TAMU BIOL 319 Lab 7
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Frequency
The number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time.
Amplitude
the height of the wave from baseline to crest
Waveform
shape and form of a signal
Wavelength
the length from the crest of one peak to the crest of the next peak
What is the percentage of skeletal muscle that makes up the cell mass of the body?
40%
Upper motor neuron lesions
loss of muscle function as a consequence of strokes damaging neurons in the brain
Muscle fibers
muscle cells; organized into fascicles
Skeletal muscle is controlled
voluntary
Excitability
ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Contractility
ability to shorten when stimulated
Extensibility
ability to be stretched
Elasticity
ability to be stretched and recoil to the resting cell length
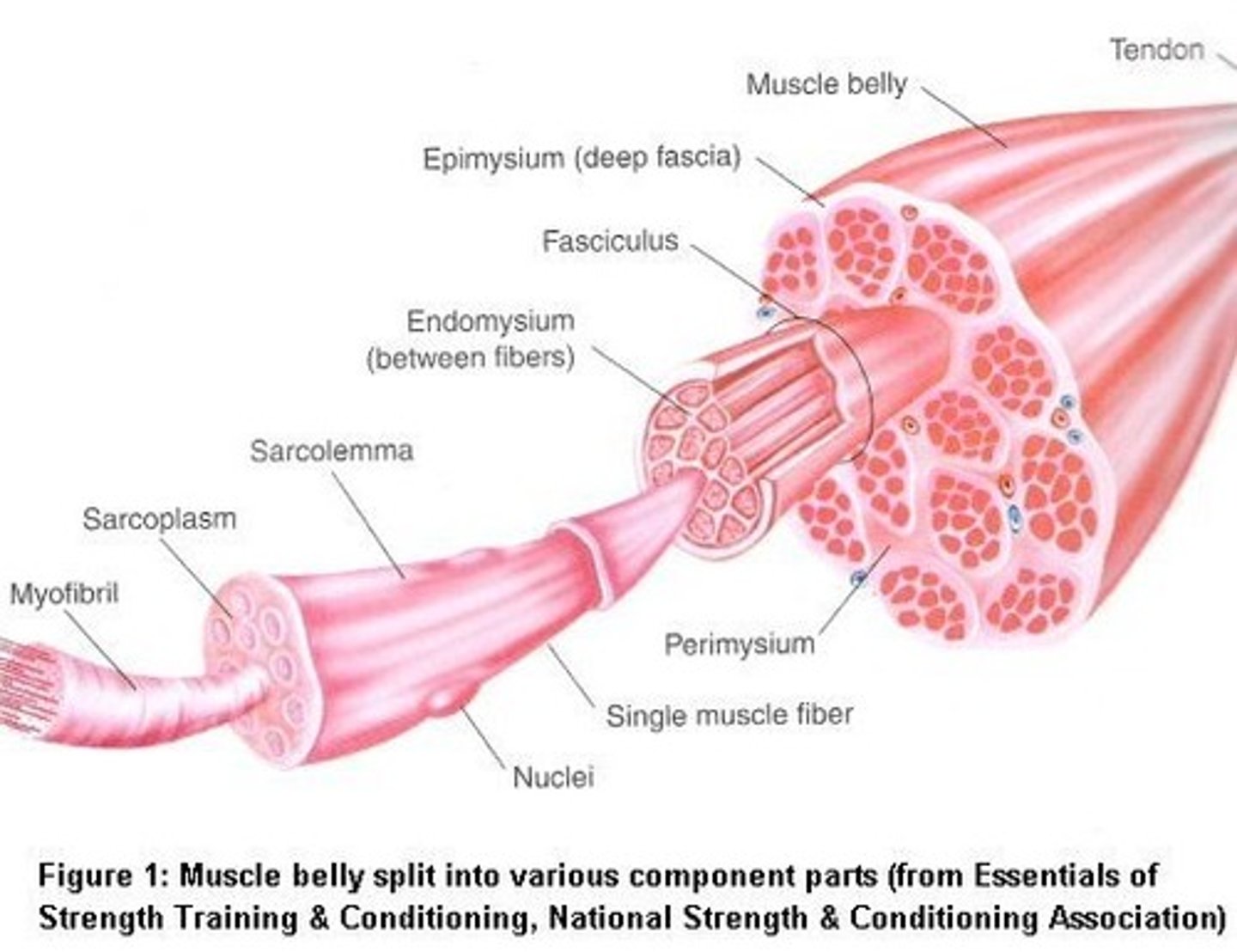
Tendons
connective tissues that attaches muscle to bone
mostly collagen, rope-like extensions
Direct attachment
epimysium fused to periosteum of bone or perichondrium of cartilage
Indirect attachment
muscle attachment in which the epimysium form a tendon that merges into the periosteum
more durable, smaller, common
Ex: aponeurosis (sheet-like)
2 or more muscles usually work
Antagonistically
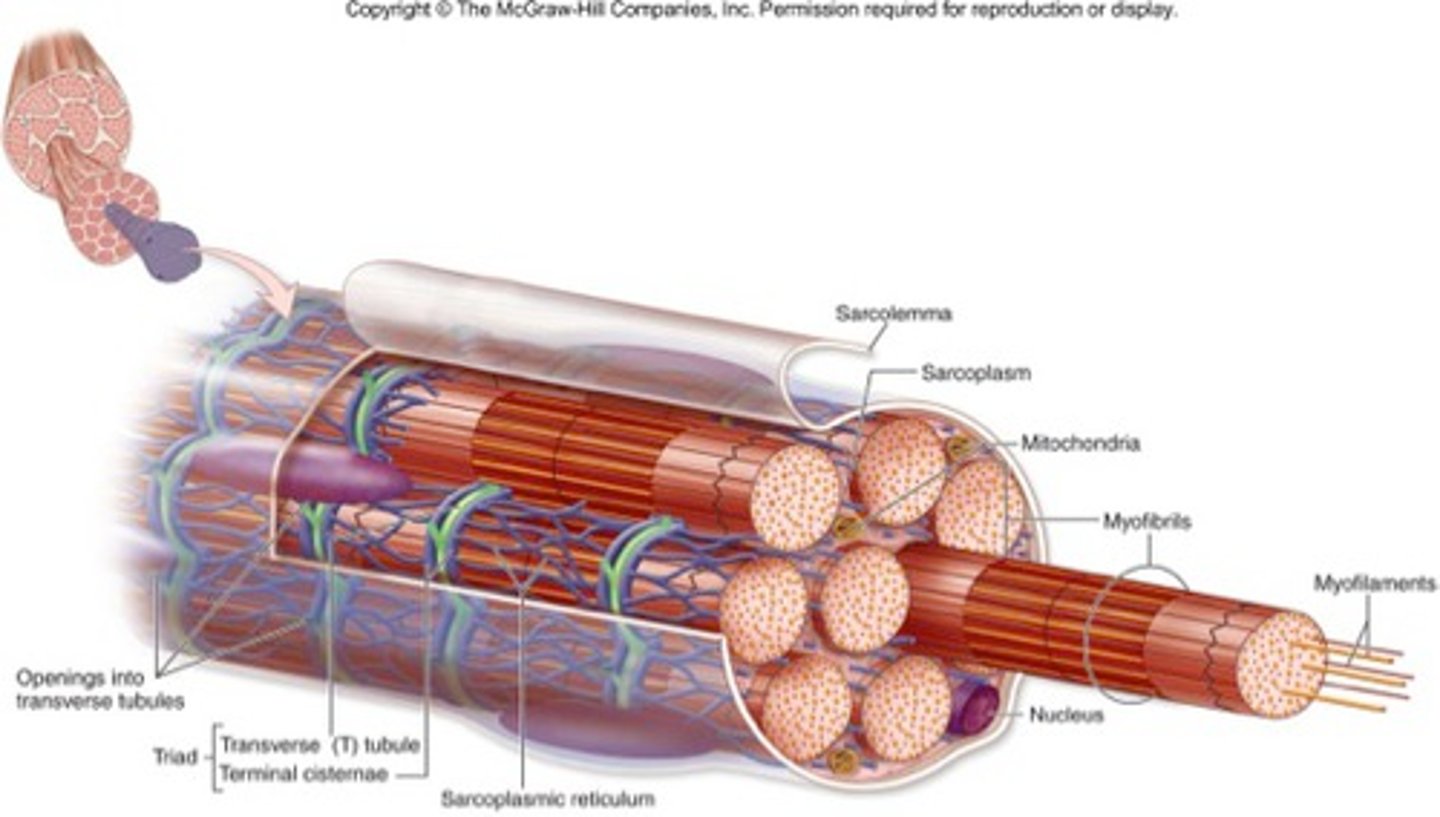
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
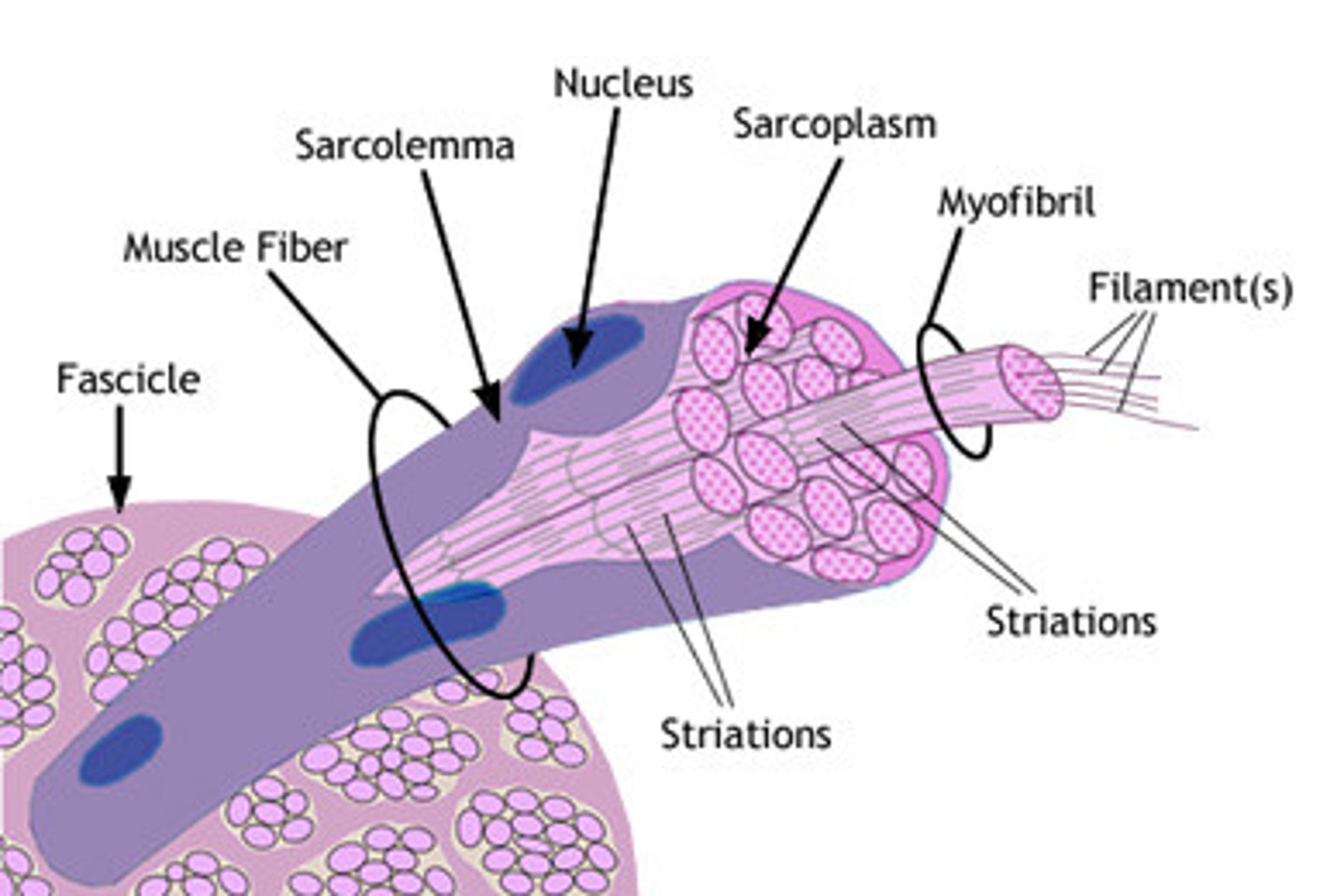
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm
Myoglobin
stores oxygen in muscle cells
Glycosomes
granules of stored glycogen that can be broken down to supply ATP from glucose for energy
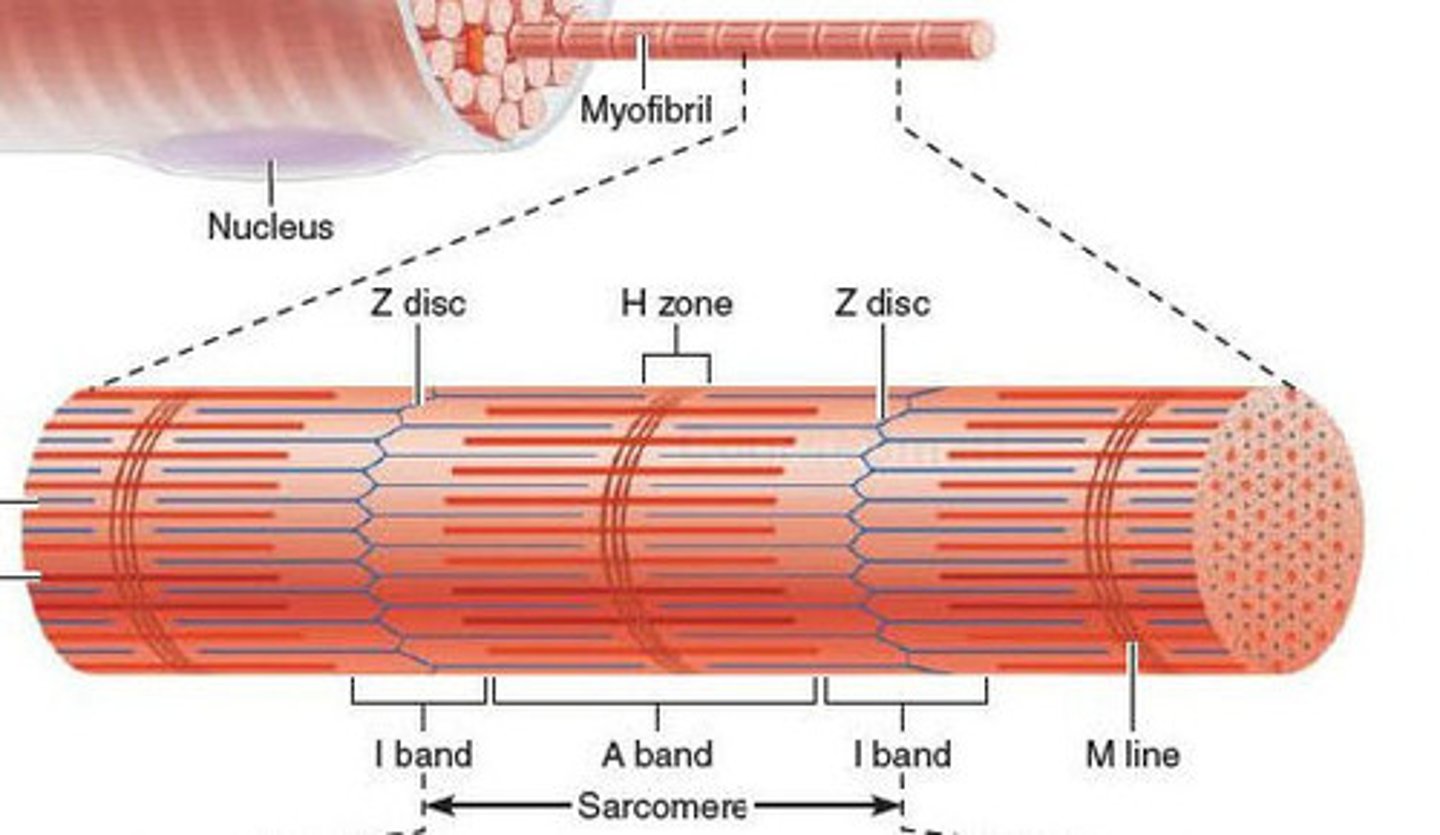
Myofibrils
repeating units of sarcomeres
Takes up most of the intracellular volume of skeletal muscle cells
Sarcomeres
smallest "atomic" contractile units of skeletal muscle fibers
runs from Z line to Z line
runs from each half I band to half I band with an A band in the middle
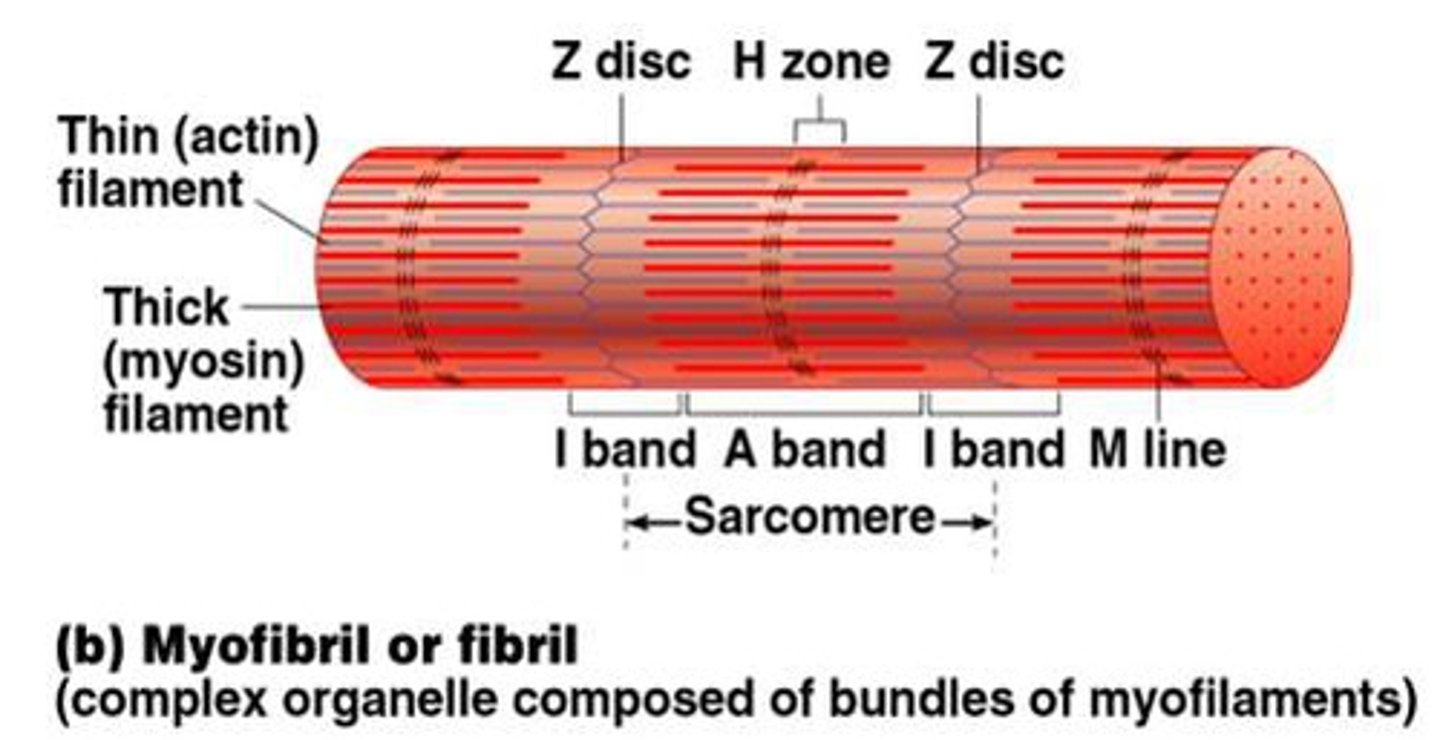
A band
dark band
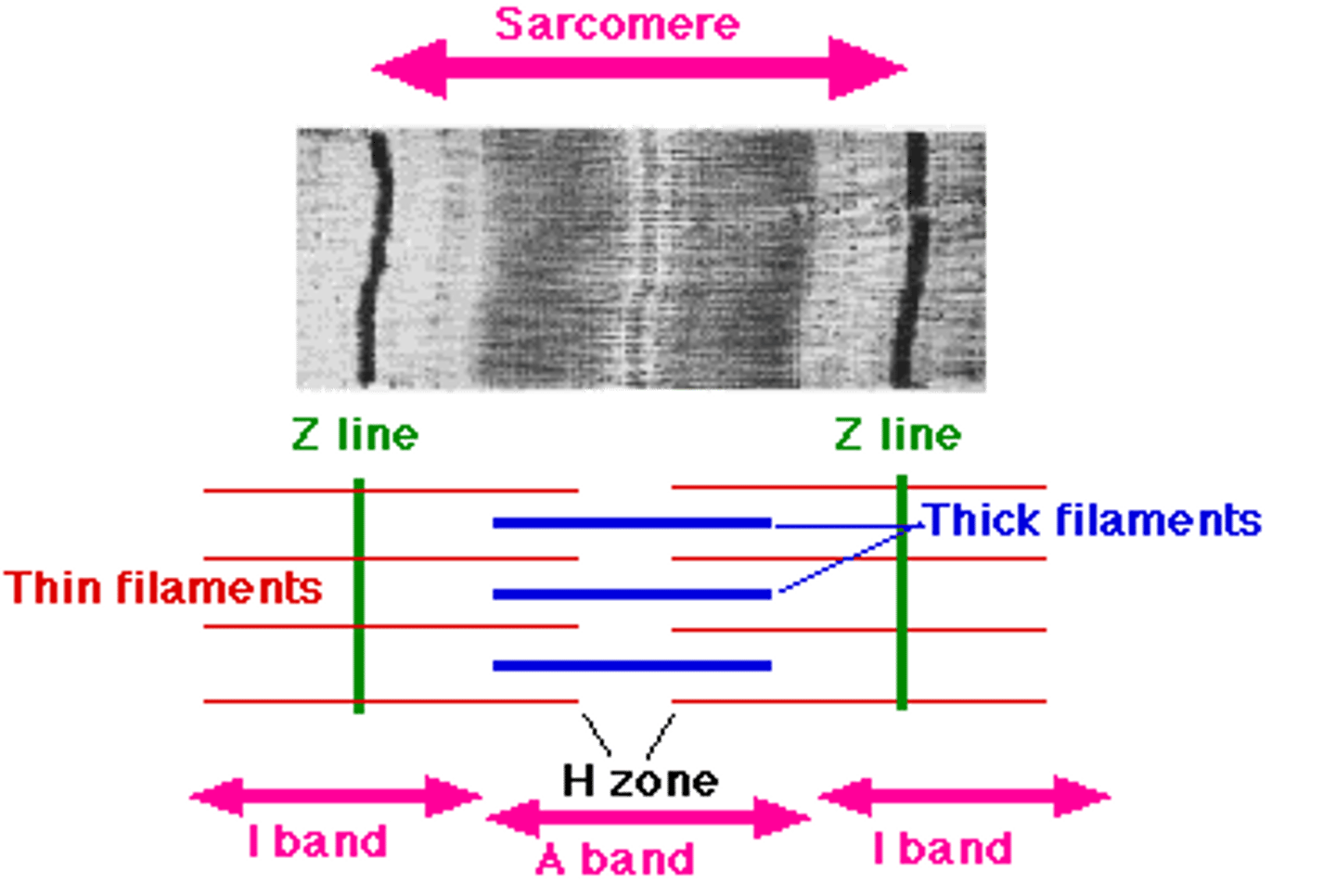
I band
light band
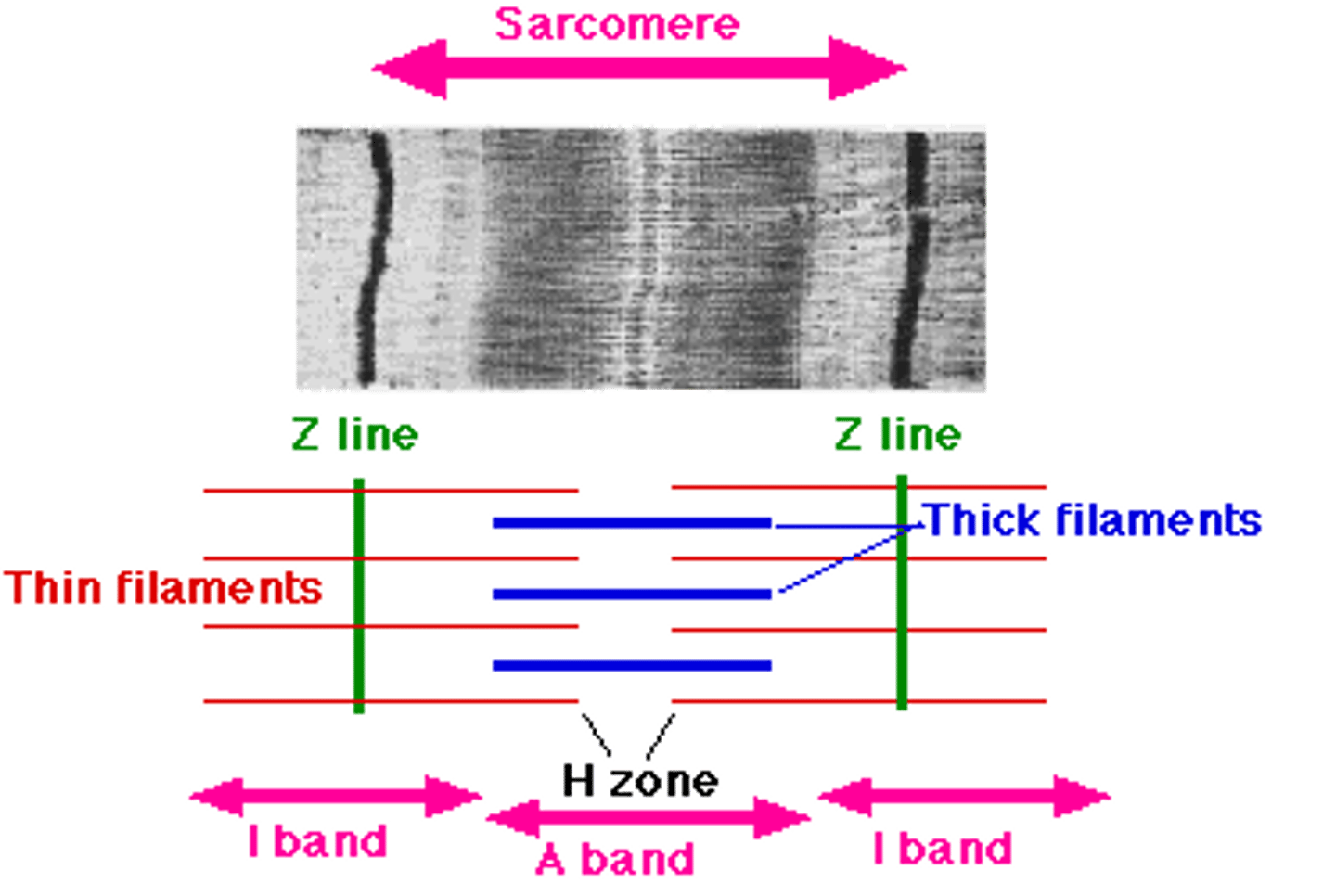
H zone (band)
each A band has a middle region that is slightly light
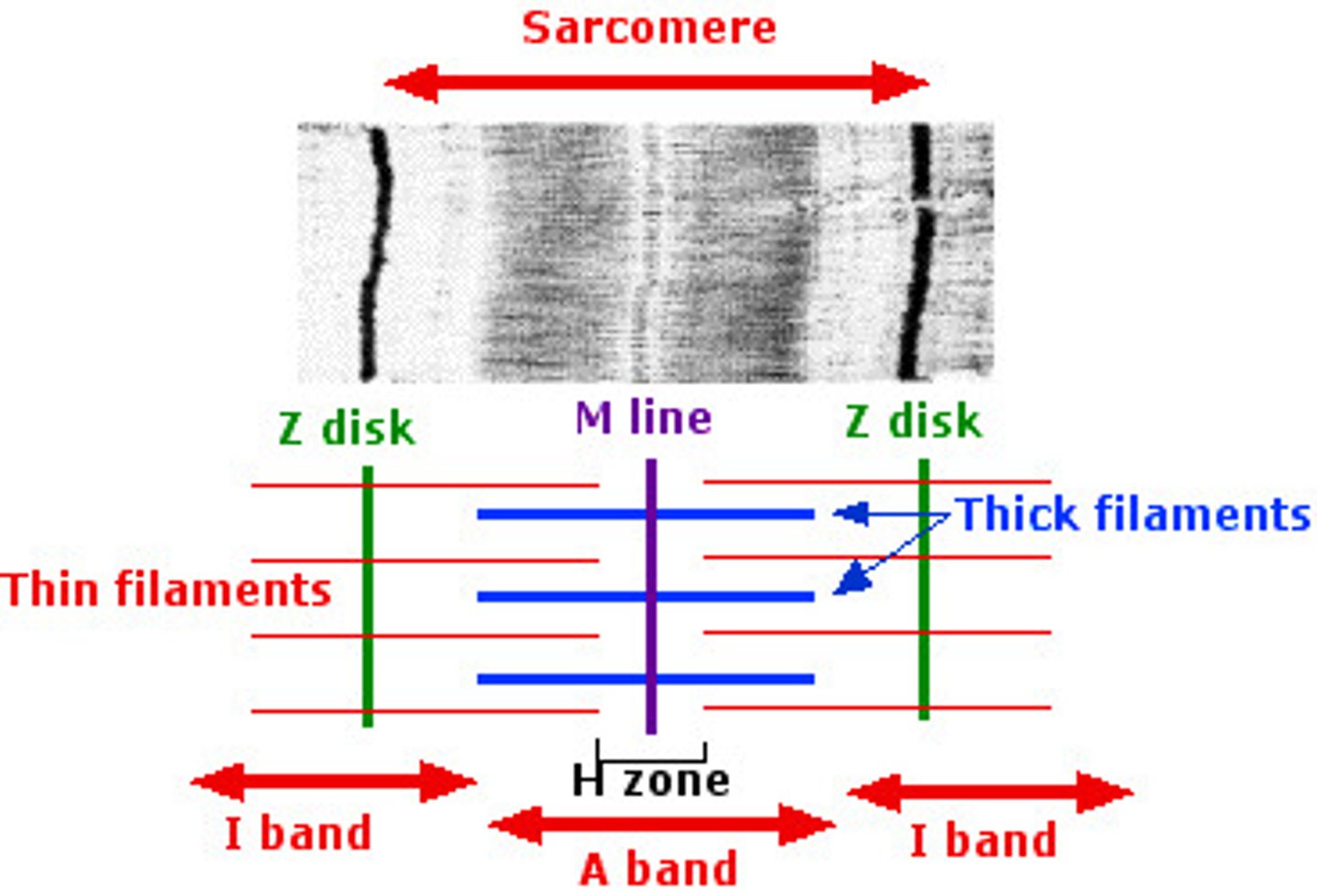
Z line (disc)
dark midline of the I band
Thick filaments
composed of myosin; run the length of the A band
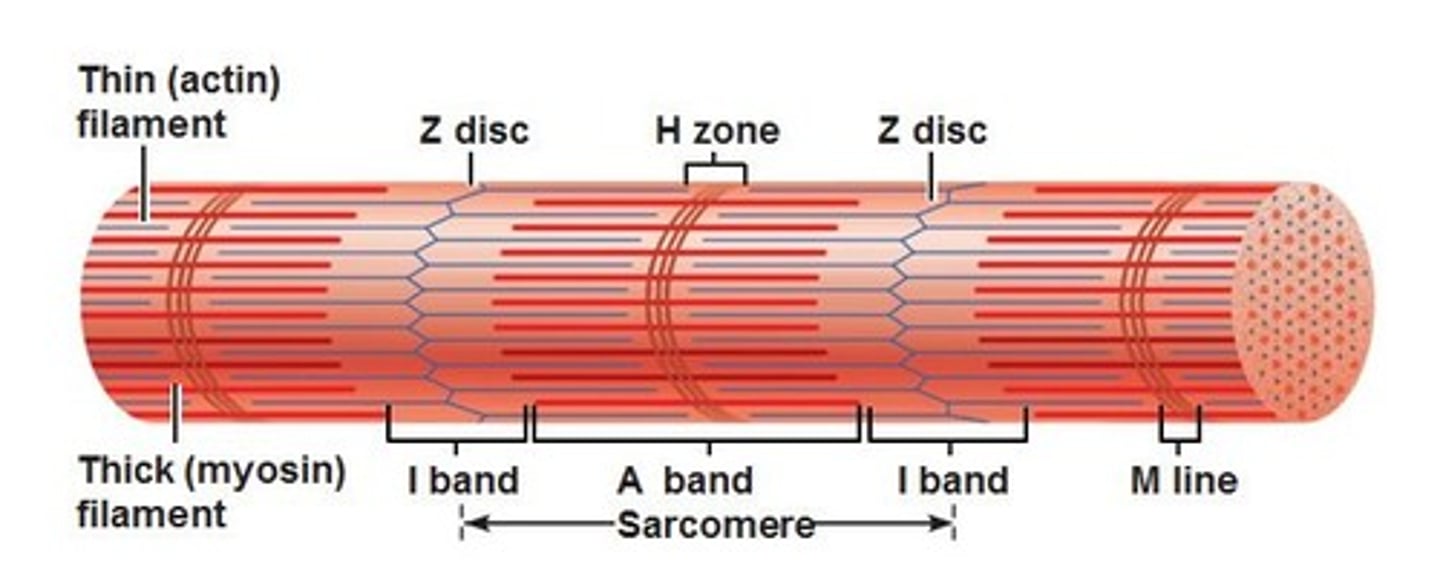
Thin filaments
helix of 2 actin subunit strands; tropomyosin and troponin
Troponin
composed of 3 globular polypeptides each with a different function
One binds to actin, another binds to tropomyosin, calcium ions binds to the third
Titin
what elastic filaments are made of
runs from the Z line to the thick filaments to hold them in place and provide flexible recoil to the sarcomere as it contracts, relaxes, and stretches.
Once titin reaches its normal extension, it stiffens and resists further over-stretching of the muscle
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Controls, stores, releases calcium to controlmuscle fiber contraction
T tubules
At the A and I band junction
elongated tubular extensions of the sarcolemma dive deeply into the cell
Triad
T tubule + terminal cisterns
Polarization
inside of cell is more negative compared to outside
Depolarization
less negative
Repolarization
membrane becomes more negative
potassium exits the cell down its concentration gradient
Refractory period
during repolarization, the cell cannot be stimulated again until the membrane is sufficiently negative