Unit 1: intro to business management
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:45 PM on 6/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
Stakeholders
a person, group, or organisation that can affect or be affected by an organisations actions, objectives and policies and therefore have an interest or stake in the actions of the business
2
New cards
Stakeholder concept
priority to stakeholders rather than shareholders
3
New cards
Internal stakeholders
* employees (pay, conditions, job security)
* shareholders (profit, vision, liquidity, efficiency)
* managers (financial performance, customer perception, profits, sales targets)
* shareholders (profit, vision, liquidity, efficiency)
* managers (financial performance, customer perception, profits, sales targets)
4
New cards
External Stakeholders
* suppliers (speed of payment, level and regularity of orders, fairness of treatment)
* customers (value, service, quality, ethical considerations)
* government (taxation, compliance with legislation such as health and safety, jobs created)
* banks and other creditors (liquidity, gearing)
* special interest groups (pressure groups)
* competitors
* customers (value, service, quality, ethical considerations)
* government (taxation, compliance with legislation such as health and safety, jobs created)
* banks and other creditors (liquidity, gearing)
* special interest groups (pressure groups)
* competitors
5
New cards
pressure groups
a group that tries to influence public policy in the interest of a particular cause
6
New cards
Stakeholder conflict
* not possible to satisfy all stakeholders all the time
* conflict will always arise from new developments, business activities
* conflict will always arise from new developments, business activities
7
New cards
Stakeholder mapping
Allows managers to assess how to deal with conflicting stakeholder objectives
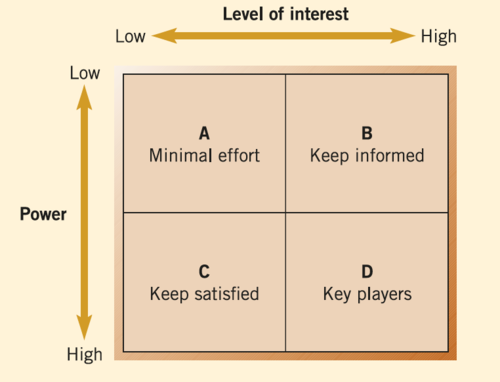
8
New cards
Group A
minimal effort
9
New cards
Group B
keep informed
10
New cards
Group C
keep satisfied. this is a must as they have the power to influence other groups
11
New cards
Group D
Key players (maximum effort)
12
New cards
STEEPLE analysis
Social, Technological, Economic, Ecological, Political, Legal, Ethical
strategic planning tool used to focus on the opportunities and threats of the external environment that affects a business
strategic planning tool used to focus on the opportunities and threats of the external environment that affects a business
13
New cards
competitive advantage
the ability of an organization to produce goods or services more effectively than competitors do
14
New cards
economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises
15
New cards
Purchasing economies of scale
Buying resources in bulk to get a discount from suppliers
16
New cards
Technical economies of scale
Reductions in unit costs arising from the effective use of technology
17
New cards
Financial economies of scale
A situation where large firms are able to borrow money on better terms than smaller firms
18
New cards
Marketing economies of scale
marketing costs can be spread over a higher level of sales
19
New cards
Managerial economies of scale
Larger businesses can afford to hire specialist functional managers
20
New cards
diseconomies of scale
related to management problems of trying to control and direct an organisation with many thousands of workers
21
New cards
communication problems
large scale operations will often lead to poor feedback to workers. can lead to poor decision making due to inadequate or delayed information and management inefficiency
22
New cards
small buisness definition
less than 100 employees in US, 50 in Europe
23
New cards
Internal growth
expansion from within a business by expanding the range of products and/or locations and/or factories
24
New cards
External growth
When a business takes over or merges with another business
25
New cards
Merger
the combination of 2 similarly sized companies combined to form a new company
26
New cards
Takeover
when another company buys over 50% of the shares of a company and becomes controlling owner
27
New cards
aquisition
When a company purchases another company and takes over
28
New cards
Horizontal integration
acquiring a rival company in the same industry
29
New cards
Vertical Integration
the need to control the supply chain process either forward (towards the customer) or backwards (to monitor and secure raw material supplies)
30
New cards
conglomerate
Merger or takeover of a business in a different industry or market
31
New cards
joint venture
2 or more businesses agree to work closely together on a particular project and create a separate business division to do so
32
New cards
strategic alliance
a partnership formed to create competitive advantage on a worldwide basis
33
New cards
Franchising
a business that uses the name, logo, and trading system of an existing successful business
34
New cards
Globalization
the growing integration and interdependence of the world’s economies causing customers around the globe to have increasingly similar habits and tastes
35
New cards
multinational corporation
a company that operates, owns and controls resources outside of its country of origin
36
New cards
what is a business
* an entity which tries to combine human, physical and financial resources into processing goods and services to respond to and satisfy customer needs
37
New cards
the production process inputs - capital
* amount of money needed to run a business
* man-made goods like machines, buildings, vehicles and equipment needed for a business to operate
* investment - increasing spending on capital
* man-made goods like machines, buildings, vehicles and equipment needed for a business to operate
* investment - increasing spending on capital
38
New cards
the production process inputs - land
* space where business is operated
* raw materials and natural resources that are used in making a product
* raw materials and natural resources that are used in making a product
39
New cards
the production process inputs - labour and manpower
* physical and mental efforts of people to produce products/services
40
New cards
the production process inputs - enterprise/entrepreneurship
* management, organisation, and planning of other three factors of production
* actions of entrepreneur who shows initiative and takes risks to set up, invest and run a business
* actions of entrepreneur who shows initiative and takes risks to set up, invest and run a business
41
New cards
the production process outputs - products and services
* goods are physical products like, cars, computers, books and food
* services are intangible products like haircuts, bus rides, education and health care
* services are intangible products like haircuts, bus rides, education and health care
42
New cards
business functions
* human resources
* finance and accounts
* marketing
* operations
* finance and accounts
* marketing
* operations
43
New cards
primary sector
extracts raw materials
44
New cards
secondary sector
manufactures goods
45
New cards
tertiary sector
the service industry
46
New cards
quaternary sector
provides information services (IT)
47
New cards
reasons for starting a business
* pursuing a passion
* opportunity
* a good idea
* income potential
* new lifestyle
* autonomy/own boss
* challenge
* creativity
* opportunity
* a good idea
* income potential
* new lifestyle
* autonomy/own boss
* challenge
* creativity
48
New cards
steps in starting up a business
* identifying market opportunities
* sourcing capital (finance)
* determining a location
* building a customer base
* sourcing capital (finance)
* determining a location
* building a customer base
49
New cards
reasons why new businesses fail
* not investigating the market (market research)
* business plan problems
* too little financing
* bad location, internet pressure and marketing
* rigidity (not adapting to change)
* expanding too fast
* business plan problems
* too little financing
* bad location, internet pressure and marketing
* rigidity (not adapting to change)
* expanding too fast
50
New cards
problems faced by start ups
* competition
* building a customer base
* lack of record keeping
* lack of working capital
* poor management skills
* changes in business environment
* building a customer base
* lack of record keeping
* lack of working capital
* poor management skills
* changes in business environment
51
New cards
elements of a business plan
* business description
* competitor analysis
* management team and personnel
* marketing strategies
* operations
* financial forecasts
* competitor analysis
* management team and personnel
* marketing strategies
* operations
* financial forecasts
52
New cards
private sector
business owned and controlled by individuals or groups of individuals
53
New cards
public sector
organisations accountable to and controlled by central or local government. often provide essential goods and services for people
54
New cards
privatisation
the sale of a public sector organisation to the private sector
55
New cards
profit based organisations
* sole trader
* partnership
* private limited company (LTD)
* public limited company (PLC)
* partnership
* private limited company (LTD)
* public limited company (PLC)
56
New cards
sole trader
a business that is owned and controlled by one person
57
New cards
partnership
a legal agreement between 2 or more people to own, finance and run a business
58
New cards
private limited company (LTD)
shareholders are limited to family, friends and business partners. shares cannot be sold to the public
59
New cards
public limited company (PLC)
shares are listed on the stock exchange and can be freely bought and sold by anyone
60
New cards
unlimited liability
the financial obligation of business owners in the event of business failure is to repay all business debts (even if it means selling off their personal possessions)
61
New cards
limited liability
the financial obligation of business owners for business debts is no more than the amount of capital they invested in the enterprise. this is because business owners with limited liability have a separate legal identity from their business
62
New cards
non-profit and non-governmental organisations (NGOs)
charities and pressure groups
63
New cards
social enterprise
a proper business that makes its money in socially responsible ways and uses most of any surplus to benefit society
64
New cards
microfinance
aka microcredit, a type of banking service provided to unemployed or low-income individuals
65
New cards
cooperatives
people-centred enterprises, owned, controlled and run by and for their members to realise their common economic, social and cultural needs
66
New cards
corporation
a legal entity that is separate and distinct from its owners
67
New cards
mission statement
where an organisation formally sets out and publicises its core objectives. it declares an organisations purpose (present)
68
New cards
vision statement
where an organisation sets out where it would like to be in the long term (future) based on its core objectives
69
New cards
aim of mission and vision statements
* give strategic decision making an overall sense of direction
* provide employees and managers with a sense of strategic direction of the business
* motivate employees and managers within the business and provide them with a reference point for their own aims and values
* attract outside stakeholders such as customers, banks, and investors to an organisation
* provide employees and managers with a sense of strategic direction of the business
* motivate employees and managers within the business and provide them with a reference point for their own aims and values
* attract outside stakeholders such as customers, banks, and investors to an organisation
70
New cards
common business objectives
* survival/breakeven
* cost minimisation
* growth (market share)
* profit maximisation
* profit satisfaction - achieve enough profit to make owners happy but not making as much profit as possible
* cost minimisation
* growth (market share)
* profit maximisation
* profit satisfaction - achieve enough profit to make owners happy but not making as much profit as possible
71
New cards
aims
long-term goals that a business wants to achieve in the future
72
New cards
objectives
are targets set by an organisation to achieve its corporate aims
73
New cards
strategy
the long term plan that sets out the ways a business is going to achieve its corporate aims
74
New cards
tactics
specific techniques used by a business to achieve its objectives
75
New cards
ethical objectives
objectives influenced by moral values
76
New cards
corporate social responsibility (CSR)
where an organisation considers the interests of society by taking responsibility for the effects their decisions and activities have on customers, employees, communities, and the environment
77
New cards
SWOT analysis
a planning tool used by organisations as a method for guiding business strategy by considering the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
* strengths and weaknesses (internal)
* opportunities and threats (external)
* strengths and weaknesses (internal)
* opportunities and threats (external)
78
New cards
ANSOFF matrix
identify growth strategies. has 4 categories:
1. market penetration (existing products in existing market)
2. product development (new products in existing market)
3. market development (existing products in new market)
4. diversification (new products in new market)
1. market penetration (existing products in existing market)
2. product development (new products in existing market)
3. market development (existing products in new market)
4. diversification (new products in new market)
79
New cards
social
demographics such as
* population size
* population structure
* lifestyle
* age groups
* fashions or tastes
* education levels
* population size
* population structure
* lifestyle
* age groups
* fashions or tastes
* education levels
80
New cards
technological
* state of technological advancements
* introduction of new technologies
* infrastructure
* research and development costs
* introduction of new technologies
* infrastructure
* research and development costs
81
New cards
economic
* GDP growth rate
* inflation rates
* interest rates
* exchange rates
* the business cycle
* unemployment rates
* inflation rates
* interest rates
* exchange rates
* the business cycle
* unemployment rates
82
New cards
environmental
* weather and climate
* flora and fauna of the region
* environmental pressure group activity
* carbon footprints
* flora and fauna of the region
* environmental pressure group activity
* carbon footprints
83
New cards
political
* type of government
* attitude towards, free markets, imposition of tariffs, trade policies, business incentives offered and the stability of the government
* attitude towards, free markets, imposition of tariffs, trade policies, business incentives offered and the stability of the government
84
New cards
legal
* competition law
* health and safety at work
* consumer protection
* employee protection
* health and safety at work
* consumer protection
* employee protection
85
New cards
ethics
the code of ethics followed by most people in the region and the tendency of the people to be ethical, corruption, fair trade
86
New cards
gearing
the extent of a firms external borrowing
87
New cards
competitive advantage
ability to compete against domestic and international rivals
88
New cards
alienation of the workplace
employees lose sense of purpose and achievement and they can become demotivated
89
New cards
poor coordination and slow decision making
increasing department and number of countries a business operates in can lead to a businesses inability to make rapid decisions