than the body.
14
Men’s arms are ___ cm more than their height, and girls arms are ___ cm more than their height
5
1.2
palmer crease, Trisomy 21
Down’s syndrome
Short 4th metacarpal, wide arm carrying angle, low posterior hairline, high arched palate, wide spaced nipples, webbed neck, very curvy nails
Turner’s syndrome – 45 X,O
Incurving of the fifth finger, small triangular face, one limb bigger than the other
Russell-Silver syndrome
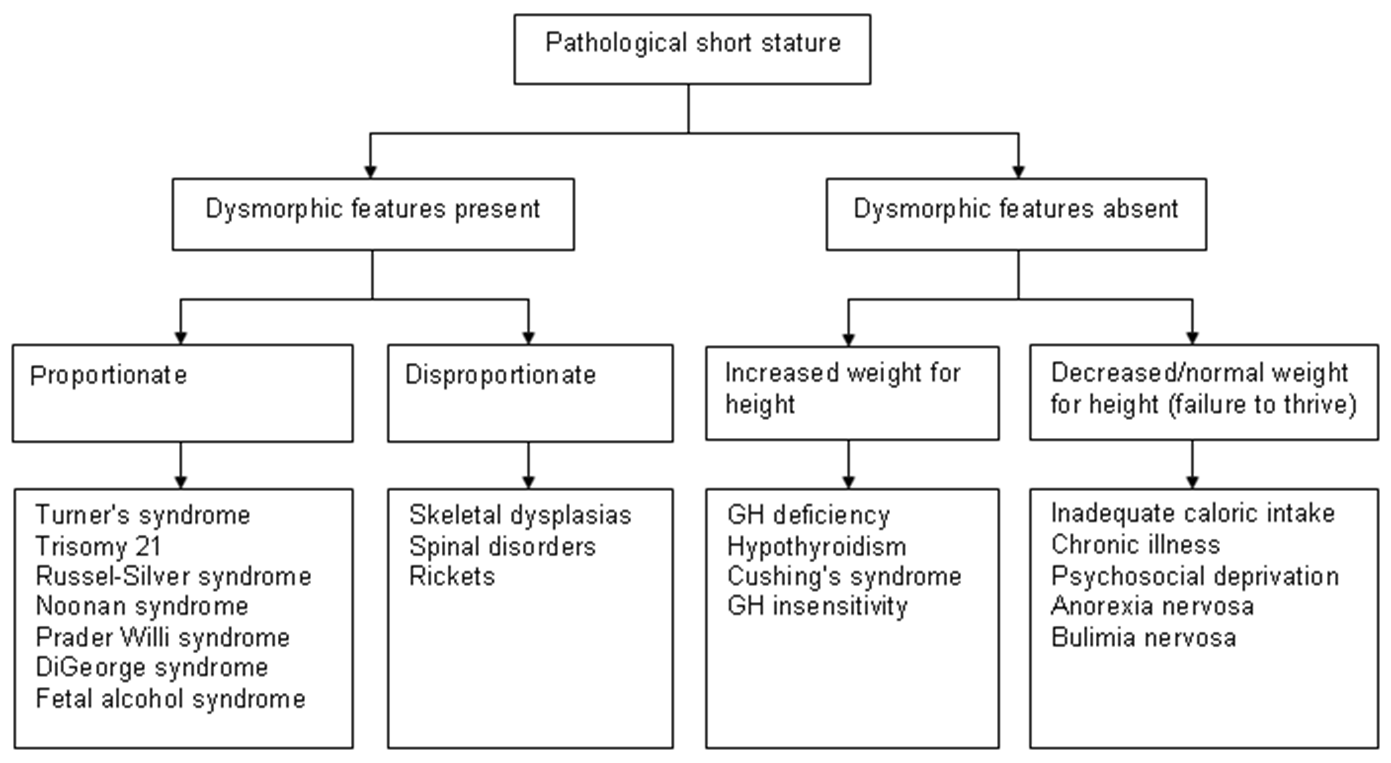
Diagnostic algorithm
Lab work for short stature
•Bone age xray
•CBC with differential (edema, chonic disease), ESR (inflammatio) , chem-14 (liver), Total IgA and TTG IgA (celiac)
•TSH and Free T4, IGF-1 and IGF-BP3
•Can’t measure “growth hormone” levels, because it is secreted in a pulsatile fashion
Child has evidence of growth failure
Delayed bone age
Normal labs except low IGF-1 and IGF-BP3
Next step:
GH stimulation test
It’s the only way to actually measure growth hormone, since it is pulsatile in secretion
Give 2 drugs while fasting: clonidine, L-dopa, arginine, glucagon, insulin, or exercise
Measure GH levels every 30 minutes for 3 hours
If GH levels don’t get above 10 ng/ml, you are diagnosed with Growth Hormone Deficiency
GH stimulation test
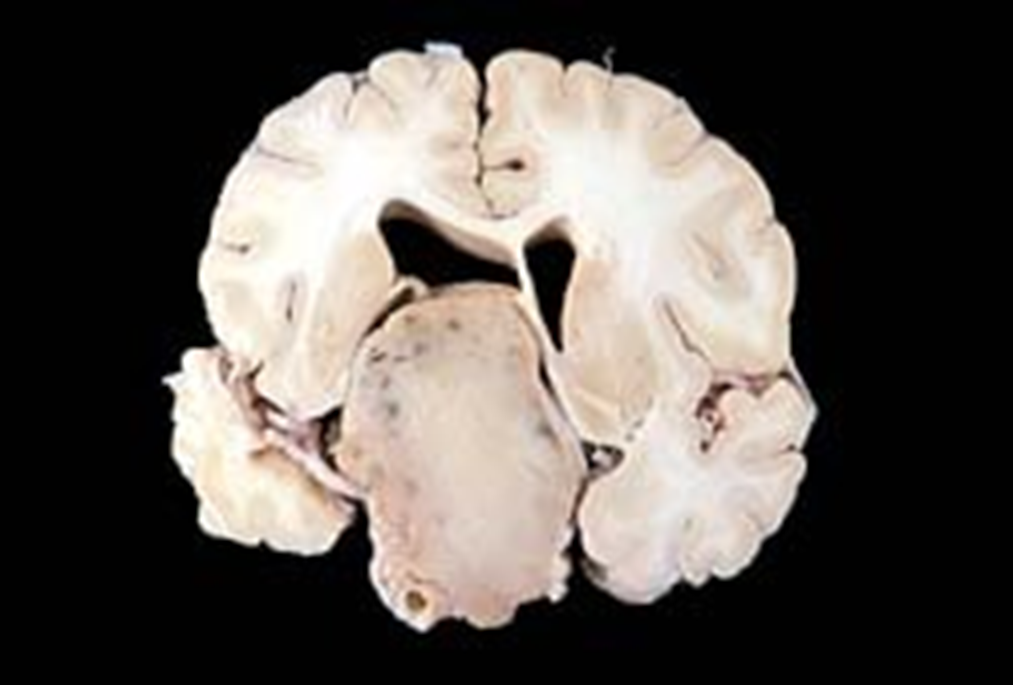
Craniopharyngioma
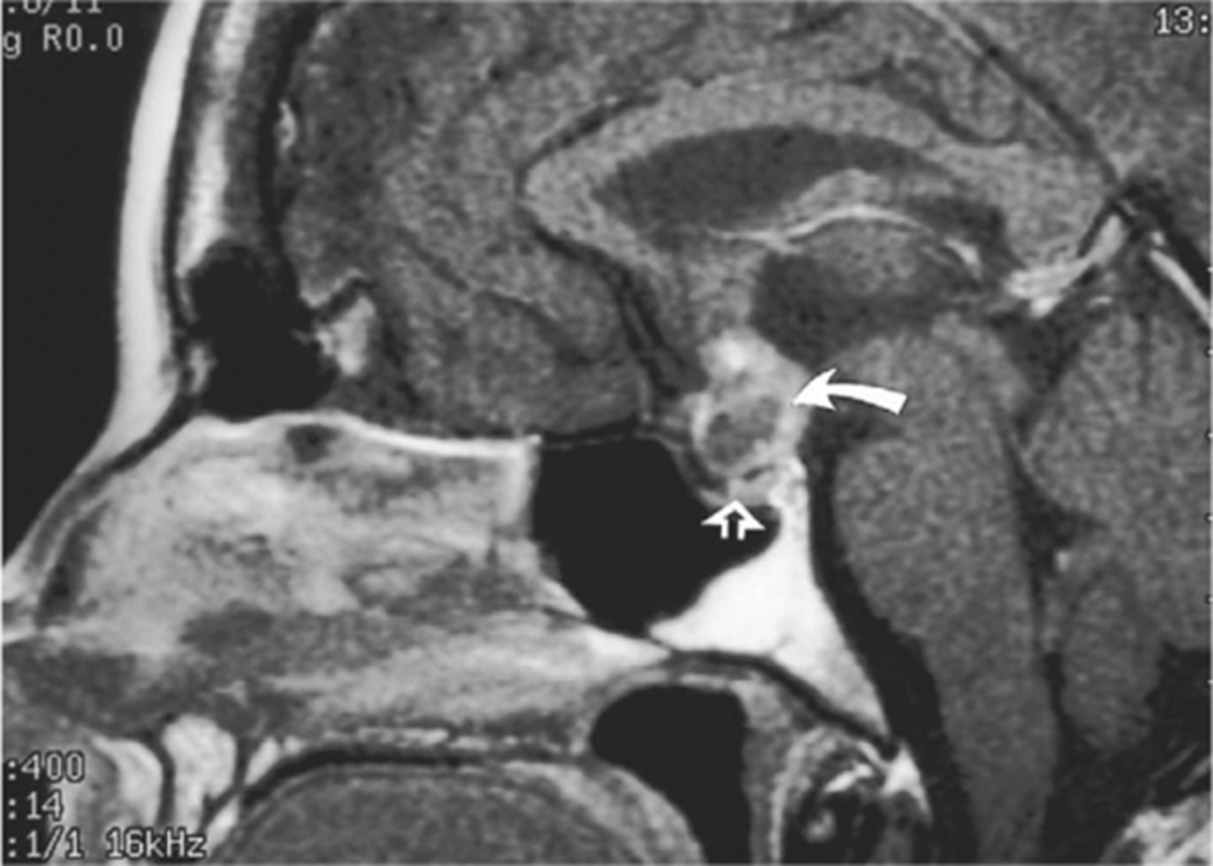
Craniopharyngioma
Growth hormone, or ______, is given by a SQ injection once a day
Somatotropin
Cost of growth hormone
It costs $100 per milligram
Most kids are on 1-2 mg per day
This is $100 a day, minimum
That is $3000 a month, minimum
$36,000 - $72,000 a year per child
Some insurance plans – patient pays 20% of the cost of the drug ($600-1000/month cash)
__ causes all body tissues to grow faster
GH
Prostate and Breast Cancers have high levels of ____
IGF-1
Side effects of GH therapy
Headaches “Pseudotumor cerebri”
Joint pain
Diabetes
Worsening scoliosis
Decrease fat mass
Increased muscle mass
GH deficiency in adults (usually from a brain injury, such as a car crash)
If they can make a little bit of GH, they will be okay, but if they have absolutely no GH, then they do have other medical problems
They get excess fat, have very little muscle mass (weak and tired), weak bones (fracture), poor heart health (high cholesterol, high triglycerides, high LDL, low HDL)