b2 - scaling up
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dosnt include labelling of the heart for that visit :https://www.geoguessr.com/vgp/3805
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
whats a concentration gradient
occurs when the concentration of particles is higher in one area than another- like a gradient/slope of concentration
what does it mean when somethings against a concentration gradient
moving from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration ( like going uphill)
what does it mean when somethings going down a concentration gradient
moving from and area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (like going downhill)
how does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion
the bigger the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
in what substances does diffusion happen
in liquids and gases
what are the 3 ways substances can move in and out of cells
diffusion
active transport
osmosis
whats active transport
movement of particles across a membrane from a lower to a higher concentration - against a concentration gradient (opposite of diffusion)
what are the differences between active transport and diffusion
active transport requires energy, diffusion dosnt
active transport is against the concentration gradient whereas diffusion is down a concentration gradient
whats a partially permeable membrane
a membrane with very small holes in it to allow small molecules through but larger molecules cant pass through
what kind of molecule can diffuse through cell membranes
small molecules e.g. glucose, amino acids water and oxygen
big molecules e.g. starch and proteins cant fit through the membrane
whats water potential
the potential (likelihood) of water molecules to diffuse out or into a solution
what does it mean of you have high water potential
you have a high concentration of water molecules
true or false - water can pass both ways across a membrane during osmosis
true - water molecules move about randomly all the time
what are turgid cells
cells full of water by the process of osmosis
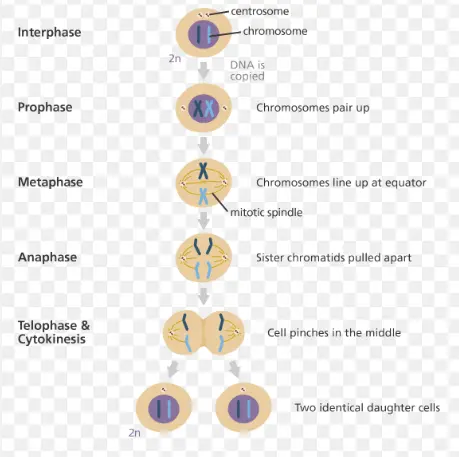
what are the 4 stages in the cell cycle of mitosis
gap phase 1
synthesis
gap phase 2
mitosis
what happens in gap phase 1 in the cell cycle
the cell grows and new cell protein and structures are made
what happens in synthesis in the cell cycle
the cell replicates its DNA so when it splits during mitosis the two new cells will contain identical DNA
how id DNA replicated during synthesis
molecule of DNA splits
bases on free floating nucleotide pair up with matching bases on the DNA
cross ties link between the new and old DNA bases and so the new nucleotide join together so two new DNA molecules identical to the original one are formed
1. the cell has 2 copies of its dna all spread out in long strings
2. before the cell divides, the dna forms x shaped chromosomes
3. the chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and the cell fibres pull them apart. the two arms of each chromosomes got to opposite ends of the cell
4. membranes form around each of the sets of chromosomes. These become the nuclei of these new cells
5. you now have two cells containing the same dna to each other and the parent cell
* dont have a nucleus so can carry more oxygen
* small and flexible so can pass easily through capillaries
what are stem cells
undifferentiated cells which can divide by mitosis to become new cells which can then differentiate
where are stem cells present
embryos
adult animals
meristems in plants
what are the uses of embryonic stem cells
can grow into any type of cell found in the body
all tissues and organs can be potentially regrown
however transplanted tissues and organs may be rejected by the patients immune system
difficult to obtain and store embryonic stem cells
what are the uses of adult stem cells
Adult stem cells are found only in specific areas of the body and can only develop into a limited number of cell types e.g. bone marrow, breasts and intestines.
however as from the same body, would not reject their own cells
why are stem cells so important
because they have the potential to develop into different types of cells in the body which can be used for development, growth and repair
surface area - larger surface area, higher number of particles able to move in given time
what are the 3 main factors affecting the movement of substances
surface to volume ratio
temperature
concentration gradient
how does the surface to volume ratio affect the movement of substances
rate of diffusion,osmosis or active transport is higher in cells with larger surface area to volume ratio
how does the temperature affect the movement of substances
as the temperature increases, particles move in and out of cells faster as they have more energy
how does the concentration gradient affect the movement of substances
substances move in and out of the cell faster if theres a big difference in concentration between the inside and outside of the cell
of there are more particles on one side, there are more there to move across
why is diffusion quicker in a single celled organism
substances can diffuse straight into and out across the membrane as they only have to travel a short distance
they have a relativity large surface area to volume ratio which means they are able to exchange enough substance across the cell membrane to supply the volume of the cell
why is it more difficult to diffuse substances in multicellular organisms
its too slow as some cells are deep inside the organism meaning its a long way from them to the outer environment
larger organism have a low surface area to volume ratio meaning you cant supply enough substances through the small outer surface for the large volume organism
how do multicellular organisms exchnange substances
they cant do it through their outer membrane so have to use specialised exchange surfaces
what are some examples of transport systems in animals
circulatory system and the digestive system
what are examples of transport systems in plants
xylem and phloem
how are exchange surfaces in specialised exchange organs adapted to maximise effectiveness
walls are thin so only have short distance to travel
large surface exchange area
in animals have lots of blood vessels to get stuff in and out of the blood quickly
permeable membranes
how are the lungs adapted for gas exchange
the alveoli where the gas exchange takes place have a large surface area, thin walls, a good blood supply and a moist lining for dissolving gases
how are villi adapted to exchange nutrients
small intestine contains villi dissolve food molecules are absorbed quicker into the blood
they have a single layer of surface cells whihc increase surface area
have a very good blood supply to assist quick absorption
explain how the structure of a leaf allows gases to diffuse in and out of cells
leaves are broad so have a large surface area for diffusion
they’re thin which means gases only have to travel a short distance
air spaces inside the leaf lets gases move easily between the cells and increases the surface area increasing the chance of oxygen to get into cells
underneath of leaf covered in stomata through which carbon dioxide diffuses into leaf and water vapour diffuses out
describe the transport of water and mineral ions into a root hair cell
water is drawn into root hair cell by osmosis as there is usually a higher concentration of water in the soil than inside the plant
mineral ions move into the root hair cell by active transport since the concentration of minerals is usually higher in the root hair cells than the soil (otherwise minerals would diffuse out of the root hair cells)
how are root hair cells adapted to take in water and mineral ions
cells on plant roots grow into long hairs which stick out into soil
each branch of root covered in these microscopic hairs
gives plant big surface area for absorbing water and mineral ions from soil
what are the advantages to mammals having a double circulatory system
returning blood to the heart after its picked up oxygen at the lungs means it can be pumped out around the body at a higher pressure
this increases rate of blood flow at the tissues (blood can be pumped around body faster) so more oxygen is delivered to the cells
important for mammals ad take up a lot of oxygen maintaining body temp
describe the route that of blood in a double circulatory system
blood flows into two atria from vena cava and pulmonary vein
atria contracts pushing blood into the ventricles
the ventricles contract forcing blood into pulmonary artery and the aorta and out the heart
blood then flows into organs through arteries and returns through veins
the atria fills up again and the cycle starts over
what are the 3cdifferent types of blood vessels found in the circulatory system
arteries
capillaries
veins
how are arteries adapted to their function
heart pumps blood out at high pressure so the artery walls are strong and elastic
walls are thick compared to size of lumen
contain thick layers of muscle to make them strong and elastic fibres to make them stretch and spring back
how are capillaries adapted to their function
carry the blood really close to every cell in the body so can exchange substances with them
permeable walls so substances can diffuse in and out
supply food and oxygen and take away waste (co2)
walls one cell thick - increases rate of diffusion
how are veins adapted to their function
blood is at low pressure so walls dont need to be as thick
bigger lumen than arteries to help blood flow
valves to keep blood flowing in right direction
why is the left ventricular wall thicker than the right ventricular wall
has to pump blood further around the body compared to the right side
what side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
the right side of the heart
whats the functions of valves in the heart
valves stop the blood from flowing backwards
how is cardiac muscle adapted to its function
cardiac muscle contains lots of mitochondria to provide the cells with ATP so the cardiac muscle can contract
what is plasma
liquid that carries everything in blood
what are 2 waste products carried away in plasma
carbon dioxide ( carried from body cells to the lungs to be breathed out)
urea ( carried from liver to the kidneys where its removed in urine)
how is plasma adapted to its function
Plasma is clear and watery. This makes it suitable to transport molecules as many of them are soluble in water.
what is the function of red blood cells
to transport oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in the body
how are red blood cells adapted to their function
small and biconcave disc shape to give large surface area to volume ratio for absorbing + releasing oxygen
dont have a nucleus - frees up space for more haemoglobin so they can carry more oxygen
small and flexible so can pass through capillaries
whats the importance of haemoglobin in red blood cells
enables red blood cells to carry oxygen around the body
in the lungs, haemoglobin binds to oxygen to become oxyhaemoglobin
in body tissues oxyhaemoglobin splits up to release oxygen to the cells
* phospherous to make dna and cell membranes
whats the transpiration stream
the movement of water through the xylem tissue
why is the transpiration stream constant in a plant
evaporation and diffusion of water from the leaves create a shortage of water in the leaves
means more water is drawn up from the rest of the plant through the xylem vessels to replace it
causes more water to be drawn up through the roots
whats the 4 benefits of the transpiration stream in a plant
constant stream of water from ground helps keep plant cool
provides plant with constant supply of water for photosynthesis
water creates turgor pressure in the plant cells to help support the plant and stop it wilting
minerals needed by the plant can be bought in from soil along with the water
how are phloem adapted to their function
cells are arranged end to end to form phloem tubes with sieve plates inbetween them to allow movement of substances through the plant
whats the 3 things transpiration rate affected by
increase in light intensity
increase in temperature
increase in air movement
how is the transpiration rate affected by an increase in light intensity
brighter the light, greater the transpiration rate
increases the rate of photosynthesis causing stomata to open and let c02 in
stomata close when dark as photosynthesis cant happen in the dark
when stomata are closed water cant escape
how is the transpiration rate affected by an increase in tenperature
the warmer it gets , faster transpiration happens
when warm, water particles have more energy to evaporate an diffuse out of stomata
how is the transpiration rate affected by an increase in air movement
lots if air movement (wind) around leaf transpiration happens faster
if air around leaf is still water vapour surrounds leaf and dosnt move away
means high concentration of water particles outside of leaf as well as inside it so diffusion dosnt happen as quickly
if windy, water vapour is swept away maintaining low concentration of water in the air outside leaf
what are some adaptations plants have to reduce water loss from their leaves
waxy cuticle to make it waterproof
more stomata on lower side of leaf to slow diffusion as its more protected from the wind and cooloer
a shrub lives in a dry desert. Its stomata are small and located on the lower surface of its leaves. How does this help the shrub survive in the desert
having stomata on lower surface of leaf slows diffusion ad its more protected from wind and cooler
small stomata helps reduce water loss which helps it survive as low availability if water means it needs to conserve as much water as it can
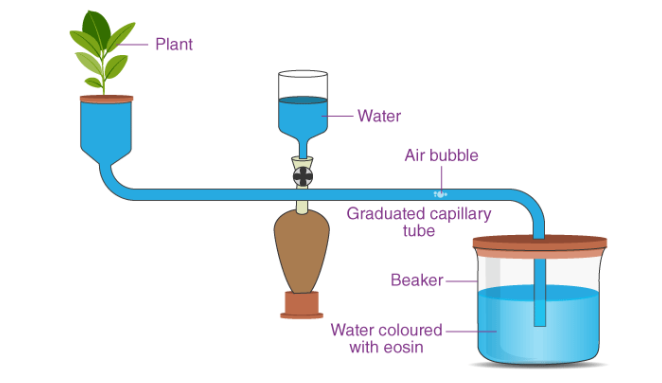
2. Assemble the potometer in water and insert the shoot underwater.
3. Remove the apparatus from the water but keep the end of the capillary tube submerged in a beaker of water.
4. Check that the apparatus is water and air tight.
5. Dry the leaves and allow the shoot time to acclimatise and then shut the tap.
6. Remove the end of the capillary tube from the beaker of the water until one air bubble has formed, then put the end back into the water.
7\. Record the starting position of the air bubble.
8\. Start the stopwatch and record the distance moved by the bubble per unit time, the rate of air bubble movement is an estimate of the transpiration rate.