Crude oil
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is crude oil?
It is a mixture of hydrocarbons
Describe the industrial process of fractional distillation separating crude oil into fractions
Crude oil is heated in a furnace and the gas is passed into the fractionating column
The oil evaporates at a range of temperatures and condenses due to the top of the column is cooler
When each hydrocarbon reaches a temperature lower than their boiling point, they condense into a liquid into various fractions
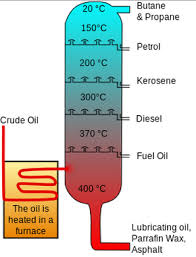
List the name and uses of the main fractions obtained from crude oil
Refinery gases - domestic heating and cooking
Gasoline - fuel for cars
Kerosene - fuel for aircraft
Diesel - fuel for some cars and trains
Fuel oil - fuel for large ships and in some power stations
Bitumen - surface roads and roofs
Describe trend of colour
Darker colour at the bottom, longer molecules
Describe trend of boiling point
The higher the column, the shorter the molecule, the lower the temp of vaporising and condensing, the lower the boiling point
Describe trend of viscosity
The higher the column, the shorter the molecule, the less viscous
What is a fuel?
It is a substance that releases heat when burned
What are the possible products of complete combustion?
carbon dioxide
water
What are the possible products of incomplete combustion?
carbon monoxide
water
Why is carbon monoxide poisonous?
Carbon monoxide reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of the haemaglobin. The lack of red blood cells lead to breathing difficulties and later death.
What are the products of nitrogen and oxygen can be produced in high temperatures of car engines?
nitrogen monoxide
nitrogen dioxide
How does combustion of some impurities in hydrocarbon fuels result in the formation of sulfur dioxide?
When the fuels are burnt, the sulfur is oxidised to form sulfur dioxide
How does sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen contribute to acid rain?
When they are emitted into the atmosphere, they react with rain water to creat H+ ions
What is cracking?
It is the process by which longer chain hydrocarbons are split into shorter, more useful hydrocarbons
What type of reaction is cracking
a thermal decomposition reaction
What are the conditions required for cracking?
Silica/ alumina as a catalyst
temperature of 600 - 700 'C
What are the expected products of cracking?
Alkanes
Alkenes
Why is cracking necessary?
The demand for smaller chained alkanes are greater, however the supply for longer chained alkanes are greater, therefore in need for cracking