Myeloid Cells and the Innate Immune Response
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Myeloid Cells
Subset of leukocytes in the innate immune system.
Granulocytes
Type of myeloid cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
Neutrophils
Primary phagocytes in innate immune response.
Eosinophils
Combat multicellular parasites and allergic reactions.
Basophils
Release histamine in allergic responses.
Mast Cells
Release mediators like histamine during inflammation.
Monocytes
Circulate in blood, differentiate into macrophages.
Macrophages
Phagocytose pathogens and present antigens.
Dendritic Cells
Bridge innate and adaptive immunity, antigen presenting.
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
Detect broad classes of pathogens, trigger immune response.
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Recognize PAMPs, activate immune signaling pathways.
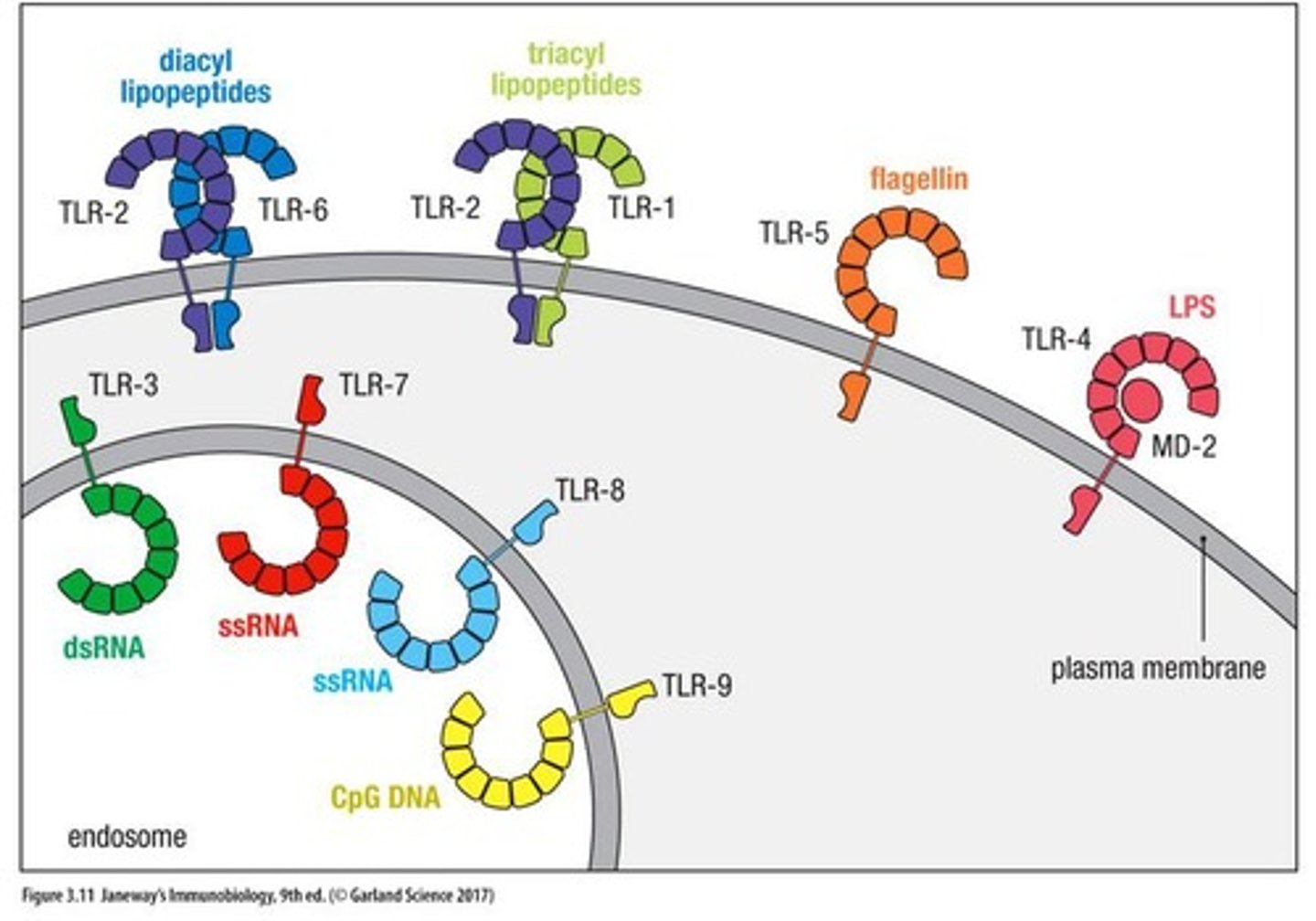
NOD-like Receptors (NLRs)
Intracellular sensors for detecting bacterial infections.
C-type Lectin Receptors (CLRs)
Bind carbohydrates, detect fungal components.
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
Molecular patterns recognized by TLRs on pathogens.
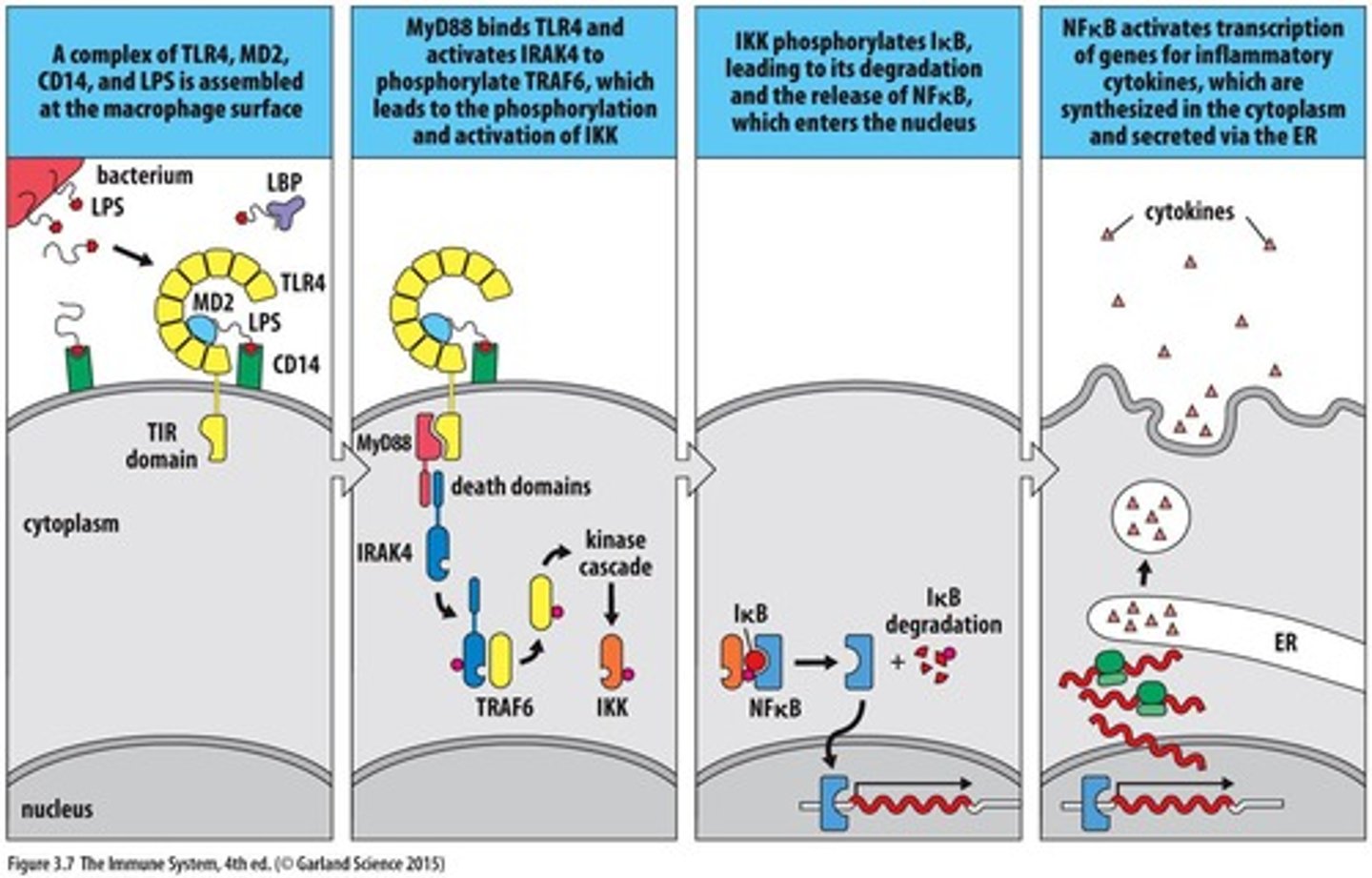
NF𝚱B
Master transcription factor for inflammatory responses.
Inflammasome
Multi-protein complex activating inflammatory cytokines.
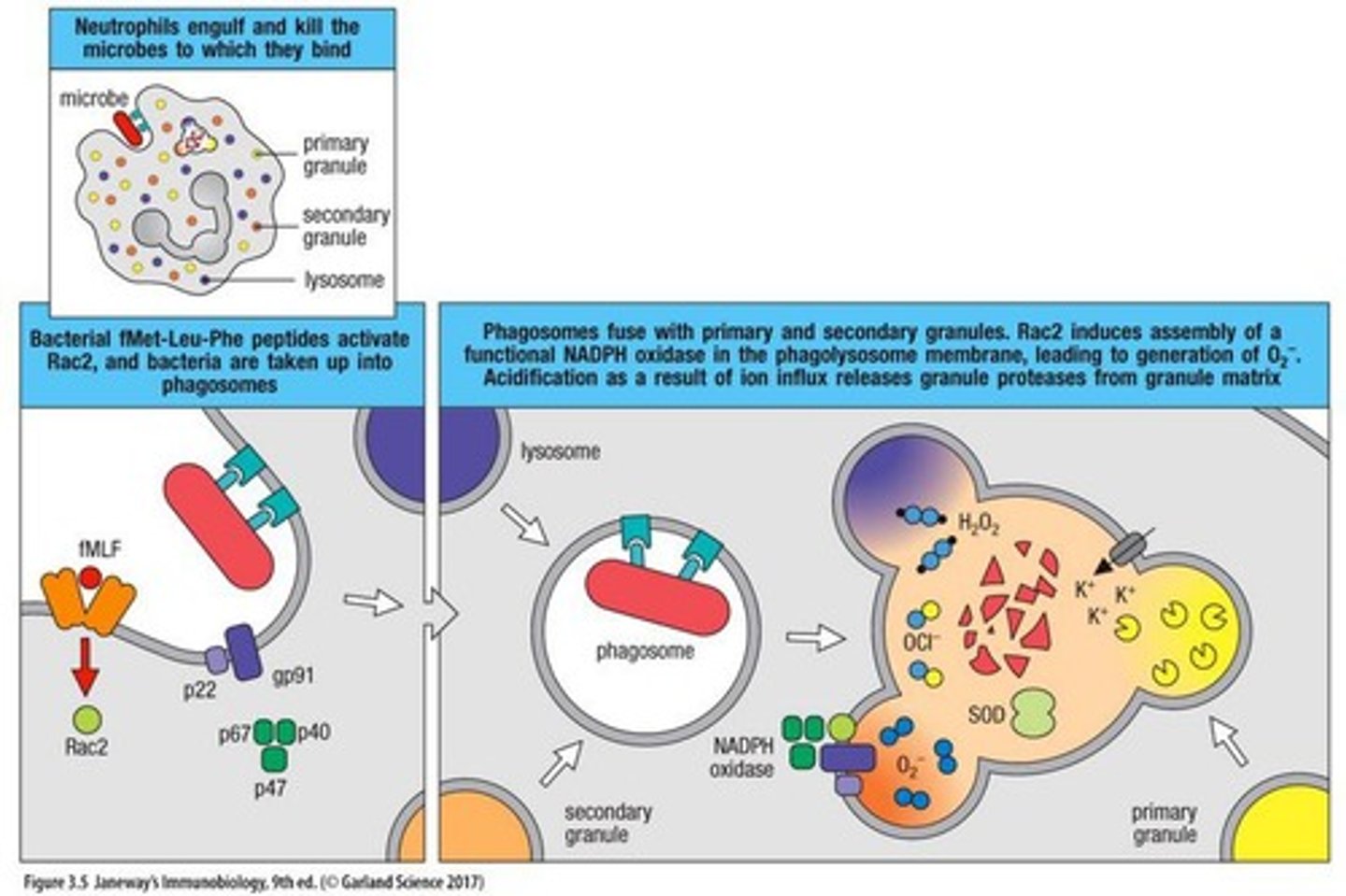
Phagocytosis
Uptake and destruction of pathogens by phagocytes.
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Toxic oxygen species produced during phagocyte activation.
NADPH Oxidase
Enzyme complex generating ROS in phagocytes.
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
NADPH oxidase deficiency leading to infection susceptibility.
Granuloma
Chronic inflammatory response to persistent infections.
Granuloma
Localized inflammatory response involving macrophages.
Multi-nucleated giant cell
Fused macrophages in chronic inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Medications to reduce inflammation in patients.
Anti-fungal drugs
Medications targeting fungal infections.
Antimicrobial proteins
Proteins that directly combat pathogens.
Lysozyme
Enzyme in tears and saliva with antibacterial properties.
Defensins
Peptides secreted by phagocytes at mucosal sites.
Histatins
Proteins active against fungi in oral cavity.
Granulocytes
White blood cells containing inflammatory mediators.
Neutrophils
Type of granulocyte that engulfs pathogens.
Basophils
Granulocytes involved in allergic responses.
Eosinophils
Granulocytes that combat parasitic infections.
Mast cells
Cells releasing histamine during allergic reactions.
Mast cell degranulation
Release of mediators from mast cells.
Prostaglandins
Lipid mediators increasing vascular permeability.
Leukotrienes
Mediators attracting neutrophils and causing bronchoconstriction.
Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF)
Mediates bronchoconstriction and recruits eosinophils.
NETs
Neutrophil extracellular traps capturing pathogens.
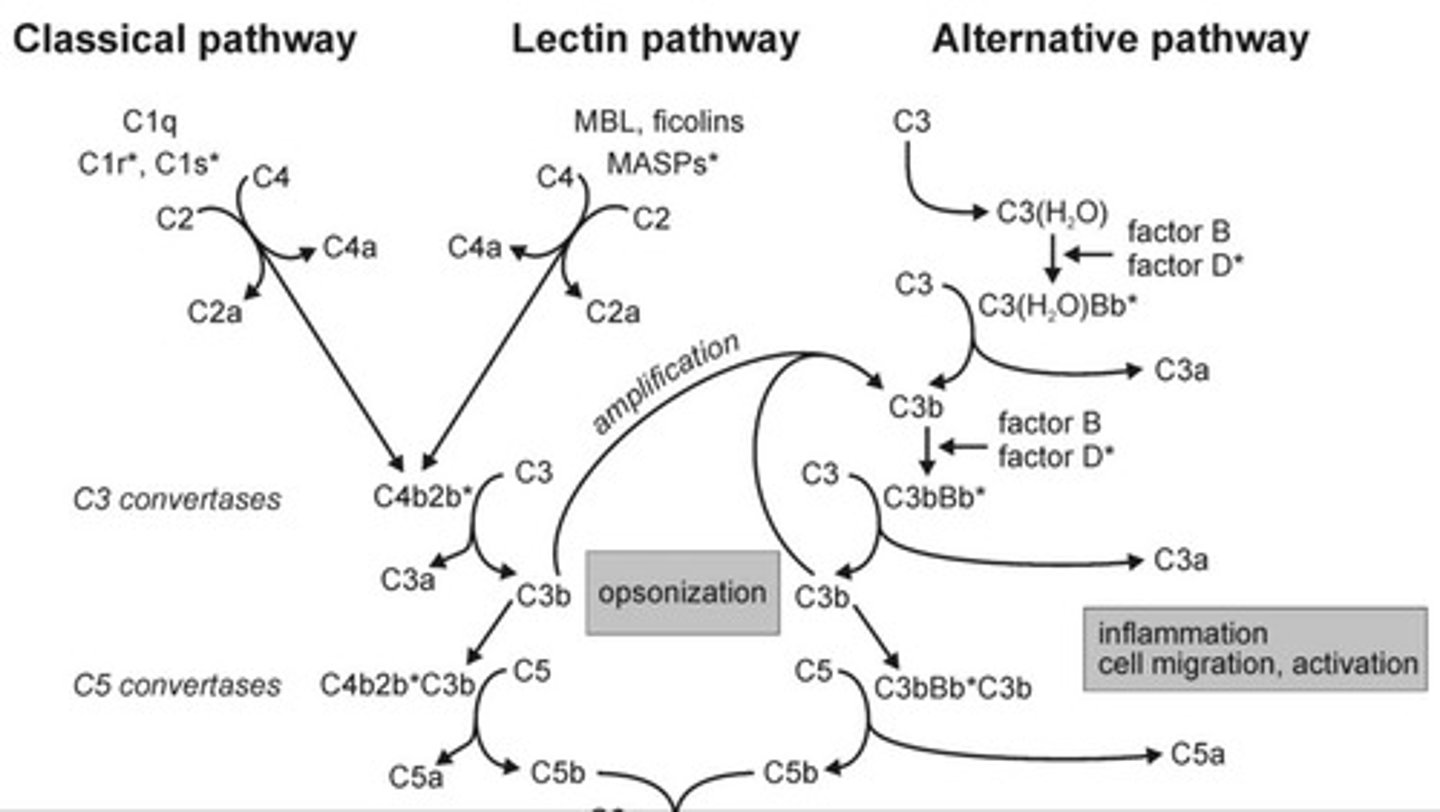
C3 Convertase
Enzyme cleaving C3 into C3a and C3b.
Opsonization
Process enhancing phagocytosis of pathogens.
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
Complex forming pores in bacterial membranes.
Decay activating factor (DAF)
Prevents complement activation on self-cells.
Factor H
Regulates C3b cleavage to prevent self-damage.
Nisseria meningitidis
Pathogen that inactivates C3b to evade immune response.
Staphylococcus aureus
Bacterium inhibiting complement components.
Pathogen Entry
Initial access point for invading pathogens.
Pathogen Recognition
Identifying pathogens that breach physical barriers.
TLR
Toll-like receptors; recognize pathogens.
NLR
NOD-like receptors; detect intracellular pathogens.
CLR
C-type lectin receptors; bind carbohydrates on pathogens.
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing and destroying pathogens.
Antimicrobial Proteins
Proteins that inhibit pathogen growth.
Granule Release
Discharge of cytotoxic substances to kill pathogens.
NETs
Neutrophil extracellular traps; trap and kill pathogens.
Complement MAC
Membrane Attack Complex; lyses pathogen membranes.
Inflammation
Response to infection; recruits immune cells.
NFkB Activation
Transcription factor activated by TLRs and NLRs.
Complement Pathway
Series of proteins aiding in pathogen elimination.
C3a
Anaphylatoxin; promotes inflammation and immune response.
CD18
Cell surface marker for leukocyte adhesion.
TLR4
Specific TLR that recognizes bacterial lipopolysaccharides.
C9
Component of the complement system; forms MAC.
C3b
Complement component that opsonizes pathogens.
Classical Pathway
Complement activation pathway triggered by antibodies.
Lectin Pathway
Complement pathway activated by lectin binding.
CCR1
Chemokine receptor aiding macrophage migration.
CCR5
Chemokine receptor involved in immune cell trafficking.
LFA-1
Integrin important for leukocyte adhesion and migration.