Core Practical 6: Chlorination of 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is reflux
the continuous vaporation and condensation of volatile reactants/reagents until a reaction is complete
heatign under reflux equiptment
- round bottom flask (pear shaped)
- reflux condenser with water entering at the bottom and leaving on the top
- top of the reflux condenser being open
- the flask being heated using an electric heater, water or oil bath or a sand tray
- anti-bumping granules
when can reflux be used
- oxidising a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid
- oxidising a secondary alcohol to a ketone
- converting a holgenoalkane to an alcohol
- converting an alcohol to a bromoalkane by reacting it with potassium bromide and 50% sulfuric acid
distillation meaning
distillation is a method used to seperate liquids with different boiling points, by evaporation (boiling) and condensation
what is fractional distillation
used to separate liquids with similar boiling points (within 25 degrees Celsius), by evaporation and condensation using a fractionating column
distillation equiptment
- round-bottomed or pear-shaped flask containing the mixture
- a still-head filled with a thermometer, the bulb of which must be positioned level with the outlet of the still-head
- condenser with the water going in at the bottom and leaving at the top
- an open receiving vessel, such as a beaker, or an adapter open to the air joined to a flask
- the flask being heated using electrical heater, a water or oil bath or sand tray
safety precautions (reflux & distillation)
- distillation or heating under reflux must be carried out if you covered if a vapor of one of the reactants or products is harmful poisonous or irritant
- if a mixture is being heated under reflux or distilled, there must be some outlet to the air. if there is not, pressure will build up in the apparatus which will then fly apart, spraying hot, flammable, and often corrosive liquid around
- gloves should be worn when corrosive substances are being used. such substances must always be handled with care
- the flask she never be heated with a naked bunsen flame. this is because almost all organic substances are flammable and if the liquid being heated were to you spill over the flask or crack, a fire would result
Synthesis of a haloalkane from an alcohol
Measure 8 cm3 of 2-methylpropan-2-ol in a measuring cylinder
Pour the 2-methylpropan-2-ol into a separating funnel
Using a fume hood, add 20 cm3 of concentrated hydrochloric acid to the separating funnel in small portions of 2 - 3 cm3 making sure to release the pressure by opening the stopper after each addition
Leave the separating funnel to stand in the fume hood for 20 minutes and gently shake the separating funnel at 2 minute intervals
Allow the layers to separate and dispose of the lower aqueous layer by opening the tap
Add add sodium hydrogen carbonate solution in small portions to the funnel and gently shake the funnel, again, release the pressure at regular intervals
This removes acidic impurities
Once these layers have separated, open the tap once more and dispose of the queues layer
Pour the organic layer into a clean dry conical flask and add two spatulas of magnesium sulfate
This will remove water
Once clear, decant the liquid into distillation apparatus
Distill the liquid and collect the distillate in the range of 47 - 53oC
why fume cupboard required
This practical requires a fume hood as concentrated hydrochloric acid is very volatile at room temperature and hydrogen chloride gas is released from the solution quickly when the cover to a container or bottle is removed.
Why is CaCl2 used?
To ensure unreacted alcohol goes into lower layre
Why is NaHCO3 used?
To react with acid and remove acid impurities
why is bung opened
To release pressure from CO2 produced
How do you know that chlorination reaction is complete?
Turns from cloudy to clear
What safety precautions needed in chlorination?
- 2 methylpropan2-ol is flammable
- HCl is toxic, carry out in fume cupboard
- Wear gloves so reactancts don't contact skin
- CaCl2 is irritant
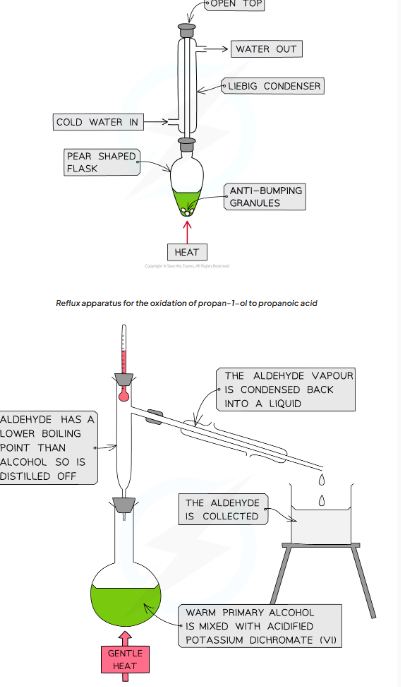
Synthesis and purification of propanal and propanoic acid
Carefully add 20 cm3 of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution, K2Cr2O7 (aq), to a 50 cm3 pear-shaped flask and cool the flask in an iced water bath
Set up the reflux apparatus keeping pear shaped flask cool
Place anti-bumping granules into the pear shaped flask
Measure out 1 cm3 of propan-1-ol
Using a pipette, slowly add the propan-1-ol drop wise into the reflux condenser
When the propan-1-ol has been added remove the ice bath and allow to warm up to room temperature
Position the flask over an electric heater or in a water bath and heat for 20 minutes
Propan-1-ol is flammable, therefore. naked flames should not be used when heating which is why the use of an electric heater or water bath is an important safety precaution
Purify the product using distillation apparatus
Hazards, risks and precautions of oxidation of propan-1-ol
The alcohols used are flammable and often harmful to health, e.g, propan‐1‐ol, butan‐1‐ol, pentan‐1‐ol
The alcohols should be kept away from naked flames, e.g. a Bunsen burner
Avoid contact with the skin and breathing in the vapour
A fume cupboard can be used for harmful alcohols
Potassium dichromate is a strong oxidising agent and should be handled with care
Spillages should be mopped up right away with plenty of water
why are anti-bumping granuels used?
anti bumping granules prevent teh mixture from boiling over and rising into the condenser. They break up large bubbles so the mixture boils more smoothly
Why is ice bath used in oxidation?
Propan-1-ol has a low boiling point, so it doesn't evaporate