Textile Fibers: Types, Properties, and Identification Methods
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are natural fibers?
Fibers found in nature, obtained from plants or animals.
What are the sources of plant fibers?
Plant fibers come from stems, leaves, and seeds.
Name three types of animal fibers.
Wool, cashmere, and mohair.
What are manufactured fibers made from?
Manufactured fibers are made from a chemical solution.
What is a spinnerette?
A device used to create filaments in the production of manufactured fibers.
What are the three techniques used to produce filament fibers?
Dry spinning, wet spinning, and melt spinning.
What determines fiber structure?
Fiber structure is determined by physical attributes, chemical composition, and molecular formation.
What are some physical properties of fibers?
Length, shape, surface, longitudinal configuration, and diameter.
How are fibers classified by chemical composition?
Fibers with similar chemical composition are grouped in the same category.
What are the properties of fiber performance?
Abrasion resistance, absorbency, chemical effects, cover, elasticity, environmental conditions, flammability, flexibility, hand, luster, pilling, resiliency, static electricity, strength, thermoplasticity, and wicking.
What is abrasion resistance in fibers?
The ability to resist wear from rubbing; some fibers like nylon have high abrasion resistance.
What does absorbency refer to in fibers?
The ability of a fiber to take in moisture; hydrophilic fibers absorb water easily.
What factors affect the chemical effects on fibers?
The type of chemical, its strength, and the time of exposure.
What is the cover property of fibers?
The ability to occupy an area; thicker fibers cover more area than thin fibers.
Define elasticity in fibers.
The ability to increase in length under tension and return to original length when released.
How do environmental conditions affect fibers?
Different fibers react differently; for example, wool needs mothproofing, while nylon can lose strength in sunlight.
What are the classifications of fibers based on flammability?
Fibers can be flammable, flame-resistant, or flameproof.
What does flexibility in fibers refer to?
The capability of a fiber to bend easily without breaking; thinner fibers usually have better drapability.
What is meant by the 'hand' of a fiber?
The way a fiber, yarn, or fabric feels when handled, influenced by its shape, surface, and configuration.
What factors affect the luster of fibers?
Luster is affected by the smoothness of the surface, crimp, cross-sectional shape, and fiber length.
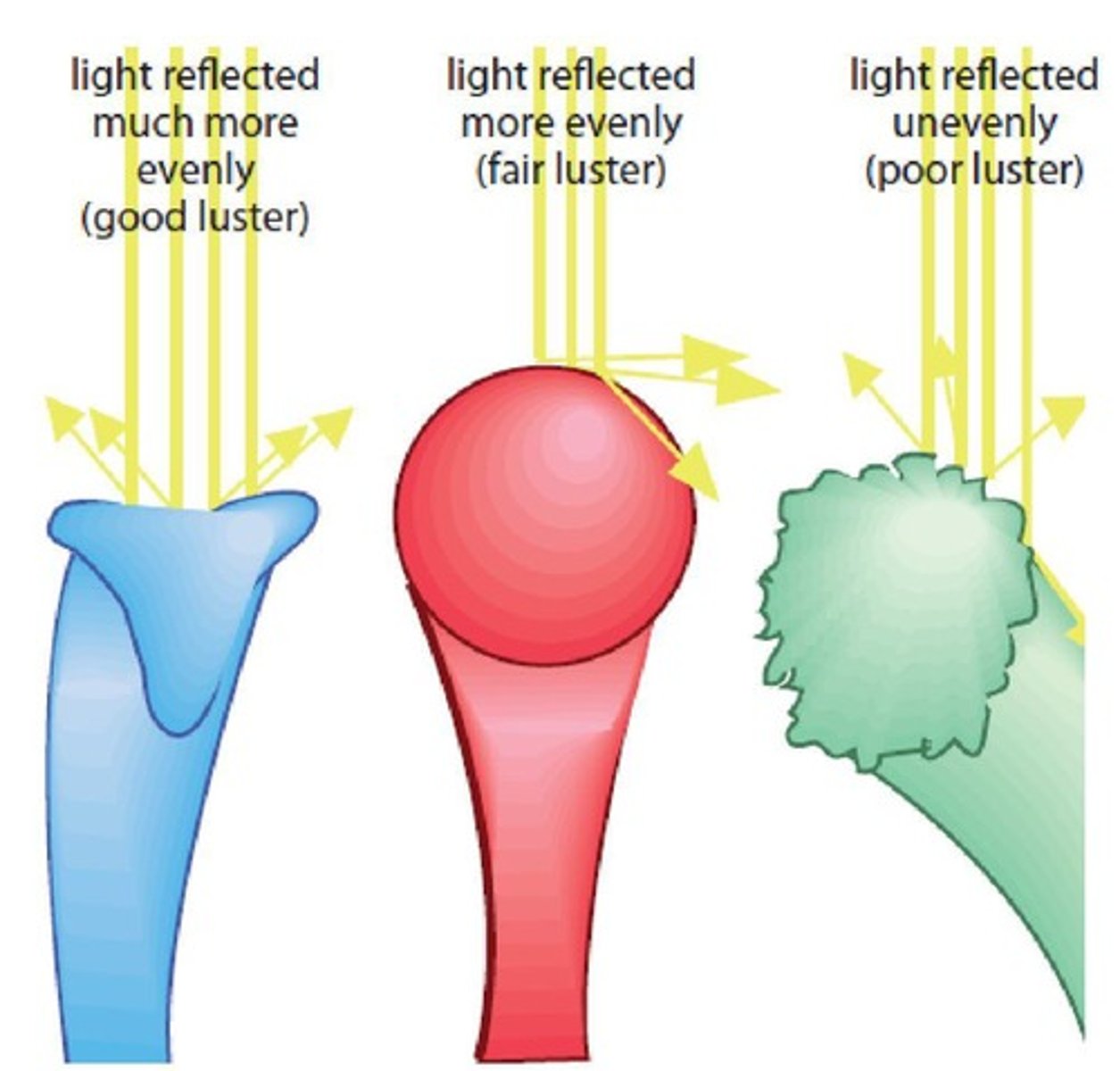
What is pilling in fibers?
The formation of groups of short or broken fibers on the surface of the fabric.
Define resiliency in fibers.
The capability of a material to spring back to shape after being creased, twisted, or distorted.
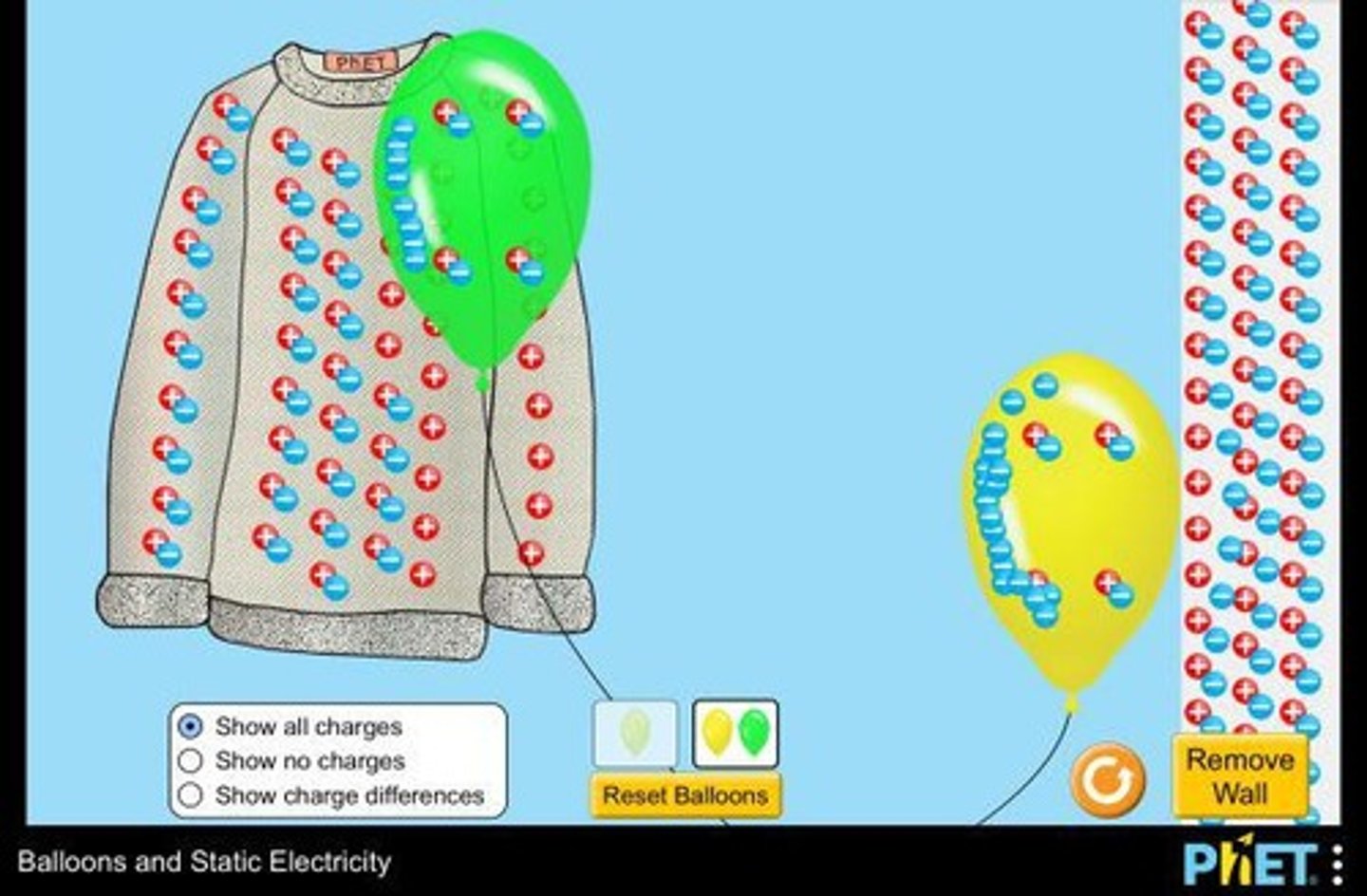
What is static electricity in fibers?
The frictional electric charge caused by rubbing two dissimilar materials, leading to effects like clothing clinging.
What does strength refer to in fibers?
The fiber's ability to withstand stress; strong fibers include glass, nylon, and polyester.
What is thermoplasticity in fibers?
The ability of fibers to withstand heat exposure; thermoplastic fibers can soften and be molded when heated.
What is wicking in fibers?
The ability of a fiber to transfer moisture from one section to another, desirable in workout clothes.
How can fibers be identified?
Through burning tests that assess melting or burning characteristics, odor of fumes, and residue appearance.
What sectors does the textile industry supply?
Apparel, interior furnishings, and industrial products.
What are the major segments of the textile industry?
Fibers, yarns, fabrics, dyeing, printing, and finishing.
Which countries are significant in international textile trade?
China, Middle East, Italy, and the Americas.
What percentage of U.S. textile and apparel imports in 2019 were apparel products?
75.3 percent.
What was the value of fiber, textile, and apparel exports from the U.S. in 2020?
$25.4 billion.
What factors affect the textile industry?
Technology, economy, political environment, and climate change.
What are textiles used for in interiors?
Furniture, bath, kitchen, and bed applications.
What are industrial textiles used for?
Luggage, flags, boat sails, bandages, and dust filters.
What does 'put-up' refer to in textiles?
Fabric packaging, including shorts, remnants, and pound goods.
What is a textile mill?
A company that owns textile machinery and makes fabric.
What is the role of converters in the textile industry?
They buy greige (unfinished) goods to have dyed or finished.
What are jobbers in the textile industry?
Buyers from mills, converters, and garment manufacturers, often purchasing discontinued items.
What is the primary source of fabrics?
Mills, converters, and importers.
What is the significance of overseas agents in the textile industry?
They represent exporters or importers overseas, essential for international business.
What is the impact of low labor costs on the U.S. textile industry?
Creates high demand for foreign products considered superior.
What is the timeline for fabric design in market planning?
Fabric design begins 1.5 to 2 years before retail sales.
What are some global issues related to the textile industry?
Air and water pollution, waste disposal, health and safety of workers.

What does Fair Trade indicate about a product?
Produced without labor exploitation and using environmentally sustainable practices.
Name two major international Fair Trade organizations.
Fair Trade Labeling Organization International (FLO) and International Federation for Alternative Trade (IFAT).
What is the role of a visual merchandiser in the textile industry?
To create appealing displays that attract customers.
What are some careers in the textile industry?
Fashion designer, textile engineer, trend forecaster, and creative director.
What is the significance of trade shows in the textile industry?
They provide platforms for showcasing new products and networking.