Speech Disorders Module 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Hard Palate
The bony front part of the roof of the mouth, which separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. It plays a crucial role in speech production and articulation.
Soft Palate
The soft tissue at the back of the roof of the mouth, which aids in closing off the nasal passages during swallowing and is essential for certain speech sounds.
Pharynx
The muscular tube that connects the mouth and nasal passages to the esophagus and larynx, playing a key role in swallowing and speech production.
Velopharyngeal Mechanism
The system involving the soft palate and pharyngeal walls that controls airflow between the oral and nasal cavities, critical for proper speech production.
Embryonic
tissue related to the early stages of development in an organism, particularly in relation to the formation of structures like the palate.
Mandibular Processes
The paired structures that form the lower jaw during embryonic development, contributing to the formation of the mandible and lower lip.
Maxillary Processes
The paired structures that contribute to the formation of the upper jaw and parts of the face during embryonic development.
Frontonasal Process
The embryonic structure that contributes to the formation of the forehead and nose, playing a crucial role in facial development.
Maxilla
Upper jaw, fuses medially during embryogenesis to form the maxillary bone, which supports the upper teeth and contributes to the formation of the hard palate.
Mandible
The lower jawbone that holds the lower teeth in place and is the only movable bone of the skull.
Philtrum
The vertical groove between the base of the nose and the upper lip, formed during embryonic development.
Philtrum Ridge
The raised area on either side of the philtrum that contributes to lip shape and facial aesthetics.
Faucial Pillars
The vertical folds of tissue located at the back of the oral cavity that form the boundary between the oral cavity and the oropharynx, playing a role in swallowing and speech.
Median Palatine Suture
The fibrous joint that connects the two palatine processes of the maxilla, running down the center of the hard palate.
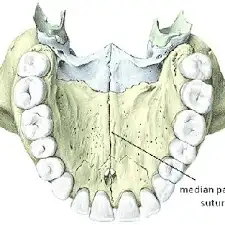
Incisive Foramen
The opening in the bone located at the anterior part of the hard palate, allowing for the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
Alveolus
The bony socket in the jaw that holds the roots of the teeth, playing a crucial role in dental health and oral function.
Nasal Septum
The cartilage and bone structure that divides the nasal cavity into two nostrils, playing a key role in respiratory function and airflow.
Premaxilla
a small, triangular-shaped bone located at the front of the upper jaw
Velopharyngeal Valving
The mechanism that controls the airflow between the nasal cavity and the oral cavity during speech and swallowing, crucial for producing certain speech sounds.
Velopharyngeal Port
The opening between oral and nasal cavities, important for speech, blowing, whistling, sucking, swallowing, vomiting
Important for all vowels and most consonants
Velopharyngeal Incompetence (VPD)
Velopharyngeal valve does not close consistently and completely during the production of oral sounds, results in abnormal resonance, airflow and articulation
Craniofacial Anomalies
Malformations that affect the head and face, and often cause speech problems.
Complete Cleft Lip
Separation of upper lip tissue into the nostril floor
Incomplete Cleft Lip
Minor “V” shaped notch in vermilion border
Complete Cleft Palate
Hard palate and Soft Palate are deformed
Incomplete Cleft Palate
Soft palate is only deformed
Overt Submucous Cleft
Muscular cleft in the region of the soft palate. It is covered by thin layer of mucosal membrane.
Sometimes not detected until later in childhood
Some signs that it is present are:
Bifid uvula
Bluish color/furrow in the middle of the soft palate zona pellucida
Notch that can be felt in hard palate
Occult Submucous Cleft
Upon oral mechanism evaluation, the palate appears normal; Lacks the classic triad; However, the muscle fibers are abnormally oriented (as in a submucous cleft).
Microform Cleft Lip
a mild form of cleft lip that appears as a notch or slight indentation in the lip
Causes of Speech Disorders Secondary to Cleft
Nasal Obstruction
Short Upper Lip
Dental/Occlusal Abnormalities
Palatal Fistula
Hearing Loss
Tonsils and Adenoids
Velopharyngeal Dysfunction
Obligatory Error
Caused by structural abnormalities, requires physically management or surgery to correct
Compensatory Errors
Learned maladaptive articulations, can be treated with speech therapy
Eustachian tube
The tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, helping to equalize air pressure in the ear and drain fluid from the middle ear
Tensor Veli Palatini
Tenses palate, it helps open the Eustachian tube to equalize pressure
Conductive Hearing Loss
cause of speech disorders secondary to clefts, pressure equalizing tubes often used to help
Hypernasality
most perceptible on vowels, sounds like /s/, /b/, /k/, results from too much sound resonating through the nose, certain letters and sounds should not have air escaping through the nose during speech, almost always requires surgical or prosthetic management
Hyponasality
results from too little air escaping through the nose (sounds like talking with a stuffy nose), most perceptible on nasal consonants, but also vowels
Cul-de-sac resonance
where sound gets trapped within a cavity in the vocal tract (like the throat or nose), causing speech to sound muffled and low in volume due to a blockage at the exit of that cavity
Mixed Nasality
when a person has hypernasal resonance on sounds that should not be nasalized and they are hypo nasalized on the other sounds
Nasal Fricatives
Compensatory articulation, directs air through their nose instead of their mouth
Pharyngeal Plosives
stopped air flow between tongue and posterior pharyngeal wall
Pharnyngal fricatives/affricate
Turbulent air flow between tongue and posterior pharyngeal wall
Glottal stop
Vocal folds adduct and open (like a grunt)
Nasal Emission
air audibly goes through the nose, Air from nose during speech due to leak in VP valve, Occurs in pressure-sensitive consonants such as plosives, fricatives, and affricates, particularly voiceless
Dysphonia
Hoarseness, Raspy or strained voice, weak voice, voice fatigue
Oral Mechanism Evaluation
Dentition and occlusion, Oral cavity size for tongue movement and placement, Presence of fistulae, Signs of submucous cleft, Movement and symmetry of the uvula, Size of the tonsils, Signs of upper airway obstruction (mouth breathing), Signs of oral motor dysfunction (movement and coordination of articulators), Use /ae/ not /ah/ (mouth opens bigger!)
Perceptual Ratings
Best way to assess is during connected speech. An alternative test includes asking client to produce a sentence full of oral sounds (e.g., Stop the bus) with the nose unoccluded and then occluded.
Nasal Emission Tests
Seescape, Straw (put a straw in the child’s nose and see if you hear the noise), Mirror (Put a mirror under a kid’s nose and see if it fogs up)
Instrumental Procedures
Nasometry, nasopharyngoscopy, some centers use pressure flow studies
Videofluoroscopy
Direct, Allow view of valve, especially elevation of velum and length of pharyngeal wall, Radiation exposure; not good for small openings
Nasoendoscopy
Examines the nasal cavity, including the sinuses, Commonly used by ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists, Can be performed with moderate sedation and local anesthesia
Nasopharyngoscopy
Direct, Good for viewing small VP openings and vocal folds, Invasive/uncomfortable, use of nasal spray, Can be used to assess the soft palate and velopharyngeal dysfunction (VPD), Can be used to evaluate voice disorders
Aerodynamic Instrumentation
Indirect, Measures air pressure in VP functions, Cannot see VP valve
Seescape
detects nasal emissions
Nasometer
Measures acoustic energy from oral and nasal cavities, Gives an objective nasalance score: ratio of oral/total (nasal plus oral) energy
Craniofacial Team
Speech therapy, Dental and orthodontic treatment, prosthetic appliances, surgery
Dental/Orthodontic Treatment
Maxillary expansion device (preschool), Bone graft to alveolus (~ 7 yrs), Maxillary advancement surgery (14–19 yrs old)
Surgical Repair
Cleft lip: Generally repaired in 1-2 stages at 2.5-6 months of age Goal: optimal aesthetic outcome; Cleft palate: Generally repaired around 9-12 months, may require secondary Goal: functional, normal speech (Good resonance, Adequate intra-oral pressure)
Prosthetic Appliances
Use of palatal lift, palatal obturator, or speech bulb obturator
Speech Therapy
Considered ineffective and inappropriate as a means to correct VPD when there is inappropriate nasality or nasal emission due to abnormal physiology. Therapy is effective and appropriate for: Compensatory articulation problems secondary to VPD that cause nasal emission, Misarticulations that cause nasal air emission or hypernasality that is phoneme specific, Hypernasality or variable resonance due to apraxia, Hypernasality or nasal emission following surgical correction
Pharyngeal Flap
Suture flap from posterior pharyngeal wall to velum
Pharyngeal Augmentation
Inject substance into posterior pharyngeal wall
Sphincter Pharyngoplasty
Suture posterior faucial pillars to posterior pharyngeal wall
Furlow Z-Plasty
Lengthen velum
Palatal Lift
useful for inadequate muscle control
Palatal Obturator
useful for nasal regurgitation during feeding
Speech Bulb
useful for speaking and swallowing, aiming to improve function, speech, and, ultimately, quality of life for the patient
Velocardiofacial Syndrome
Often called Digeorge syndrome, has VPD, minor cardiac anomalies, microcephaly, long face, small jaw, thin upper lip, wide nasal bridge, Delayed speech and language development, Learning disabilities
Robin Sequence
Small jaw that is also posteriorly placed, Posteriorly placed tongue, Horseshoe shaped palatal cleft
Stickler Syndrome
Groups of hereditary conditions characterized by flattened face, eye problems, hearing loss and joint problems, Genetic mutations affect production of collagen, Pierre Robin Sequence common
Hemifacial Microsomia
Also known as Facio-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum and Goldenhar syndrome, Unilateral hypoplasia of face, Hearing loss
Crouzon Syndrome
Wide-shaped skull, Wide-spaced eyes, Protruding eyes, Small maxilla: Hyponasality, Cleft palate, Hearing loss, Learning difficulties
Treacher Collins Syndrome
Underdeveloped cheekbones, maxilla and mandible, Downward slant of eyes, Robin sequence common, Cleft palate and VPD
Micrognathia
a condition where the lower jaw (mandible) is significantly smaller than normal
Retrognathia
a dental and skeletal condition where the lower jaw (mandible) is positioned too far back in relation to the upper jaw (maxilla)
Glossoptosis
a condition where the tongue falls backward and obstructs the airway
Distraction Osteogenesis
a surgical technique that involves gradually separating two segments of bone to create new bone in the gap
Hypertelorbitism
Wide-spaced eyes
Exorbitism
Protruding eyes