9.5 Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
distinguished by their maximal shortening velocities and the predominant pathway they use to form ATP: ∙
slow-oxidative fibers (type 1) ∙
fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers (type 2A) ∙
fast-glycolytic fibers (type 2X)
Describe why there are differences in maximal shortening velocities
due to different myosin enzymes with high or low ATPase activities, giving rise to fast and slow fibers.
Describe oxidative, glycolytic and fast-glycolytic fibers?
Oxidative fibers have many mitochondria and possess a high amount of the oxygen-binding protein myoglobin.
Glycolytic fibers have few mitochondria but have a high concentration of glycolytic enzymes and little or no myoglobin.
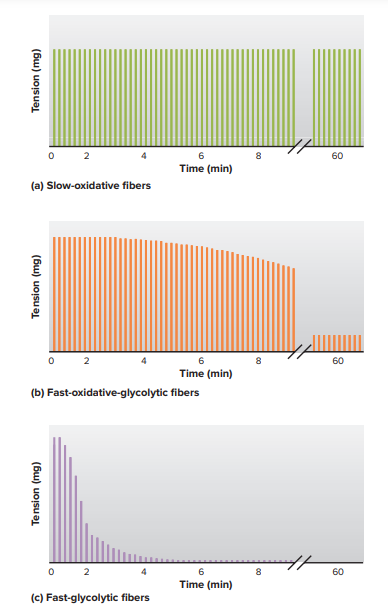
Fast-glycolytic fibers have a larger average diameter than oxidative fibers and therefore produce greater tension, but they also fatigue more rapidly.
What are the major characteristics of the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Slow-oxidative fibers (type 1) have relatively low myosin-ATPase activity and high oxidative capacity. They generally are the smallest-diameter fibers and generate the least tension, but are very resistant to fatigue because they have many mitochondria. Fast Oxidative-glycolytic fibers (type 2A) have high myosin-ATPase activity and high oxidative capacity (and intermediate glycolytic activity). They are intermediate in size and generate intermediate tension; they are somewhat able to resist fatigue. Fast-glycolytic fibers (type 2X) have both high myosin-ATPase activity and high glycolytic capacity. They are typically the largest fibers, generate the greatest tension, have few mitochondria, and fatigue rapidly.
How is ATP used in skeletal muscle?
What are type I fibres Slow-oxidative fibres vs type II fibres Fast-glycolytic fibres in terms of characteristics
Type I fibres Slow-oxidative fibres
– Smaller in size – High mitochondrial density – High capillary density – Much myoglobin
Type II fibres Fast-glycolytic fibres
– Larger in size – Low mitochondrial density – Low capillary density – No myoglobin
What is the rate at which muscle fatigue develops in the fibres?