Chemistry Unit 3
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Mass
the amount of matter in an object (measured in g)
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Volume
the amount of space something takes up (measured in mL and cm^3)
Density
A measure of the mass of a material in a given volume (measured in g/cm^3 or g/mL)
Liquid Layers
If you pour liquids together that don't mix & have different densities, they will form liquid layers. The liquid with the highest density will be on the bottom. The liquid with the lowest density will be on the top.

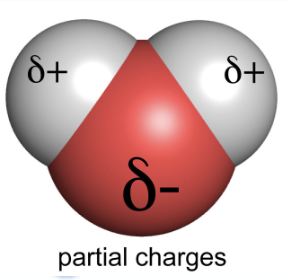
polar molecule
a molecule that has one end that is slightly negative and one end that is slightly positive. This occurs due to unequal sharing of electrons by the atoms (polar covalent bonds).
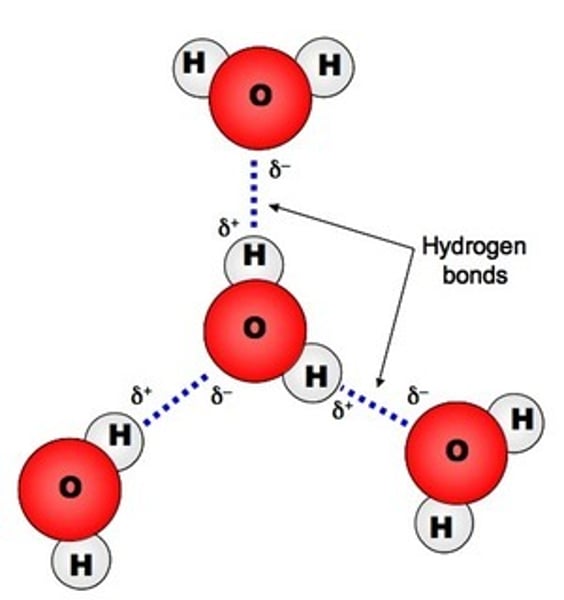
Hydrogen Bonding
A slightly positive hydrogen atom on one molecule is attracted to a slightly negative O, N, or F atom on another molecule
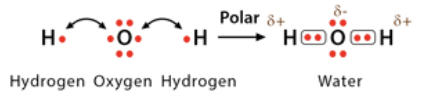
Polar covalent bond
electrons are unequally shared between two atoms which causes one atom to be slightly negative, and one to be slightly positive
Cohesion
is the attraction between water molecules
Surface tension
The cohesion at the surface of a liquid

Adhesion
A molecule's tendency to stick to other types of molecules

Hydrophilic
Attracted to water

Hydrophobic
Water fearing

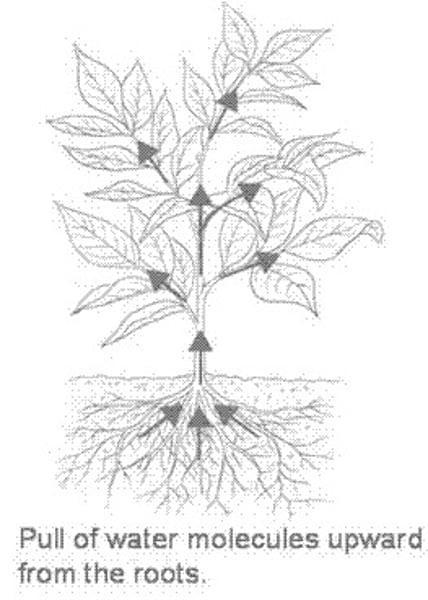
capillary action
The combined force of adhesion and cohesion which allows molecules to travel upwards through slim tubes, cylinders, or permeable substances
Specific Heat
the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 ℃

Why is ice able to float on liquid water?
Due to water's hydrogen bonds, it expands when it freezes, and becomes less dense than water, so it floats.

Solution
a homogenous mixture of two or more substances (Solute + Solvent)

Solute
a substance that is dissolved
Solvent
the substance that dissolves a solute
Aqueous solution
A solution where water is the solvent
Concentration
A measure of the amount of solute that has been dissolved in a given amount of solvent
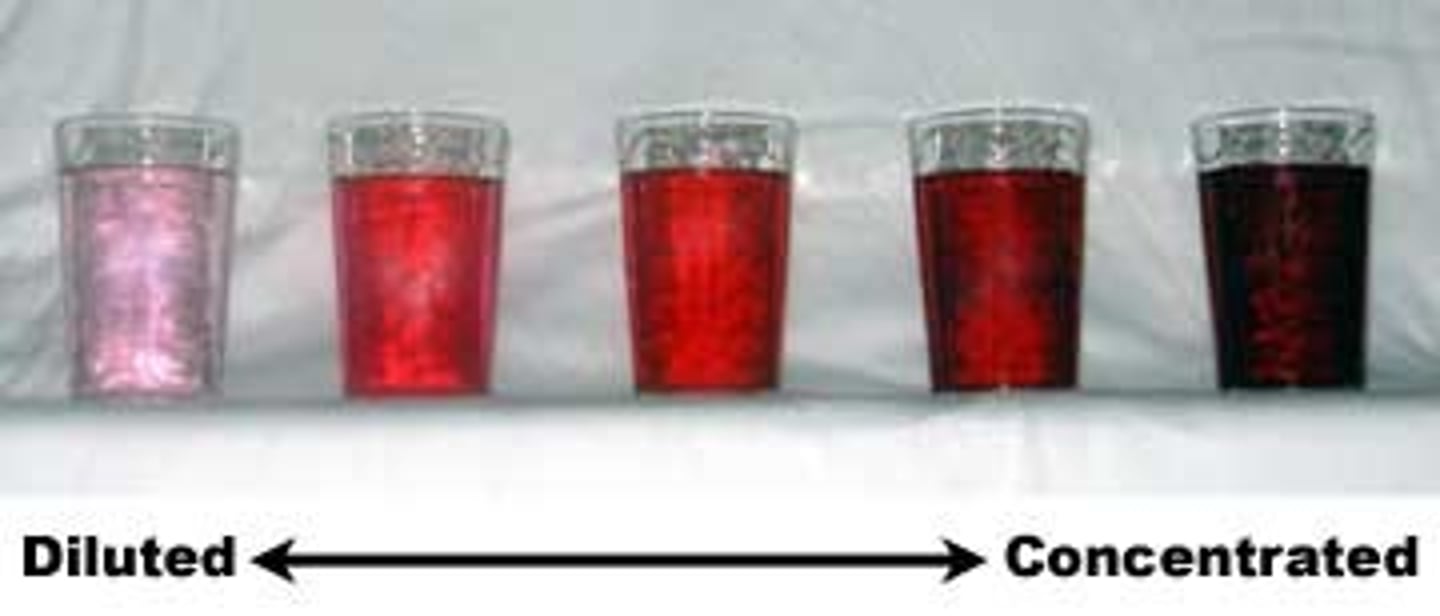
Diluted
relatively small amount of solute compared to the amount of solvent
Concentrated
relatively large amount of solute compared to the amount of solvent
Solubility
The ability to be dissolved
Soluble
able to be dissolved (polar molecules can dissolve in water)
Insoluble
not able to be dissolved (nonpolar molecules don't dissolve in water)
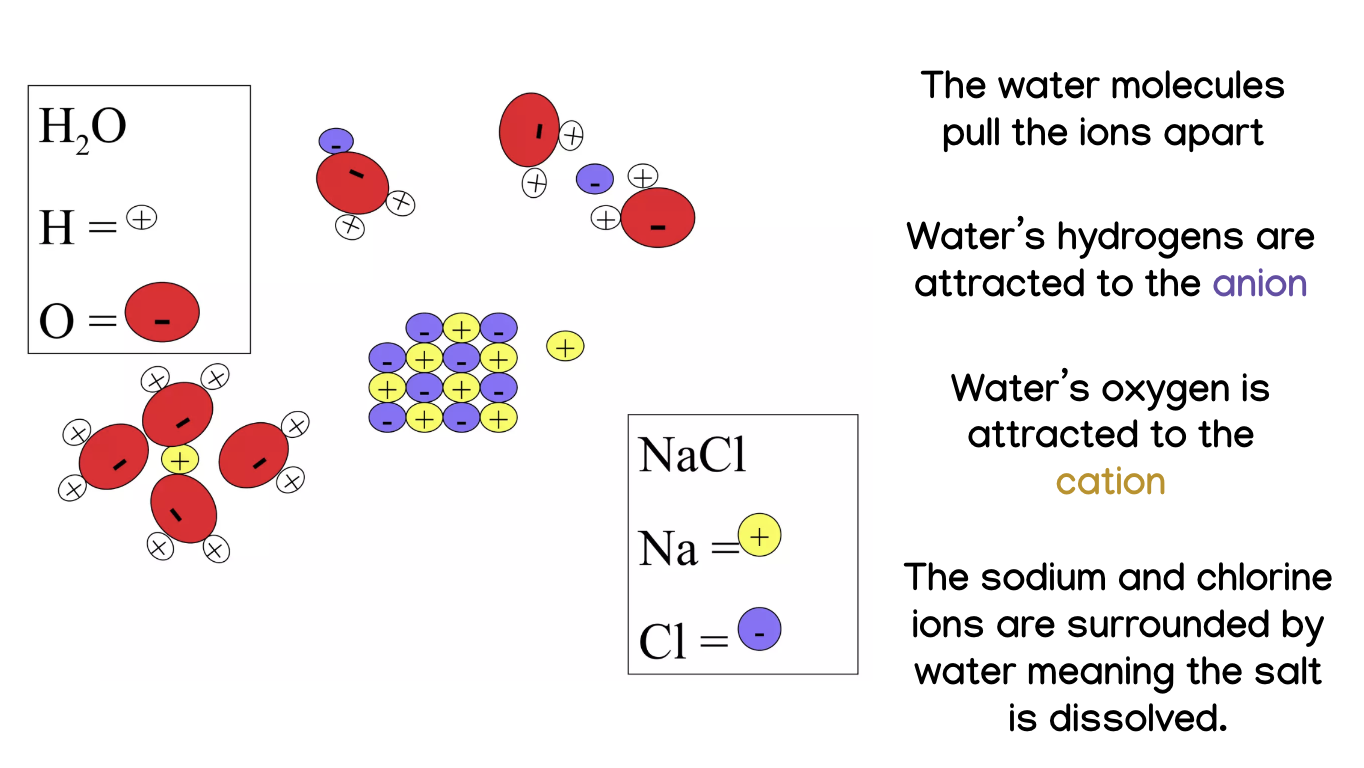
What happens when salt dissolves in water?
The water molecules pull the ions apart because water's hydrogens are attracted to the anion and its oxygen is attracted to the cation
What are three things that make the solute dissolve faster?
stirring, increasing the temperature, and increasing the surface area
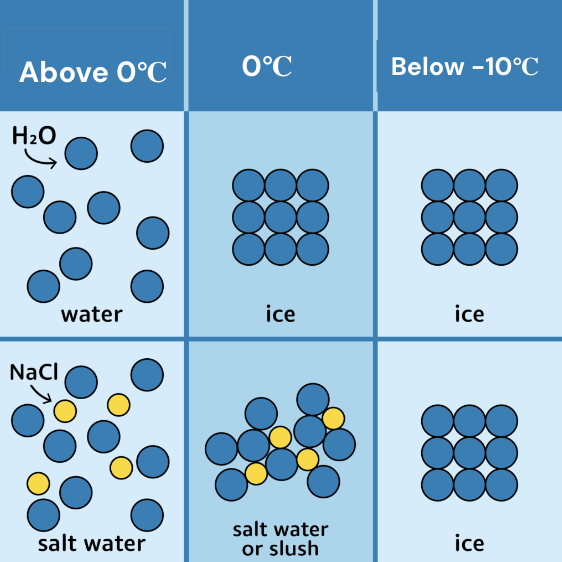
Why do we salt the roads before a snow storm?
Adding salt lowers the freezing point of water because it gets in the way of the hydrogen bonds forming
Unsaturated
a solution that contains less dissolved solute
Saturated
a solution that contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute
Supersaturated
solution that contains more than the maximum amount of dissolved solute