Unit 4: Evolution & Viruses and Unit 5: Ecology & Environmental Sciences
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:07 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
Homology
- the quality of being similar or corresponding in position or value or structure or function
- by common descent!!!
- by common descent!!!
2
New cards
Parsimony
- the simplest answer
- humans and bacteria didn't arrive at this genetic code individually. they inherit it from previous ancestors, earlier organisms, who had that genetic code and now all organisms have it
- humans and bacteria didn't arrive at this genetic code individually. they inherit it from previous ancestors, earlier organisms, who had that genetic code and now all organisms have it
3
New cards
Convergence
- science is predicated on repeatability
- a "built in test" for evolution
- a "built in test" for evolution
4
New cards
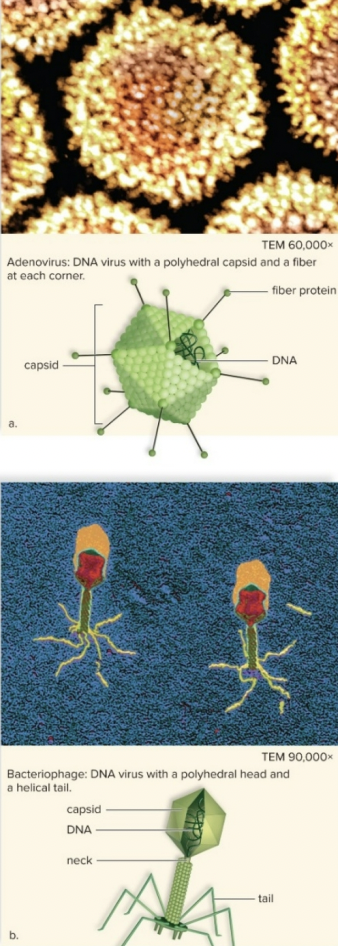
Virus
• Obligate intracellular parasites
• Two Parts:
1. Genetic Material (DNA or RNA)
2. Protein Capsid (surrounds genetic material)
• Sometimes present: Envelope (remnants of plasma membrane of a previously infected cell which aids entry to new cells for infection)
• Two Parts:
1. Genetic Material (DNA or RNA)
2. Protein Capsid (surrounds genetic material)
• Sometimes present: Envelope (remnants of plasma membrane of a previously infected cell which aids entry to new cells for infection)
5
New cards
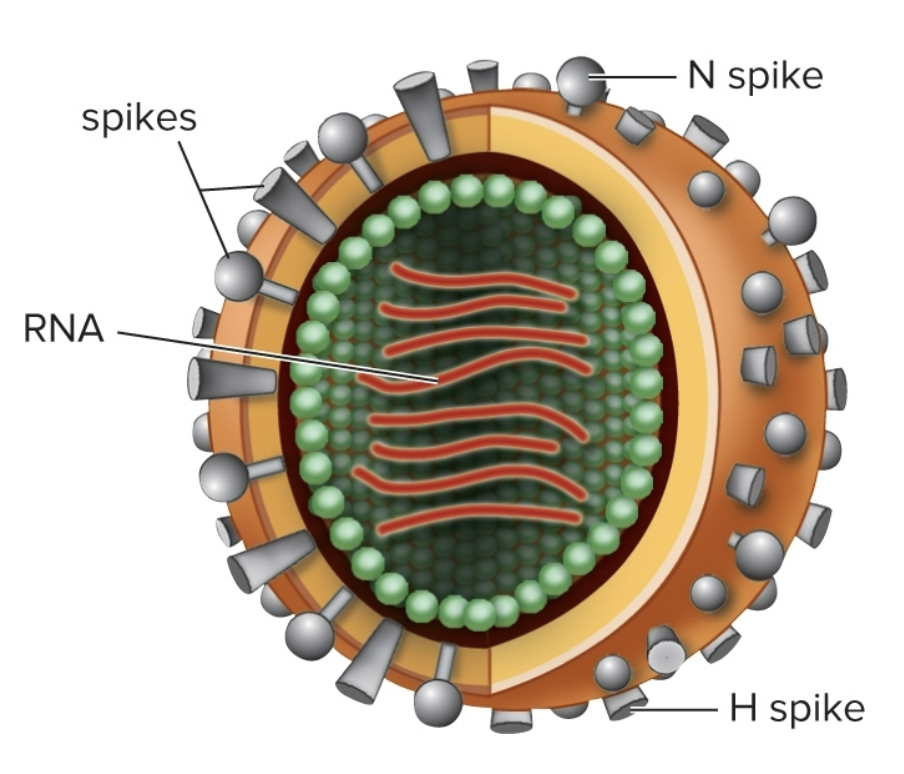
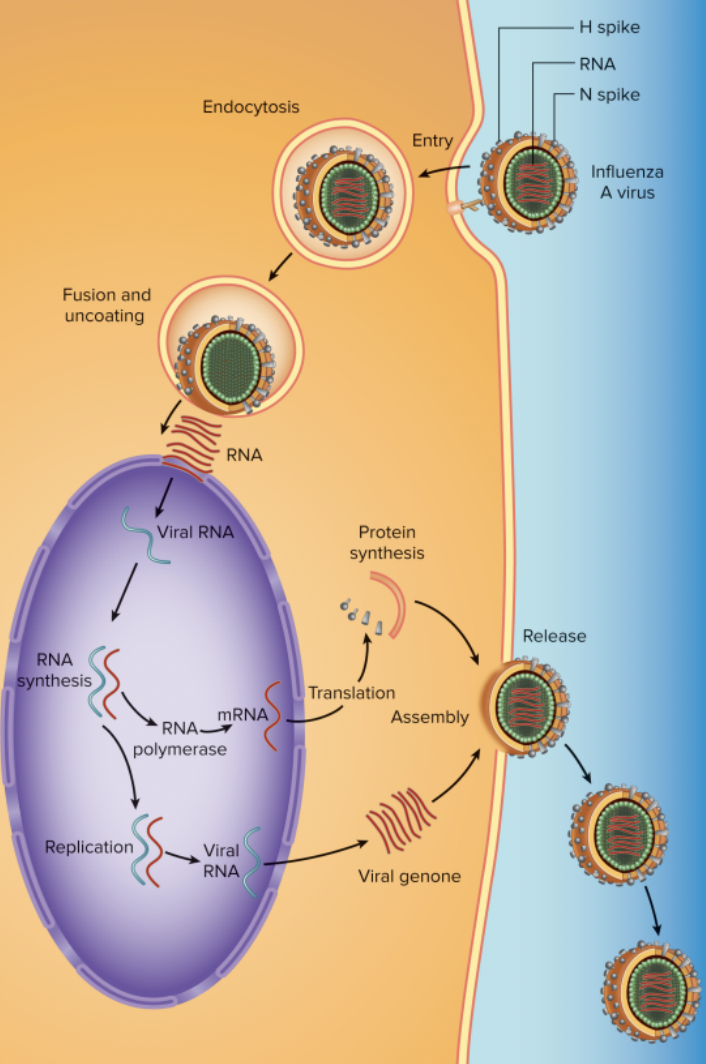
Influenza
• RNA Genetic Material
• Envelope Present
• Glycoprotein “spikes” that determine strain
• Influenza A:
- H Spikes: finds receptors on host cell
- N Spikes: Breaks down mucous membranes in the respiratory tract to make penetrating host cell easier
• Envelope Present
• Glycoprotein “spikes” that determine strain
• Influenza A:
- H Spikes: finds receptors on host cell
- N Spikes: Breaks down mucous membranes in the respiratory tract to make penetrating host cell easier
6
New cards
Naming Influenza Viruses
1. Host (if not human)
2. Type (A or B)
3. Strain, which H/N Spikes present
4. Year of Isolation
2. Type (A or B)
3. Strain, which H/N Spikes present
4. Year of Isolation
7
New cards
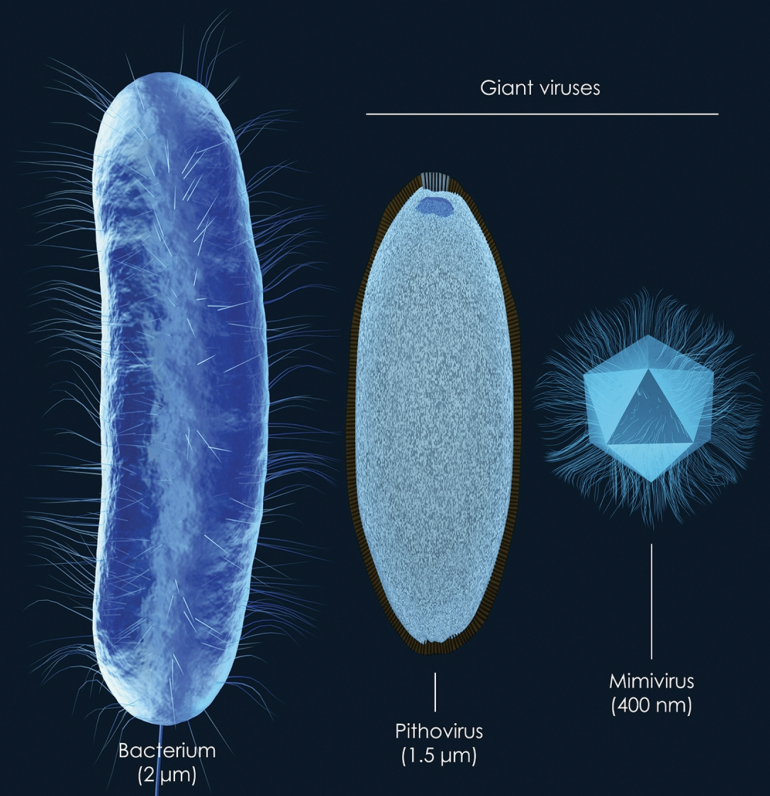
Viruses are not alive
• Viruses cannot process energy and rely on host cells to make copies of their genetic material
• Exception: Giant Viruses can make their own proteins
• Exception: Giant Viruses can make their own proteins
8
New cards
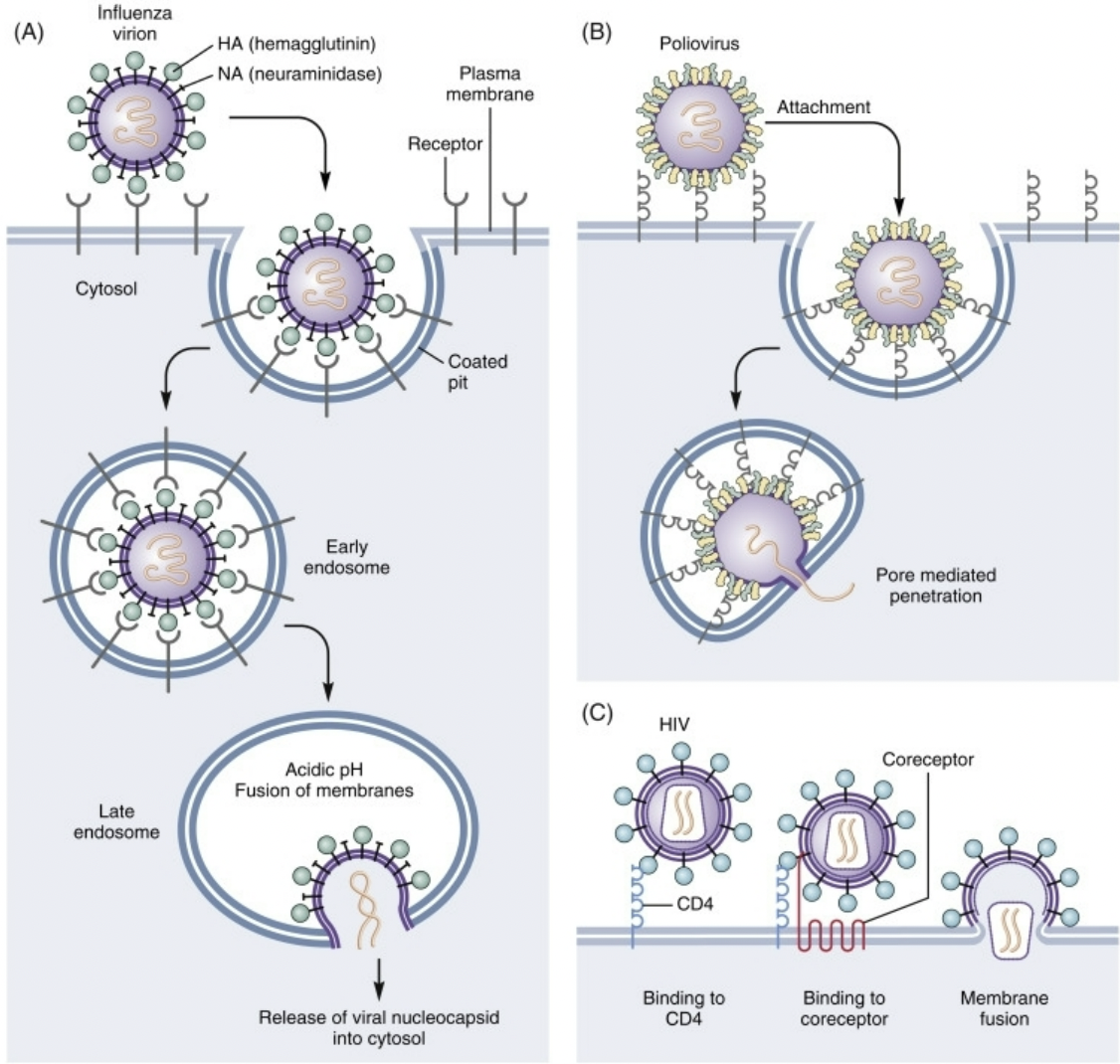
Infecting Cells
• Protein spikes are specialized to infect particular cell types
• Bind to surface proteins to allow virus entry
• Bind to surface proteins to allow virus entry
9
New cards
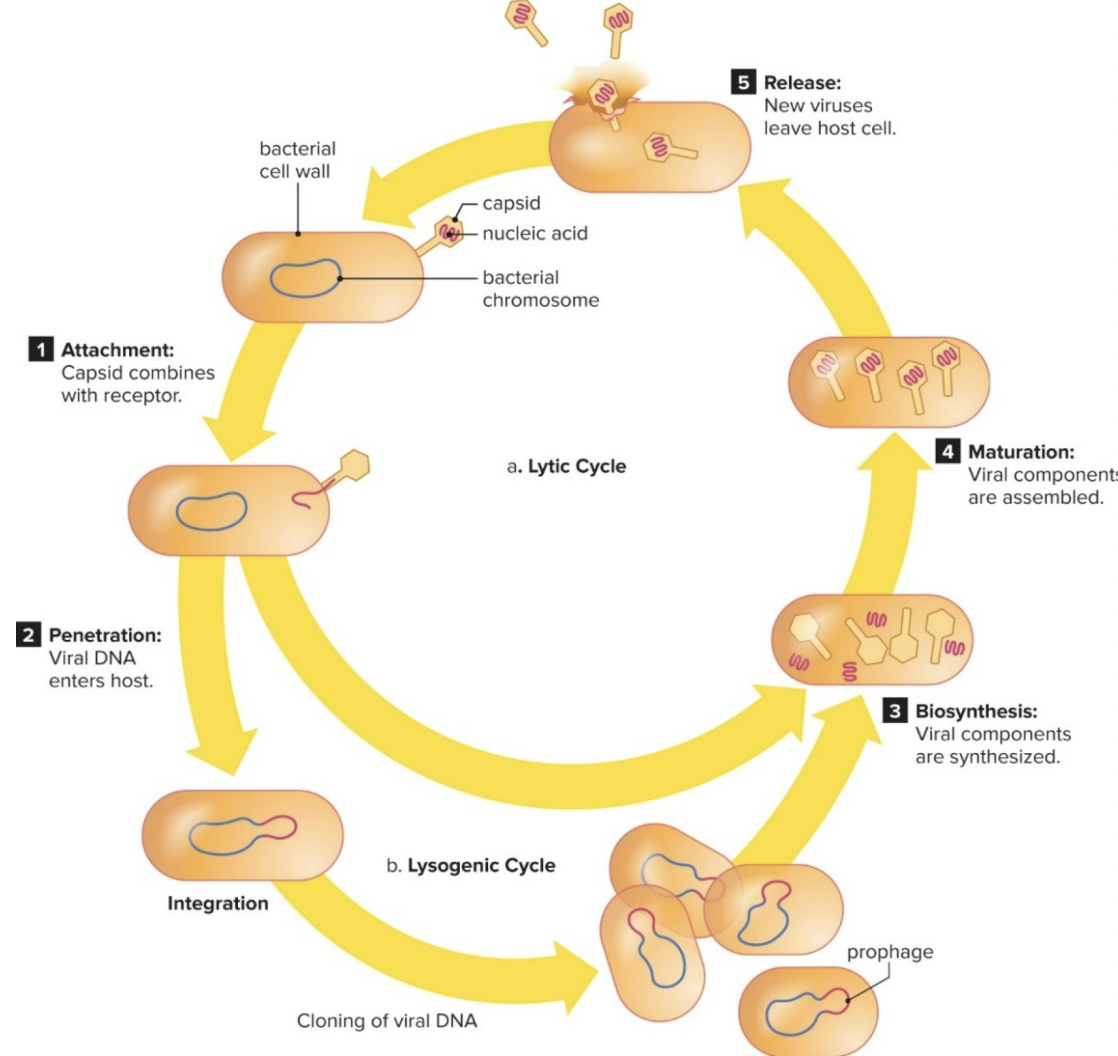
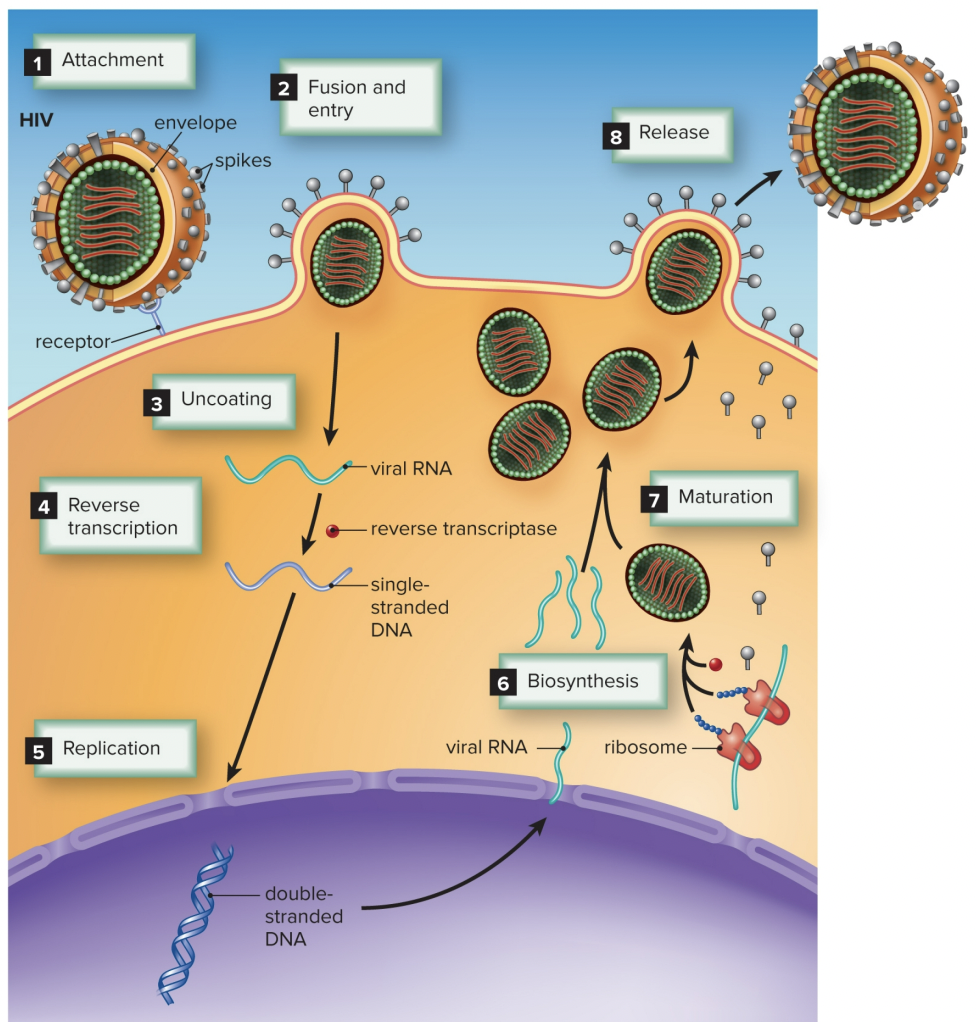
Viral Life Cycle
1. Attachment
2. Penetration
3. Biosynthesis
4. Maturation
5. Release
2. Penetration
3. Biosynthesis
4. Maturation
5. Release
10
New cards
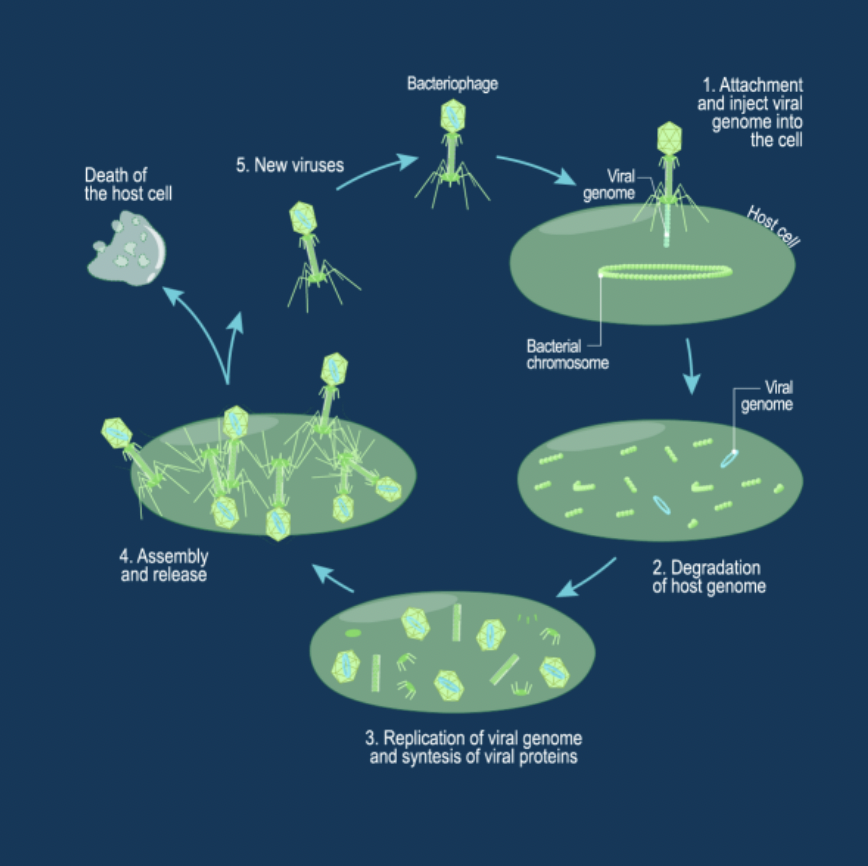
Lytic Cycle
• Virus begins biosynthesis/replication immediately
• Host cell is broken apart to release new virus capsids
• Influenza, common cold
• Host cell is broken apart to release new virus capsids
• Influenza, common cold
11
New cards
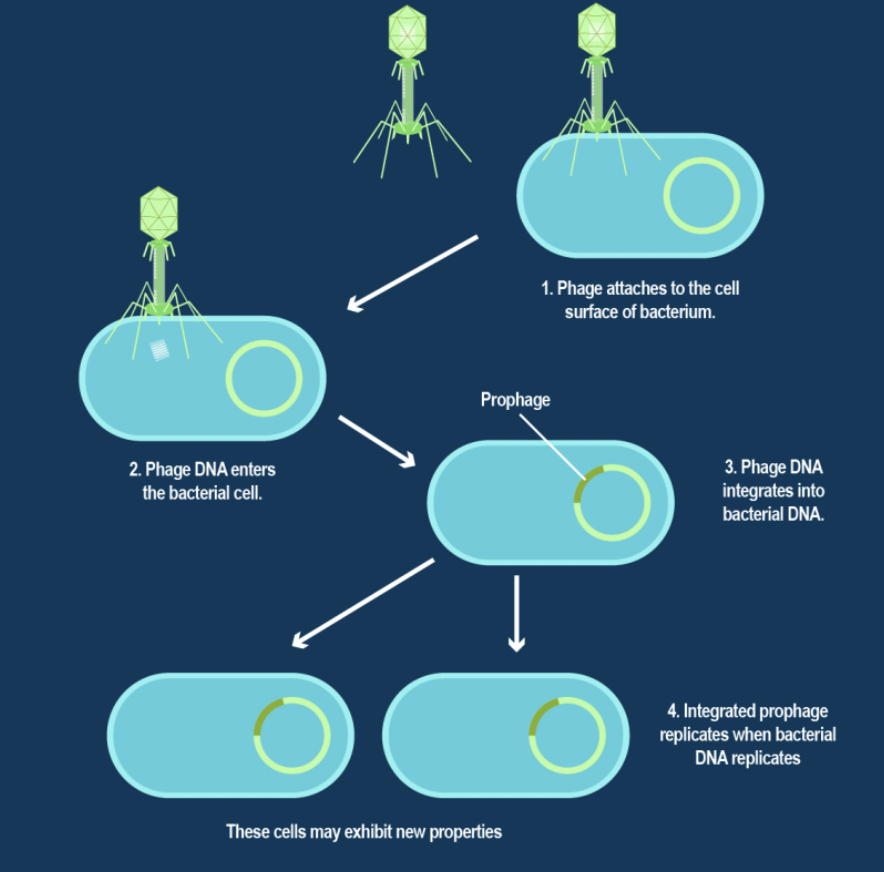
Lysogenic Cycle
• Viral DNA integrates into host genome after penetration
• Virus remains inactive or latent, host cells divide with viral DNA
integrated in genome
• Sickness occurs long after initial infection (HIV)
• Virus remains inactive or latent, host cells divide with viral DNA
integrated in genome
• Sickness occurs long after initial infection (HIV)
12
New cards
RNA Viruses
• Must use RNA polymerase to manufacture mRNA for protein synthesis
- Many mistakes made by RNA Polymerase leads to mutations and fast viral evolution
- Many mistakes made by RNA Polymerase leads to mutations and fast viral evolution
13
New cards
Retroviruses
•Use reverse transcriptase to turn RNA into DNA before biosynthesis
(HIV)
(HIV)
14
New cards
Influenza Infection
• Infects respiratory epithelial cells, replication begins immediately, leading to inflammation
• Body responds by sending immune cells which release cytokines, a chemical your body interprets as a warning signal of infection, leading to more inflammation
• Body responds by sending immune cells which release cytokines, a chemical your body interprets as a warning signal of infection, leading to more inflammation
15
New cards
Influenza Symptoms
• Set in very quickly (over the course of an hour or two)
• Cough, fever, chills, aches and pains, headache, loss of
appetite, nausea
- Mostly caused by immune response, not the Influenza virus itself
• “Stomach flu” is NOT Influenza!
• Cough, fever, chills, aches and pains, headache, loss of
appetite, nausea
- Mostly caused by immune response, not the Influenza virus itself
• “Stomach flu” is NOT Influenza!
16
New cards
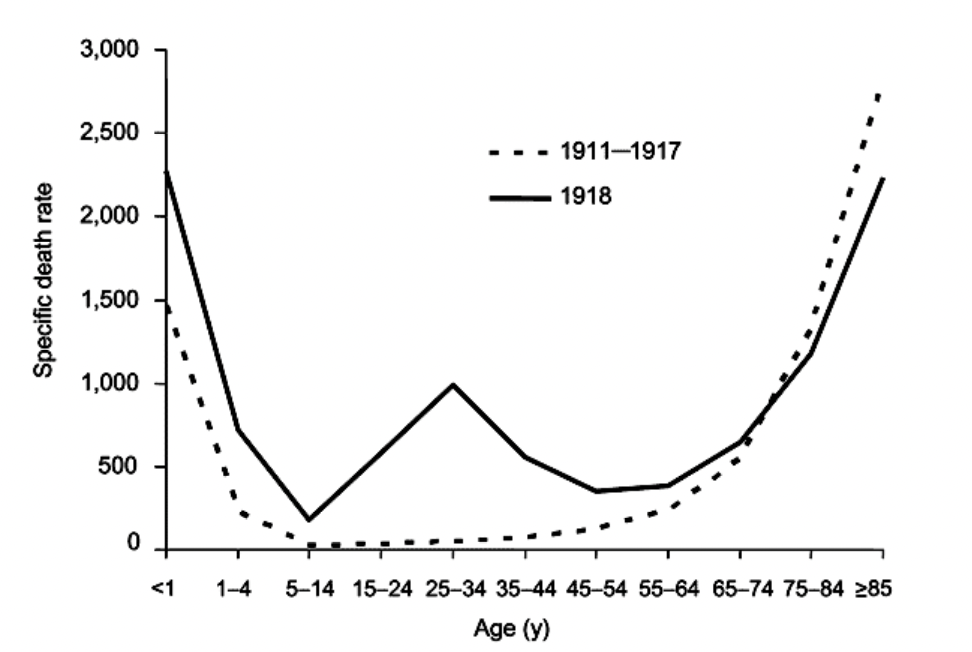
Spanish Flu Epidemic of 1918
• H1N1 virus killed between 1-5% of earth’s population
- ~20% of people infected died
- ~20% of people infected died
17
New cards
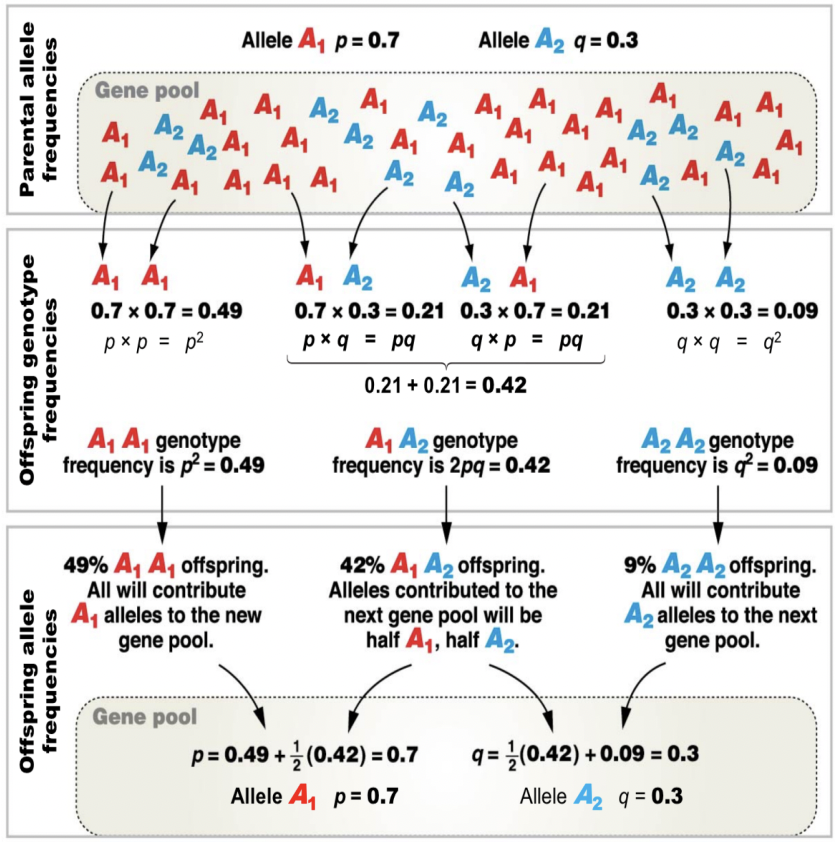
Evolution
• A change in allele frequencies in a population over time
• Unifying theory of biology
- “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.” - Theodosius Dobzhansky
• p² + 2pq + q² = 1
• Unifying theory of biology
- “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.” - Theodosius Dobzhansky
• p² + 2pq + q² = 1
18
New cards
Georges Buffon (1707−1788)
Earth was much older than previously believed, which went against Church

19
New cards
Georges Cuvier (1769−1832)
- Religious
- Documented fossil discoveries (Irish Elk)
- Documented fossil discoveries (Irish Elk)

20
New cards
Jean-Baptiste Lamarack (1744−1829)
- Living species might change over time
- Believed acquired characteristics get passed on to offspring (wrong)
- Believed acquired characteristics get passed on to offspring (wrong)

21
New cards
Charles Lyell (1797−1875)
- Geologist
- Uniformitarianism: all geological processes that happened in the past are still happening today
- Geological forces had gradually shaped the earth
- Uniformitarianism: all geological processes that happened in the past are still happening today
- Geological forces had gradually shaped the earth

22
New cards
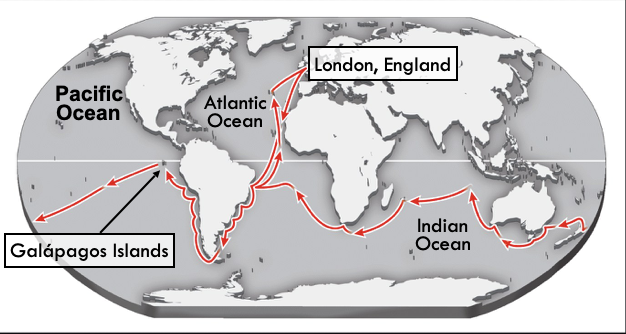
Charles Darwin
- Born to a wealthy family
- Fascinated by the natural world
- Went to medical school and seminary school (transferred from Edinborough to Cambridge)
- In 1831, joined the crew of the HMS Beagle for a five-year global surveying expedition
- Fascinated by the natural world
- Went to medical school and seminary school (transferred from Edinborough to Cambridge)
- In 1831, joined the crew of the HMS Beagle for a five-year global surveying expedition

23
New cards
Voyage of the HMS Beagle
24
New cards
Observations from the Voyage of the Beagle
1. Island species have a strong resemblance to species on nearby mainland
2. Extant (living) species have a strong resemblance to extinct species discovered as fossils
2. Extant (living) species have a strong resemblance to extinct species discovered as fossils
25
New cards
Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
- Similarities between island/mainland species and living/fossil species could not be a coincidence
- Overtime species that colonize new habitats gradually change to form new, but similar, species
- Only the best-adapted individuals can reproduce, thus over time species become better adapted to the environment
- Hesitated to publish
- Darwin sat on his idea for decades because he didn't know the mechanism for heritability and he had 10 kids
- Overtime species that colonize new habitats gradually change to form new, but similar, species
- Only the best-adapted individuals can reproduce, thus over time species become better adapted to the environment
- Hesitated to publish
- Darwin sat on his idea for decades because he didn't know the mechanism for heritability and he had 10 kids
26
New cards
Alfred Russel Wallace
- Naturalist that explored South America and Indonesia
- Sent paper to Darwin in 1858 postulating the exact same mechanism for species change
- Sent paper to Darwin in 1858 postulating the exact same mechanism for species change

27
New cards
Joint Presentation to the Linnaean Society
- Darwin and Wallace shared credit for the idea in a presentation in 1858
- Darwin published his abstract in 1859: On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life
- Darwin published his abstract in 1859: On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life
28
New cards
Darwin’s Postulates
Requirements for natural selection to lead to evolution:
1. There must be variation in a trait
2. The trait must be heritable from parent to offspring
3. The trait must lead to differential reproductive success
4. This differential reproductive success is not random, but rather tied to differences in heritable reproductive success
1. There must be variation in a trait
2. The trait must be heritable from parent to offspring
3. The trait must lead to differential reproductive success
4. This differential reproductive success is not random, but rather tied to differences in heritable reproductive success
29
New cards
Condition 1: Variation for a Trait
- Any gene with multiple alleles in a population has variability
- Variation is the raw material of evolution; the engine of evolutionary change
- Variation is the raw material of evolution; the engine of evolutionary change
30
New cards
Mutations
- Changes in DNA sequences
- Can lead to new alleles or new gene regulation mechanisms for selection to act upon
- Mutations that increase the number of offspring an individual can produce will increase in frequency in the population over generations
- Mutation rate in each gene is low, but they accumulate over time
- Billions of years is loooong time
- Where does a mutation need to take place to be passed on to the next generation?
- Can lead to new alleles or new gene regulation mechanisms for selection to act upon
- Mutations that increase the number of offspring an individual can produce will increase in frequency in the population over generations
- Mutation rate in each gene is low, but they accumulate over time
- Billions of years is loooong time
- Where does a mutation need to take place to be passed on to the next generation?
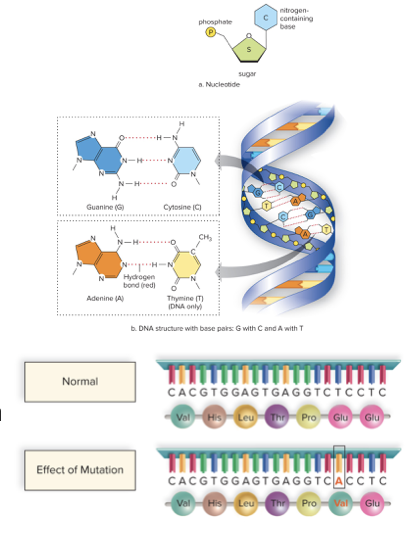
31
New cards
Condition 2: Heritability
The trait must be passed from parent to offspring through genetic information (e.g., offspring inherit their traits from their parents)
32
New cards
Condition 3: Differential Reproductive Success
- Individuals with one version of the trait must produce more offspring than those with a different version of the trait
- Observations that led to this condition:
1. More organisms are born than can survive
2. Organisms continually struggle for existence
3. Some organisms are more likely to win this struggle to survive and reproduce
- Observations that led to this condition:
1. More organisms are born than can survive
2. Organisms continually struggle for existence
3. Some organisms are more likely to win this struggle to survive and reproduce
33
New cards
“Survival of the Fittest”
- Fitness: A measure of the relative amount of reproduction of an individual with any phenotype
- Survival + Reproduction rate
- Alleles carried by an individual with high fitness will increase in a population over time
- The population will evolve because the relative allele frequencies in this population are changing
- Survival + Reproduction rate
- Alleles carried by an individual with high fitness will increase in a population over time
- The population will evolve because the relative allele frequencies in this population are changing
34
New cards
Alleles that make you More Likely to Escape a Predator
- Higher Red Blood Cell Count
- Stronger muscle fibers
- Higher bone density
- Quicker nerve impulses
- Intelligence to pick fastest escape route
- Bigger lungs
- Streamlined body shape
- Better eyesight
- Better hearing
- Better sense of smell
- Stronger muscle fibers
- Higher bone density
- Quicker nerve impulses
- Intelligence to pick fastest escape route
- Bigger lungs
- Streamlined body shape
- Better eyesight
- Better hearing
- Better sense of smell
35
New cards
Types of Natural Selection: Directional Selection
- Individuals with one extreme from the range of variation will have higher fitness
- Ex: Farmers only allow turkeys with the biggest breasts to mate
- Ex: Farmers only allow turkeys with the biggest breasts to mate
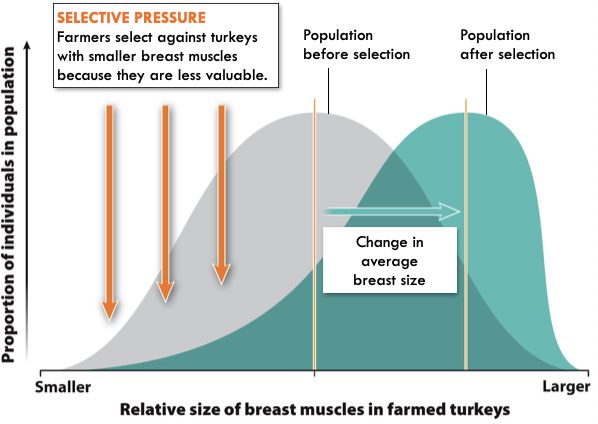
36
New cards
Types of Natural Selection: Stabilizing Selection
- Individuals with intermediate genotypes will have higher fitness
- Ex: Baby birth weight
- Ex: Baby birth weight
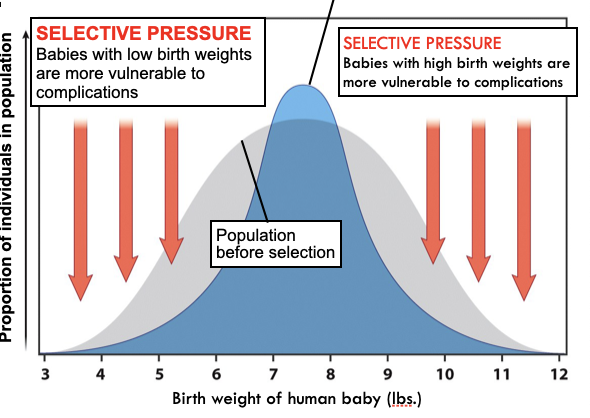
37
New cards
Types of Natural Selection: Disruptive Selection
Individuals with extreme phenotypes experience the highest fitness, and those with intermediate phenotypes have the lowest
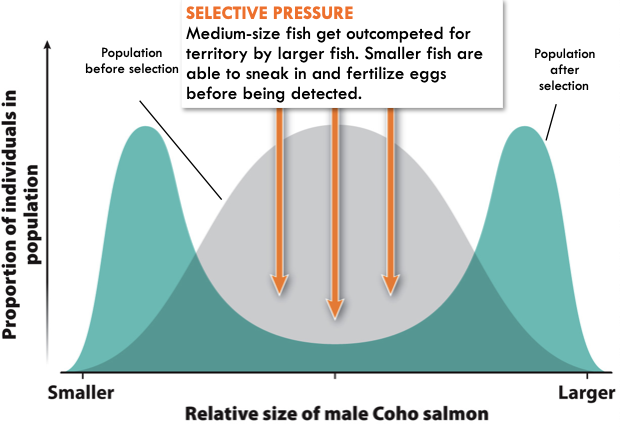
38
New cards
Evidence for Evolution
1. Fossil Record: Physical record of organisms that lived in the past
2. Comparative Anatomy and Embryology: Growth, development, and body structures of major groups of organisms
3. Molecular Biology: DNA similarities
4. Laboratory and Field Experiments: Use of the scientific method to study evolutionary mechanisms
2. Comparative Anatomy and Embryology: Growth, development, and body structures of major groups of organisms
3. Molecular Biology: DNA similarities
4. Laboratory and Field Experiments: Use of the scientific method to study evolutionary mechanisms
39
New cards
Fossil Record
- Hundreds of millions of fossils have been found
- 250,000 species
- Hard parts get preserved
- Teeth, bones, shells, seeds
- Soft parts replaced by minerals
- Traces: Imprints, tracks, burrows
- Limitations:
1. Huge!
2. Biased in favor of abundant organisms with hard parts living in certain locations
- Value
1. Transitional species
- 250,000 species
- Hard parts get preserved
- Teeth, bones, shells, seeds
- Soft parts replaced by minerals
- Traces: Imprints, tracks, burrows
- Limitations:
1. Huge!
2. Biased in favor of abundant organisms with hard parts living in certain locations
- Value
1. Transitional species

40
New cards
Comparative Anatomy and Embryology
- Homologous structures reveal common evolutionary origins
- If humans did not have bony fish ancestors, why do human embryos have gills early in development?
- If humans did not have bony fish ancestors, why do human embryos have gills early in development?
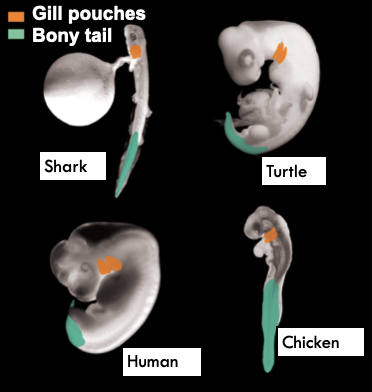
41
New cards
Developmental Regulatory Genes
- Genes that activate protein coding genes early in development
- Tell protein coding genes where to build body parts, but not HOW to build body parts
- Great morphological diversity can be achieved with relatively small genetic change if that change occurs in developmental regulatory genes
- Tell protein coding genes where to build body parts, but not HOW to build body parts
- Great morphological diversity can be achieved with relatively small genetic change if that change occurs in developmental regulatory genes
42
New cards
HOX Genes
- Low (or no) variation because all members of same species want bodies arranged in same manner
- And all vertebrates want head, torso, and limbs in roughly the same spots
- Highly conserved between species at high level
- Differences only occur at levels telling embryo HOW to make body part
- And all vertebrates want head, torso, and limbs in roughly the same spots
- Highly conserved between species at high level
- Differences only occur at levels telling embryo HOW to make body part

43
New cards
Hox Mutants
- Very small genetic changes can result in enormous morphological differences
- Makes morphological diversification much more likely to occur
- Makes morphological diversification much more likely to occur
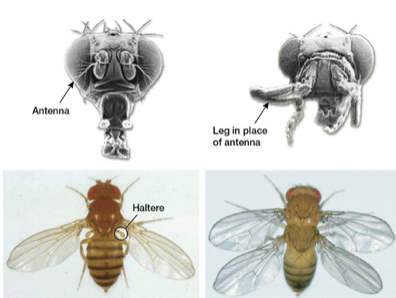
44
New cards
The similarities in the bone structure of the forelimbs of mammals demonstrate...
common ancestry
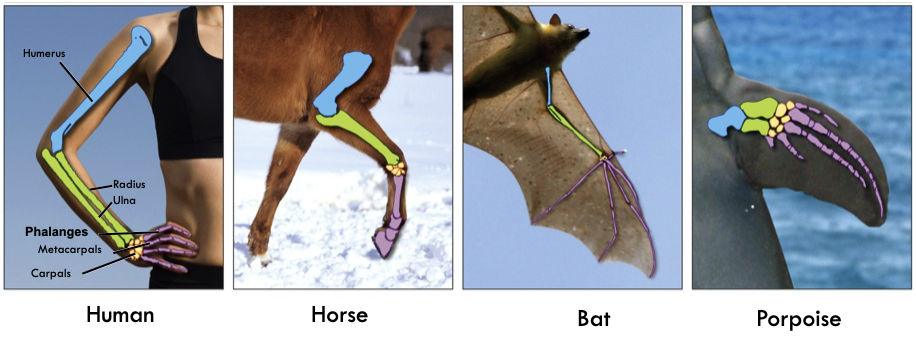
45
New cards
Vestigial Structures
- Apparently useless anatomical features reveal evolutionary past
- Vampire bats still have molar teeth, even though the consume an all liquid diet
- Vampire bats still have molar teeth, even though the consume an all liquid diet
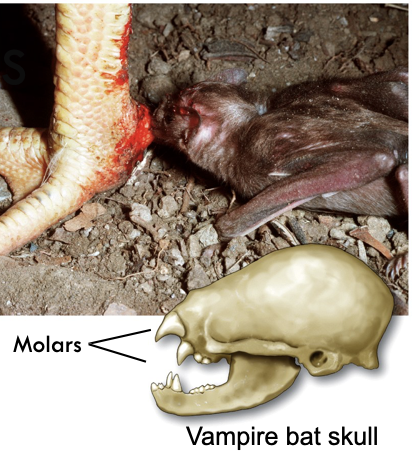
46
New cards
Convergent Evolution
- Different starting organisms come to perform the same function through convergent evolution
- Produces analogous structures
- Produces analogous structures

47
New cards
Molecular Biology
- All living organisms have the same genetic code
- DNA is more similar in more closely related organisms
- DNA is more similar in more closely related organisms
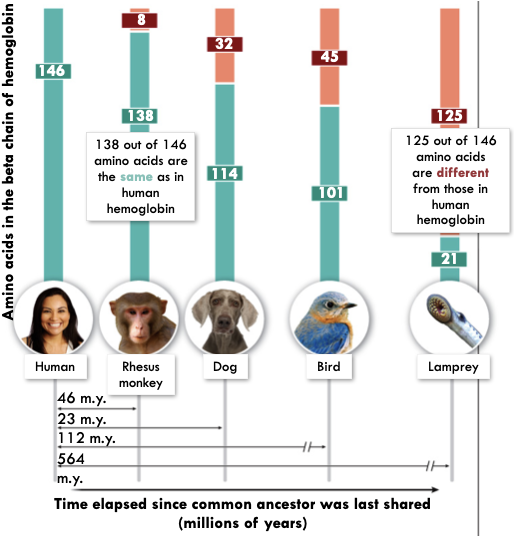
48
New cards
Australian Marsupials and their Placental Counterparts
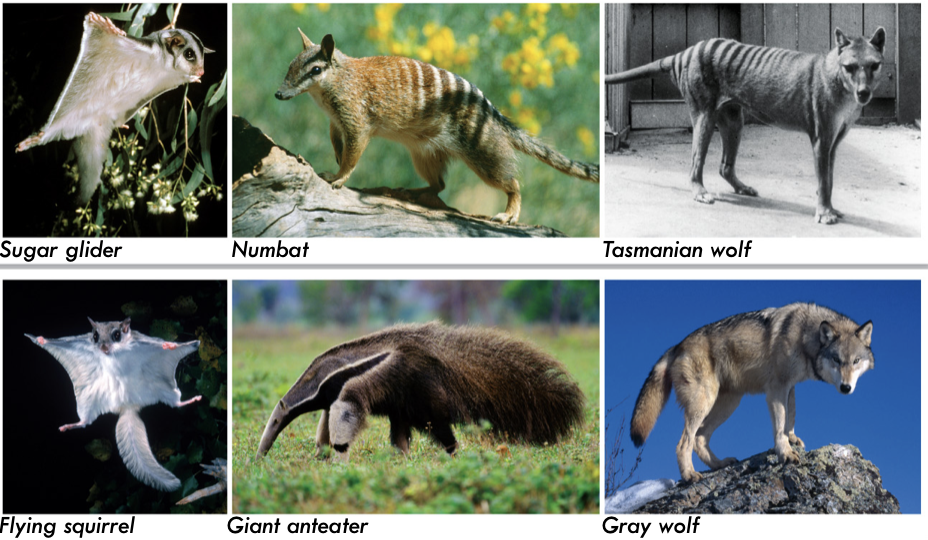

49
New cards
Laboratory and
Field Experiments
Multigenerational experiments show evolution in progress
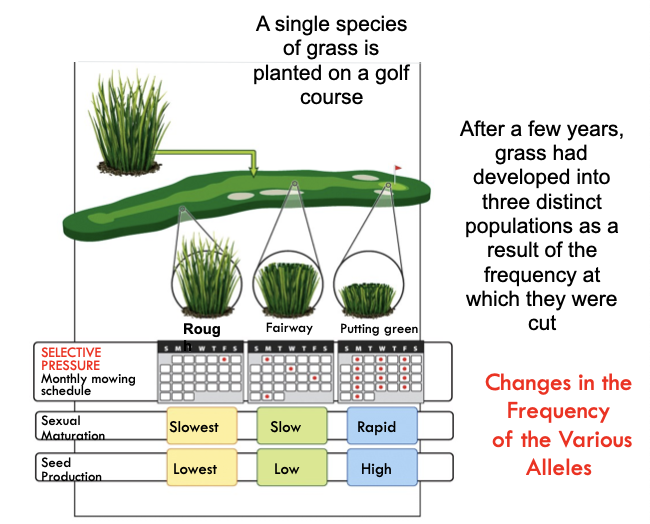
50
New cards
Evolution in Action
Fruit flies
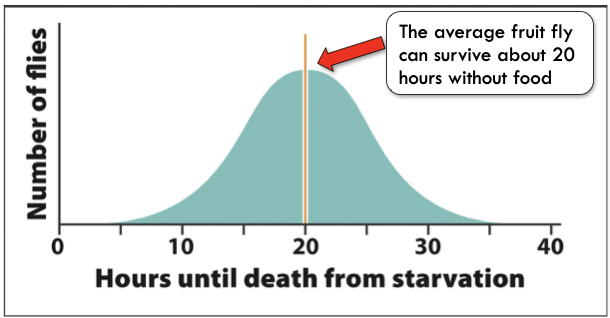
51
New cards
Experimental
Set Up
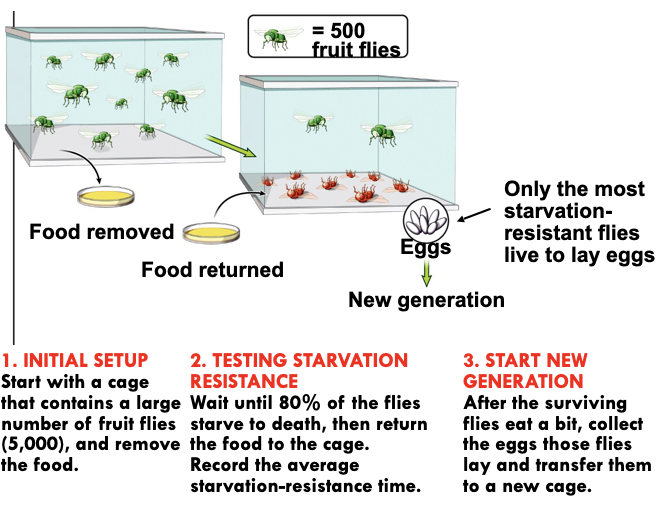
52
New cards
Results
Note: There is no way to differentiate between 20th percentile flies and 1st percentile flies in any generation.
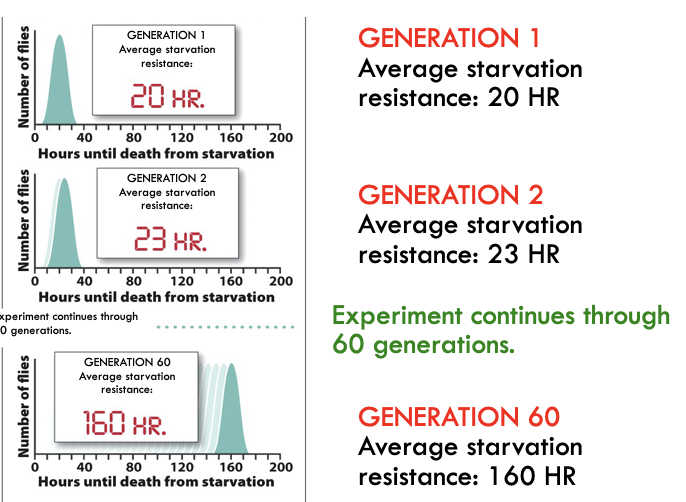
53
New cards
Antigens
- Spikes on virus capsid notify body that pathogen is present
- Once identified, body knows exactly how to fight that virus if ever infected again in the future
- What if the spikes change?
- Once identified, body knows exactly how to fight that virus if ever infected again in the future
- What if the spikes change?
54
New cards
Evolution & Viruses
- Viruses infect cells with what becomes loose genetic material – one cell simultaneously infected with multiple viruses can combine that DNA, easily creating new strains
- Viruses mutate easily, creating new strains
- Viruses mutate easily, creating new strains
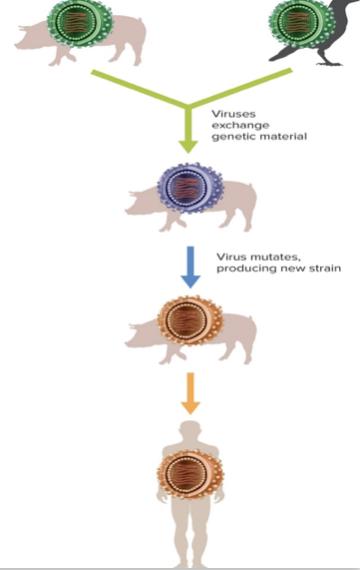
55
New cards
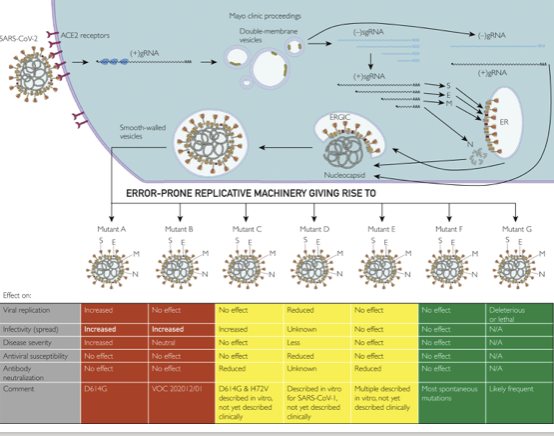
Viral Evolution Requires Infected Hosts
- SARS-COV-2 variants are all the result of evolution within infected hosts
- Selection favors variants that are more transmissible and that evade protection from vaccines or previous infection
- Selection favors variants that are more transmissible and that evade protection from vaccines or previous infection
56
New cards
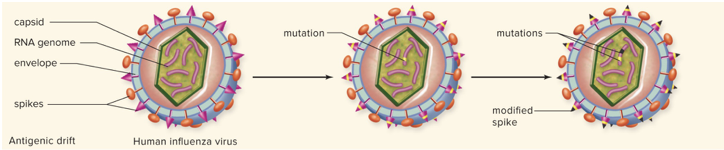
Viral Evolution: Antigenic drift
- Small changes in surface spikes on virus makes it harder for immune system virus recognize it as a known pathogen (or make vaccines less effective)
- Mutations caused by sloppy proofreading by copying enzymes
- Mutations caused by sloppy proofreading by copying enzymes
57
New cards
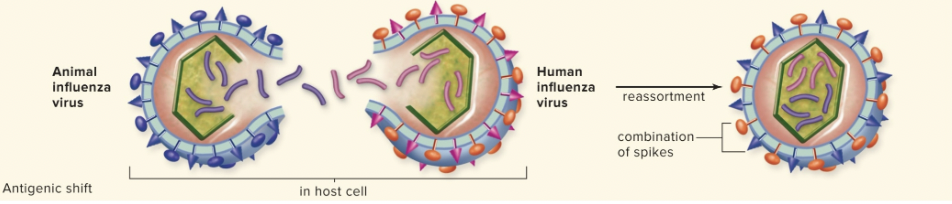
Viral Evolution: Antigenic Shift
Two forms of a virus infect the same cell, causing host cell to produce viral particles from both viruses, assembling a new strain with unique spikes
58
New cards
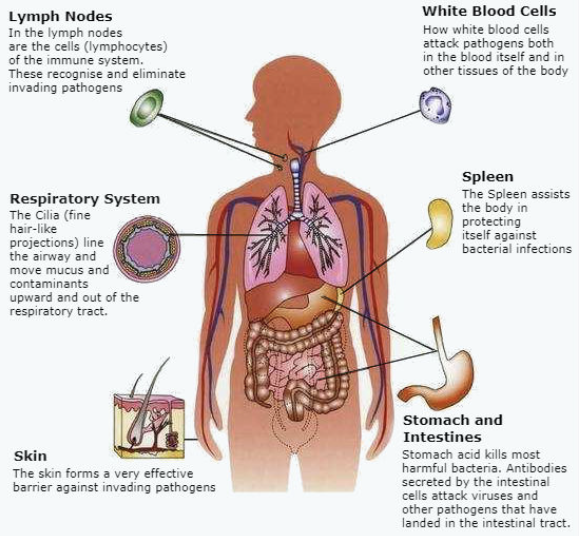
Immune System
- Protects your body from foreign pathogens
- Viruses, bacteria, toxins, eukaryotic parasites
- Viruses, bacteria, toxins, eukaryotic parasites
59
New cards
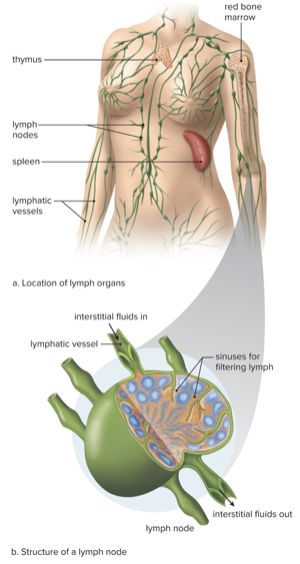
Major Immune System Organs
- Lymph Nodes: Filter pathogens from lymph fluid
- Red Bone Marrow: Site of lymphocyte white blood cell production and (B-Cell) maturation
- Spleen: Filter blood
- Thymus: Site of T-Cell maturation
- Red Bone Marrow: Site of lymphocyte white blood cell production and (B-Cell) maturation
- Spleen: Filter blood
- Thymus: Site of T-Cell maturation
60
New cards
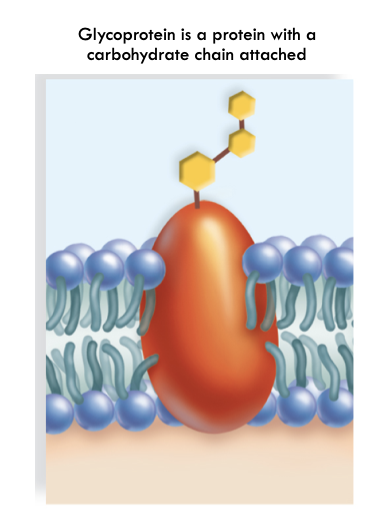
Self vs. Non-Self Recognition
- Correct Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Glycoproteins must be present on plasma membrane of cell
- Natural Killer Cells: Kill cells not displaying correct MHC-I Glycoproteins
- Natural Killer Cells: Kill cells not displaying correct MHC-I Glycoproteins
61
New cards
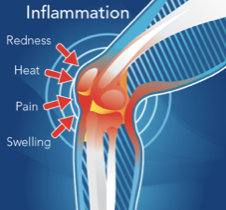
Innate Immune System
- Immune system people are born with and requires no experience/prior exposure to work
- Fast-acting, but not disease specific and it cannot defeat all pathogen types
- Inflammation: Swelling, redness at site of wound or infection
- White blood cells kill & remove pathogens, debris, dead cells
- Clotting factors close wound to stop bleeding
- Fast-acting, but not disease specific and it cannot defeat all pathogen types
- Inflammation: Swelling, redness at site of wound or infection
- White blood cells kill & remove pathogens, debris, dead cells
- Clotting factors close wound to stop bleeding
62
New cards
Innate Immunity: Physical Barriers
- Protect pathogens from entering body
- Examples:
Skin
Mucous membranes
Stomach Acid
- Examples:
Skin
Mucous membranes
Stomach Acid
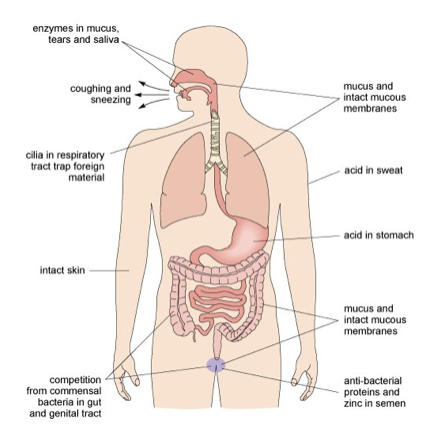
63
New cards
Innate Immunity: Cytokines
- Chemical signals of immune system that trigger other immune cells to fight pathogen
- Example: Histamine
Increases blood flow to region, increasing immune cell presence and preventing spread of pathogen (triggers inflammatory response)
- Example: Histamine
Increases blood flow to region, increasing immune cell presence and preventing spread of pathogen (triggers inflammatory response)
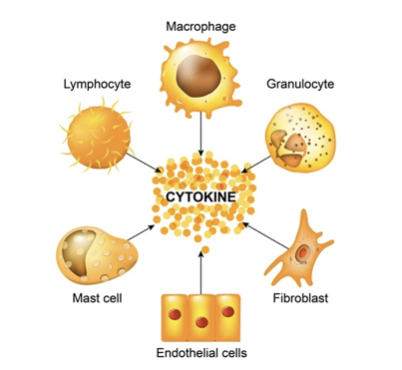
64
New cards
Innate Immunity: Leukocytes
Phagocytize (engulf and kill) pathogens immediately upon arrival at infection site
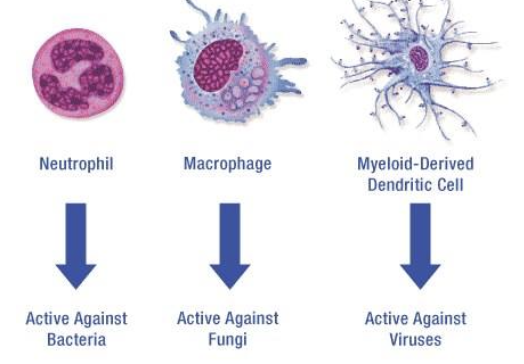
65
New cards
Inflammatory Response
1. Damaged tissues secrete histamine, which increases blood flow to the area to deliver WBCs and clotting factor
2. Macrophages identify and destroy bacteria/viruses present
3. Neutrophils clean up the area
4. Clotting factors close wound
2. Macrophages identify and destroy bacteria/viruses present
3. Neutrophils clean up the area
4. Clotting factors close wound
66
New cards
Adaptive Immune System
- Fights specific pathogens, but cannot do so right away on first infection
- You will get sick before this part of your immune system is working
-Has a memory
- Once you’ve been infected by a pathogen, your immune system will remember how to recognize it in the future, creating a much swifter response
- You will get sick before this part of your immune system is working
-Has a memory
- Once you’ve been infected by a pathogen, your immune system will remember how to recognize it in the future, creating a much swifter response
67
New cards
Antigens
- Any substance that produces a specific immune response by the body
- Flu: Protein Spikes
- Usually pathogen-specific proteins or large carbohydrates
- Flu: Protein Spikes
- Usually pathogen-specific proteins or large carbohydrates
68
New cards
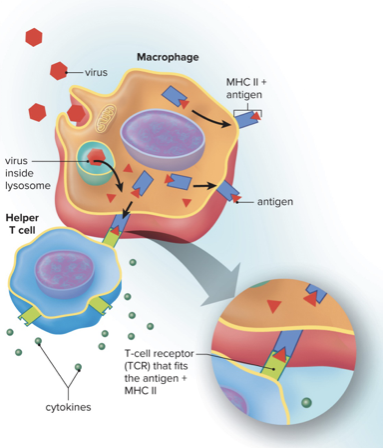
Adaptive Immune Response
Step 1: Exposure To a Pathogen
- Pathogen will have antigens on it, which help immune system recognize it
- WBCs phagocytize pathogen, kill it, then take part of antigen to T-Cells, which begins adaptive response
- WBCs phagocytize pathogen, kill it, then take part of antigen to T-Cells, which begins adaptive response
69
New cards
Adaptive Immune Response
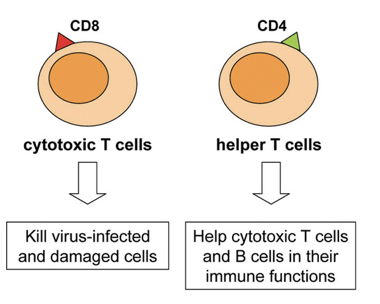
Step 2: T-Cells Recognize the Antigens
- T-Cells Mature in the Thymus
- Cytotoxic T-Cells: Kill cells that have been infected by pathogen
- Helper T-Cells: Take antigens to lymph nodes to present to B-Cells
- Cytotoxic T-Cells: Kill cells that have been infected by pathogen
- Helper T-Cells: Take antigens to lymph nodes to present to B-Cells
70
New cards
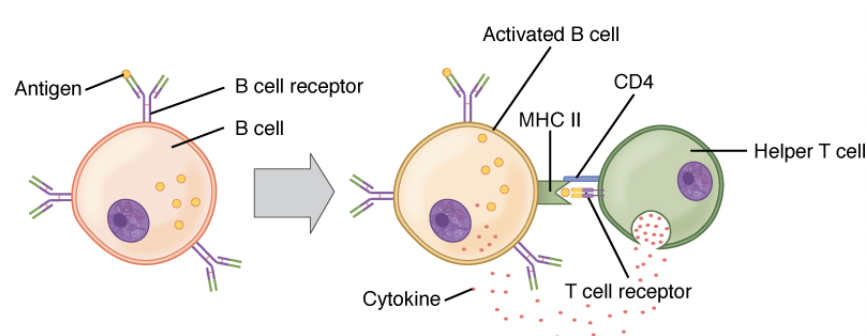
B-Cells
- Mature in Bone marrow
- Produce antibodies to target specific pathogens
- Release these antibodies into blood
1. Bind free-floating pathogens
2. Give all WBCs the ability to detect pathogen
- Produce antibodies to target specific pathogens
- Release these antibodies into blood
1. Bind free-floating pathogens
2. Give all WBCs the ability to detect pathogen
71
New cards
Adaptive Immune Response
Step 3: Immunity
- Once B-Cells share antibodies, immune system targets pathogens and infected cells
- Infection is defeated
- Infection is defeated
72
New cards
Adaptive Immune Response
Step 4: Memory
- Once infection is controlled, B-Cells and T-Cells become memory cells
- They don’t kill cells/look for antigens, but they remain in immune system waiting to see the antigens again
- If re-exposed, the immune response can skip steps 1, 2, and 3 and just start killing infected cells and pathogens right away, so you won’t feel sick again
- They don’t kill cells/look for antigens, but they remain in immune system waiting to see the antigens again
- If re-exposed, the immune response can skip steps 1, 2, and 3 and just start killing infected cells and pathogens right away, so you won’t feel sick again
73
New cards
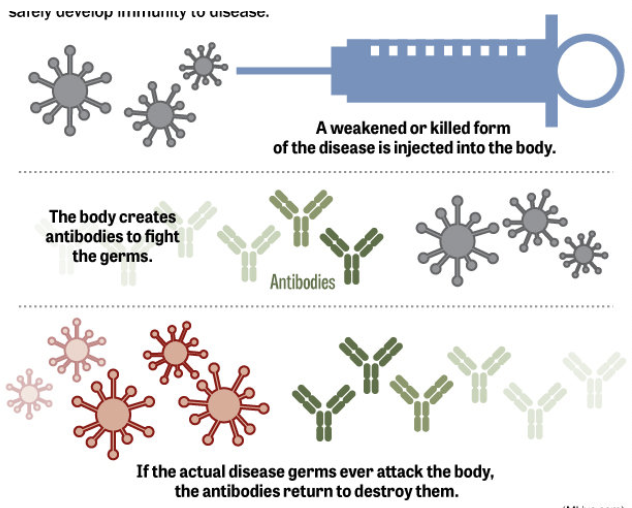
Vaccines
- Exposure to a virus, bacteria, or toxin triggers a small immune response
- Adaptive immune system means you won’t get the illness in the future
- Usually an injection, but can be a pill
- Sometimes you need regular boosters to keep immunity levels high
- Adaptive immune system means you won’t get the illness in the future
- Usually an injection, but can be a pill
- Sometimes you need regular boosters to keep immunity levels high
74
New cards
How Vaccines Work:
Individual
Level
75
New cards
Vaccines: Population Level
- All infectious agents must spread to new hosts in order to survive and reproduce
- Spreading requires susceptible people in population
- If a population has high vaccination level, there aren’t enough potential hosts for spread to happen quickly (low probability of infected person meeting a susceptible person), aka Herd Immunity
- Spreading requires susceptible people in population
- If a population has high vaccination level, there aren’t enough potential hosts for spread to happen quickly (low probability of infected person meeting a susceptible person), aka Herd Immunity
76
New cards
R0, Basic Reproduction Number
Expected number of people to whom an infected individual will spread the illness if the entire population is susceptible
- SAR-COV-2 R0 depends on variant
1. Alpha: ~2.5
2. Delta: ~7
3. Omicron: 8 - 12
- SAR-COV-2 R0 depends on variant
1. Alpha: ~2.5
2. Delta: ~7
3. Omicron: 8 - 12
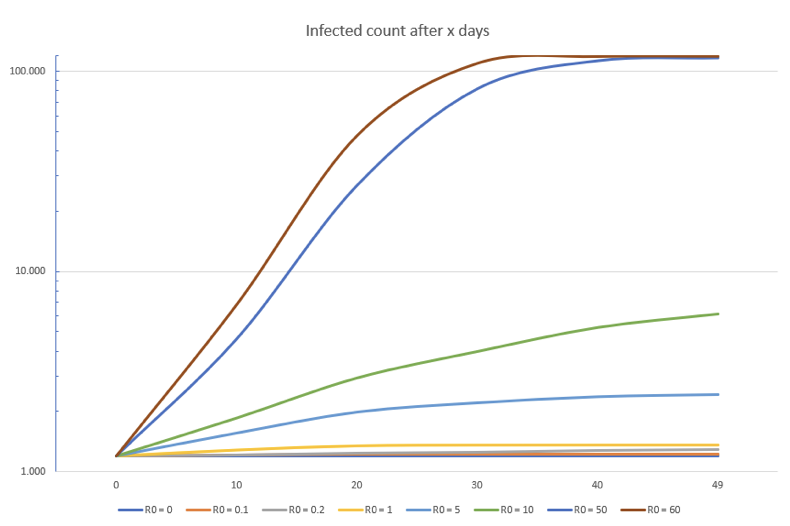
77
New cards
Life Before Modern Vaccines
Outbreaks of disease would kill off whole families and decimate communities
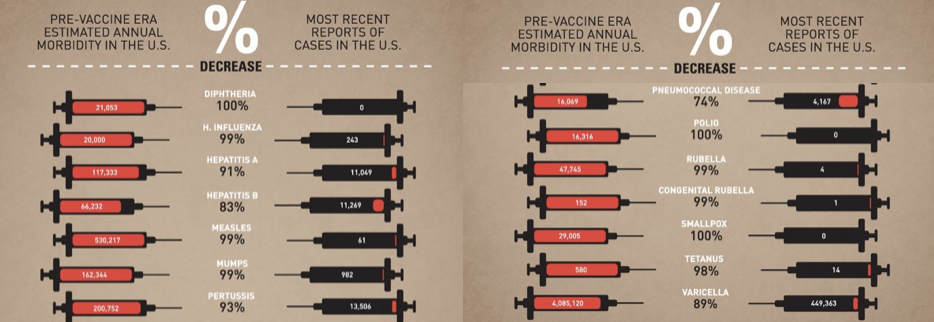
78
New cards
Invention of Smallpox Vaccine
- Eduard Jenner in 1796
- Observed:
1. Milkmaids often were infected with cowpox, which was mild in humans
2. Milkmaids with cowpox NEVER had smallpox
- Observed:
1. Milkmaids often were infected with cowpox, which was mild in humans
2. Milkmaids with cowpox NEVER had smallpox
79
New cards
Smallpox
- Virus causing characteristic sores on body
- 30% of people who got it died
- Globally eradicated by vaccination in 1980
- 30% of people who got it died
- Globally eradicated by vaccination in 1980
80
New cards
Polio
- Virus causes paralysis
- Can attack diaphragm muscles (Iron lungs)
- Often temporary, but not always
- Eradicated by vaccination in America in 1994
- Can attack diaphragm muscles (Iron lungs)
- Often temporary, but not always
- Eradicated by vaccination in America in 1994
81
New cards
Polio Vaccination
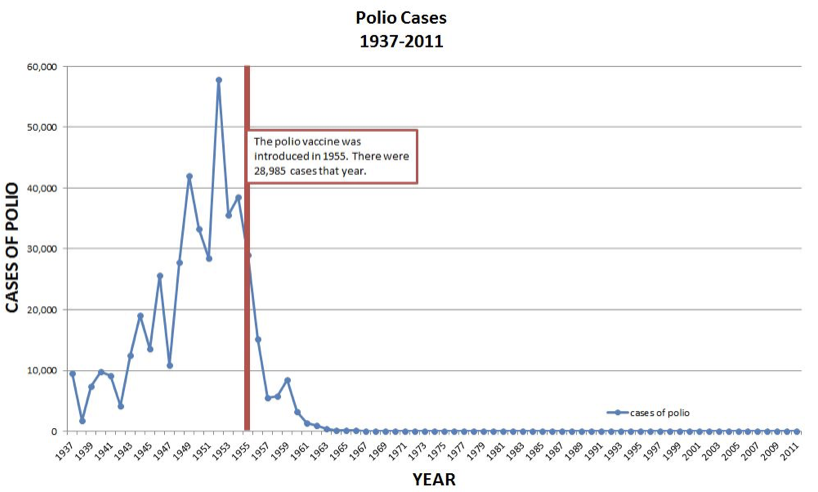
82
New cards
Measles
- Virus causes extremely high (sometimes deadly) fever and a rash
- Erases adaptive immune system!
- Extremely contagious
- Vaccine introduced in 1963
- Erases adaptive immune system!
- Extremely contagious
- Vaccine introduced in 1963
83
New cards
Types of Vaccines
1. Live Attenuated Virus
2. Toxoid
3. Component
4. Conjugate
5. Whole Killed Virus
6. mRNA
2. Toxoid
3. Component
4. Conjugate
5. Whole Killed Virus
6. mRNA
84
New cards
Live Attenuated Virus Vaccine
- Live virus, but it is modified to be weaker
- Not strong enough to cause you to be sick, but triggers immune response
- Live virus replicates in your blood as part of this process
- Immunocompromised people cannot get this type because their immune system isn’t strong to enough to fight off even the weakest virus
- Examples: MMR, Chicken Pox
- Not strong enough to cause you to be sick, but triggers immune response
- Live virus replicates in your blood as part of this process
- Immunocompromised people cannot get this type because their immune system isn’t strong to enough to fight off even the weakest virus
- Examples: MMR, Chicken Pox
85
New cards
Toxoid Vaccine
- Inactivated version of a bacterial toxin
- The toxin produced by the bacteria is dangerous, not the bacteria
- Examples: Diphtheria, Tetanus
- The toxin produced by the bacteria is dangerous, not the bacteria
- Examples: Diphtheria, Tetanus
86
New cards
Component Vaccine
- Produced from just the surface antigen that triggers an immune response
- Example: Hepatitis B
- Example: Hepatitis B
87
New cards
Conjugate Vaccine
- Bacterial infections
- Take plasma membrane sugars from bacteria and combine them with a protein the immune system recognizes as a pathogen
- Example: Meningitis
- Take plasma membrane sugars from bacteria and combine them with a protein the immune system recognizes as a pathogen
- Example: Meningitis
88
New cards
Whole Killed Vaccine
- Entire virus, but it is killed before being made into a vaccine
- Still develop a strong immune response, but requires more boosters because the immune response is weaker than a live virus version
- Immunocompromised people can get this kind of vaccine
- Examples: Flu, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid
- Still develop a strong immune response, but requires more boosters because the immune response is weaker than a live virus version
- Immunocompromised people can get this kind of vaccine
- Examples: Flu, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid
89
New cards
Influenza Vaccine
- Whole killed virus vaccine or component vaccines
- YOU CANNOT GET THE FLU FROM YOUR FLU SHOT!
- Must enter production before flu season, so scientists predict the most likely strains the previous year
- Sometimes they don’t predict well
- YOU CANNOT GET THE FLU FROM YOUR FLU SHOT!
- Must enter production before flu season, so scientists predict the most likely strains the previous year
- Sometimes they don’t predict well
90
New cards
mRNA Covid Vaccines
Injects mRNA enclosed in a lipid nanoparticle, allowing the host cells to make the viral protein for recognition by the immune system
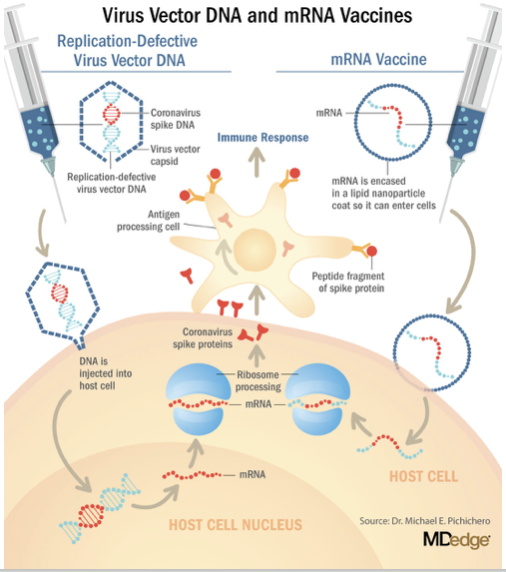
91
New cards
Vaccine Development
1. Pre-Clinical Stage: Lab tests on animals
2. First In-Human Studies: Healthy adults only
3. Second In-Human Studies: Given to at-risk populations, like children
4. Phase 3 Studies: Large sample size testing under many conditions
5. Approval given by committee of public health experts and doctors before production for public begins (can take years and years)
2. First In-Human Studies: Healthy adults only
3. Second In-Human Studies: Given to at-risk populations, like children
4. Phase 3 Studies: Large sample size testing under many conditions
5. Approval given by committee of public health experts and doctors before production for public begins (can take years and years)
92
New cards
Vaccine Skepticism
- Smallpox vaccination became mandatory under the law in Europe and the US in the 1800s
- Spawned many “Anti-Vaccination Leagues”
- Spawned many “Anti-Vaccination Leagues”
93
New cards
Current Vaccine Controversies
1. People believe vaccines cause autism
2. People believe vaccines have toxic ingredients
3. People believe children are given too many vaccines too quickly
4. People believe vaccines have side effects too severe to justify using them
2. People believe vaccines have toxic ingredients
3. People believe children are given too many vaccines too quickly
4. People believe vaccines have side effects too severe to justify using them
94
New cards
Autism Spectrum Disorder
- A group of developmental disorders that can lead to difficulty communicating or functioning
- There is a huge range of symptoms, hence the “spectrum”
- There is a huge range of symptoms, hence the “spectrum”
95
New cards
Temple Grandin
- Professor of Animal Science at Colorado State University
- Diagnosed with ”brain damage” as a child, diagnosed as Autistic in her 40’s
- Public advocate for Autism research and rights
- Revolutionized how cattle and other animals raised for meat are slaughtered
- Pioneered humane handling based on animal behavior principles
- Invented “hug box” to help people with sensory overload
- Diagnosed with ”brain damage” as a child, diagnosed as Autistic in her 40’s
- Public advocate for Autism research and rights
- Revolutionized how cattle and other animals raised for meat are slaughtered
- Pioneered humane handling based on animal behavior principles
- Invented “hug box” to help people with sensory overload
96
New cards
Controversy: Autism and Vaccines
- Study linking Measles-Mumps-Rubella Vaccine (MMR) to Autism published in English medical journal The Lancet in 1998 by Andrew Wakefield indicated that MMR vaccines cause autism
- Study of 12 children
- All received MMR & had intestinal abnormalities
- 8 of 12 developed autism
- Wakefield recommended that Measles, Mumps, and Rubella be administered in three different shots
- Vaccination Rates Dramatically decreased after the study was published
- Study of 12 children
- All received MMR & had intestinal abnormalities
- 8 of 12 developed autism
- Wakefield recommended that Measles, Mumps, and Rubella be administered in three different shots
- Vaccination Rates Dramatically decreased after the study was published
97
New cards
Other Studies Can Find absolutely No Evidence of A link Between Vaccines & Autism
- Dozens of large studies preformed, none found any link
No link with MMR
No link with Mercury
No link with vaccine schedule
- Pooled together there were 1.25 MILLION children in these studies
No link with MMR
No link with Mercury
No link with vaccine schedule
- Pooled together there were 1.25 MILLION children in these studies
98
New cards
Issues with Wakefield’s Study
- When scientists and journalists compared the clinical records of the children in the study with Wakefield's paper, it was clear Wakefield has falsified his data for the paper
- Wakefield also conducted his research unethically, performing colonoscopies, spinal taps, and barium meal tests on small children without permission
- Wakefield also conducted his research unethically, performing colonoscopies, spinal taps, and barium meal tests on small children without permission
99
New cards
Undeclared Conflicts of Interest
- Wakefield’s research was paid for by a lawyer in the process of suing pharmaceutical companies over the MMR vaccine
- Nine months before he called for single measles vaccines, Wakefield filed a patent for one
- He did not disclose either of these facts to the Lancet, which is required by ethics rules
- Nine months before he called for single measles vaccines, Wakefield filed a patent for one
- He did not disclose either of these facts to the Lancet, which is required by ethics rules
100
New cards
Investigation and retraction
- The Lancet retracted Wakefield’s paper in light of this information
- This means the journal is essentially disavowing the article, meaning its results can’t be trusted and should not be cited by others
- Wakefield lost his license to practice medicine in the UK
- This means the journal is essentially disavowing the article, meaning its results can’t be trusted and should not be cited by others
- Wakefield lost his license to practice medicine in the UK