gen bio- lecture 1: memory and learning
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 1 key things to remember
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
neurons
excitable cells that transmit signals
synapse
junction where a neuron sends a chemical signal to another cell
process of learning/memory making (5 steps)
nerve impulse/electrical impulse
presynaptic terminal/presynaptic neuron
neurotransmitter
ion channel with receptor site @ synaptic cleft/synapse
postsynaptic neuron
** creates physical change in the brain to form new connections
neuronal development (when does it occur)
occurs before birth
gene expression is…
HOW dna is used
signal transduction is…
WHEN expression of a gene occurs
neuronal plasticity
“nerve cell remodeling”
modifying connections throughout life based on EXPERIENCES
connection between activity @ synapse and memory
amount of activity @ synapse tells brain what is important —> retention
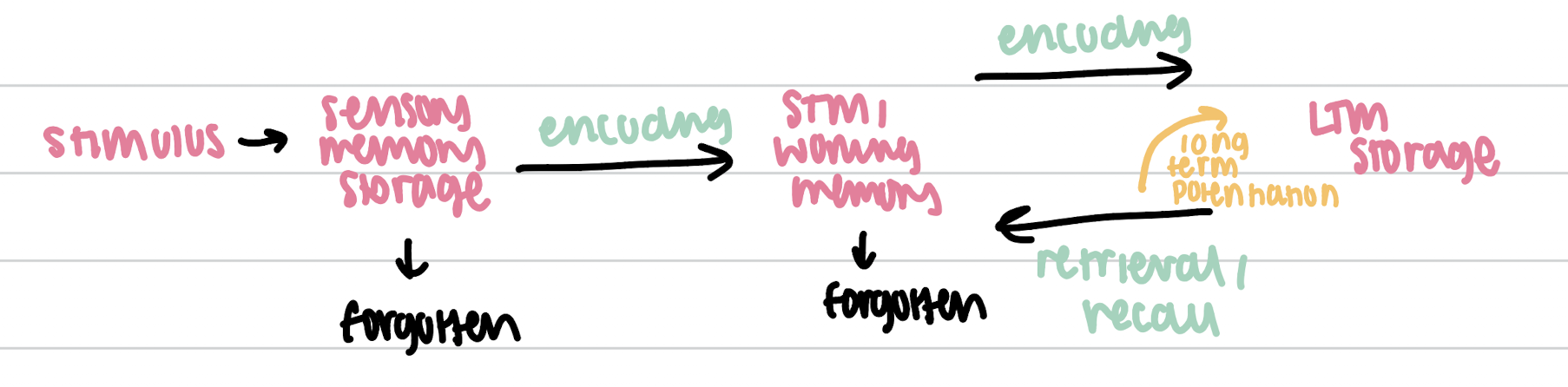
memory
“storage”
process where data/info is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed
learning
“application”
use of memory to reduce the likelihood of a negative outcome
sensory memory
what you experience (5 senses)
short term/working memory
what you are aware of NOW
held for a short amount of time
7 ± 2 items (5-9 items)
long term memory
permanent connections in brain
unlimited storage
methods of getting things into long term memory (6 ways)
repeating info
chunking: associating things in chunks
mnemonic devices
self-referencing/connecting
teaching it
spacing out information
encoding
translating info from outside into something our brain understands
retrieval
bring stored memory from LTM to STM
long term potentiation
a PROCESS not a type of memory
persistent strengthening of the synapse based on your activities
creates PHYSICAL change in brain and long lasting increase in signaling between neurons
figure for this process